当前位置:网站首页>Address mapping of virtual memory paging mechanism
Address mapping of virtual memory paging mechanism
2022-06-24 21:12:00 【The smell of tobacco】
summary
Previous articles Virtual memory The paging mechanism is briefly introduced . There is another question , That is how to map the logical address in the virtual memory to the physical address ? Let's make a brief analysis today .
For a paged address , It usually contains two elements :
- Page number : Page
- Offset : The number of bytes of the current page
The following addr_virtual(p, o) Represents a logical address , With addr_real(p, o) Represents a physical address ( The physical address is also paged ).
A page table
The first step is to think about , If you want to find the corresponding physical address according to a logical address , Then the corresponding relationship must be stored somewhere , Because mapping is irregular . What data structure should be used to store ?
Because in paging , page Is a minimum unit , Therefore, we only need the mapping relationship of page numbers , Logical and physical addresses have the same page size , The offset is exactly the same .
according to key seek value, This is not a map Well . Look at this again map Of key, Page numbers are all numbers , And it's sequential . This is just an array . beautiful , It's an array .
in other words , This page table is indexed by logical page numbers , One dimensional array with physical page number as value . The process of address translation is as follows :

The elements in the page table do not just store physical page numbers , Some additional flag bits are also stored , Used to identify the properties of the current page , A few simple examples :
- Existential bit : Whether it is currently loaded into memory . If it is not loaded, the operating system is required to load
- Modify bit : Whether the current page has been modified in memory . If modified , When reclaiming physical memory, you need to write it to the hard disk
- Kernel permissions : Whether the current page needs kernel mode to access
- Whether to read bits
- Whether bits can be written
- Is it executable
- wait
Because each process has its own virtual memory , So each process needs its own page table .
In order to improve operation efficiency , This translation process is completed by hardware , Both CPU Memory management unit in mmu To complete .
Is it easy to see ? good , Introduction completed , This concludes the article .
Problems and solutions
ha-ha , To make fun of . How could it be so easy to end . Now let's briefly analyze the problems of this simple model . According to the experience of the algorithm , Most algorithms are implemented , Or the time complexity is too high , Or the space complexity is too high .
Time issues
Imagine the steps to access a memory :
- Look up the page table to find the corresponding physical address
- Access physical address
The operation of looking up the page table is also a memory access . in other words , CPU Each memory access requires an additional memory access . The execution time is doubled directly .
Solution
The solution is that we have now used rotten : cache . Memory to CPU There are already L1L2 cache , stay mmu There is also a cache of page tables in TLB. The steps for each address translation are as follows ( Ignore missing pages ):
- see
TLBWhether there is a cache in , If there is direct access - if
TLBDoes not exist in the , Get from the memory page table and putTLB
TLB The premise of existence , Is that the access of the program is local . finally , It is the locality of the program that saves us .
Space problem
Let's simply calculate how much space is needed to store this page table .
stay 32 position CPU in , The accessible logical address space is 4G. Suppose the page size is : 4kb, Then the total number of pages is :
4G / 4kb = (2^32) / (2^12) = 2^20 = 1mb
suppose , Each element of the page table needs 4 Bytes , Then the total space required is : 4mb. Each process just needs to store the page table 4mb. And it's still 32 position , If it is 64 Who? ? You can calculate it , The result is exaggerated .
Solution
Learn from the idea of memory paging , We divide memory into n A page , You can load it on demand . Again , You can also divide a large page table into n A small page table , Then you can partially load , Both Multi level page table
Explain with the simplest two-level page table , The virtual memory is roughly divided as follows :

The structure of the page table is roughly as follows :

Be careful , At this time, the page number in the logical address stores two contents :
- Index of the first level page table
- Index of secondary page table
Why does multi-level page table solve the problem of space ? Again, according to the local principle of the program , Most of the corresponding values in the first level page table are empty , Most of the secondary page tables are not loaded into memory .
Now let's calculate again , still 32 position CPU, The size of the page is still 4kb, The element size in the page is still 4 byte . At this point, assume that each element of the first level page table is responsible for 4mb Space . Then the total number of pages occupied by the first level page table is : 4G / 4mb = (2^32) / (2^22) = 2^10. The space occupied by the first level page table is : (2^10) * (2^2)=4kb
The total number of pages in each secondary page table is : 4mb / 4kb = (2^22) / 2(12) = 2^10 = 1024, Occupancy space : (2^10) * (2^2) = 4kb
Only the first level page table is resident in memory , The second level page table only needs to load part of it . The space drops directly .
however , It brings a new problem , Now get a physical address , Need to access memory twice , This is slower than before ? Don't forget what just happened TLB, With this layer of cache , Most of the visits are in mmu It's going on inside . Again , The locality principle of the program saved us .
Multi level page table , Expand the secondary page table further , You can get a multi-level page table , I won't repeat .
The locality of the program
Know how the address is mapped , How does it help us to write programs in ordinary times ?
Page conversion is based on the locality of the program , So when we write code , Try to ensure that what you write is local , for instance :
int main() {
int i, j;
int arr[1024][1024];
// The first way
for(i = 0; i < 1024; i++){
for(j = 0; j < 1024; j++){
global_arr[i][j] = 0;
}
}
// The second way
for(j = 0; j < 1024; j++){
for(i = 0; i < 1024; i++){
global_arr[i][j] = 0;
}
}
}
The purpose of the above code is very simple , Give me a 1024*1024 Initializes a two-dimensional array of . Can you see the difference between the two methods ?
Traversal methods are different , Mode one Is a line by line traversal , Mode two Is a column by column traversal .
We know , Two dimensional arrays are stored sequentially in memory . in other words , A two-dimensional array : [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]], The storage order in memory is : 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6.
And our array , Each row 1024 individual int Elements , Is precisely 4kb The size of a page .
therefore , Mode one The order in which pages are accessed is : page1, page1 ... page1024, page1024, Per page access 1024 Next time , Switch to the next page , Co occurring 1024 Next page switching
and , Mode two The order in which pages are accessed is : page1, page2...page1024 ... page1, page2...page1024, Visit each page in turn , Per page access 1024 Time , Co occurring 1024*1024 Next page switching
High performance, lower judgment , Mode one More in line with the principle of locality , Mode two Your visit is too jumping .
Of course , Now when the memory is large , Everything is loaded into memory , meanwhile TLB Cached all page mappings , There is no difference between the two methods . however :
- if
TLBCapacity is insufficient , The new cache will eliminate the old cache , Frequent access to different pages will cause more cache invalidations - If memory capacity is insufficient , Writing a new page will weed out the old page , Frequent access to different pages will result in more memory swapping in and out .
Words alone are no proof
Of course , Words alone are no proof , In order to have an intuitive feeling about the switching mechanism of the above page , We go through getrusage Function to get the page switching information of the program . The code is as follows :
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/resource.h>
const int M = 1024;
// Increase the size of the column , To make the effect obvious . 10mb
const int N = 1024*10;
// Because the stack size is limited , Therefore, the variable is promoted to global , Put it in the pile
int global_arr[1024][1024*10];
int main() {
int i, j;
// The first way
for(i = 0; i < M; i++){
for(j = 0; j < N; j++){
global_arr[i][j] = 0;
}
}
// The second way
// for(j = 0; j < N; j++){
// for(i = 0; i < M; i++){
// global_arr[i][j] = 0;
// }
// }
struct rusage usage;
getrusage(RUSAGE_SELF, &usage);
printf(" Page recycle times : %ld\n", usage.ru_minflt);
printf(" Number of page breaks : %ld\n", usage.ru_majflt);
}
It is still relatively simple for computers to run such a small program , It won't make any difference , Therefore, the memory of the process should be limited . I am through restriction docker Available memory :
docker run -it -m 6m --memory-swap -1 debian bash
good , Everything is available. , Let's see the results :
Mode one

Mode two
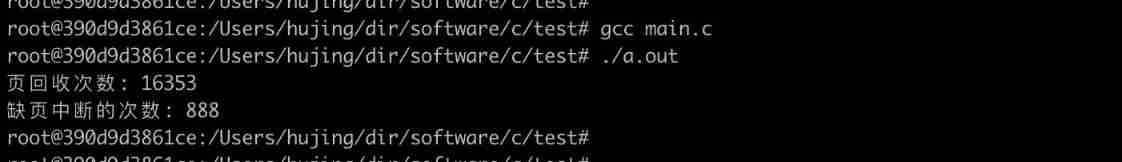
You can see , Mode one Want to compare Mode two Is much better .
so , Procedures with high performance requirements , When you have no optimization direction , Locality may help you .
Link to the original text : https://hujingnb.com/archives/698
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
What are the problems with traditional IO? Why is zero copy introduced?
Handling of garbled JMeter response data - three solutions

Several common command operations in win system

It was Tencent who jumped out of the job with 26k. It really wiped my ass with sandpaper. It gave me a hand

Visitor model -- generation gap between young and middle-aged people

How to apply agile development ideas to other work

Sequence stack version 1.0

伯克利、MIT、剑桥、DeepMind等业内大佬线上讲座:迈向安全可靠可控的AI
Talking about the range of data that MySQL update will lock

Pytest testing framework
随机推荐
Format method and parse method of dateformat class
What does virtualization mean? What technologies are included? What is the difference with private cloud?
Reflection - class object function - get method (case)
DAPP system customization of full chain hash game (scheme design)
Minimum cost and maximum flow (template question)
Interpreter mode -- formulas for dating
Rename and delete files
网络安全审查办公室对知网启动网络安全审查
Curl command
Enjoy yuan mode -- a large number of flying dragons
Is the waiting insurance record a waiting insurance evaluation? What is the relationship between the two?
Learn to use a new technology quickly
等保备案是等保测评吗?两者是什么关系?
伯克利、MIT、剑桥、DeepMind等业内大佬线上讲座:迈向安全可靠可控的AI
maptalks:数据归一化处理与分层设色图层加载
Record a deletion bash_ Profile file
How to apply agile development ideas to other work
The four stages of cloud computing development have finally been clarified
go_ keyword
List set Introduction & common methods
