当前位置:网站首页>[course assignment] floating point operation analysis and precision improvement
[course assignment] floating point operation analysis and precision improvement
2022-06-21 13:06:00 【51CTO】
Abstract
- What is it?
disadvantages- Why?
- How do you do it?
Convert decimals to fractions
Using arrays
C Function library settings
Math library- experiment
Python Fractional operation
Using arrays
C Function library settings
Math library- summary
references
https://baike.baidu.com/item/%E6%B5%AE%E7%82%B9%E8%BF%90%E7%AE%97%E5%99%A8
https://www.jianshu.com/p/6073b6ecc1e5
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/57010602
http://c.biancheng.net/view/314.html
List of articles
- IEC Floating point standard
- fenv.h The header file
- STDC FP_CONTRACT Compilation instructions
- The math library broke its heart for floating-point arithmetic
- 《 Design and implementation of fast single precision floating point arithmetic unit 》
- 《 be based on FPGA Research on floating point arithmetic unit 》
- 1. introduction
- 2. Floating point means
- 3. Research on normalized floating point number basic operation and hardware circuit
- 《 be based on RISC-V Floating point instruction set FPU Research and design of 》
- 《 Research on high precision algorithm based on multi part floating point representation 》
- The history of floating point numbers
- The definition of floating point numbers
- == Problems with floating point numbers ==
- 1.2 Research status of floating point arithmetic units at home and abroad
- 2.1 Floating point format parsing
- The third chapter Research on Algorithm of floating point arithmetic unit
- 3.1 Floating point addition and subtraction
- 3.2 Floating point multiplication
- 3.3 Floating point division

C Primer Plus
float、double、long double
- float Is the basic floating point type in the system . It can at least accurately represent 6 Significant digits , Usually 32 position .
- double May represent a larger floating point number . It may mean more than float More significant figures and bigger indices . It can at least accurately represent 10 Significant digits , Usually 64 position .
- long double May represent a larger floating point number . It can express ratio double More significant figures and bigger indices .
Floating point constants
By default , The compiler assumes that floating-point constants are double Accuracy of type . hypothesis some yes float Variable of type ,some = 4.0 * 2.0; Usually ,4.0 and 2.0 Will be stored as 64 Bit double type , Multiplication with double precision , Then truncate the product to float The width of the type . This will improve the calculation accuracy , But it will slow down the running speed of the program .
Add... After the floating point number f or F Suffixes override the default settings , The compiler treats floating-point constants as float type , Use l or L Suffixes make numbers long double type .
Print floating point values
jiaming
@jiaming
-
System
-
Product
-
Name:
/
tmp$ .
/
float.
o
32000.000000
can
be
weitten
3.200000e+04
And
it
's 0x1.f4p+14 in hexadecimal, powers of 2 notation
2140000000.000000
can
be
written
2.140000e+09
0.000053
can
be
written
5.320000e-05
jiaming
@jiaming
-
System
-
Product
-
Name:
/
tmp$
cat
float.
c
/*************************************************************************
> File Name: float.c
> Author: jiaming
> Mail: [email protected]
> Created Time: 2020 year 12 month 27 Japan Sunday 16 when 33 branch 11 second
************************************************************************/
int
main()
{
float
aboat
=
32000.0;
double
abet
=
2.14e9;
long
double
dip
=
5.32e-5;
printf(
"%f can be weitten %e\n",
aboat,
aboat);
// c99
printf(
"And it's %a in hexadecimal, powers of 2 notation\n",
aboat);
printf(
"%f can be written %e\n",
abet,
abet);
printf(
"%Lf can be written %Le\n",
dip,
dip);
return
0;
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
- 29.
- 30.
- 31.
Overflow and underflow of floating-point values
jiaming
@jiaming
-
System
-
Product
-
Name:
/
tmp$ .
/
tmp.
o
inf
jiaming
@jiaming
-
System
-
Product
-
Name:
/
tmp$
cat
tmp.
c
/*************************************************************************
> File Name: tmp.c
> Author: jiaming
> Mail: [email protected]
> Created Time: 2020 year 12 month 27 Japan Sunday 16 when 59 branch 35 second
************************************************************************/
int
main()
{
float
toobig
=
9.9E99;
printf(
"%f\n",
toobig);
return
0;
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
Floating point rounding error
jiaming
@jiaming
-
System
-
Product
-
Name:
/
tmp$ .
/
tmp.
o
4008175468544.000000
jiaming
@jiaming
-
System
-
Product
-
Name:
/
tmp$
cat
tmp.
c
/*************************************************************************
> File Name: tmp.c
> Author: jiaming
> Mail: [email protected]
> Created Time: 2020 year 12 month 27 Japan Sunday 16 when 59 branch 35 second
************************************************************************/
int
main()
{
float
a,
b;
b
=
2.0e20
+
1.0;
a
=
b
-
2.0e20;
printf(
"%f\n",
a);
return
0;
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
as a result of : The computer lacks enough decimal places to complete the correct calculation .2.0e20 yes 2 In the back 20 individual 0. If you add this number 1, Then what has changed is 21 position . Calculate correctly , The program must store at least 21 Digit number , and float Types of numbers usually store only exponentially scaled down or enlarged numbers 6 or 7 Significant digits . under these circumstances , The calculation must be wrong . On the other hand , If you put 2.0e20 Change to 2.0e4, The calculation result is no problem . because 2.0e4 Add 1 Just change the second 5 A number in bits ,float The precision of the type is sufficient for such an operation .
IEC Floating point standard
Floating point model
International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) Issued a set of standards for floating-point computing (IEC 60559).
C99 Most of the new floating point tools ( Such as ,fenv.h Header files and some new math functions ) Are based on this , in addition ,float.h The header file defines some IEC Floating point model related macros .
Representative symbol (±1)
Represents the base number . The most common value is 2, Because floating-point processors usually use binary numbers .
Represents the integer exponent , Limit the minimum and maximum values . These values depend on the number of digits set aside to store the index .
The representative cardinality is
The possible number . for example , The base number is 2 when , The possible numbers are 0 and 1; In hexadecimal , The possible numbers are 0~F.
Represents precision , The base number is
when , Represents the number of significant digits . Its value is limited by the number of digits reserved for storing significant digits .
give an example :
24.51=(±1)10^3(2/10+4/100+5/1000+1/10000+0/100000)
Assume the sign is positive , base b by 2,p yes 7( use 7 Bit binary number means ), The index is 5, The valid number with storage is 1011001.
24.25=(±1)2^5(1/2+0/4+1/8+1/16+0/32+0/64+1/128)
Normal and below normal values
give an example :
Decimal system b=10; Precision of floating point values p=5;
Index = 3, Effective number .31841(.31841E3)
Index = 4, Effective number .03184(.03184E4)
Index = 5, Effective number .00318(.00318E5)
The first 1 The two kinds of precision are the highest , Because we use all the in the valid numbers 5 Bits available bits . Normalizing floating-point nonzero values is the 1 The bit significand is a non-zero value , This is also the usual way to store floating-point numbers .
hypothesis , Minimum index (FLT_MIN_EXP) by -10, Then the minimum specification value is :
Index = -10, Effective number = .10000(.10000E-10)
Usually , Multiply or divide by 10 It means that the index increases or decreases , But in this case , If divided by 10, But I can't reduce the index any more . however , This representation can be obtained by changing the significant number :
Index = -10, Effective number = .01000(.01000E-10)
This number is called below normal , Because this number does not use the full precision of the significant number , Lost a bit of information .
For this assumption ,0.1000E-10 Is the minimum non-zero normal value (FLT_MIN), The minimum nonzero below normal is 0.00001E-10(FLT_TRUE_MIN).
float.h Macro in FLT_HAS_SUBNURM、DBL_HAS_SUBNORM、LDBL_HAS_SUBNORM Characterizes how the implementation handles below normal values . Here are the values that these macros may use and their meanings :
- -1: Not sure
- 0: non-existent ( May use 0 Replace lower than normal values )
- 1: There is
math.h The library provides some methods , Include fpclassify() and isnormal() macro , It can identify when the program generates a lower than normal value , This will lose some accuracy .
Evaluation scheme
float.h Macro in FLT_EVAL_METHOD It determines the evaluation scheme of the floating-point expression used in the implementation :
- -1: Not sure
- 0: For operations within the range and precision of all floating-point types 、 Constant evaluation
- 1: Yes double Type of precision within and float、double Operation within the scope of type 、 Constant evaluation , Yes long double Within the scope of long double Type of operation 、 Constant evaluation
- 2: For all floating point type ranges and long double Operations and constant evaluation within type precision
Round off
float.h Macro in FLT_ROUNDS Determines how the system handles rounding , The rounding scheme corresponding to the specified value is as follows :
- -1: Not sure
- 0: Zero truncation
- 1: Round to the nearest value
- 2: The trend is endless
- 3: Towards infinity
The system can define other values , Corresponding to other rounding schemes , Some systems provide schemes to control rounding , under these circumstances ,fenv.h Medium festround() Function provides programming control .
In decimal ,8/10 or 4/5 Can accurately represent 0.8. But most computer systems store results in binary , In binary ,4/5 Expressed as a wireless circular decimal :
0.1100110011001100…
therefore , In the 0.8 Stored in the x In the middle of the day , Round it to an approximate value , Its specific value depends on the rounding scheme used .
Some implementations may not be satisfied IEC 60559 The requirements of , for example , The underlying hardware may not meet the requirements , therefore ,C99 Defines two macros that can be used as preprocessor instructions , Check whether the implementation conforms to the specification .
fenv.h The header file
Provides some ways to interact with floating-point environments . Allows the user to set the float control mode value ( This value manages how floating-point operations are performed ) And determine the floating point status criteria ( Or abnormal ) Value ( Report information about the operation effect ), for example , The control mode setting specifies the rounding scheme : Set a status flag if floating-point overflow occurs in the operation , The operation of setting the status flag is called throwing an exception .
STDC FP_CONTRACT Compilation instructions
FPU You can combine floating-point expressions of multiple operators into one operation , But you can calculate them independently .
The math library broke its heart for floating-point arithmetic
For example look ,
C90 Math library :
C99 and C11 The library provides... For all these functions float The type and long double Function of type :
loglp(x) The value represented is the same as log(1+x) identical , however loglp(x) Different algorithms are used , For the smaller x The calculation is more accurate . therefore , have access to log() Function to perform ordinary operations , But for the high precision and x It's worth less , use loglp() Functions are better .
Computer system structure
Compare real numbers with floating-point numbers
Scope of representation | Representation precision | Uniqueness | |
The set of real Numbers | Infinite | continuity | No redundant |
Floating point numbers | Co., LTD. | Discontinuous | redundancy |
Floating point table number range
A floating-point data representation requires 6 Two parameters to define .
Two numerical :
m: The value of the mantissa , It also includes the code system of mantissa ( Original code or complement code ) And number system ( Decimal or integer );
e: The value of the step code , Generally, code shift is adopted ( Also called partial code 、 Add code 、 I'll wait ) Or complement , Integers ;
Two bases :: Base of mantissa , There are usually binary , Quaternary 、 octal 、 Hexadecimal and decimal, etc ;
: The basis of the order code , Of all the floating-point data representations seen so far ,
Are all 2.
Two words long :
p: Mantissa length , there p It does not refer to the binary digits of mantissa , When when , Every time 4 Binary bits represent one bit mantissa ;
q: Order code length , Because the basis of the order code is usually 2, therefore , In general ,q Is the binary digits of the order code part .
In the computer , Data is always stored in storage units , And the word length of the computer's storage unit is limited , therefore , The number and range of floating-point numbers that any floating-point representation can represent are limited .
Use the original code in the mantissa 、 Pure decimal , The order code adopts code shift 、 Floating point representation of integers , Normalize floating-point numbers N The range of tables is :
Mantissa in original code 、 Normalize the table number range of floating-point numbers in pure decimal
Table number range | Normalized mantissa | Order code | Normalize floating-point numbers |
Maximum positive number | |||
Minimum positive number | |||
Maximum negative number | |||
Minimum negative number |
When the mantissa is represented by a complement , The table number range of the positive number interval is exactly the same as that of the mantissa when the original code is used , The table number range of negative number interval is :
Mantissa complement 、 Normalize the table number range of floating-point numbers in pure decimal
Table number range | Normalized mantissa | Order code | Normalize floating-point numbers |
Maximum positive number | |||
Minimum positive number | |||
Maximum negative number | |||
Minimum negative number |
Floating point table number precision
Table number precision is also called table number error , The fundamental reason for the table count accuracy of floating-point numbers is the discontinuity of floating-point numbers , Because the word length of any floating-point representation is always limited . If the word length is 32 position , The maximum number of floating-point numbers that can be represented by this floating-point representation is individual , In mathematics, real numbers are continuous , It has an infinite number of , therefore , A representation of floating-point numbers. The number of floating-point numbers that can be represented is only a small part of real numbers , That is, a subset of it , We call it the set of floating-point numbers for this floating-point representation .
Floating point set F The table number error of can be defined as , Make N Is a set of floating point numbers F Any given real number in , and M yes F Is closest to N, And used instead of N Floating point number , Then the absolute table number error :, Relative table error
.
Because in the same floating-point representation , The length of the mantissa significant bit of the normalized floating-point number is determined , therefore , The relative table count error of normalized floating-point numbers is determined , Because the distribution of normalized floating-point numbers on the number axis is uneven , Therefore, its absolute table error is uncertain . This is the opposite of the way fixed-point numbers are expressed , The absolute error of the fixed-point number representation is definite , The relative error is uncertain .
There are two direct causes of floating point number table error , One is two floating point numbers a and b Are in a floating-point set of some kind of floating-point representation , and a and b The result of the operation may not be in this floating-point set , Therefore, it must be represented by a floating-point number closest to it in this floating-point set , Thus, the table number error is caused . The other is to convert data from decimal to binary 、 Quaternary 、 Error may occur in octal or hexadecimal .
The first reason :
give an example ,q=1,p=2,rm=2,re=2
All the floating-point numbers that can be represented by a floating-point representation
1(1.1) | 0(1.0) | -1(0.1) | -2(0.0) | |
0.75(0.11) | 3/2 | 3/4 | 3/8 | 3/16 |
0.5(0.10) | 1 | 1/2 | 1/4 | 1/8 |
-0.5(1.10) | -1 | -1/2 | -1/4 | -1/8 |
-0.75(1.11) | -3/2 | -3/4 | -3/8 | -3/16 |
If there are two floating point numbers :a1=1/2,b1=3/4 Within the defined floating point set , And the result of their addition :a1+b1=5/4, Is not in this set of floating point numbers , To do this, you must use the nearest in the set of floating-point numbers 5/4 Floating point number 1 or 3/2 Instead of
So as to generate absolute meter number error : or
The relative table error is : or
Another reason : The process of raw data entering the computer from the outside , Generally speaking, data is converted from decimal system to binary system 、 Quaternary 、 Octal or hexadecimal, etc . Because the length of the physical data storage unit is always limited , Thus, table number error may occur .
Put the decimal number 0.1 In a binary computer , Circular decimals appear , namely :
0.1(10)
=0.000110011001100···(2)
=0.0121212···(4)
=0.06146314···(8)
=0.1999···(16)
The mantissa of finite length cannot be used to express this number accurately , So there is a problem how to deal with the lower part of the mantissa that cannot be expressed , It is usually rounded . There are many ways to round , Different rounding methods produce different table number errors . In order to obtain as high table count accuracy as possible within a limited tail number length , Rounding must be done after normalization .
0.1(10)
=0.110011001100···(2)x2-3
=0.121212···(4)x4-1
=0.6146314···(8)x8-1
=0.1999···(16)x160
Decimal system 0.1 Multiple representations of floating point numbers :
Base value of mantissa | Step symbol | Order code | Tail symbol | mantissa |
rm=2 | 0 | 101 | 0 | 1100110011001100 |
rm=4 | 0 | 111 | 0 | 0110011001100110 |
rm=8 | 0 | 111 | 0 | 1100110011001100 |
rm=16 | 1 | 000 | 0 | 0001100110011001 |
For different mantissa base values rm, The lower part of the mantissa to be processed during rounding is also different , The final result after rounding will not be the same . In general , With the mantissa base value rm The increase of , The prefix in the normalized binary mantissa "0" The more you have . Only in the mantissa base value rm=2 when , To ensure that there is no prefix in the normalized mantissa "0", So as to obtain the highest accuracy of table number .
The table number precision of specifications and floating-point numbers is mainly related to the mantissa base value rm And mantissa length p of , In general , It is considered that the accuracy of the last digit of the normalized mantissa is half , such , The table count precision of normalized floating-point numbers can be expressed as follows :
When rm>2 when ,
Conclusion : When the mantissa length of a floating-point number ( Refers to the number of binary digits ) Phase at the same time , Mantissa base value rm, take 2 It has the highest precision of table number . When the mantissa base value rm>2 when , The table number precision of floating-point numbers is the same as that of rm=2 It will cost times , Equivalent to the mantissa reduced
Binary bits .
《 Design and implementation of fast single precision floating point arithmetic unit 》
Tianhongli , Yan Huiqiang , Zhaohongdong . Design and implementation of fast single precision floating point arithmetic unit [J]. Journal of Hebei University of technology ,2011,40(03):74-78.
The arithmetic unit is CPU An important part of , As a typical PC Computers generally have at least one fixed-point arithmetic unit , stay 586 In previous models , Due to the limitation of hardware conditions and technology at that time , Floating point arithmetic units generally appear in the form of coprocessors ,90 After the age , With the development of hardware technology , Floating point arithmetic unit FPU Can be integrated into CPU Inside , among FPGA( Field programmable gate array ) Technology makes it a reality .
In the development of computer systems , The most widely used representation of real numbers is the floating-point representation . Floating point numbers, on the other hand , There are two forms : Denormalized and normalized floating point operations . Normalized floating point operation requirements : Before operation 、 After the operation, they are normalized numbers , This operation can obtain the largest significant number in the computer , Therefore, standardized floating-point operations are generally used in computers .
This paper designs a fast single precision floating-point arithmetic unit :

- Single precision floating-point number normalization and data type discrimination module : According to the form of input data , Normalize the mantissa .
- Single precision floating-point addition and subtraction preprocessing module : When two normalized single precision floating-point numbers are added or subtracted , First, we must deal with the order code and symbol . Order code division , To align , That is to say, the small order is in line with the large order . The sign of the result of the operation is consistent with that of the largest floating-point number .
- Parallel single precision floating-point addition and subtraction module : Whether you add or subtract , It is necessary to use complement plus operation to complete . When two numbers are added together , Add directly with the complement of two numbers . When two numbers are subtracted , The subtracted number takes the complement directly , Subtract first and negate , Then find the complement , Then add the two numbers . The adder is realized by fast parallel addition .
- Single precision floating-point multiplication or division preprocessing module : When two floating-point numbers are multiplied or divided , The sign of the operation result is equal to the XOR operation of the two number symbols involved in the operation . The order code value of the operation result is : Multiplication E=E 1 +E 2 -7FH; In addition to the operation E=E 1 -E 2 +7FH.(E The order code of the result ,E1 Is the order code of the multiplicand or divisor ,E 2 Is the order code of a multiplier or divisor ).
- Parallel single precision floating point multiplication module : For this multiplier, the unsigned 24*24 Parallel array multiplier , This design method will greatly shorten the time required for multiplication .
- Parallel single precision floating-point division module : Prejudgment 0, If the divisor is 0, Then send an error message ; otherwise , Let the dividend and divisor go directly into the parallel divider ( Do not restore the remainder array divider ) In the process of operation .
- Operation result processing module : Round the result of the operation 、 normalized 、 Identify data types and other operations .
《 be based on FPGA Research on floating point arithmetic unit 》
Dadandan . be based on FPGA Research on floating point arithmetic unit [D]. Inner Mongolia University ,2012.
1. introduction

FPGA( Field programmable gate array )
It is a configurable logic block matrix and connected by programmable interconnection IOB A programmable semiconductor composed of . Using hardware description language to describe the function of digital system , After a series of conversion procedures 、 Automatic placement and routing 、 Simulation and other processes ; Finally, generate the configuration FPGA Device data file and download to FPGA in . In this way, the application specific integrated circuit meeting the requirements of users is realized , It really achieves the goal of self-designed by users 、 The purpose of developing and producing integrated circuits by oneself .

2. Floating point means
According to whether the position of the decimal point is fixed , It is divided into fixed-point representation and floating-point representation .
The representation range of floating-point numbers is mainly determined by the number of bits of the order code , The precision of significant digits is mainly determined by the digits of mantissa .
Normalize floating-point numbers

3. Research on normalized floating point number basic operation and hardware circuit
Floating point addition and subtraction
General operation rules of floating point operation :
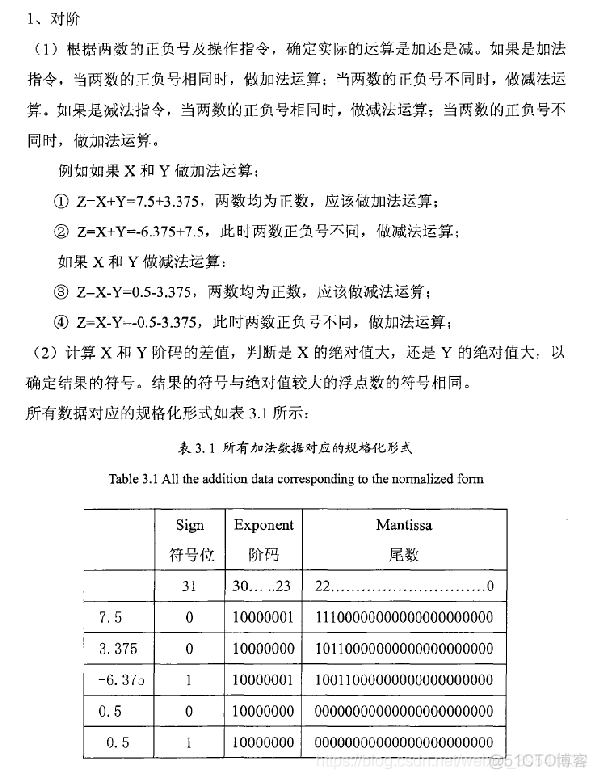
Z=X+Y=-0.5+3.375=2.875, explain IEEE754 Floating point addition process .
X=-0.5,1.0x2-1,s=1,e=-1+127=126,f=0. Use this method to find Y.
Y=3.375, 1.1011x21,s=0,e=1,f=1011.
X: 1 01111110 00000000000000000000000
Y: 0 10000000 10110000000000000000000
because X and Y Different order codes , Mantissa cannot be subtracted directly , To put X The mantissa of is shifted to the right 2 position , such X and Y You have the same order code .
0 10000000 01110000000000000000000(2.875)
The general addition and subtraction operation steps of normalized floating-point numbers must go through the opposite order 、 Add or subtract the mantissa 、 Mantissa normalization 、 Round off 、 There are several steps to judge the overflow .
- Antithetic order

2. Add or subtract the mantissa

3. Mantissa normalization

4. Round off 、 Judgment overflows

Multiplication floating point operation


Floating point division


《 be based on RISC-V Floating point instruction set FPU Research and design of 》
[1] Panshupeng , Liuyouyao , Jiaojiye , Li Zhao . be based on RISC-V Floating point instruction set FPU Research and design of [J/OL]. Computer engineering and Application :1-10[2021-01-02].http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.2127.TP.20201112.1858.002.html.
Floating point processor as an accelerator , Working in parallel with integer pipeline , And share large-scale computing from the main processor 、 High latency floating point instructions . If these instructions are executed by the main processor , Because of floating-point division 、 Operations such as square root, multiplication and accumulation require a lot of computation and a long waiting time , It will slow down the main processor , There will also be a loss of accuracy , So floating-point processors help speed up the entire chip .
Many embedded processors , Especially some traditional designs , Floating point operations are not supported . Many functions of floating-point processors can be emulated through software libraries , Although it saves the additional hardware cost of floating-point processors , But the speed is obviously slower , Not enough to meet the real-time requirements of embedded processors . In order to improve the performance of the system , The floating-point processor needs to be implemented in hardware .
《 Research on high precision algorithm based on multi part floating point representation 》
[1] Du peibing . Research on high precision algorithm based on multi part floating point representation [D]. National Defense University of science and technology ,2017.
The history of floating point numbers
The definition of floating point numbers
Problems with floating point numbers
《 be based on FPGA Research and implementation of single and double precision floating point arithmetic unit based on 》
[1] Wangjingwu . be based on FPGA Research and implementation of single and double precision floating point arithmetic unit based on [D]. Xi'an Petroleum University ,2017.
1.2 Research status of floating point arithmetic units at home and abroad
stay CPU The initial stage of structural design , Floating point arithmetic units are not integrated in CPU Internal , It is a separate chip called a floating point coprocessor , Its function is to assist CPU Process data together . from Intel Of 80486DX CPU Start ,FPU Was integrated into CPU Inside .
2.1 Floating point format parsing
The third chapter Research on Algorithm of floating point arithmetic unit
3.1 Floating point addition and subtraction
3.2 Floating point multiplication
3.3 Floating point division
边栏推荐
- Is it safe to open a securities account by downloading the app of qiniu business school? Is there a risk?
- 如何手动删除浮动ip
- 居家办公初体验之新得分享| 社区征文
- An error "\.\global\vmx86" is reported when vmware12 virtual machine is opened: the system cannot find the specified file.
- Qinglong panel, JD timed task library, script library
- AGCO AI frontier promotion (6.21)
- 塔米狗分享:产权交易的方式及其产权交易市场数据化意义
- PostgreSQL logical storage structure
- Pretraining Weekly No. 50: No Decode converter, neural prompt search, gradient Space reduction
- uva11729
猜你喜欢

Add a description to the form component

Distributed transaction processing scheme big PK

hands-on-data-analysis 第二单元 第四节数据可视化

CVPR2022 | 上科大x小红书首次提出动作序列验证任务,可应用于体育赛事打分等多场景

Apache shardingsphere 5.1.2 release | new driving API + cloud native deployment to create a high-performance data gateway

Centos7 deploying MySQL environment

Educoder web exercises - structural elements

塔米狗分享:产权交易的方式及其产权交易市场数据化意义

How to read AI summit papers?

Repair for a while, decisively reconstruct and take responsibility -- talk about CRM distributed cache optimization
随机推荐
百度交易中台之钱包系统架构浅析
Educoder web exercise - validating forms
居家办公初体验之新得分享| 社区征文
UVA1203 Argus
Implementation principle and application practice of Flink CDC mongodb connector
cartographer_ceres_scan_matcher_2d
Iclr2022 | training billion level parameter GNN for molecular simulation
Add a description to the form component
Not only zero:bmtrain technology principle analysis
如何手动删除浮动ip
UVA1203 Argus
Display all indexes of a table in Oracle
[deeply understand tcapulusdb technology] tmonitor system upgrade
高效远程办公手册| 社区征文
Data types in redis
SSH password free login
Repair for a while, decisively reconstruct and take responsibility -- talk about CRM distributed cache optimization
南京大学 静态软件分析(static program analyzes)-- introduction 学习笔记
Kube-prometheus grafana安装插件和grafana-image-renderer
Educoder web exercises -- text level semantic elements