当前位置:网站首页>Pattern recognition - 1 Bayesian decision theory_ P1
Pattern recognition - 1 Bayesian decision theory_ P1
2022-06-24 21:29:00 【Druid_ C】
Knowledge structure (P1+P2)
- Summary
- Minimum error rate Bayesian decision
- Minimum risk Bayesian decision
- Classifier design
- The discriminant function under Gaussian density
1.1 Summary
Prior probability : Probability based on experience or previous data analysis .
Posterior probability : The probability that the data will be corrected again .
Probability density function : Describe the output value of random variables , A function of the probability of being near a certain value . The probability that the value of a random variable falls within a certain region is the integral of the probability density function in this region . When the probability density function exists , Cumulative distribution function  It's the integral of the probability density function . Probability density functions are generally marked in lowercase
It's the integral of the probability density function . Probability density functions are generally marked in lowercase  .
.
Class conditional probability density function : Assume x It's a continuous random variable , Its distribution depends on the category status p(x|ω). That is, the category status is ω At the time of the x The probability density function of .
The feature space : Eigenvector  Situated d Viogerid space , Write it down as
Situated d Viogerid space , Write it down as  .
.
Bayesian decision theory The starting point of this paper is to make use of the quantitative tradeoff between the decision-making of different classifications of probability and the decision-making cost of response . It makes the following assumptions : That is, the decision problem can be described in the form of probability , And assume that all relevant probability structures are known .
Loss function : , Indicates when the category is
, Indicates when the category is  The decision taken
The decision taken  The loss caused , Short for
The loss caused , Short for  .
.
Discriminant function : Some functions used to express decision rules . A set of discriminant functions is usually defined 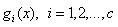 Used to represent multi class decision rules . If
Used to represent multi class decision rules . If  To any
To any  All set up , Will
All set up , Will  belong to
belong to  class . Refer to Bayesian decision rules , A series of discriminant functions can be defined :
class . Refer to Bayesian decision rules , A series of discriminant functions can be defined :
Decision making : about c Class classification problem , According to the decision rules, we can put d Dimensional feature space is divided into c Decision making areas  , The boundary of the decision area is the decision surface . These decision surfaces are Hypersurfaces in feature space , Obviously, two adjacent decision-making surfaces , The value of its discriminant function is equal . namely , If
, The boundary of the decision area is the decision surface . These decision surfaces are Hypersurfaces in feature space , Obviously, two adjacent decision-making surfaces , The value of its discriminant function is equal . namely , If  and
and  adjacent , Then their decision surface equations satisfy
adjacent , Then their decision surface equations satisfy  .
.
Equal density trajectory : In the discriminant function under Gaussian density , The equal density trajectory is a super ellipsoid ( The direction of its principal axis is determined by the eigenvector of the matrix , The length of the principal axis is proportional to its eigenvalue ). From the multivariate normal distribution, we can know , When its exponential term is equal to a constant , density p(x) The value of does not change , Therefore, the equifunction points are points of constants obtained by using the following equation , namely :
covariance : Used to measure the overall error of two variables , The expectation of making the overall error of two variables , For example, for two random variables X and Y The covariance between is recorded as Cov(X,Y).
Covariance matrix : It is the generalization of two random variables to high-dimensional random vectors . set up  by n Dimensional random variable , It's called matrix
by n Dimensional random variable , It's called matrix  by n Dimensional random variable X The covariance matrix of , Write it down as D(X), among
by n Dimensional random variable X The covariance matrix of , Write it down as D(X), among 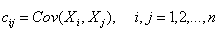 by X Components of
by X Components of 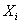 and
and  The covariance .
The covariance .
Markov distance : sample x To center μ The calculation of follows the following formula :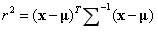
Euclidean distance :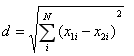
1.2 Minimum error rate decision
Problem description :
To a c Class problem 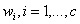 , Eigenvectors
, Eigenvectors  , A priori probability is known
, A priori probability is known  And conditional probability density function
And conditional probability density function  . Its task is to measure the observed samples
. Its task is to measure the observed samples  , Choose which category is the most reasonable ( Minimum error rate )?
, Choose which category is the most reasonable ( Minimum error rate )?
Bayesian decision making :
Posterior probability :
Decision making rules :
Error rate :
Minimum error rate :
Several equivalent forms of Bayesian decision making :
1.3 Minimum risk decision
In practical application scenarios , It is not enough to minimize the error rate of decision making , We should also consider the risks arising from the judgment . So the concept of loss is introduced , When considering the loss caused by misjudgment , Not just based on the size of a posteriori probability , It is necessary to consider whether the decision taken has the least loss . For a given x, Consider making a decision about it  , but
, but  The specific category status is unknown , Therefore, conditional risk should be considered .
The specific category status is unknown , Therefore, conditional risk should be considered .
Problem description : Yes c Class problem ,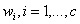 , Eigenvectors
, Eigenvectors  , A priori probability is known
, A priori probability is known  , Conditional probability density function
, Conditional probability density function  , The decision space contains a A decision
, The decision space contains a A decision  , And the loss function
, And the loss function  . Its task is : If a sample is observed
. Its task is : If a sample is observed  , Which category should they be classified into to minimize the risk ?
, Which category should they be classified into to minimize the risk ?
Conditional risk and expected risk :
Conditional risk : , It's a random variable
, It's a random variable  Function of , It can be calculated as follows :
Function of , It can be calculated as follows :
Expected risk :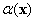 , Treat decision rules as random variables
, Treat decision rules as random variables  Function of . For all possible samples in the feature space
Function of . For all possible samples in the feature space  The expected loss from the decision taken is :
The expected loss from the decision taken is :
Minimum risk Bayesian decision is to minimize the expected risk  .
.
computational procedure :
- Using Bayes formula to calculate posterior probability :

- Use decisions to calculate risk :

- Choose the decision with the least risk among various decisions :
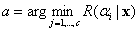
There are two kinds of situations : For two cases , There is no rejection (a=c=2), Yes :

The decision rule is :
namely :
Other equivalent forms : No loss of generality , It can be assumed  , Therefore, the decision rule can also be expressed as :
, Therefore, the decision rule can also be expressed as :
and 
0-1 loss: In the classification problem , Usually each category state is associated with c Class about , And decision  It is usually interpreted as a category status , Be adjudicated as
It is usually interpreted as a category status , Be adjudicated as  . If a decision is taken
. If a decision is taken  The actual category is
The actual category is  , So in i=j The criterion is correct , Otherwise, misjudgment will occur . Avoid misjudgment , It is necessary to find a rule to make the probability of misjudgment ( Error rate ) To minimize the . The loss function in this case is “0-1 Loss ”, Also known as “ Symmetry loss ” function :
, So in i=j The criterion is correct , Otherwise, misjudgment will occur . Avoid misjudgment , It is necessary to find a rule to make the probability of misjudgment ( Error rate ) To minimize the . The loss function in this case is “0-1 Loss ”, Also known as “ Symmetry loss ” function :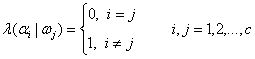
The risk corresponding to this loss function is the average error probability , Because the conditional risk is :
Minimize the average error rate (MAP):
Yes, give i≠j, If  , It's called
, It's called  .
.
1.4 classifier
Classifier design : The classifier can be seen as calculating c A discriminant function , A machine that selects the class corresponding to the maximum value of the discriminant function as the classification result .
The discriminant function in two cases :
For two cases , Just define a discriminant function :
The decision surface equation in two cases :g(x)=0. When x When it is one dimension , The decision surface is a point ; When x When it is two-dimensional , The decision surface is a line ; In three dimensions , The decision-making side is one side , The higher dimension is a hypersurface .
Classification error rate :
Talk about error probability and error integral , Note that this knowledge point should have been placed after the discriminant function of normal distribution , But because of the typesetting problem, I put it here first .
- Average misclassification probability in two cases :

- Average misclassification probability in multi class cases :

- The average classification accuracy in multi class case :

Summary
- In fact, it's easy to know some conceptual formulas , But it takes a lot of effort to deeply understand and skillfully use . The understanding of Bayesian decision theory is based on Conditional probability 、 Understanding of full probability formula and Bayes formula . As for the normal distribution discriminant function, you need to have a solid and comprehensive understanding of the normal distribution and its related properties .
- This chapter basically revolves around There are two kinds of situations an .
- MD The formula editor is hard to use .
- In this chapter, you need to master some “ distance ” The concept of , About distance ( Euclidean distance 、 Min's distance 、 Markov distance 、 Manhattan distance 、 Cosine distance 、 Hamming distance, etc ) See the column :[ Address ]
边栏推荐
- Rip/ospf protocol notes sorting
- Static routing job
- Address mapping of virtual memory paging mechanism
- Appium desktop introduction
- 基于STM32的物联网下智能化养鱼鱼缸控制控制系统
- JMeter implementation specifies concurrent loop testing
- Reflection - class object function - get method (case)
- Am, FM, PM modulation technology
- memcached全面剖析–3. memcached的删除机制和发展方向
- It was Tencent who jumped out of the job with 26k. It really wiped my ass with sandpaper. It gave me a hand
猜你喜欢
Page replacement of virtual memory paging mechanism

C语言实现DNS请求器

Common data model (updating)
基于C语言实现的足球信息查询系统 课程报告+项目源码+演示PPT+项目截图
![[cloud native learning notes] kubernetes Foundation](/img/c9/bd9ac90dd0dd27c450db33ad6b2fa5.jpg)
[cloud native learning notes] kubernetes Foundation

Codeforces Round #720 (Div. 2)

EditText controls the soft keyboard to search

Microsoft Certification (dynamic 365) test

Sleep revolution - find the right length of rest

Does the developer want to change to software testing?
随机推荐
AntDB数据库在线培训开课啦!更灵活、更专业、更丰富
Tso hardware sharding is a header copy problem
Handwritten RPC the next day -- review of some knowledge
Poj1061 frog dating (extended Euclid)
Static routing job
JUnit unit test
What does CTO (technical director) usually do?
Memcached comprehensive analysis – 5 Memcached applications and compatible programs
Functional analysis of ebpf sockops
Basic database syntax learning
Memcached comprehensive analysis – 3 Deletion mechanism and development direction of memcached
SYSCALL_ Define5 setsockopt code flow
VIM usage
go_ keyword
DHCP operation
Pytest testing framework
Address mapping of virtual memory paging mechanism
[cloud native learning notes] kubernetes Foundation
123. 买卖股票的最佳时机 III
ping: www.baidu. Com: unknown name or service