当前位置:网站首页>leetcode622. Design cycle queue (C language)
leetcode622. Design cycle queue (C language)
2022-07-01 13:53:00 【Brant_ zero】

Catalog
One 、 Topic link and introduction
Two 、 General train of thought
One 、 Topic link and introduction
622. Design loop queue - Power button (LeetCode)
Implement a circular queue , Its characteristics are first in, first out (FIFO) principle , The tail of the team is connected behind the head of the team to form a cycle , This topic is to realize its function .
Two 、 General train of thought
① Create a size of k+1 Array of . Use head and tail Two variables to record the changes of data in the array ;
② When saving data ,tail The pointer moves back ; When deleting data ,head The pointer moves forward .
③ Because it needs to be stored k Data , We open up k+1 The purpose of the space is to prevent overwriting when storing data , When tail+1==head When the queue is full .
3、 ... and 、 Specific steps
3.1 Create structure
There is one head The variable represents the head of the queue ,tail Indicates the end of the queue ,k Indicates the size of the queue ,a Open up an array .
typedef struct {
int *a;
int k;
int head;
int tail;
} MyCircularQueue;3.2 Queue creation
Because the structure is not easy to control , And the function parameters of the following topics are passed in the form of structure pointers , So we need to use structural variables when we want to initially create obj To control .
And because of the function scope , So when we create this structure, we need to use malloc To open up , In this way, when the function is destroyed, the variables we create will not be destroyed , And can successfully return the structure pointer .
MyCircularQueue* myCircularQueueCreate(int k) {
// Control the structure (MyCircularQueue) The pointer to
MyCircularQueue* obj=(MyCircularQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyCircularQueue));
// open up k+1 The array space of
obj->a=(int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*(k+1));
obj->head=0;
obj->tail=0;
obj->k=k;
return obj;
}3.3 Queue insertion
Our thinking is , Insert data into a[tail] The location of , Then make tail++ , In this way, data can be inserted into the queue .
Here's a question , Because we are a circular queue , If that happens :
head Because deleting data leads to moving forward , And then when you insert the data tail Out of Array .
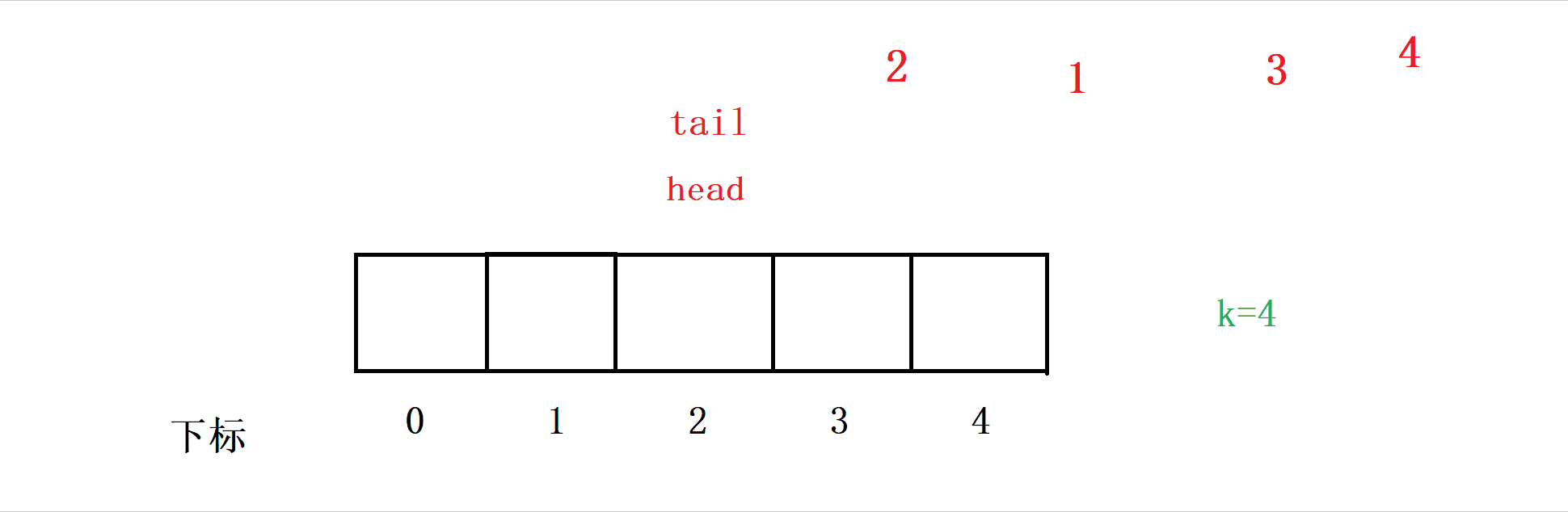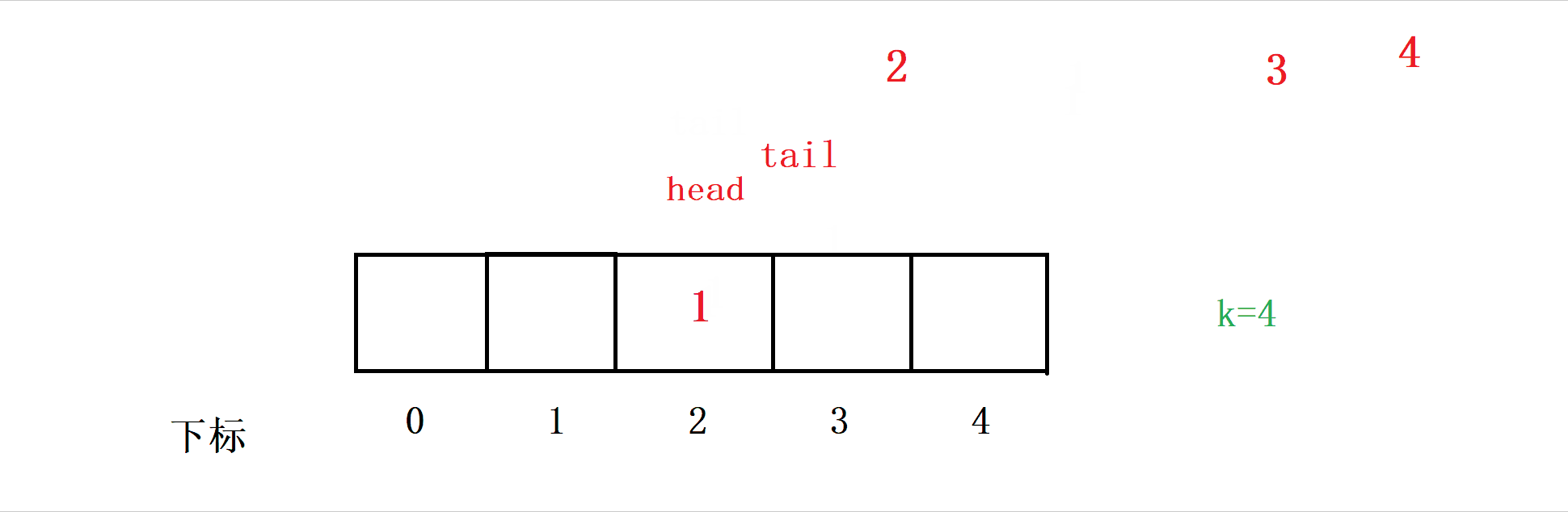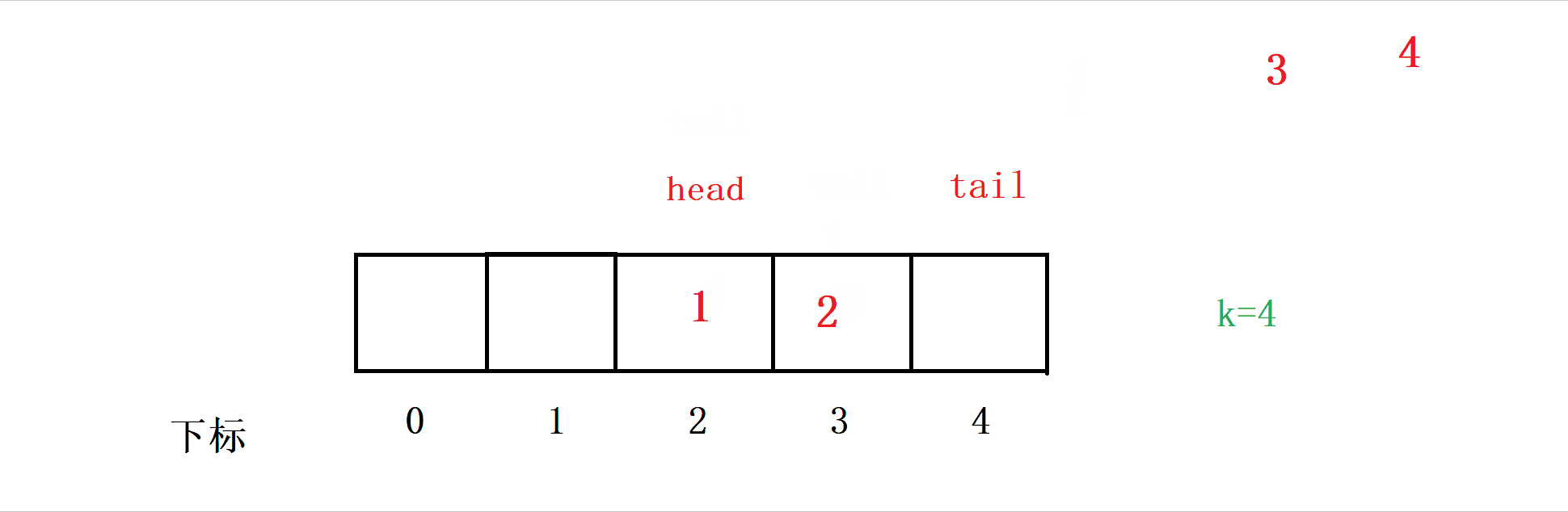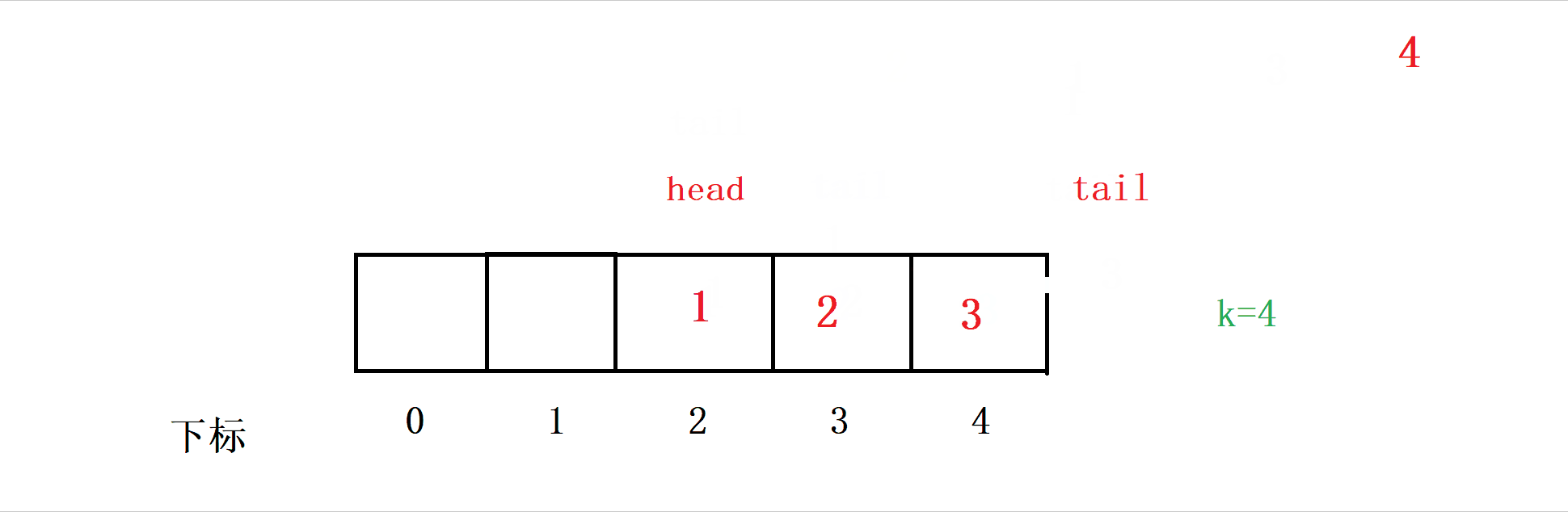
So at this time, we have to judge , If so tail==k+1 when , We are going to let tail Return to the right .
bool myCircularQueueEnQueue(MyCircularQueue* obj, int value) {
// If the queue is not full , Go straight back to false, Insert the failure
if(myCircularQueueIsFull(obj))
return false;
obj->a[obj->tail]=value;
obj->tail++;
//obj->tail%=(k+1)
if (obj->tail==obj->k+1)
{
obj->tail=0;
}
return true;
}3.4 Delete data
Want to delete data , Only the head Move forward one space . Of course , The following situations may also occur .

So we can also judge , When head==k+1 when , We will head Move to the opposite .
bool myCircularQueueDeQueue(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
if (myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj))
return false;
++obj->head;
if (obj->head==obj->k+1)
{
obj->head=0;
}
return true;
}3.5 The queue is empty
Our thinking is , In the initial state of the queue head and tail All save the same subscript , namely head==tail==0, And we stipulated tail+1==head Is full , So only when head and tail The queue is empty only when it is equal
bool myCircularQueueIsEmpty(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
return obj->head==obj->tail;
}3.6 Queue full
Below we have two ways to determine whether the queue is full

Two : Let's take a look at Two In this case , Set a temporary variable temp by tail+1, If tamp==head It means that the queue is currently full and returns true.
Let's take a look at Two In this case , Set a temporary variable temp by tail+1, If tamp==head It means that the queue is currently full and returns true.
The first One In this case , Set a temporary variable temp by tail+1, If temp==k+1, take temp Set as 0, To determine tamp Is it equal to head, If it is equal to , It means full , return true.
bool myCircularQueueIsFull(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
int next=obj->tail+1;
// In fact, it is to judge again tail Whether it is at the end of the array .
if (next==obj->k+1)
next=0;
return next==obj->head;
}3.7 Queue header data
It's very simple , Go straight back to head The data at the subscript is enough .
int myCircularQueueFront(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
if (myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj))
return -1;
else
return obj->a[obj->head];
}3.8 End of queue data
There are two situations here :①tail Not set 0 ②tail Set to zero .

If tail Set to zero , Because at the beginning of the program , We judge whether the queue is empty , therefore k There must be data at the location , We go straight back k The data at the subscript is enough .

int myCircularQueueRear(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
if (myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj))
return -1;
if (obj->tail==0)
{
return obj->a[obj->k];
}
//return obj->a[(obj->tail+k)%(k+1)]
return obj->a[obj->tail-1];
}3.9 Destruction of queues

We first release the array a, Then release the queue .
void myCircularQueueFree(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
free(obj->a);
free(obj);
}Four 、 Code section
// Use arrays to implement
typedef struct {
int *a;
int k;
int head;
int tail;
} MyCircularQueue;
MyCircularQueue* myCircularQueueCreate(int k) {
MyCircularQueue* obj=(MyCircularQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyCircularQueue));
// open up k+1 Space
obj->a=(int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*(k+1));
obj->head=0;
obj->tail=0;
obj->k=k;
return obj;
}
bool myCircularQueueIsEmpty(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
return obj->head==obj->tail;
}
bool myCircularQueueIsFull(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
int next=obj->tail+1;
if (next==obj->k+1)
next=0;
return next==obj->head;
}
bool myCircularQueueEnQueue(MyCircularQueue* obj, int value) {
if(myCircularQueueIsFull(obj))
return false;
obj->a[obj->tail]=value;
obj->tail++;
//obj->tail%=(k+1)
if (obj->tail==obj->k+1)
{
obj->tail=0;
}
return true;
}
bool myCircularQueueDeQueue(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
if (myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj))
return false;
++obj->head;
if (obj->head==obj->k+1)
{
obj->head=0;
}
return true;
}
int myCircularQueueFront(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
if (myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj))
return -1;
else
return obj->a[obj->head];
}
int myCircularQueueRear(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
if (myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj))
return -1;
if (obj->tail==0)
{
return obj->a[obj->k];
}
//return obj->a[(obj->tail+k)%(k+1)]
return obj->a[obj->tail-1];
}
void myCircularQueueFree(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
free(obj->a);
free(obj);
}边栏推荐
- Uni app realizes advertisement scroll bar
- Collation and review of knowledge points of Microcomputer Principle and interface technology - pure manual
- “国防七子”经费暴增,清华足足362亿元,甩第二名101亿 |全国高校2022预算大公开...
- QT社团管理系统
- Enter the top six! Boyun's sales ranking in China's cloud management software market continues to rise
- Camp division of common PLC programming software
- IO的几种模型 阻塞,非阻塞,io多路复用,信号驱动和异步io
- How much money do novices prepare to play futures? Is agricultural products OK?
- Simplex, half duplex, full duplex, TDD and FDD
- Animesr: learnable degradation operator and new real world animation VSR dataset
猜你喜欢

QT learning management system

QT community management system

我们该如何保护自己的密码?

Introduction to distributed transactions (Seata)

龙蜥社区开源 coolbpf,BPF 程序开发效率提升百倍

04-Redis源码数据结构之字典

佩服,阿里女程序卧底 500 多个黑产群……

Kongsong (Xintong Institute) - cloud security capacity building and trend in the digital era

How will the surging tide of digitalization overturn the future?

Computer network interview knowledge points
随机推荐
Spark source code reading outline
A new book by teacher Zhang Yujin of Tsinghua University: 2D vision system and image technology (five copies will be sent at the end of the article)
Camp division of common PLC programming software
微机原理与接口技术知识点整理复习–纯手打
焱融看 | 混合云时代下,如何制定多云策略
This paper introduces an implementation scheme to enhance the favorite transaction code management tool in SAP GUI
逻辑是个好东西
机器学习总结(一):线性回归、岭回归、Lasso回归
After being laid off for three months, the interview ran into a wall everywhere, and the mentality has begun to collapse
Leetcode question 1: sum of two numbers (3 languages)
QT learning management system
Error:Kotlin: Module was compiled with an incompatible version of Kotlin. The binary version of its
详细讲解面试的 IO多路复用,select,poll,epoll
20个实用的 TypeScript 单行代码汇总
uni-app实现广告滚动条
小程序- view中多个text换行
The best landing practice of cave state in an Internet ⽹⾦ financial technology enterprise
Grafana reports an error: error= "failed to send notification to email addresses: [email protected] : 535 Error:
建立自己的网站(21)
10. Page layout, guess you like it