当前位置:网站首页>Thesis reading (53):universal advantageous perturbations
Thesis reading (53):universal advantageous perturbations
2022-06-23 18:04:00 【Inge】
List of articles
1 summary
1.1 subject
2017CVPR: Universal anti disturbance (Universal adversarial perturbations)
1.2 Method
The point is as follows :
1) It shows that for a given cutting-edge neural network classifier , Only a universal and minimal disturbance can cause high probability misclassification of natural images ;
2) Put forward a kind of A systematic algorithm for computing general perturbations , It is shown that the most advanced deep neural network is very susceptible to this disturbance , And the human eye can almost detect ;
3) Further empirical analysis of these universal perturbations , And show their application in neural network Good generalization performance ;
4) The existence of universal perturbation reveals the important geometric correlation between the high-dimensional decision boundaries of classifiers . It further outlines the potential security vulnerabilities in a single direction in the input space , Attackers may use these directions to destroy classifiers on most natural images .
1.3 Code
Tensorflow:https://github.com/LTS4/universal
Torch:https://github.com/NetoPedro/Universal-Adversarial-Perturbations-Pytorch
1.4 Bib
@inproceedings{
Moosavi:2017:17651773,
author = {
Seyed-Mohsen Moosavi-Dezfooli and Alhussein Fawzi and Omar Fawzi and Pascal Frossard},
title = {
Universal adversarial perturbations},
booktitle = {
{
IEEE} Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition},
pages = {
1765--1773},
year = {
2017}
}
2 Universal disturbance
Make μ \mu μ Indicates that the image is in space R d \mathbb{R}^d Rd The distribution on , k ^ \hat{k} k^ Is a tool for acquiring images x ∈ R d x\in\mathbb{R}^d x∈Rd Assessment tags k ^ ( x ) \hat{k}(x) k^(x) Classifier . The purpose of this paper is Find a perturbation vector v ∈ R b v\in\mathbb{R}^b v∈Rb, It can fool k ^ \hat{k} k^ In most cases μ \mu μ On the data points of :
k ^ ( x + v ) ≠ k ^ ( x ) f o r ′ ′ m o s t ′ ′ x ∼ μ . \hat{k}(x+v)\neq\hat{k}(x)\ for ''most'' \ x\sim\mu. k^(x+v)=k^(x) for′′most′′ x∼μ. The universal disturbance represents a fixed disturbance independent of the image , It will cause the labels of most images sampled from the data distribution to change . Here we focus on distribution μ μ μ Represents a natural image set , So it contains a lot of variability . In this case , Universal small perturbations that mislead most images will be discovered . seek v v v Need to meet the following constraint :
1) ∥ v ∥ p ≤ ξ \|v\|_p\leq\xi ∥v∥p≤ξ ;
2) P x ∼ μ ( k ^ ( x + v ) ≠ k ^ ( x ) ) ≥ 1 − δ \mathbb{P}_{x\sim\mu}(\hat{k}(x+v)\neq\hat{k}(x))\geq1-\delta Px∼μ(k^(x+v)=k^(x))≥1−δ.
here ξ \xi ξ Used to control the v v v The intensity of , δ \delta δ Used to control the misleading rate .
Algorithm
Make X = { x 1 , … , x m } X=\{x_1,\dots,x_m\} X={ x1,…,xm} It means that it obeys the distribution μ \mu μ A collection of images . Based on constraints and optimization objectives , The algorithm will be in X X X Iterate over and build the universal perturbation step by step , Such as chart 2. In each iteration , Calculate the current perturbation point x i + v x_i+v xi+v The minimum disturbance sent to the decision boundary of the classifier v i v_i vi, And it is aggregated to the current instance of universal disturbance .
chart 2: The semantic representation of the proposed algorithm in computing universal perturbations . spot x 1 x_1 x1、 x 2 x_2 x2, as well as x 3 x_3 x3 In superposition state , Different classification areas A \mathcal{A} A Displayed in different colors . The purpose of the algorithm is to find the minimum disturbance , Make a point of x i + v x_i+v xi+v Move out of the correct classification area
Assume that the current generic perturbation v v v Data points cannot be fooled x i x_i xi, We solve the following optimization problems to find data points that can be cheated x i x_i xi Additional perturbation of the minimum norm of v i v_i vi:
Δ v i ← arg min r ∥ r ∥ 2 s . t . k ^ ( x i + v + r ) ≠ x ^ i . (1) \tag{1} \Delta v_i\leftarrow\argmin_r\|r\|_2\qquad s.t.\qquad \hat{k}(x_i+v+r)\neq\hat{x}_i. Δvi←rargmin∥r∥2s.t.k^(xi+v+r)=x^i.(1) To ensure that constraints are met ∥ v ∥ p ≤ ξ \|v\|_p\leq\xi ∥v∥p≤ξ, The updated universal perturbation is further projected to a radius of ξ \xi ξ、 Center in 0 0 0 Of ℓ p \ell_p ℓp On the ball . therefore , Projection operations are defined as :
P p , ξ ( v ) = arg min v ′ ∥ v − v ′ ∥ 2 s . t . ∥ v ′ ∥ p ≤ ξ . \mathcal{P}_{p,\xi}(v)=\argmin_{v'}\|v-v'\|_2\qquad s.t.\qquad\|v'\|_p\leq\xi. Pp,ξ(v)=v′argmin∥v−v′∥2s.t.∥v′∥p≤ξ. then , The update rule changes to v ← P p , ξ ( v + Δ v i ) v\leftarrow\mathcal{P}_{p,\xi}(v+\Delta v_i) v←Pp,ξ(v+Δvi). The data set X X X The quality of the universal disturbance will be improved by the multiple transmission of . The algorithm will be applied to perturbed data sets X v : = { x 1 + v , … , x m + v } X_v:=\{x_1+v,\dots,x_m+v\} Xv:={ x1+v,…,xm+v} The fooling rate of exceeds the threshold 1 − δ 1-\delta 1−δ Stop when :
Err ( X v ) : = 1 m ∑ i = 1 m 1 k ^ ( x i + v ) ≠ k ^ ( x i ) ≥ 1 − δ . \text{Err}(X_v):=\frac{1}{m}\sum_{i=1}^m1_{\hat{k}(x_i+v)\neq\hat{k}(x_i)}\geq1-\delta. Err(Xv):=m1i=1∑m1k^(xi+v)=k^(xi)≥1−δ. Algorithm 1 Show more details . X X X Number of data points in m m m It doesn't take much to compute a pair of global distributions μ \mu μ Effective universal perturbation . Special , m m m It can be set to a value much smaller than the training sample .
The proposed algorithm involves solving the formula at each transfer 1 At most of the optimization problems in m m m An example , Here the Deepfool To deal with this problem efficiently . It is worth noting that , Algorithm 1 It is not possible to find a minimum universal perturbation that fools as many sample points as possible , Only one perturbation with a sufficiently small norm can be found . X X X Different random shuffles will naturally lead to various universal perturbations that satisfy the required constraints v v v.
3 Universal disturbance and depth network
This section analyzes how the leading edge deep learning classifier responds to Algorithm 1 Robustness of universal perturbations in .
First experiment in , Evaluate different algorithms in ILSVRC 2012 Verify the universal perturbation on the data set , And show Fooling rate , That is, the proportion of the image label that will change after the universal disturbance . The experiment will take place in X = 10000 X=10000 X=10000; p = 2 p=2 p=2 and p = ∞ p=\infty p=∞ Proceed under , The corresponding ξ \xi ξ Respectively 2000 2000 2000 and 10 10 10. These values are chosen to obtain perturbations whose norm is significantly smaller than the image norm , So when added to a natural image , Disturbances are imperceptible . surface 1 It shows the experimental results . Each result is reported in the set used to calculate the disturbance X X X And validation set ( It is not used in the calculation of general disturbance ). The results show that the universal perturbation has a high fooling rate .
chart 3 It shows GoogleNet Visualization results of disturbed images . in the majority of cases , Universal disturbances are imperceptible , Such image perturbations effectively fool many leading edge classifiers .
chart 4 The universal perturbation results of different networks are shown . It should be noted that , Universal perturbations are not unique , Because many different universal perturbations can be generated for the same network ( Both satisfy the two required constraints ).
chart 5 It shows X X X Different universal perturbations under different random shuffles . The results show that the universal perturbations are different in similar modes . Besides , This is also confirmed by calculating the normalized inner product between two pairs of disturbed images , Because the normalized inner product does not exceed 0.1, This shows that different universal perturbations can be found .
The second experiment Used to verify X X X The influence of the size of the on the universal disturbance . chart 6 It shows GoogleNet In different X X X The fooling rate . Experiments show that only in X = 500 X=500 X=500 when , The fooling rate can reach 30%.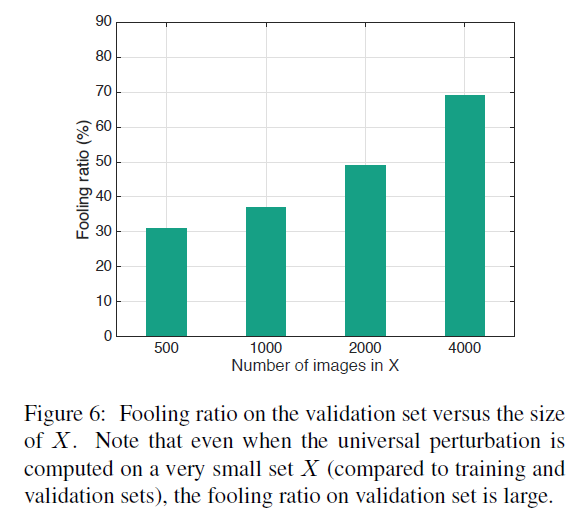
3.1 Cross model universality
After calculating the disturbance at an unknown data point , It can be proved that they are universal across models , That is, on a special network such as VGG-19 The disturbance of training , It can still be on another network, such as GoogleNet Effective on . surface 2 Shows the cross model fooling rate .
3.2 Visualization of universal disturbance performance
In order to visually demonstrate the utility of universal perturbations on natural images , We will ImageNet The label distribution on the validation set is visualized : Undirected graph G = ( V , E ) G=(V,E) G=(V,E), Where the fixed point represents the label , edge e = ( i → j ) e=(i\rightarrow j) e=(i→j) Indicates that the icon label changes from... After the disturbance is applied i i i Be misled into j j j, Such as chart 7.
3.3 Fine tuning of universal perturbations
It is used to test the performance of the network after fine-tuning using the disturbed image . Use VGG-F framework , And fine tune the network based on the modified training set , The universal perturbation is added to a small number of clean training samples : For each training point , With 0.5 The probability of adding generic perturbations , And the original sample is 0.5 Probability retention . To explain the diversity of universal perturbations ,10 Two precomputed universal perturbations will be randomly selected . The network will be fine tuned five times on the modified dataset . Set during fine adjustment p = ∞ p=\infty p=∞ And ξ = 10 \xi=10 ξ=10. The results showed that the fooling rate decreased .
4 The vulnerability of neural networks
This section is used to illustrate the vulnerability of neural networks to pervasive disturbances . First, compare it with other types of disturbances , Explain the uniqueness of universal perturbations , Include :
1) Random disturbance ;
2) Against disturbance ;
3) X X X Up against the sum of disturbances ;
4) The mean value of the image .
chart 8 Different disturbances are shown ξ \xi ξ And ℓ 2 \ell_2 ℓ2 The fooling rate under the norm . Specially , The great difference between the universal disturbance and the random disturbance indicates that , Universal perturbations utilize some geometric correlations between different parts of the classifier decision boundary . in fact , If the direction of the decision boundary near different data points is completely irrelevant ( And it has nothing to do with the distance of decision boundary ), Then the norm of the optimal universal perturbation will be equal to that of the random perturbation . further , The random perturbation norm required to deceive a particular data point is precisely expressed as Θ ( d ∥ r ∥ 2 ) \Theta(\sqrt{d}\|r\|_2) Θ(d∥r∥2), among d d d Is the dimension of the input space . about ImageNet Classification task , Yes d ∥ r ∥ 2 ≈ 2 × 1 0 4 \sqrt{d}\|r\|_2\approx2\times10^4 d∥r∥2≈2×104. For most data points , This is better than the universal perturbation ( ξ = 2000 \xi = 2000 ξ=2000) One order of magnitude larger . therefore , The substantial difference between random disturbance and universal disturbance indicates that the geometry of decision boundary explored at present is redundant .
For each image in the validation set x x x, The anti disturbance vector obtained is r ( x ) = arg min r ∥ r ∥ 2 s . t . k ^ ( x + r ) ≠ k ^ ( x ) r(x)=\argmin_r\|r\|_2\ s.t.\ \hat{k}(x+r)\neq\hat{k}(x) r(x)=rargmin∥r∥2 s.t. k^(x+r)=k^(x). Obviously r ( x ) r(x) r(x) The decision boundary with the classifier is x + r ( x ) x+r(x) x+r(x) Orthogonal at . therefore r ( x ) r(x) r(x) To capture decision boundaries in x x x Local geometric features in adjacent regions . In order to quantify the correlation between different regions of the classifier decision boundary , Defines the validation set n n n Normal vector matrix of decision boundary near data points :
N = [ r ( x 1 ) ∥ r ( x 1 ) ∥ 2 ⋯ r ( x n ) ∥ r ( x n ) ∥ 2 ] N=\left[\frac{r(x_1)}{\|r(x_1)\|_2} \cdots \frac{r(x_n)}{\|r(x_n)\|_2} \right] N=[∥r(x1)∥2r(x1)⋯∥r(xn)∥2r(xn)] For binary classifier , The decision boundary is a hyperplane 、 N N N The rank of is 1, And all normal vectors are collinear . In order to more generally capture the correlation in the decision boundary of complex classifiers , We calculate the matrix N N N The singular value of . adopt CaffeNet Calculated matrix N N N The singular value of is as follows chart 9. The figure shows when N N N Column the singular values obtained when sampling randomly and uniformly from the unit sphere . Although the singular value of the latter decays slowly , but N N N The singular value of decays rapidly , This proves that the decision boundary of the deep network has large correlation and redundancy . More precisely , This indicates that there is a low dimension d ′ ≪ d d'\ll d d′≪d Subspace S S S, It contains most of the normal vectors of the decision boundary in the region around the natural image . Suppose that the existence of universal perturbations that fool most natural images is due to the existence of such a low dimensional subspace , The subspace captures the correlation between different regions of the decision boundary . in fact , This subspace “ collect ” The normals of decision boundaries in different regions are given , Therefore, the disturbance belonging to this subspace may deceive the data points . To test this hypothesis , We choose a norm ξ = 2000 ξ = 2000 ξ=2000 The random vector of , Of the former 100 A subspace traversed by a singular vector S S S, And calculate the fooling rate of different image sets ( That is, a group that has not been used to calculate SVD Image ). This disturbance can deceive the near 38% Image , So it shows that in this subspace S S S The random direction in is obviously better than the random disturbance ( This disturbance can only deceive 10% The data of ).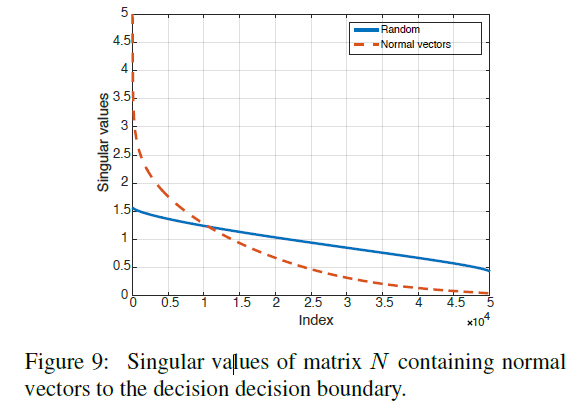
chart 10 It shows the relevance subspace in the capture decision boundary S S S. It should be noted that , The existence of this low dimensional subspace explains chart 6 The surprising generalization properties of the universal perturbations obtained in , Among them, people can use very few images to construct relatively generalized universal perturbations .
Different from the above experiment , The proposed algorithm does not select a random vector in this subspace , Instead, choose a specific direction to maximize the overall fooling rate . This explains the use of S S S Random vector strategy and algorithm in 1 The difference between the obtained fooling rates .

边栏推荐
- QML类型:Loader
- Latex编译成功但是无法输出到PDF
- 对抗攻击与防御 (1):图像领域的对抗样本生成
- Which securities company is good for opening a mobile account? Is online account opening safe?
- 一元二次方程到规范场
- Kdevtmpfsi processing of mining virus -- Practice
- How to make validity table
- Single fire wire design series article 10: expanding application - single fire switch realizes double control
- 单火线设计系列文章10:拓展应用-单火开关实现双控
- Listen attentively and give back sincerely! Pay tribute to the best product people!
猜你喜欢
csdn涨薪秘籍之Jenkins集成allure测试报告全套教程

《致敬百年巨匠 , 数藏袖珍书票》

论文阅读 (56):Mutli-features Predction of Protein Translational Modification Sites (任务)

客服系统搭建教程_宝塔面板下安装使用方式_可对接公众号_支持APP/h5多租户运营...

esp8266-01s 不能连接华为路由器解决方法

论文阅读 (52):Self-Training Multi-Sequence Learning with Transformer for Weakly Supervised Video Anomaly

Self supervised learning (SSL)

How to solve the problem that the esp8266-01s cannot connect to Huawei routers

论文阅读 (55):Dynamic Multi-Robot Task Allocation under Uncertainty and Temporal Constraints

论文阅读 (51):Integration of a Holonic Organizational Control Architecture and Multiobjective...
随机推荐
Kotlin practical skills you should know
[esp8266-01s] get weather, city, Beijing time
How to design a seckill system - geek course notes
How to design a seckill system?
百度智能云5月产品升级观察站
论文阅读 (48):A Library of Optimization Algorithms for Organizational Design
论文阅读 (55):Dynamic Multi-Robot Task Allocation under Uncertainty and Temporal Constraints
How to quickly obtain and analyze the housing price in your city?
VNC Viewer方式的远程连接树莓派
Self supervised learning (SSL)
Deploy LNMP environment and install Typecho blog
Answer 01: why can Smith circle "allow left string and right parallel"?
Easygbs playback screen is continuously loading. Troubleshooting
Explanation of the principle and code implementation analysis of rainbow docking istio
ACM players take you to play with the array!
论文阅读 (54):DeepFool: A Simple and Accurate Method to Fool Deep Neural Networks
JS custom error
Answer 03: why can Smith circle "allow left string and right parallel"?
Drawing black technology - easy to build a "real twin" 2D scene
13. IP address and subnet partitioning (VLSM)