当前位置:网站首页>Related problems of pointer array, array pointer and parameter passing
Related problems of pointer array, array pointer and parameter passing
2022-06-29 10:12:00 【On the Pearl River】
Catalog
Catalog
1. Pointer array : An array of pointers , It's an array , It's just that it doesn't store integers 、 Floating point but pointer .
2. Array pointer : A pointer to an array , It's a pointer .
3. The ginseng
Conclusion :
Pointer array : An array of pointers , It's an array , It's just that it doesn't store integers 、 Floating point but pointer
form :int* arr[10] :
Be careful :arr Is and [ ] First combine with * combination , because [ ] The priority ratio * high

Use :
Through the pointer array , We can use one-dimensional array to realize two-dimensional array
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int arr1[] = { 1,2,3,4,5 };
int arr2[] = { 2,2,3,4,5 };
int arr3[] = { 3,2,3,4,5 };
int* parr[3] = { arr1,arr2,arr3 };
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
int j = 0;
for(j=0;j<5;j++)
{
printf("%d ", *(parr[i] + j));
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}Array pointer : A pointer to an array , It's a pointer .
We all know :
Integer pointer : A pointer that can point to shaped data
Floating point pointer : A pointer that can point to floating-point data
Array pointer : A pointer to an array , It's a pointer .
form : int (*p2) [10]; It's a Array pointer , It's an array , The array has 10 Elements , Every element int type ,p2 Is a pointer array minus p2, The rest is p2 The type of ,int(* ) [10]
notes : because p1 Is and [ ] First combine with * combination , because [ ] The priority ratio * high
Use :
Want to use array pointers well , First, master the following contents :
We know that the array name is usually the address of the first element of the array , But there are two exceptions !!
special : The following is the address of the entire array
* sizeof( Put a separate array name ), notes :sizeof(arr+0) Do not put an array name alone
* & Array name ,
Look at the code :(arr It represents the address of the first element of the array , Writing with a pointer array is complicated )
The following cases are less useful , Array pointers are commonly used for 2D and 3D arrays
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9 };
int(*p)[9] = &arr;
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < 9; i++)
{
printf("%d ", *(*p + i));
}
return 0;
}
( When the argument is a two-dimensional array name , Formal parameters can be received with array pointers )
Particular attention :
* This topic arr It's an array name , Represents the address of the first element of the array
* The first element of a two-dimensional array is the first row of the two-dimensional array ( Passed by this topic arr, Is the address of a one-dimensional array )
* Receive a pointer , This pointer points to an array , So we can use array pointer to realize
The above code is as follows :
#include <stdio.h>
void print_arr1(int arr1[3][5], int row, int col)
{
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < row; i++)
{
int j = 0;
for (j = 0; j < col; j++)
{
printf("%d ", arr1[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
}
void print_arr2(int(*p)[5], int row, int col)
{
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < row; i++)
{
int j = 0;
for (j = 0; j < col; j++)
{
printf("%d ", *(*(p + i) + j));
}
printf("\n");
}
}
int main()
{
int arr[3][5] = { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10 };
print_arr1(arr, 3, 5);
print_arr2(arr, 3, 5);
return 0;
}The ginseng
The above involves array parameter passing , In this section, I will summarize the parameters of one-dimensional array 、 Two dimensional array parameters 、 First level pointer parameter transfer 、 The core content of two-level pointer parameter transfer
One dimensional array parameters
①

②

The code is as follows :
void test1(int arr[10])
{}
void test1(int arr[])
{}
void test1(int* p)
{}
int main()
{
// One dimensional array
int arr[10] = { 0 };
test1(arr);
return 0;
}
void test2(int* arr2[20])
{}
void test2(int** p)
{}
int main()
{
// Pointer array pass parameter
int* arr2[20] = { 0 };
test2(arr2);
return 0;
}Two dimensional array parameters :
Array name of two-dimensional array , Represents the address of the first element , It's actually the address on the first line

The code is as follows :
void test(int arr[3][5])
{}
void test(int arr[][5])
{}
void test(int arr[][])
{}
void test(int (*arr)[5])
{}
void test(int* arr)
{}
void test(int* arr[5])
{}
void test(int** arr)
{}
int main()
{
int arr[3][5] = { 0 };
test(arr);
return 0;
}First level pointer parameter transfer :
Take a different perspective , If the argument part of a function is a pointer , How to write the arguments

The code is as follows :
void print(int* p)
{}
int main()
{
int a = 10;
int* ptr = &a;
int arr[10] = { 0 };
print(&a);
print(ptr);
print(arr);
return 0;
}The secondary pointer transmits parameters :
Another angle , If the formal parameter of a function is a second-order pointer , How to write the arguments
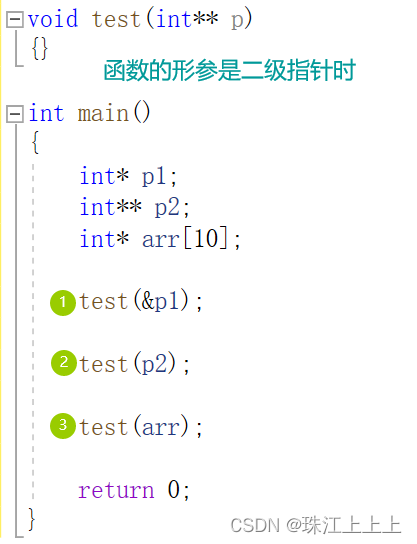
The code is as follows :
void test(int** p)
{}
int main()
{
int* p1;
int** p2;
int* arr[10];
test(&p1);
test(p2);
test(arr);
return 0;
}Conclusion :
If it helps you ,
Don't forget it give the thumbs-up + Focus on Oh , Crab
If it helps you ,
Don't forget it give the thumbs-up + Focus on Oh , Crab
If it helps you ,
Don't forget it give the thumbs-up + Focus on Oh , Crab
边栏推荐
- Leetcode MySQL database topic 180
- To 3 --- 最后的编程挑战
- Community Union
- 单片机集成开发环境Keil5的使用
- Caused by: org. apache. xerces. impl. io. MalformedByteSequenceException: Invalid byte 3 of 3-byte UTF-8
- Codeforces Round #652 (Div. 2)
- Codeforces Round #659 (Div. 2)
- FreeRTOS (VIII) - time management
- Flutter 基础组件之 GridView
- Dynamic linking of virtual machine stack of JVM
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
If I were in Beijing, where would it be better to open an account? In addition, is it safe to open an account online now?
FreeRTOS (IX) - queue
ImageView图片填充问题
HDU 4578 Transformation(线段树+有技巧的懒标记下放)
Nacos environmental isolation
Caused by: org. apache. xerces. impl. io. MalformedByteSequenceException: Invalid byte 3 of 3-byte UTF-8
2019.10.16训练总结
In XML layout, the button is always displayed on the top layer
1147 Heaps (30 分)
Setinterval, setTimeout and requestanimationframe
内网穿透工具frp使用入门
JVM之TLAB
JVM四种调用方法的指令
Pipeline details of IPC (interprocess communication)
JVM之虚拟机栈之动态链接
L2-026 小字辈 (25 分)
leetcode MYSQL数据库题目176
Codeforces Round #645 (Div. 2)
FreeRTOS(九)——队列
弧形 View 和弧形 ViewPager