当前位置:网站首页>Codeforces Round #744 (Div. 3) 解题报告
Codeforces Round #744 (Div. 3) 解题报告
2022-06-11 21:18:00 【dplovetree】
文章目录
A. Casimir’s String Solitaire
题意:
对于一个字符串,有两种操作:
1、选择字符串中的一对‘A’和‘B’,删除他们;
2、选择字符串中的一对‘B’和‘C’,删除他们;
问能否通过一系列操作把字符串变成空串。
思路:
计三种字符的个数,只要’B’的个数是’A’和‘C’的个数和即可。
代码:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
int main(){
int t;
cin>>t;
while(t--){
string s;
cin>>s;
int cnt1=0,cnt2=0,cnt3=0;
for(int i=0;i<s.length();i++){
if(s[i]=='A')cnt1++;
else if(s[i]=='B')cnt2++;
else cnt3++;
}
if(cnt2==cnt1+cnt3)cout<<"YES\n";
else cout<<"NO\n";
}
return 0;
}
B. Shifting Sort
题意:
给你一个长度为 n , n < = 50 n,n<=50 n,n<=50的序列,每次可以选择一个区间,循环向左位移几位,即区间头部几位移到区间末尾,其他树向前补上空格;
用 x < = n x<=n x<=n次操作使序列变成升序,输出操作序列。
思路:
用结构体存储操作序列,如果有的数已经在位置上了就不操作。因为 n < = 50 n<=50 n<=50直接暴力枚举即可。
代码:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
struct node{
int l,r,d;
}z[100];
int cnt=0;
int s[100];
int a[100];
int main(){
int t;
cin>>t;
while(t--){
cnt=0;
int n;
cin>>n;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)cin>>s[i];
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
int pos=i;
for(int j=i+1;j<=n;j++){
if(s[j]<s[pos])pos=j;
}
if(pos==i)continue;
cnt++;
z[cnt].l=i;z[cnt].r=n;
z[cnt].d=pos-i;
for(int j=i;j<pos;j++){
a[j-i+1]=s[j];
}
for(int j=pos;j<=n;j++){
s[j-z[cnt].d]=s[j];
}
for(int j=n-z[cnt].d+1;j<=n;j++){
s[j]=a[j-n+z[cnt].d];
}
}
cout<<cnt<<endl;
for(int i=1;i<=cnt;i++){
cout<<z[i].l<<" "<<z[i].r<<" "<<z[i].d<<endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
C. Ticks
题意:
给你一个 n ∗ m n*m n∗m的网格,每次可以在网格上涂一个形如‘V’字形的图形,一个V形图案的大小定义为V字边的长度。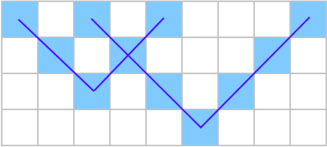
如图左边的V大小为2,右边的大小为3。
初始图为空白的,判断是否能通过在图上画几个大小 大于给定值的V形,让图变成给定图。
思路:
同样数据范围很小,可以暴力一点。
直接枚举每个星号做为V的下部顶点的情况,如果V的大小大于给定值,就把这些星号做个标记。
最后检查是否所有的星号都做了标记。
代码:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
int n,m,k;
char mp[11][30];
int vis[11][30];
void dfs(int x,int y){
int dep=0;
for(int i=1;i<=20;i++){
int nx=x-i,ny1=y-i,ny2=y+i;
if(nx<1||ny1<1||ny2>m||mp[nx][ny1]!='*'||mp[nx][ny2]!='*')break;
dep++;
}
if(dep>=k){
vis[x][y]=1;
for(int i=1;i<=20;i++){
int nx=x-i,ny1=y-i,ny2=y+i;
if(nx<1||ny1<1||ny2>m||mp[nx][ny1]!='*'||mp[nx][ny2]!='*')break;
vis[nx][ny1]=1;vis[nx][ny2]=1;
}
}
}
int main(){
int t;
cin>>t;
while(t--){
cin>>n>>m>>k;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)cin>>mp[i]+1;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
for(int j=1;j<=m;j++)vis[i][j]=0;
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
for(int j=1;j<=m;j++){
if(mp[i][j]=='*'){
dfs(i,j);
}
}
}
int f=1;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
for(int j=1;j<=m;j++){
if(mp[i][j]=='*'&&!vis[i][j])f=0;
}
}
if(f)cout<<"YES\n";
else cout<<"NO\n";
}
return 0;
}
D - Productive Meeting
题意:
一堆人交流,两个人每交流一次他们交流的次数就会少一次(狗头,问最多的交流次数
思路:
贪心
因为我们不希望有人退出会议(退出会议代表选择变少了,更容易出现剩一个人权值很大的情况),因此每次都取拥有最大a[i]的和次大a[i]的两个人开展对话,这样一定是最优的。或者可以每次取最大和最小的。
让交流次数多的人先交流,直到只剩一个人或者都不能交流了
优先队列里直接排序了
代码一:
每次取最大和次大的人交流。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define pii pair<int, int>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
struct node {
int a, b;
}b[200005];
signed main() {
int t;
cin>>t;
while (t--) {
int n;
cin >> n;
priority_queue<pii> q;
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++) {
int x;
cin>>x;
if(x) q.push({
x, i});
}
int cnt=0;
while (!q.empty()) {
if (q.size() == 1) break;
pii x=q.top();
q.pop();
pii y=q.top();
q.pop();
++cnt;
b[cnt].a=x.second;
b[cnt].b = y.second;
x.first--;
y.first--;
if (x.first!=0) q.push(x);
if (y.first!=0) q.push(y);
}
cout<<cnt<<endl;
for(int i=1; i<=cnt; i++) cout<<b[i].a<<" "<<b[i].b<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
代码二:
每次选取最大和最小的人谈话, 这样最大的人就会尽可能的小。
用set维护
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define pii pair<int, int>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
struct node {
int a,b;
}b[200005];
signed main() {
int t;
cin>>t;
while (t--) {
int n;
cin >> n;
set<pii> s;
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++) {
int x;
cin>>x;
if(x)s.insert({
x, i});
}
int cnt=0;
while (!s.empty()) {
if (s.size() == 1) break;
auto it=s.begin();
pii x=*it;
s.erase(it);
it=--s.end();
pii y=*it;
s.erase(it);
++cnt;
b[cnt].a=x.second;
b[cnt].b = y.second;
x.first--;
y.first--;
if (x.first!=0) s.insert(x);
if (y.first!=0) s.insert(y);
}
cout<<cnt<<endl;
for(int i=1; i<=cnt; i++) cout<<b[i].a<<" "<<b[i].b<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
E1. Permutation Minimization by Deque
思路:
要求字典序最小的方案,贪心即可,记录当前序列第一位的值,如果放的值比 front的值小,就放在front,能使字典序变小,否则放在 back
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
int n;
int s[200050];
deque<int>d;
int main(){
int t;
cin>>t;
while(t--){
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)scanf("%d",&s[i]);
int pre=s[1];d.push_back(s[1]);
for(int i=2;i<=n;i++){
if(pre>s[i]){
pre=s[i];
d.push_front(s[i]);
}else d.push_back(s[i]);
}
while(!d.empty()){
int x=d.front();
d.pop_front();
printf("%d ",x);
}
printf("\n");
}
}
E2. Array Optimization by Deque
思路:
还是贪心的思路,可以证明一定是放在当前最优的位置即可。
考虑用 离散化+线段树维护。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
int n;
int s[200050];
vector<int>v;
int tr[800050];
void build(int p,int l,int r){
tr[p]=0;
if(l==r)return;
int mid=l+r>>1;
build(2*p,l,mid);
build(2*p+1,mid+1,r);
}
void update(int p,int l,int r,int x){
if(l==r){
tr[p]++;
return;
}
int mid=l+r>>1;
if(x<=mid)update(2*p,l,mid,x);
else update(2*p+1,mid+1,r,x);
tr[p]=tr[2*p]+tr[2*p+1];
}
int query(int p,int l,int r,int x,int y){
if(x>y)return 0;
if(x<=l&&r<=y)return tr[p];
int ans=0;
int mid=l+r>>1;
if(x<=mid)ans+=query(2*p,l,mid,x,y);
if(mid<y)ans+=query(2*p+1,mid+1,r,x,y);
return ans;
}
int main(){
int t;
cin>>t;
while(t--){
scanf("%d",&n);
v.clear();
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)scanf("%d",&s[i]),v.push_back(s[i]);
sort(v.begin(),v.end());
v.erase(unique(v.begin(),v.end()),v.end());
int len=v.size();
build(1,1,len);
ll ans=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
int pos=lower_bound(v.begin(),v.end(),s[i])-v.begin();
int res1=query(1,1,len,1,pos);
int res2=query(1,1,len,pos+2,len);
ans+=min(res1,res2);
update(1,1,len,pos+1);
}
printf("%lld\n",ans);
}
}
F. Array Stabilization (AND version)
思路:
相当于序列循环变换 长度为d,因为是 与操作,原来是0的位置之后还是0,循环变换之后 ,0可以去改变1,用 bfs 模拟实现即可。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
int n,d;
queue<int>q;
int vis[1000050];
int s[1000050];
int main(){
int t;
cin>>t;
while(t--){
scanf("%d%d",&n,&d);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
scanf("%d",&s[i]);
if(s[i])vis[i]=1e9;
else vis[i]=0,q.push(i);
}
while(!q.empty()){
int x=q.front();q.pop();
int nex=(x+d)%n;
if(vis[nex]>vis[x]+1){
vis[nex]=vis[x]+1;
q.push(nex);
}
}
int ans=0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
ans=max(ans,vis[i]);
}
if(ans==1e9)printf("-1\n");
else printf("%d\n",ans);
}
}
G. Minimal Coverage
很好的一道题目,有一个 d p dp dp优化小技巧。
题意:
有 1 e 4 1e4 1e4个线段,要把他们按顺序放在一维数轴上,第一个随便放,接下来的线段的起点必须从上一个线段的终点开始,左右方向无所谓,要求总覆盖的长度最小
思路:
首先考虑状态转移,设三维状态 d p [ i ] [ j ] [ k ] dp[i][j][k] dp[i][j][k],分别枚举起点、下界和上界,覆盖的长度就是 上界 - 下界。但是三维的状态肯定会 T。
考虑优化掉一维状态。
我们可以固定下界,这样 dp 转移就是多起点转移了,但是多起点很容易实现,多设置一些初始状态即可。这样我们只需要记录以 i i i 作为起点的最小上界去转移。
像这种下界是 枚举量,起点是过程量,我们可以考虑用平移、固定下界的方法省去一维 dp;
代码:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
int n,d;
int s[10050];
int dp[10050][2060];
int main(){
int t;
cin>>t;
while(t--){
cin>>n;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)cin>>s[i];
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
for(int j=0;j<=2000;j++)dp[i][j]=1e9;
for(int i=0;i<s[1];i++)dp[1][i]=i+s[1];
for(int i=s[1];i<=2000;i++)dp[1][i]=i;
for(int i=2;i<=n;i++){
for(int j=0;j<=2000;j++){
if(dp[i-1][j]==1e9)continue;
if(j+s[i]<=2000){
dp[i][j+s[i]]=min(dp[i][j+s[i]],max(dp[i-1][j],j+s[i]));
}
if(j-s[i]>=0){
dp[i][j-s[i]]=min(dp[i][j-s[i]],max(dp[i-1][j],j));
}
}
}
int ans=1e9;
for(int i=0;i<=2000;i++)ans=min(ans,dp[n][i]);
cout<<ans<<endl;
}
}
边栏推荐
- Regular check matches positive integer or decimal limit between [0-100] and [0-1000]
- 第二部分 数据链路层
- Release of version 5.6 of rainbow, add multiple installation methods, and optimize the topology operation experience
- [Game Theory - introduction]
- Application analysis of Poe image acquisition card in machine vision industrial computer
- 为什么需要微服务
- Lr-link Lianrui makes its debut at the digital Expo with new products - helping the construction of new infrastructure data center
- Online excel file parsing and conversion to JSON format
- ORA-04098: trigger ‘xxx.xxx‘ is invalid and failed re-validation
- Pyqt5 technical part - set the default value of qcombobox drop-down box and get the current selection of the drop-down box
猜你喜欢
Compilation process of program

BCC tool tool usage

JMeter load test finds the maximum number of concurrent users (including step analysis)

新品发布:国产单电口千兆网卡正式量产!

Why should I use iwarp, roce V2, nvme of and other protocols for 100g network transmission

Flutter implements the JD address selection component

Redis fourth session - redis high performance principle (multiplexing) and high availability analysis (backup, master-slave)

IDEA中,运行yarn命令,显示无法加载文件,因为在此系统上禁用运行脚本
Tensorflow 2. X Getting Started tutorial

第二部分 数据链路层
随机推荐
RANSAC extract cylinder (matlab built-in function)
stream中文排序
频域滤波器
2022年6月9日 16:29:41 日记
[Game Theory - introduction]
php pcntl_fork 创建多个子进程解析
Implement AOP and interface caching on WPF client
Which Bluetooth headset is better within 500? Inventory of gifts for girls' Day
Go language for loop
BCC tool tool usage
Release of version 5.6 of rainbow, add multiple installation methods, and optimize the topology operation experience
[game theory complete information static game] strategic game
数据库每日一题---第9天:销售员
Work assessment of spectral analysis of Jilin University in March of the 22nd spring -00079
Goland中在文件模板中为go文件添加个人声明
Online excel file parsing and conversion to JSON format
Release of version 5.6 of rainbow, add multiple installation methods, and optimize the topology operation experience
Three waves of changes in cloud computing
[thinking about life] words and sounds
Redis第四话 -- redis高性能原理(多路复用)和高可用分析(备份、主从)