From the official account :BiggerBoy
One 、 What is? etcd?
etcd Pronunciation is /ˈɛtsiːdiː/, The origin of the name ,“distributed etc directory.”, intend “ Distributed etc Catalog ”, It shows that it stores the configuration information of large-scale distributed systems .
A sentence on the official website
A distributed, reliable key-value store for the most critical data of a distributed system.
Translated and understood as : A warehouse for storing the most critical data in a distributed system , It's distributed 、 Reliable key value pairs for the warehouse .
First, it is a data storage warehouse , Its features are distributed 、 Reliable , The data storage format is key value pair storage , It is mainly used to store key data in distributed systems .
In addition, in the official FAQ In the document
https://etcd.io/docs/v3.5/faq/ That's the explanation etcd Of :
etcd Is a consistent distributed key value store . It is mainly used as a separate coordination service in a distributed system . And it is designed to save a small amount of data that can be completely put into memory .
This indicates that its data is stored in memory , And it is recommended to save a small amount of data . Seeing the coordination service, we will soon think of Zookeeper, also Zookeeper It is also a distributed coordinator of distributed high availability , Data also exists in memory . What's the difference between them ? I'll talk about .
Two 、etcd The origin of
With CoreOS and Kubernetes And other projects are increasingly popular in the open source community , They're all used in projects etcd Component as a highly available 、 Highly consistent service discovery repository , Gradually become the focus of developers . In the era of cloud computing , How to make services access to computing cluster quickly and transparently , How to make shared configuration information quickly discovered by all machines in the cluster , more importantly , How to build such a set of high availability 、 Security 、 Easy to deploy and fast response service cluster , Has become an urgent problem to be solved .etcd It's good news to solve these problems
actually ,etcd As a subject Zookeeper And doozer Inspired projects , Besides having similar functions , It has the following 4 Characteristics {![ To quote Docker Official documents ]}.
Simple : be based on HTTP+JSON Of API Let you use it curl The command is easy to use .
Security : Optional SSL Customer authentication mechanism .
Fast : Each instance supports 1000 write operations per second .
trusted : Use Raft The algorithm fully realizes the distributed .
With the development of cloud computing , People pay more and more attention to the problems involved in distributed systems . Accept the last article
3、 ... and 、etcd Application scenarios of
3.1 Scene one : Service discovery
Service discovery (Service Discovery) To solve one of the most common problems in Distributed Systems , That is, how can processes or services in the same distributed cluster find each other and establish connections . essentially , Service discovery is to find out whether there are processes listening in the cluster udp or tcp port , And you can search and connect by name . To solve the problem of service discovery , We need to have three pillars , Be short of one cannot .
A strong consistency 、 Highly available service storage directory . be based on Raft Algorithm etcd By nature, it is such a highly consistent and available service storage directory .
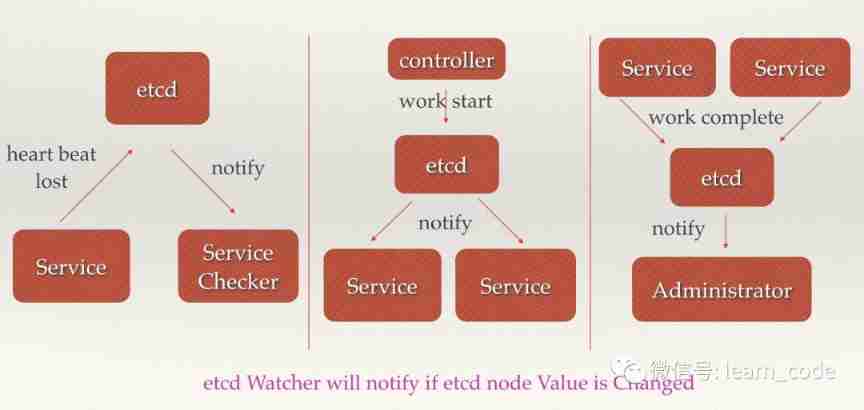
A mechanism for registering services and monitoring the health status of services . Users can go to etcd Registration service in , And set the registered service key TTL, Keep the heartbeat of the service regularly to achieve the effect of monitoring the health status .
A mechanism for finding and connecting services . By means of etcd The services registered under the specified topic can also be found under the corresponding topic . To make sure the connection , We can deploy one... On every service machine proxy Mode etcd, This ensures access to etcd The services of the cluster can be connected to each other .
chart 1 The service discovery diagram is shown .
chart 1 Service discovery diagram
Let's take a look at the specific application scenarios corresponding to service discovery .
In the framework of microservice collaborative work , Service dynamic add . With Docker The popularity of containers , A variety of micro services work together , There are more and more cases that constitute a relatively powerful architecture . The need to add these services transparently and dynamically is growing . Through the service discovery mechanism , stay etcd The directory in which a service name is registered , Store the... Of available service nodes in this directory IP. In the process of using the service , Just find the available service nodes from the service directory to use . The collaboration of microservices is shown in the figure 2 Shown .
chart 2 Microservices work together
PaaS Application multi instance and instance failure restart transparency in the platform .PaaS Applications in the platform generally have multiple instances , By domain name , Not only can multiple instances be accessed transparently , It can also realize load balancing . However, an instance of the application may fail to restart at any time , At this point, you need to dynamically configure domain name resolution ( route ) Information in . adopt etcd The service discovery function of can easily solve this dynamic configuration problem , Pictured 33 Shown .
Transparent cloud platform
chart 3 Transparent cloud platform
3.2 Scene two : Message publishing and subscription
In distributed systems , The most suitable communication mode between components is message publishing and subscription mechanism . To be specific , Build a configuration sharing center , The data provider publishes messages in this configuration center , And message users subscribe to topics they care about , Once there's a news release on the subject , Will notify subscribers in real time . In this way, centralized management and real-time dynamic update of distributed system configuration can be realized .
Some configuration information used in the application is stored in etcd Centralized management . This kind of scenario is usually used like this : The app takes the initiative to start from etcd Get the configuration information once , meanwhile , stay etcd Register one on the node Watcher And wait for , Every time the configuration is updated later ,etcd Will notify subscribers in real time , So as to obtain the latest configuration information .
Distributed search services , The meta information of the index and the node status information of the server cluster machine are stored in etcd in , For each client subscription . Use etcd Of key TTL The function ensures that the machine status is updated in real time .
Distributed log collection system . The core work of this system is to collect logs distributed on different machines . Collectors are usually based on application ( Or topic ) To assign collection task units , So you can etcd Create one on to apply ( Or topic ) Named directory P, And put this application ( Or topic ) All related machines ip, Stored in the directory as a subdirectory P Next , Then set a recursive etcd Watcher, Monitor applications recursively ( Or topic ) Changes to all information in the directory . In this way, the machine IP( news ) In the event of change , It can inform the collector to adjust the task allocation in real time .
Information in the system needs dynamic automatic acquisition and manual intervention to modify information request content . The usual solution is to expose the interface , for example JMX Interface , To get some runtime information or submit a modification request . And introduce etcd after , Just store the information in the designated etcd Directory , You can pass HTTP The interface is accessed directly from the outside .
chart 4 Message publishing and subscription
3.3 Scene three : Load balancing
stay Scene one Load balancing is also mentioned in , Load balancing mentioned in this article refers to soft load balancing . In distributed systems , To ensure high availability of services and data consistency , Data and services are usually deployed in multiple copies , So as to achieve peer-to-peer service , Even if one of the services fails , It does not affect the use of . This kind of implementation will lead to the decline of data writing performance to a certain extent , But it can realize the load balance of data access . Because every peer service node has complete data , So the user's access traffic can be divided into different machines .
etcd The information access stored in the distributed architecture supports load balancing .etcd After clustering , Every etcd All of the core nodes can handle the user's requests . therefore , The message data with small amount of data but frequent access is directly stored in etcd It's also a good choice , For example, the second level code table commonly used in business system . The working process of secondary code table is generally like this , Store the code in the table , stay etcd The specific meaning represented by the stored code in , The business system calls the table lookup process , You need to look up the meaning of the code in the table . So if you store a small amount of data in the secondary code table in etcd in , It is not only convenient to modify , It's also easy to access a lot .
utilize etcd Maintain a load balancing node table .etcd You can monitor the status of multiple nodes in a cluster , When a request is sent , The request can be polled and forwarded to multiple surviving nodes . similar KafkaMQ, adopt Zookeeper To maintain the load balance between producers and consumers . You can also use it etcd To do it Zookeeper The job of .
chart 5 Load balancing
3.4 Scene 4 : Distributed notification and coordination
Distributed notification and coordination discussed here , Similar to message publishing and subscription . Both use etcd Medium Watcher Mechanism , Through registration and asynchronous notification mechanism , Realize the notification and coordination between different systems in the distributed environment , So as to process the data change in real time . The implementation is usually : Different systems are in etcd Register the same directory on , Simultaneous setting Watcher Monitor changes in the directory ( If there is a need for changes to subdirectories , Can be set to recursive mode ), When a system is updated etcd The catalog of , So set up Watcher The system will be notified , And deal with it accordingly .
adopt etcd Perform low coupling heartbeat detection . The detection system and the detected system pass etcd A directory on the is associated rather than directly associated with , This can greatly reduce the coupling of the system .
adopt etcd Complete system scheduling . A system has two parts: console and push system , The responsibility of the console is to control the push system to carry out the corresponding push work . Some operations that managers do on the console , In fact, it just needs to be modified etcd The status of some directory nodes on , and etcd Will automatically notify the registration of these changes Watcher Push system client , The push system makes the corresponding push task .
adopt etcd Complete work report . Most of the similar task distribution systems , After the subtask starts , To etcd To register a temporary working directory , And regularly report their progress ( Write progress to this temporary directory ), In this way, the task manager can know the progress of the task in real time .
chart 6 Distributed collaborative work
3.5 Scene five : Distributed lock
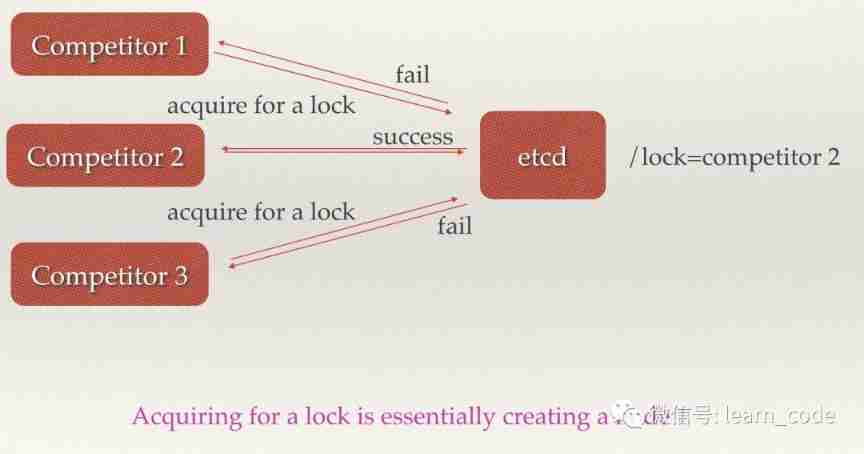
because etcd Use Raft The algorithm keeps the strong consistency of data , The values stored in the cluster for an operation must be globally consistent , So it's easy to implement distributed locks . There are two ways to use the lock service , One is to keep exclusive , Second, control the timing .
Keep exclusive , That is, only one user who tries to obtain the lock can get .etcd For this purpose, a set of distributed lock atom operations is provided CAS(CompareAndSwap) Of API. By setting prevExist value , It can ensure that when multiple nodes create a directory at the same time , There is only one success , The user can be considered to have obtained the lock .
Control timing , That is, all users who try to obtain the lock will enter the waiting queue , The order in which locks are obtained is globally unique , At the same time, it determines the execution order of the queue .etcd A set of API( Automatically create ordered keys ), When creating a value for a directory, specify POST action , such etcd Will automatically generate a current maximum value of key in the directory , Store this new value ( Client number ). You can also use API List all key values in the current directory in order . At this time, the value of these keys is the timing of the client , The value stored in these keys can be the number representing the client .
chart 7 Distributed lock
3.6 Scene six : Distributed queues
The general usage of distributed queues is similar to the control timing usage of distributed locks described in scenario 5 , Create a first in, first out queue , Ensure that the order . Another interesting implementation is to ensure that the queue reaches a certain condition, and then execute in order . The implementation of this method can be found in /queue Create another... In this directory /queue/condition node .
condition It can represent the queue size . For example, a large task can only be executed when many small tasks are ready , Every time a small task is ready , Here it is condition Digital plus 1, Until the big task figures , Then start to perform a series of small tasks in the queue , Finally carry out the big task .
condition It can indicate that a task is not in the queue . This task can be the first executor of all sorting tasks , It can also be a point in the topology where there is no dependency . Usually , You must perform these tasks before you can perform other tasks in the queue .
condition It can also represent other kinds of notifications to start executing tasks . It can be specified by the control program , When condition When there is a change , Start Queue task .
chart 8 Distributed queues
3.7 Scene seven : Cluster monitoring and Leader campaign for
adopt etcd It's very simple and real-time to monitor , The following two features are used .
The previous scenes have already mentioned Watcher Mechanism , When a node disappears or changes ,Watcher It will discover and inform the user as soon as possible .
Nodes can be set TTL key, Like every other 30s towards etcd Sending a heartbeat means that the node is still alive , Otherwise, the node disappears .
In this way, the health status of each node can be detected in the first time , To complete the monitoring requirements of the cluster .
in addition , Using distributed locks , Can finish Leader campaign for . For some long time CPU To calculate or use IO operation , It only needs to be elected Leader To calculate or process once , Then copy the results to others Follower that will do , So as to avoid repeated labor , Save computing resources .
Leader The classic application scenario is to build a full index in the search system . If each machine is indexed separately , Not only does it take time , And there is no guarantee of index consistency . By means of etcd Of CAS Mechanism election Leader, from Leader Index calculation , Then distribute the calculation results to other nodes .
chart 9 Leader campaign for
3.8 Scene 8 : Why etcd without Zookeeper?
Read “
By contrast ,Zookeeper It has the following disadvantages :
complex .Zookeeper The deployment and maintenance of is complex , Administrators need to master a series of knowledge and skills ; and Paxos Strong consistency algorithm is also famous for its complexity and incomprehension ; in addition ,Zookeeper The use of is also complex , The client needs to be installed , The official only offers java and C Interface between two languages .
Java To write . This is not right Java Biased , It is Java Itself is biased towards heavy applications , It introduces a lot of dependencies . The operation and maintenance personnel generally hope that the machine cluster is as simple as possible , It is not easy to make mistakes in maintenance .
Slow development .Apache Unique to foundation projects “Apache Way” Controversial in the open source community , One of the major reasons is the slow development of the project due to the huge structure and loose management of the foundation .
and etcd As a rising star , Its advantages are obvious .
Simple . Use Go The language is easy to write and deploy ; Use HTTP Easy to use as an interface ; Use Raft The algorithm ensures strong consistency and makes it easy for users to understand .
Data persistence .etcd The default data is persisted as soon as it is updated .
Security .etcd Support SSL Client security authentication .
Last ,etcd As a young project , In high-speed iteration and development , This is both an advantage , It's also a disadvantage . The advantage is that its future has unlimited possibilities , The disadvantage is that the iteration of the version makes the reliability of its use impossible to guarantee , Unable to get the inspection of large projects used for a long time . However , at present CoreOS、Kubernetes and Cloudfoundry And other well-known projects are used in the production environment etcd, So in general ,etcd It's worth trying .
Reference resources https://etcd.io/docs/v3.5/faq/
Excerpt from
http://www.sel.zju.edu.cn/blog/2015/02/01/etcd%E4%BB%8E%E5%BA%94%E7%94%A8%E5%9C%BA%E6%99%AF%E5%88%B0%E5%AE%9E%E7%8E%B0%E5%8E%9F%E7%90%86%E7%9A%84%E5%85%A8%E6%96%B9%E4%BD%8D%E8%A7%A3%E8%AF%BB/