当前位置:网站首页>In place reversal of a LinkedList
In place reversal of a LinkedList
2022-06-11 08:18:00 【Scarecrow 0.0】
Pattern: In-place Reversal of a LinkedList, List flip
The introduction comes from :https://www.zhihu.com/question/36738189/answer/908664455 author : Poor farmer
Among the many problems , The title may require you to flip the nodes of a certain paragraph in the linked list . Usually , The requirement is that you have to turn in place , Is to reuse these built nodes , Without using extra space . This is the time , In situ flip mode is about to play its power .
This mode flips one node at a time . Generally, you need to use multiple variables , A variable points to the header node ( Image below current), Another one (previous) It points to the node we just finished processing . In this way of fixed step size , You need to set the current node first (current) Point to previous node (previous), Move to the next . meanwhile , You need to previous Always update to the node you just handled , To ensure correctness .

How can we identify this pattern ?
- If you are asked to go Flip list , When additional space cannot be used
Classic title :
1、Reverse a LinkedList (easy)
Invert a single chain table .
Example :
Input : 1->2->3->4->5->NULL
Output : 5->4->3->2->1->NULL
Advanced :
You can reverse the list iteratively or recursively . Can you solve the problem in two ways ?
Their thinking :pre Point to the header of the reverse linked list .current Point to the next node of the header of the inverted linked list . p Point to the reversed node .
1->2->3->4->5->null
1<-2<-pre(p) (p)current->3->4->5->null
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * public class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next; * ListNode(int x) { val = x; } * } */
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
// 1->2->3->4->5->null
// 1<-2<-pre(p) (p)current->3->4->5->null
if (head == null)
return null;
ListNode p = head;
ListNode pre = null;
ListNode current;
while (p != null){
current = p.next; // Save the next node of the original linked list
p.next = pre; // The broken node points to the head of the inverted linked list
pre = p; // Reversing the linked list header is equal to the newly added node
p = current; // Continue to reverse the next node
}
return pre;
}
}
2、Reverse a Sub-list (medium)
Reverse from position m To n The linked list of . Please use a scan to complete the inversion .
explain :
1 ≤ m ≤ n ≤ Chain length .
Example :
Input : 1->2->3->4->5->NULL, m = 2, n = 4
Output : 1->4->3->2->5->NULL
Their thinking : According to the reverse pattern of the previous question .
Create a new head node
res, Guarantee If the child chain is reversed from the first node There can be a previous nodepreHead.preHeadSave the previous node of the inverted node . for examplem = 1when , The previous node value is the head node :(preHead)0->1->2->3->4->5->NULLpreHead.next.nextTo reverse the end node of the linked listnext. Used to point to the node that is broken after reversing (cur).preHead.nextTo reverse the last node of the end node of the linked listnext. Used to point to the inverted header node (pre).Finally back to
res.nextThat is, the next reference of the chain header node .3. 4. For example, this question :


class Solution {
public ListNode reverseBetween(ListNode head, int m, int n) {
if (m == n || head == null)
return head;
ListNode res = new ListNode(0); // Create a chain header node , Ensure that when reversing from the first node , There can be a previous node
res.next = head;
ListNode preHead = res; // Point to the previous node of the inverted rotor linked list (preHead)1->2->3->3->5->NULL
for (int i = 1; i < m; i++) {
preHead = preHead.next;
}
// Reverse linked list operation
ListNode p = preHead.next;
ListNode pre = null; // After reversing (pre)4->3->2->NULL
ListNode cur = null; // After reversing (cur)5->NULL
for (int i = m; i <= n; i++) {
// Reverse operation
cur = p.next;
p.next = pre;
pre = p;
p = cur;
}
preHead.next.next = cur; // The tail node of the inverted linked list points to the remaining nodes cur
preHead.next = pre; // The inverted previous node points to the inverted head node pre
return res.next;
}
}
3、Reverse every K-element Sub-list (medium)
describe :
I'll give you a list , Every time k Group of nodes to flip , Please return to the flipped list .
k Is a positive integer , Its value is less than or equal to the length of the linked list .
If the total number of nodes is not k Integer multiple , Please keep the last remaining nodes in the original order .
Example :
Here is the list :1->2->3->4->5
When k = 2 when , Should return : 2->1->4->3->5
When k = 3 when , Should return : 3->2->1->4->5
explain :
Your algorithm can only use constant extra space .
You can't just change the values inside the node , It's about actually switching nodes .
My thinking is too complicated , Write a lot of code , It depends on others . Is dubious
Details please see :https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/reverse-nodes-in-k-group/solution/kge-yi-zu-fan-zhuan-lian-biao-by-powcai/
k = 2 General idea of recursion :

I feel like I'm scribbling , The diagram and code are clear …
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseKGroup(ListNode head, int k) {
ListNode cur = head; // Explore the child chain from the node down
int count = 0; // Record whether the sub chain is long enough
while (cur != null && count != k){
cur = cur.next;
count++;
}
if (count == k){
// There are enough sub chains
cur = reverseKGroup(cur, k); // Continue to explore the child chain from the current node
while (count != 0){
// Reverse a linked list
count--;
ListNode p = head.next; // Record the next node of the header node
head.next = cur; // The first pass is the sub linked list returned after recursion
cur = head; // Move one node forward
head = p; // Continue from the next node
}
head = cur;
}
return head;
}
}
K = 3 The idea of non recursive tail interpolation :

I feel like I'm scribbling , The diagram and code are clear …
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseKGroup(ListNode head, int k) {
if (head == null || k == 0)
return head;
ListNode res = new ListNode(0); // New header , Point to head
res.next = head;
ListNode preHead = res; // Start with the header , Position the sub chain head
ListNode tail = res; // Start with the header , Locate the end of the child chain
while (true){
// Cycle all the time , until tail Position to the tail
int count = 0;
while (tail != null && count != k){
// The tail is not empty And The number of k
count++;
tail = tail.next;
}
if (tail == null) break; // If the tail is empty, it will not be flipped
// The tail interpolation
ListNode tempHead = preHead.next; // Record the header node of the child linked list after inversion
while (preHead.next != tail){
// Traverse to Positioned tail pointer Previous node of
ListNode cur = preHead.next; // Start from scratch , Traversal node
preHead.next = cur.next; // Navigate to the next node
cur.next = tail.next; //
tail.next = cur; // Tail insertion
}
preHead = tempHead; // Continue to reverse from the end of the sub linked list
tail = tempHead; // Continue to explore from the end of the sub linked list
}
return res.next;
}
}
边栏推荐
- Solution to the occurrence interval (space) of latex manual numbering documents
- Typescript unknown type
- 嵌入式软件面试问题总结
- Icml2022 article intéressant
- Closure and minimum dependency in database
- 使用 COCO 数据集训练 YOLOv4-CSP 模型
- Selenium click the floating menu and realize the functions of right mouse button
- Pycharm启动卡死,loading project
- Use guidelines in constraintlayout to limit the maximum width of controls
- Typescript configuring ts in koa and using koa router
猜你喜欢

如何开始参与开源社区
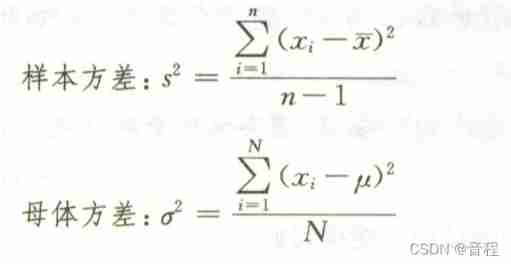
torch. Var (), sample variance, parent variance

Crawl Baidu Baipin dynamic page

Anaconda+tensorflow most effective summary version (blood and tears summary of 6 reloads)

Empty difference between postgrepsql and Oracle

字符设备驱动程序之异步通知机制

Figure seamless database integration tushare interface

torch. roll

Scrape captures 51job Recruitment Information (static page)
2022.6.7 special student simulation
随机推荐
Clipping and overlapping of YUV data
DAMENG 用户管理
TypeScript-头文件使用细节
通过ComponentCallbacks2来接收onTrimMemory等回调,并mock对应的场景
TypeScript-在koa中配置TS和使用koa-router
Image processing operation record
torch. roll
Typescript keyboard mapping
Figure seamless database integration tushare interface
字符设备驱动程序之异步通知机制
Typescript interface and type alias similarities and differences
TypeScript-声明合并
Use guidelines in constraintlayout to limit the maximum width of controls
[the most complete ENSP [installation diagram] in history!]
2022.6.6 extra long growth simulation
Use special characters to splice strings "+“
Process control: process waiting (recycling child processes)
XXL task executor calls local project
Study the Analects of entanglement
【 史上最全的ENSP【安装图解】!】