当前位置:网站首页>[C language] programmer's basic skill method - "creation and destruction of function stack frames"
[C language] programmer's basic skill method - "creation and destruction of function stack frames"
2022-07-26 08:29:00 【Anduin of the attack】
《 Function stack frame creation and destruction 》

List of articles
- 1. Preface
- 2. Problem introduction
- 3. The premise to prepare
- 4. Function stack frame maintenance
- 5. How to call stack
- 6. Function stack frame creation and destruction
- 7. General process diagram
- 8. Problem solving
- 9. Conclusion
1. Preface
The way of programming , The greatest truths are the simplest . When learning to program , We need some “ Gongfa ” To help yourself practice , Distance yourself from others . This skill is dedicated to explaining some knowledge of function stack frames , Let you know something about functions that you couldn't solve before , Make a better understanding , Next , Give Way anduin Lead you to this skill ——《 Function stack frame creation and destruction 》.
2. Problem introduction
When learning the basics , We have a lot of confusion about the following problems ?
this Seven deadly moves Can you catch ?
- How local variables are created ?
- Why is the value of uninitialized local variable a random value ?
- How functions pass parameters ? What is the order of parameters ?
- What is the relationship between formal parameters and arguments ?
- How functions are called ?
- How to return after function call ?
- How to return the return value ?
If you can't make “ movements in martial arts or traditional opera ” Coping with , Don't worry , This is the bottleneck period that every programmer will encounter when building the foundation , As long as you understand this skill , Foundation building is the beginning , Let's practice together !
3. The premise to prepare
Before learning the destruction and creation of function stack frames , We need to have a preliminary understanding of some registers and assembly instructions during the explanation .
3.1 register
- eax: Common registers , It is often used to store the return value of function calls
- esp( important ): Top register , Record the address of the top of the stack
- ebp( important ): Bottom of stack register , Record the address at the bottom of the stack
Other registers are common registers , Used to retain data .
3.2 Assembly instruction
- mov: Data mobility
- sub: Subtraction command
- add: Add command
- push: Pressing stack , Put an element from the top of the stack , change esp The location of
- pop: Out of the stack , Delete an element from the top of the stack , change esp The location of
- call: Function call
- lea:load effective address Load valid address
- rep: Repeat instruction
- stos: Copy the value in the register to the specified address
4. Function stack frame maintenance
When creating a function , The operating system will be in The stack area Open up a space for functions on . and ebp and esp They are in To the top of the stack and At the bottom of the stack , The region between them is the function Function stack frame .ebp At the bottom of the stack , Store the address at the bottom of the stack , be called Pointer at the bottom of the stack ,esp At the top of the stack , Store the address at the top of the stack , be called Top pointer of stack .
The address from the bottom of the stack to the top of the stack changes from high to low .
In the picture ,esp and ebp The maintenance is main Function stack frame of function , But when call Another function ,esp and ebp It needs maintenance The function stack frame of the calling function .
5. How to call stack
Call stack is a mechanism of compiler , When the program calls multiple functions , Track the control point that each function should return when it completes execution , Observe the calling relationship between functions .
To call the stack . This operation requires pressing F10, Enter debugging state , Then click in the window call Stack .

Continue to press F10, At the end of the program , The call stack interface will appear as follows :

and __tmainCRTStartup() and mainCRTStartup() What are these two functions ? stay crtexe.c Observation in file :

So I found main The function is to be __tmainCRTStartup() Called and __tmainCRTStartup() Has been mainCRTStartup() call , and Add The function is again main Function call . And ordinary main The return value of the function , It's on the mainret in .
We said above , Every function will open up space when it is called , So many functions are called , For this program , The stack frame of the function on the stack area is like this :
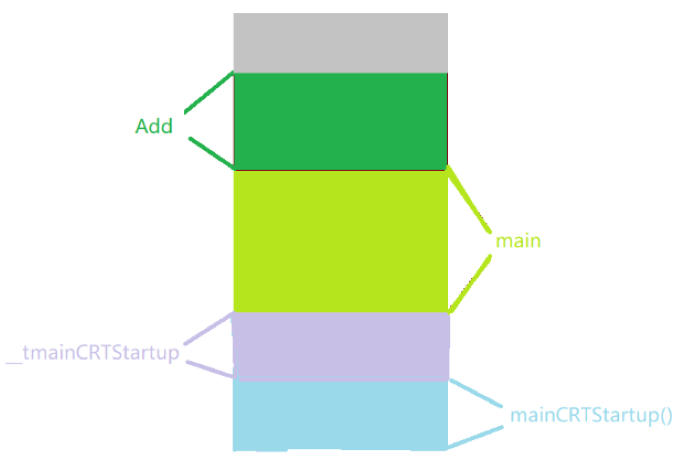
6. Function stack frame creation and destruction
Through the understanding of the above two parts , We have a preliminary understanding of function stack frames , Next, let's get to the point .
Take a simple function as an explanation case :
#include<stdio.h>
int Add(int x, int y)
{
int z = 0;
z = x + y;
return z;
}
int main()
{
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
int c = 0;
c = Add(a, b);
printf("%d\n", c);
return 0;
}
Right click the code , go to Disassembly , Look at assembly code , and Uncheck the symbol name , Explain from the perspective of compilation :
6.1 main Function stack frame creation
First , because main The function is to be __tmainCRTStartup() Called , So at first, the stack area is :

Then we observe main Assembly code in function :

Explanation of assembly instructions :
- push ebp: take ebp The values in the stack , here ebp The value of is at
To the top of the stack, Top pointer of stack esp The position of should be moved toTop of stack ebpIt's about , And address from top to bottomFrom low to high, therefore esp The value of the address atreduce 4.

- move ebp,esp: take esp Put the value of ebp in , That is to say, the pointer at the bottom of the stack ebp The value of the change ,ebp Location
MoveTo __tmainCRTStartup Ofesp It's about, here esp and ebp The values are equal . Producedmain Functional ebp.

- sub esp,0E4h: take esp Value minus in 0E4h. At this time esp Of
Value decrease,esp OfMove the position up, And then there ismain Functional esp. here esp To ebp A large space of ismain Function stack frame of function. - push ebx: take ebx Value stack of , here ebx The value of is at
To the top of the stack, Top pointer of stack esp Move your position up ,esp The value of the reduction 4. - push esi: take esi Value stack of , here esi The value of is at
To the top of the stack, Top pointer of stack esp Move your position up ,esp The value of the reduction 4. - push edi: take edi Value stack of , here edi The value of is at
To the top of the stack, Top pointer of stack esp Move your position up ,esp The value of the reduction 4.
see Memory and monitor , It is found that the order of the above three registers is edi -> esi -> ebx, And esp The value of is equal to edi The address of :0x00dEF66C identical .

lea edi,[ebp+FFFFFF1Ch]:
ShowSymbol name , take [ebp - 0E4h] Load into edi in . This position isBefore main The top of the function stack frame of the functionThe location of , Put this value in edi.move ecx,39h: hold 39h Put in ecx In the register .
move eax,0CCCCCCCCh: hold 0CCCCCCCCh Put in eax In the register .
rep stos dword ptr es:[edi]:rep Repeat instruction , take ecx The value of the data in the register is the number , Every time
repeatecx It's worth itReduce,stos Express the eax Copy the value of to the specified address ,word Is two bytes ,d by double, That's double word , tell stos onceCopy double wordsThe address of , That is, copyCCCCCCCCTo the destination address .Range of copied addresses :
ebp - 0E4h ~ ebp
Module corresponding process diagram :

Through the above process ,main The function stack frame of the function is The development is complete .
6.2 main Creation of function local variables and function calls
After the function stack frame development is completed , need Create local variables , as well as call Add function , Let's look at the assembly code for the following procedure :
notes : Previously developed CCCCCCCC The area size of is 4 Bytes .

Explanation of assembly instructions :
6.2.1 Local variable initialization
- move dword ptr [ebp - 8],0Ah: take 0Ah( Decimal system :10) Put it in ebp - 8 in , namely ebp Up 2 One unit .
( Imagine , If the variables here are not Not initialized , Then this action , The value placed in the variable is CCCCCCCC, This is hot hot , Namely Random value )
- move dword ptr [ebp - 14h],14h: take 14h(10 Base number :20), Put it in ebp - 20 in , namely
ebp Up 5 One unit. The corresponding data is a Variable up 3 One unit ( The location depends on the compiler ). - move dword ptr [ebp - 20h],0: take 0, Put it in ebp - 32 in , namely
ebp Up 8 One unit. The corresponding data is b Variable up 3 One unit .
The memory distribution corresponding to these three steps :
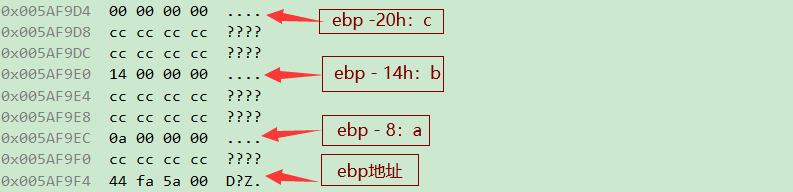
6.2.2 Function call and parameter passing
- move eax,dowrd ptr [ebp - 14h]: take ebp - 14h Put it in eax In the register , Also is to
20 Put it in eaxin . This step is a local variableb The ginseng. - push eax: take eax Value stack of , here eax The value of is at
To the top of the stack, Top pointer of stack esp Move your position up ,esp The value of the reduction 4. - move ecx,dowrd ptr [ebp - 8]: take ebp - 8 Put it in ecx In the register , Also is to
10 Put it in ecxin . This step is a local variablea The ginseng. - push ecx: take ecx Value stack of , here ecx The value of is at
To the top of the stack, Top pointer of stack esp Move your position up ,esp The value of the reduction 4.
Through these four steps, it is not difficult to observe that the function parameters are From right to left The ginseng .
- call 009F11E0: call Add function , Please remember the address of the next instruction of this instruction
009F1A50, Then press F11, Observe memory changes ,ecx The value at the top two units changes , The value of The address of the next instruction of this instruction , Immediately let call The address of the next instructionPressing stack.
The memory distribution corresponding to these five commands :

Module corresponding process diagram :

6.3 Add Function call procedure
6.3.1 Add Function stack frame creation
This process assembles instructions and main Assembly instructions created by function stack frames are similar :

Explanation of assembly instructions :
- push ebp: take ebp Value stack of , here ebp The value of is at
To the top of the stack, Top pointer of stack esp Move your position up ,esp The value of the reduction 4. - mov ebp,esp: take esp Put the value of ebp in , here ebp( come from main function ), Move to the top of the stack , and main Functional esp Same position .
- sub esp,0CCh: take esp Value minus in 0CCh.esp Move your position up , And then there is
add Functional esp. here esp To ebp A large space of isadd Function stack frame of function. - push ebx: take ebx Value stack of , here ebx The value of is at
To the top of the stack, Top pointer of stack esp Move your position up ,esp The value of the reduction 4. - push esi: take esi Value stack of , here esi The value of is at
To the top of the stack, Top pointer of stack esp Move your position up ,esp The value of the reduction 4. - push edi: take edi Value stack of , here edi The value of is at
To the top of the stack, Top pointer of stack esp Move your position up ,esp The value of the reduction 4. - lea edi,[ebp-0CCh] :
ShowSymbol name , take [ebp - 0CCh] Load into edi in , This position isBefore add The top of the function stack frame of the functionThe location of , Put this value in edi. - mov ecx,33h: hold 33h Put in ecx In the register .
- mov eax,0CCCCCCCCh: hold 0CCCCCCCCh Put in eax In the register .
- rep stos dword ptr es:[edi]: take eax in 0CCCCCCCCh Copy the value of 33h Time to corresponding address , Address range :
ebp - OCCh ~ ebp
6.3.2 Initialization and calculation of local variables

Explanation of assembly instructions :
- mov dword ptr [ebp-8],0 : take 0 Put it in ebp - 8 in , namely ebp Up 2 One unit , This step is
initializationlocal variablez. - mov eax,dword ptr [ebp+8] : take ebp + 8 Put it in eax in , namely ebp Down 2 One unit , by
main Function parameter a The value of the parameter. - add eax,dword ptr [ebp+0Ch]: take ebp + 0Ch The value in is added to eax in ,ebp + 0Ch by ebp + 12, by
main Function parameter b The value of the parameter, That is to say 10 and 20 Add up , here eax The value of 30. - mov dword ptr [ebp - 8],eax: take eax Value , Put it in ebp - 8 in ,ebp - 8 It's a local variable
z.
When Add Function x and y When adding variables , Find formal parameters and No stay Add Create in function Of , But I used main When a function passes parameters, the space pressed by the stack , explain A formal parameter is a temporary copy of an argument .
6.3.3 The calculation results return

- mov eax,dword ptr [ebp-8] : When the result returns , function
End call, local variablez The destruction, In order to return the value safely , take z = 30 Put ineax registerin .
Module corresponding process diagram :

6.4 Add Destruction of function stack frames
With the return of the calculation results , Function will also end the call , At this time Add The function stack frame of starts The destruction :

Explanation of assembly instructions :
- pop edi: Out of the stack , take edi Data pop-up ,esp Move down one unit .
- pop esi: Out of the stack , take esi Data pop-up ,esp Move down one unit .
- pop ebx: Out of the stack , take ebx Data pop-up ,esp Move down one unit .
- mov esp,ebp: hold ebp Point to esp, Also is to Add Top of stack pointer for
esp, Move toAdd At the pointer at the bottom of the stack of the function. - pop ebp: Out of the stack , hold ebp Data pop-up , Also is to
Add The pointer at the bottom of the stack pops up, At this time Add The top and bottom pointers of the stack haveOut of the stack,Add Function stack frameThe destruction, And because ebp eject , At this momentespFor maintenancemain Functional esp, The pointing position is call At the address of the next instruction . - ret: Pop a value from the top of the stack , At this time, the value at the top of the stack is
call Next instruction of instruction, Then the value pops up ,JumpTo call The next instruction , continueperform main function.
Module corresponding process diagram :
6.5 End of call
When Add After the function stack frame is destroyed , To the top of the stack The value is call Instruction next instruction , Pop up the value and jump to the instruction , Assembly instructions continue :

- add esp,8: take esp + 8, The original esp because call The value of the next instruction pops up and points to
Next element, The next two elements are local variablesa,b The space opened up when transferring parameters,esp + 8 Skip two units , At this time, the pointer at the top of the stackespLocated in registerebiIt's about . - mov dword ptr [ebp-20h],eax: Register
eaxPut the value of ebp - 20h(ebp - 32) in , That's the variablecin , here c The value of is 30.
This means that , The program calls after the function ends , from eax Read the return value in .
And the next process is main Function to destroy the stack frame , No more details here , If you are interested, you can understand for yourself …
7. General process diagram
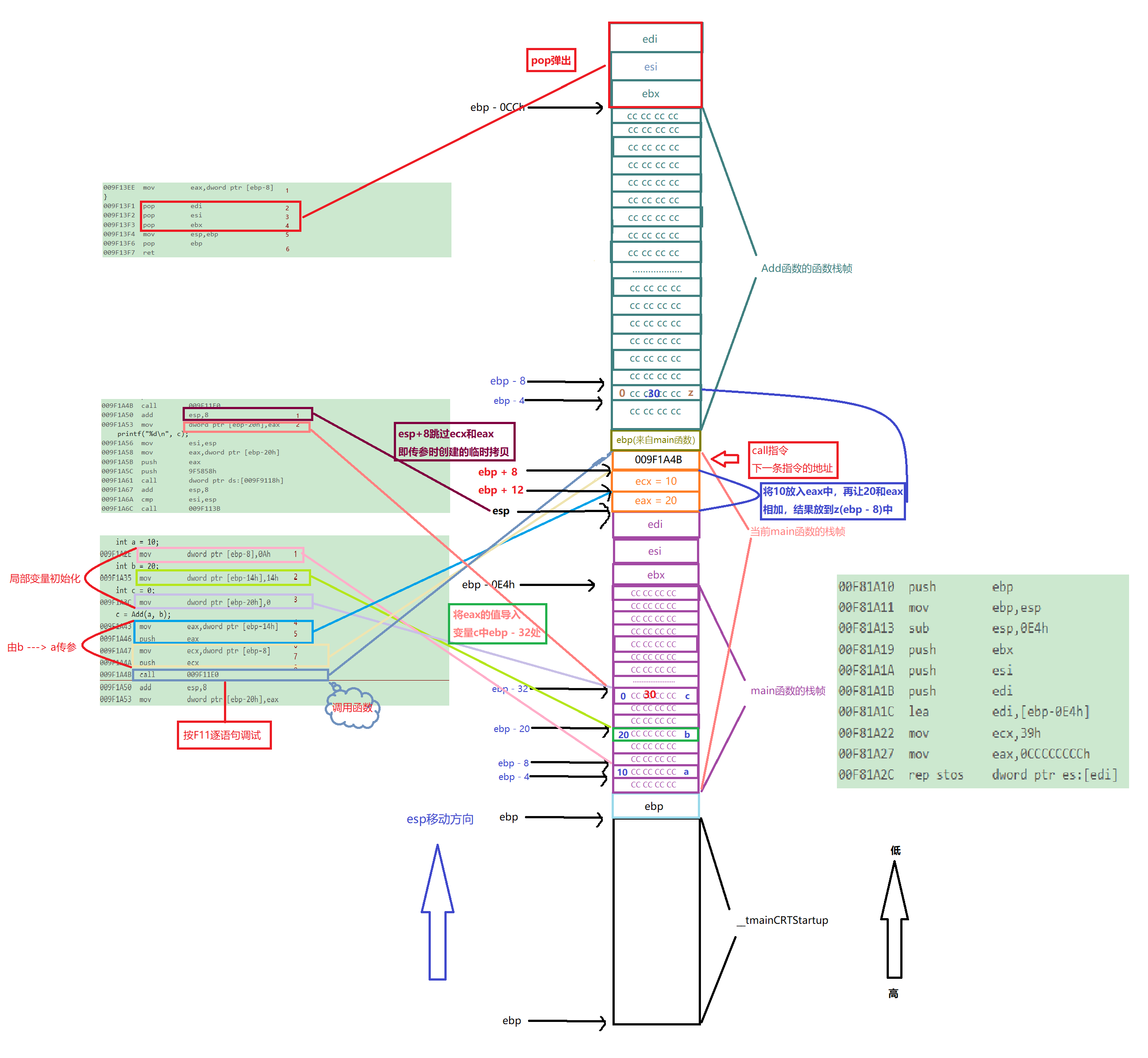
8. Problem solving
How local variables are created ?
The function stack frame is created and initially recognized as CCCCCCCC after , In the frame area of the function stack , Take a space as the region of the local variable .
Why is the value of uninitialized local variable a random value ?
After the function stack frame is created , The value stored in the area is CCCCCCCC, If the variable is not initialized , Then the value of this area remains unchanged , Then random values are generated .
How functions pass parameters ? What is the order of parameters ?
Arguments are passed , Will pass from right to left , Parameters are put into registers in turn , And press the stack , When the function is called , The function will find the parameter by pointer offset ,
Pass parameters from right to left .
What is the relationship between formal parameters and arguments ?
The values of formal and actual parameters are the same , But the calling function finds the formal parameter by pointer offset , Therefore, changing the value of the formal parameter will not affect the actual parameter .
A formal parameter is a temporary copy of an argument .
How functions are called ?
Take the top of the stack of the original function as the pointer at the bottom of the stack of the calling function , Open up new stack frames for calling functions , use call Instruction call function .
How to return after function call ?
Press... At the top of the stack before calling call The next address of the instruction , And take the top pointer of the previous function as the... Of the calling function ebp, At the end of the function call ,ebp Out of the stack , Find the last function ebp, Back to the stack frame space , Because I remember call The next address of the instruction , use ret The instruction returns the address , go back to call Below the instruction .
How to return the return value ?
adopt eax Register back .
After learning this skill , this Seven deadly moves Did you catch ? If caught , So congratulations , Your skill has been introduced .
9. Conclusion
Come here , That's all for this skill , The way of programming , It's a long way , Although you may encounter poor root bones ( The foundation is not solid ), The lethality of moves is low ( Less questions ), Emptiness has its form ( Poor drawing ability ), Yuan Shen is unstable ( Inadequate coding habits ), But these can be improved through our own efforts , I hope we can understand our own rules together on the way of programming .
If you think this skill is good , Please also leave your precious three company !
I am a anduin, One C Language beginners , I hope my blog can help you , See you next time !
边栏推荐
- 正则表达式作业
- 【EndNote】文献类型与文献类型缩写汇编
- Shell homework the next day
- Special lecture 2 dynamic planning learning experience (should be updated for a long time)
- Kotlin program control
- 2022-7-8 personal qualifying 5 competition experience (supplementary)
- 【时间复杂度空间复杂度】
- Burp suite Chapter 4 advanced options for SSL and proxy
- C # get the information of the selected file
- Shell programming
猜你喜欢

美女裸聊一时爽,裸聊结束火葬场!

Team members participate in 2022 China multimedia conference

日常一记(11)--word公式输入任意矩阵

Basic configuration of BGP

A little awesome, 130000 a month+

我,35岁了。

Burp suite Chapter 5 how to use burp target

Burp suite Chapter 3 how to use burp suite agent
Kotlin program control

2022-7-8 personal qualifying 5 competition experience (supplementary)
随机推荐
正则表达式作业
If Yi Lijing spits about programmers
Flutter text is left aligned with no blank space in the middle
mysql函数汇总之条件判断函数
2022-024arts: Longest valid bracket
Error handling response: Error: Syntax error, unrecognized expression: .c-container /deep/ .c-contai
Burp suite Chapter 7 how to use burp scanner
BGP -- Border Gateway Protocol
Template summary
Kotlin program control
2022-7-6 personal qualifying 3 competition experience
Team members participate in 2022 China multimedia conference
2022-7-7 personal qualifying 4 competition experience
2022 7/5 exam summary
import error: ‘Icon‘ is not exported from ‘antd‘. Import icon error
2022/7/9 exam summary
flink oracle cdc 读取数据一直为null,有大佬知道么
Data validation typeerror: qiao Validate is not a function
Burp suite Chapter 8 how to use burp intruder
2022-7-5 personal qualifying 2 competition experience