当前位置:网站首页>Redis - 12. Application problem solving
Redis - 12. Application problem solving
2022-06-22 11:56:00 【Q.E.D.】
1、 Cache penetration
1.1、 Problem description
When... Is introduced into the system redis After cache , When a request comes in , We'll start with redis Query in cache , If there is a cache, it will return directly , If it is not in the cache, go to db Query in ,db If there is one in, it will be thrown into the cache , But some key Corresponding to more data in db Does not exist in , Each time for this key The request for could not be fetched from the cache , Requests will be pressed to db, Which may overwhelm db.
For example, use a non-existent user id Get user information , No matter cache or database , If hackers take advantage of a large number of such attacks, they may overwhelm the database .
1.2、 Solution
1.2.1、 Cache null values
If the data returned by a query is empty ( Whether the database exists or not ), We still put this result (null) Cache , Set a very short expiration time , Up to five minutes
1.2.2、 Set up an accessible list ( White list )
Use redis Medium bitmaps Type defines a list of accessible , list id As bitmaps The offset , Every time fanwenhe bitmap Inside id Compare , If you visit id be not in bitmaps Inside , Then intercept , Access not allowed
1.2.3、 Use of Blum filter
The bloon filter (Bloom Filter) yes 1970 In, bron put forward , It's actually a very long binary vector ( Bitmap ) And a series of random mapping functions ( hash function ).
Bloom filters can be used to detect whether an element is in a collection , Its advantage is that the space efficiency and the query world are far more than the general algorithm , The disadvantage is that it has certain error recognition rate and deletion difficulty .
Hash all possible data to a large enough bitmaps in , A certain nonexistent data will be bitmaps Intercept , Thus, the query pressure on the underlying storage system is avoided .
1.2.4、 Real-time monitoring
If I found redis It's starting to drop , Need to check access objects and data , Cooperate with operation and maintenance personnel , You can set a blacklist to restrict the provision of services ( such as :IP The blacklist )
2、 Cache breakdown
2.1、 Problem description
redis A hot spot in key( High traffic key) Be overdue , At this time, a large number of requests come at the same time , Found no hits in cache , These requests go to db Yes , Lead to db The pressure increases instantaneously , May bring down db, This situation becomes a cache breakdown .

The phenomenon of cache breakdown
- Database access pressure increases instantaneously
- redis There are not a lot of key Be overdue
- redis The normal operation
2.2、 Solution
key It may be accessed at some point in time with super high concurrency , It's a very “ hotspot ” The data of , This is the time , There is a problem to consider : The cache is “ breakdown ” The problem of , Common solutions are as follows
2.2.1、 Preset hot data , Adjust the expiration time timely
stay redis Before the peak , Put some hot data into redis Inside , Monitor these hot data in the cache , Adjust expiration time in real time .
2.2.2、 Using locks
When data is not available in the cache , This is not the moment to go db Query in , Instead, get distributed locks ( such as redis Medium setnx), Get the lock and go db in load data ; The thread that does not get the lock sleeps for a period of time and then retries the entire method of obtaining data .
3、 Cache avalanche
3.1、 Problem description
key The corresponding data exists , But in a very short time, there are a lot of key Concentration expired , At this point, if a large number of concurrent requests come , No data found in cache , A large number of requests will fall on db Load data , Will db crushed , Lead to service crash .
The difference between cache avalanche and cache breakdown is : The former is massive key Concentration expired , The latter is a hot spot key Be overdue .
3.2、 Solution
The avalanche effect of cache invalidation has a terrible impact on the underlying system , Common solutions are as follows
3.2.1、 Build a multilevel cache
nginx cache +redis cache + Other caches (ehcache etc. )
3.2.2、 Use locks or queues
Lock or queue is used to ensure that there will not be a large number of threads reading and writing to the database at one time , So as to avoid a large number of concurrent requests falling on the underlying storage system in case of failure , Not for high concurrency .
3.2.3、 Monitoring cache expiration , Update in advance
Monitor cache , The delivery cache is about to expire , Update the cache in advance .
3.2.4、 Spread the cache expiration time
For example, we can add a random value to the original failure time , such as 1-5 Minutes at random , In this way, the cache expiration time repetition rate will be reduced , It's hard to trigger a collective failure .
4、 Distributed lock
4.1、 Problem description
With the needs of business development , After the original single machine deployment system is evolved into a distributed cluster system , Due to multithreading in distributed system 、 Multiple processes and distributed on different machines , This will invalidate the concurrent control lock policy in the case of the original stand-alone deployment , pure Java API It doesn't provide the ability of distributed locks , In order to solve this problem, we need a kind of cross JVM To control the access of shared resources , This is the problem of distributed lock .
4.2、 The mainstream implementation of distributed lock
- Implementation of distributed lock based on Database
- Cache based (redis etc. )
- be based on zookeeper
Every distributed lock solution has its own advantages and disadvantages
- performance :redis The highest
- reliability :zookeeper The highest
Here we are based on redis Implement distributed locks .
4.3、 Solution : Use redis Implement distributed locks
You need to use the following command to implement distributed locks
set key value NX PX The period of validity ( millisecond )
This command indicates : When key When it doesn't exist , Set the value to value, At the same time, its validity period is set
Example
set sku:1:info "ok" NX PX 10000Said when sku:1:info When it doesn't exist , Set the value to ok, And valid for 1 10000 MS .
4.3.1、 Locking process
The process is as follows , perform set key value NX PX The period of validity ( millisecond ) command , return ok Indicates successful execution , The lock is obtained successfully , When multiple clients execute this command concurrently ,redis It can ensure that only one can be executed successfully .
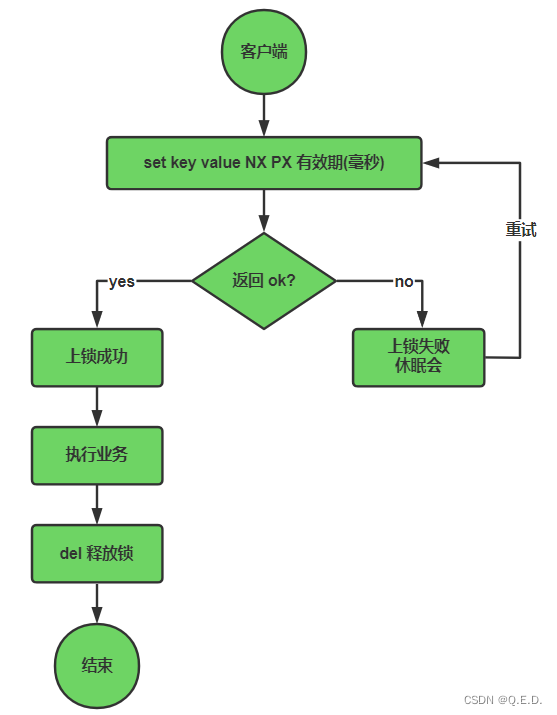
4.3.2、 Why set expiration time ?
After the client obtains the lock , Due to system problems , If the system goes down , The lock cannot be released , Other clients cannot or lock , So you need to specify a lifetime for the lock .
4.3.3、 What if the set validity period is too short ?
For example, the validity period is set 10 second , however 10 Seconds is not enough for the business party , In this case, the client needs to implement the function of life extension , Can solve this problem .
4.3.4、 Solve the problem of lock deletion by mistake
The lock may be deleted by mistake : The so-called mistakenly delete is to delete the lock held by others .
Like threads A When getting the lock , The set validity period is 10 second , But when doing business ,A The program suddenly has more card owners than 10 second , At this point, the lock may be obtained by other threads , For example, thread B Got it , then A Recovered from katon , Continue with the business , After the business is completed , To release the lock , here A Will execute del command , At this point, the lock is deleted by mistake , The result is that B The lock held was released , Then other threads will acquire the lock , It's serious .
How to solve it ?
Before acquiring the lock , Generate a global unique id, Put this id And also to key Corresponding value in , Before releasing the lock , from redis Lieutenant general this id Compare it with the local one , See if it's your own id, If yes, execute again del Release lock operation .
4.3.5、 There is still the possibility of accidental deletion ( Atomic manipulation problems )
It just said ,del Before , We'll start with redis Read from id, And then with the local id Compare the , If the same , Delete , The pseudocode is as follows
step1: Judge redis.get("key").id== Local id Is it equivalent to , If yes, execute step2
step2:del key;
At this point, if you execute step2 It's time for the system card owner , For example, the card owner 10 second , then redis Just received , During this period, the lock may be acquired by other threads , At this time, the operation of deleting by mistake occurs .
The root cause of the problem is : Judge and delete this 2 Step by step redis It is not caused by atomic operation , How to solve it ?
Need to use Lua Script to solve .
4.3.6、 Ultimate solution :Lua Script to release the lock
Will be complex or multi-step redis operation , Write it as a script , Submit to redis perform , Reduce repeated connections redis The number of times , Lifting performance .
Lua Scripts are similar to redis Business , It has certain atomicity , Will not be interrupted by other orders , You can do some redis Operation of transaction .
But notice redis Of LUA Script function , Only in redis2.6 The above version can be used .
The code is as follows :
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.script.DefaultRedisScript;
import org.springframework.http.MediaType;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.UUID;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* @className LockTest
* @date 2022/6/21
**/
@RestController
public class LockTest {
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate<String, String> redisTemplate;
@RequestMapping(value = "/lock", produces = MediaType.TEXT_PLAIN_VALUE)
public String lock() {
String lockKey = "k1";
String uuid = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
// 1. Get the lock , The period of validity 10 second
if (this.redisTemplate.opsForValue().setIfAbsent(lockKey, uuid, 10, TimeUnit.SECONDS)) {
// 2. Executive business
// todo Business
//3. Use Lua Script release lock ( It can prevent accidental deletion )
String script = "if redis.call('get',KEYS[1])==ARGV[1] then returnredis.call('del', KEYS[1]) else return 0 end ";
DefaultRedisScript<Long> redisScript = new DefaultRedisScript<>();
redisScript.setScriptText(script);
redisScript.setResultType(Long.class);
Long result = redisTemplate.execute(redisScript, Arrays.asList(lockKey), uuid);
System.out.println(result);
return " Lock acquired successfully !";
} else {
return " Locking failed !";
}
}
}4.3.7、 Distributed lock summary
To ensure that distributed locks are available , At least we need to ensure that the implementation of distributed locks meets the following four conditions at the same time
- Mutual exclusivity , Only one client can hold a lock at any time
- Do not lose the lock of life and death , Even if a client crashes while holding a lock without releasing the lock , It can also ensure that other subsequent clients can be locked
- To unlock, you need to send the bell , Lock and unlock must be the same client , The client cannot unlock other people's locks
- Locking and unlocking must be atomic
边栏推荐
- IO之Buffered流案例
- Puzzle (019) plane forward problem
- CF751E Phys Ed Online
- Development technology of NFT trading platform digital collection system
- Niuke challenge 53e problem solution & Notes on learning with flowers and trees
- 奋斗吧,程序员——第四十三章 十步杀一人,千里不留行
- More than half of 2022, no new air outlet
- Reader case of IO
- Take Wei Lai to court. What's Audi's hurry?
- IO之Reader案例
猜你喜欢

YuMinHong said that e-commerce schools may be opened in the future; Musk's son applied to sever the father son relationship; Hungry? Respond to a large number of users receiving the free order informa

APM flight mode switching -- source code explanation

Add custom fields to the time synchronization message based on uavcan protocol in Px4 code learning
![[CISCN2019 总决赛 Day1 Web4]Laravel1](/img/99/4eb4d9447ac191fb9320cd8135f019.png)
[CISCN2019 总决赛 Day1 Web4]Laravel1

Typical life cycle model of information system project

KNN classification of MATLAB (with source code) is used to realize pixel classification (set the proportion of training set by yourself) and print test accuracy
![两两交换链表中的节点[单向链表不断链原则]](/img/67/8e9f3c396a8f529a616964b69cc47f.png)
两两交换链表中的节点[单向链表不断链原则]
Puzzle (019) plane forward problem

CF751E Phys Ed Online

What is homology??? Cross domain error??? How to solve???
随机推荐
国外LEAD需要干劲、兴趣、钻研、勤奋、缺一不可
Niuke challenge 53c
Vector data of Zunyi city's benchmark land price in 2022 (WGS84)
Kruskal reconstruction tree
Set up OpenPGP key server
Security risks exist in open source code: an average of 49 vulnerabilities exist in a project
奋斗吧,程序员——第四十八章 千金纵买相如赋,脉脉此情谁诉
Explanation of 94F question in Niuke practice match
electron添加SQLite數據庫
SAP Marketing Cloud 功能概述(二)
【软工】 概论 & 过程和生命周期建模
Solution to 94d problem of Niuke practice match
Struggle, programmer -- Chapter 36 the falling flower man is independent and the tiny swift flies
关于缓存异常:缓存雪崩、击穿、穿透的解决方案
“中国巴菲特”段永平:投资有道
Cookies and sessions for answers to common interview questions
The R language dplyr package mutate function divides two numeric variables in the dataframe to create a new data column (create a new variable)
haas506 2.0开发教程-高级组件库-modem.info(仅支持2.2以上版本)
"Dare not doubt the code, but have to doubt the code" a network request timeout analysis
Two ways of traversing binary tree: preorder, inorder and postorder