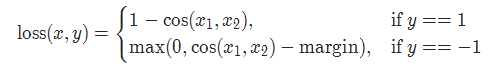当前位置:网站首页>Deep learning 19 loss functions
Deep learning 19 loss functions
2022-06-28 05:50:00 【TBYourHero】
This article summarizes 19 The loss function , And it is briefly introduced . The author of this article @ mingo_ Sensitive , Just for academic sharing , The copyright belongs to the author , If there is any infringement , Please contact the background for deletion .
tensorflow and pytorch Many of them are similar , Here we use pytorch For example .
1. L1 Norm loss L1Loss
Calculation output and target The absolute value of the difference .
torch.nn.L1Loss(reduction='mean')Parameters :
reduction- Three values ,none: Do not use reduction ;mean: return loss The average of and ;sum: return loss And . Default :mean.
2 Loss of mean square error MSELoss
Calculation output and target The mean square error of the difference between .
torch.nn.MSELoss(reduction='mean')Parameters :
reduction- Three values ,none: Do not use reduction ;mean: return loss The average of and ;sum: return loss And . Default :mean.
3 Cross entropy loss CrossEntropyLoss
When training has C It's very effective when it comes to the classification of two categories . Optional parameters weight Must be a 1 dimension Tensor, Weights will be assigned to each category . Very effective for imbalanced training sets .
In multi category tasks , Always use softmax Activation function + Cross entropy loss function , Because cross entropy describes the difference between two probability distributions , But the neural network outputs vectors , It's not in the form of a probability distribution . So we need to softmax The activation function performs a vector “ normalization ” In the form of probability distribution , And then the cross entropy loss function is used to calculate loss.

torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss(weight=None,ignore_index=-100, reduction='mean')Parameters :
weight (Tensor, optional) – Customize the weight of each category . It has to be a length of C Of Tensor
ignore_index (int, optional) – Set a target value , The target value is ignored , So that it doesn't affect The gradient of the input .
reduction- Three values ,none: Do not use reduction ;mean: return loss The average of and ;sum: return loss And . Default :mean.
4 KL Divergence loss KLDivLoss
Calculation input and target Between KL The divergence .KL Divergence can be used to measure the distance between different continuous distributions , In the space of continuous output distribution ( Discrete sampling ) When we do a direct regression on It works .
torch.nn.KLDivLoss(reduction='mean')Parameters :
reduction- Three values ,none: Do not use reduction ;mean: return loss The average of and ;sum: return loss And . Default :mean.
5 Binary cross entropy loss BCELoss
The calculation function of cross entropy in binary classification task . Error used to measure reconstruction , For example, automatic encoders . Pay attention to the value of the target t[i] For the range of 0 To 1 Between .
torch.nn.BCELoss(weight=None, reduction='mean')Parameters :
weight (Tensor, optional) – Custom each batch Elemental loss The weight of . It has to be a length of “nbatch” Of Of Tensor
6 BCEWithLogitsLoss
BCEWithLogitsLoss The loss function takes Sigmoid Layer integrated into BCELoss Class . This version is simpler than using a Sigmoid Layer and the BCELoss More stable numerically , Because after merging these two operations into one layer , You can use log-sum-exp Of Techniques to achieve numerical stability .
torch.nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss(weight=None, reduction='mean', pos_weight=None)Parameters :
weight (Tensor, optional) – Custom each batch Elemental loss The weight of . It has to be a length by “nbatch” Of Tensor
7 MarginRankingLoss
torch.nn.MarginRankingLoss(margin=0.0, reduction='mean')about mini-batch( Small batch ) The loss function for each instance in is as follows :

Parameters :
margin: The default value is 0
8 HingeEmbeddingLoss
torch.nn.HingeEmbeddingLoss(margin=1.0, reduction='mean')about mini-batch( Small batch ) The loss function for each instance in is as follows :

Parameters :
margin: The default value is 1
9 Multi label classification loss MultiLabelMarginLoss
torch.nn.MultiLabelMarginLoss(reduction='mean')about mini-batch( Small batch ) For each sample in, the loss is calculated as follows :

10 Smooth version L1 Loss SmoothL1Loss
Also known as Huber Loss function .
torch.nn.SmoothL1Loss(reduction='mean')
among

11 2 Classified logistic Loss SoftMarginLoss
torch.nn.SoftMarginLoss(reduction='mean')
12 Multi label one-versus-all Loss MultiLabelSoftMarginLoss
torch.nn.MultiLabelSoftMarginLoss(weight=None, reduction='mean')
13 cosine Loss CosineEmbeddingLoss
torch.nn.CosineEmbeddingLoss(margin=0.0, reduction='mean')
Parameters :
margin: The default value is 0
14 Multi category classification of hinge Loss MultiMarginLoss
torch.nn.MultiMarginLoss(p=1, margin=1.0, weight=None, reduction='mean')
Parameters :
p=1 perhaps 2 The default value is :1
margin: The default value is 1
15 Triplet loss TripletMarginLoss
It's similar to twin networks , Specific examples : Give me a A, And then to B、C, have a look B、C Who and A More like .

torch.nn.TripletMarginLoss(margin=1.0, p=2.0, eps=1e-06, swap=False, reduction='mean')
among :

16 Connection timing classification loss CTCLoss
CTC Connection timing classification loss , You can automatically align data that is not aligned , It is mainly used for training serialization data without prior alignment . For example, speech recognition 、ocr Identification and so on .
torch.nn.CTCLoss(blank=0, reduction='mean')Parameters :
reduction- Three values ,none: Do not use reduction ;mean: return loss The average of and ;sum: return loss And . Default :mean.
17 Negative log likelihood loss NLLLoss
Negative log likelihood loss . Used for training C There are three categories of classification problems .
torch.nn.NLLLoss(weight=None, ignore_index=-100, reduction='mean')Parameters :
weight (Tensor, optional) – Customize the weight of each category . It has to be a length of C Of Tensor
ignore_index (int, optional) – Set a target value , The target value is ignored , So that it doesn't affect The gradient of the input .
18 NLLLoss2d
Negative log likelihood loss for image input . It calculates the negative log likelihood loss per pixel .
torch.nn.NLLLoss2d(weight=None, ignore_index=-100, reduction='mean')Parameters :
weight (Tensor, optional) – Customize the weight of each category . It has to be a length of C Of Tensor
reduction- Three values ,none: Do not use reduction ;mean: return loss The average of and ;sum: return loss And . Default :mean.
19 PoissonNLLLoss
The target value is the negative log likelihood loss of Poisson distribution
torch.nn.PoissonNLLLoss(log_input=True, full=False, eps=1e-08, reduction='mean')Parameters :
log_input (bool, optional) – If set to True , loss Will be in accordance with the public type exp(input) - target * input To calculate , If set to False , loss Will follow input - target * log(input+eps) Calculation .
full (bool, optional) – Whether to calculate all of loss, i. e. add Stirling Approximation term target * log(target) - target + 0.5 * log(2 * pi * target).
eps (float, optional) – The default value is : 1e-8
Reference material :
pytorch loss function summary
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
数据仓库:分层设计详解
Maskrcnn, fast RCNN, fast RCNN excellent video
ipvs 导致syn 重传问题
5GgNB和ng-eNB的主要功能
Online yaml to JSON tool
深度学习19种损失函数
Animation de ligne
5g network overall architecture
JSP connecting Oracle to realize login and registration
安装 Ffmpefg
FB、WhatsApp群发消息在2022年到底有多热门?
V4l2 driver layer analysis
MySQL 45 talk | 05 explain the index in simple terms (Part 2)
Jenkins continues integration 2
Oracle 条件、循环语句
指定默认参数值 仍报错:error: the following arguments are required:
numpy.reshape, numpy.transpose的理解
Enum
6. graduation design temperature and humidity monitoring system (esp8266 + DHT11 +oled real-time upload temperature and humidity data to the public network server and display the real-time temperature
Error: the following arguments are required: