当前位置:网站首页>Explain in detail the arithmetic operators related to matrix operation in MATLAB (addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, point multiplication, point division, power)
Explain in detail the arithmetic operators related to matrix operation in MATLAB (addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, point multiplication, point division, power)
2022-06-10 21:26:00 【Haohong image algorithm】
Operation is the basis of algorithm , Therefore, it is necessary for us to understand how the tools we use realize the basic operations of matrices .
This blog post concludes MATLAB Arithmetic operators of matrices in .
Catalog
01- Operator “+”
A+B Representation matrix A and B Add the corresponding elements of ,A and B Must be a matrix of the same size , Unless one of them is scalar .
The first example of this situation is as follows (A、B Are matrices of the same size ):
A = [1 2 3;4 5 6;7 8 9];
B = [2 3 4;5 6 7;8 9 0];
C = A+B;
Running results :


A second example of this situation is as follows (A、B One of them is a matrix , One is scalar ):
A = [1 2 3;4 5 6;7 8 9];
b = 5;
C = A+b;



02- Operator “-”
A-B Representation matrix A And matrix B The corresponding elements in the are subtracted .A and B Must be a matrix of the same size , Unless one of them is scalar . Operator “-” You can also find the opposite number of each element in the matrix .
Operator “-” The first example code for (A、B All are matrices )
A = [1 2 3;4 5 6;7 8 9];
B = [2 3 4;5 6 7;8 9 0];
C = B-A;



Operator “-” The second example code of (A、B One of them is a matrix , One is scalar )
A = [1 2 3;4 5 6;7 8 9];
b = 2;
C = b-A;
D = A-b;


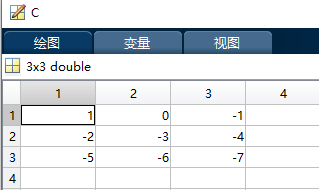

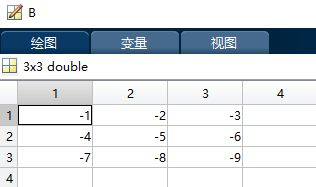
Operator “-” The third example code of ( Find the opposite number of each element in the matrix )
A = [1 2 3;4 5 6;7 8 9];
B = -A;
The operation results are as follows :
03- Operator “.*”
function :A.*B It's equivalent to a matrix A And matrices B Multiply the corresponding elements ,A and B Must be a matrix of the same size , Unless one of them is scalar .
Operator “.*” The first example code for :
A = [1 2 3;4 5 6;7 8 9];
B = [2 3 4;5 6 7;8 9 0];
C = A.*B;
Running results :
Operator “.*” The second example code of :
A = [1 2 3;4 5 6;7 8 9];
b = 3;
C = A.*b;
D = b.*A;
The operation results are as follows :

04- Operator “./”
function : Operator “./” Is the right division of elements ,A./B It means A Elements in a matrix divided by B The corresponding element in the matrix ,A and B Must be a matrix of the same size , Unless one of them is scalar .
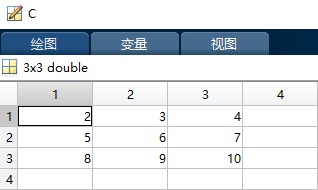
Operator “./” The first example code for is as follows :
B = [1 2 3;4 5 6;7 8 9];
A = [2 6 12;20 30 42;56 72 90];
C = A./B;
The operation results are as follows :

Operator “./” The second example code for is as follows :
A = [3 6 9;12 15 18;21 24 27];
b = 3;
C = A./b;
The operation results are as follows :


05- Operator “.\”
Operator “.\” Is the left division of elements , This operator and the operator “./” Use the same method , Just change the position of the divisor and the dividend , namely A.\B It means B Elements in a matrix divided by A The corresponding element in the matrix ,A and B Must be a matrix of the same size , Unless one of them is scalar .
The example is brief !
06- Operator “.^”
effect : Operator “.^” Is the power of the elements in the matrix .A.^B It means A Elements in are base numbers ,B The corresponding elements in are exponents . Again A and B Must be a matrix of the same size , Unless one of them is scalar .
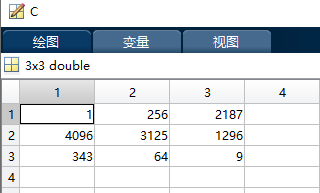
Operator “.^” The sample code of is as follows :
A = [1 2 3;4 5 6;7 8 9];
B = [9 8 7;6 5 4;3 2 1];
C = A.^B;
The operation results are as follows :

07- Operator “.'” And operators “ ’ ”
Operator “.'” And operators “ ’ ” Are used to find the transpose of a matrix , The difference lies in the treatment of complex matrices , The former is used to find the transpose of complex matrix , Do not find the conjugate complex number of each element , The latter is used to find the transpose of the complex matrix , Will find the conjugate complex number of each element .
The sample code is as follows :
A = [1 2 3;4 5 6];
B = A.';
C = A';
D = [1+2i 3+4i 5+6i];
E = D.';
F = D';
The operation results are as follows :






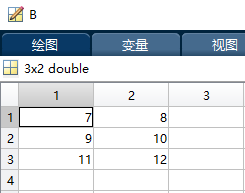
08- Operator “*”
effect :A*B According to matrix A And matrices B Multiplication of , When A and B When both are matrices , According to the operation rules of matrix multiplication ,A The number of columns of must be equal to B The number of rows is equal . If you don't want to meet this condition and use this operator , Unless one of them is scalar , At this time there is A*b=A.*b
The sample code is as follows :
A = [1 2 3;4 5 6];
B = [7 8;9 10;11 12];
C = A*B;
b = 3;
D = A*b;
F = A.*b;
The operation results are as follows :




09- Operator “/” And operators “\”( Be careful : This is very different from the left-right division of elements )
Operator “/” And operators “\” Matrix right division matrix left division . We know that a matrix has no definition of division , The related concept in linear algebra is the inverse of matrix .
that A\B and B/A What do they stand for ?
Regardless of the accuracy of the results :A\B amount to inv(A)*B
Regardless of the accuracy of the results :B/A amount to B*inv(A)
Special attention should be paid here :A\B It's not like the element division B/A, The law is the inverse of the matrix pressed by the slash .
The example and validation code are as follows :
A = [1 2;3 4];
B = [5 6;7 8];
C = A\B;
E = inv(A)*B;
D = B/A;
F = B*inv(A);
The operation results are as follows :

so C and E The result is the same , explain A\B amount to inv(A)*B

so D and F The result is the same , explain B/A amount to B*inv(A)
10- Operator “^”
Operator “^” Is a matrix power operation , Notice in the formula A^B in ,A and B It cannot be a matrix at the same time , The usage is as follows :
When A and B When both are scalars , For scalar A Of B Power .
When A For the square ,B When it is a positive integer , According to matrix A Of B Times product ;
When A For the square ,B When is a negative integer , According to matrix A The inverse of B Times product ;
When B Is a non integer , It has the following expression :
Operator “^” The sample code of is not posted .
边栏推荐
- Heap sorting and hardening heap code for memory
- LeetCode 进阶之路 - 169.多数元素
- synergy: server refused client with our name
- Redis集群配置
- Theoretical basis of distributed services
- Leetcode advanced road - 167 Sum of two numbers II - input ordered array
- Leetcode advanced road - 169 Most elements
- Serial Print() and serial The difference of write() function, and the problem of hexadecimal and string sending and receiving format in serial port communication and detailed explanation of the conver
- H265 Nalu type judgment and SPS data analysis
- 在手机上买基金安全吗?会不会被吞本金?
猜你喜欢

^29事件循环模型

^30H5 Web Worker多线程

LeetCode:1037. 有效的回旋镖————简单

Meetup Preview: introduction to the new version of linkis and the application practice of DSS
![[generation confrontation network learning part I] classic Gan and its existing problems and related improvements](/img/5a/0a4015cd4dcc21afd16ca7f895d909.png)
[generation confrontation network learning part I] classic Gan and its existing problems and related improvements

Self attention and multi head attention

Meetup预告:Linkis新版本介绍以及DSS的应用实践

Use DAP link to download the executable file separately to the mm32f5 microcontroller

牛客网:数组中出现次数超过一半的数字

Understanding deep learning attention
随机推荐
leetcode 划分数组使最大差为 K
Leetcode advanced path - Search insertion location
LeetCode:1037. 有效的回旋镖————简单
Cas de test app
牛客网:数组中出现次数超过一半的数字
72. 编辑距离 ●●●
Power set V4 recursion of brute force method /1~n
获取的网络时间 + 时区(+8)
Quick start to elastic job, three minutes to experience distributed scheduled tasks
App test case
从h264实时流中提取Nalu单元数据
Read the source code of micropyton - add the C extension class module (2)
Leetcode advanced path - reverse string
Leetcode advanced road - 136 A number that appears only once
在YUV图像上根据背景色实现OSD反色
Nodejs: official document 3 Dgram stream
LeetCode 进阶之路 - 搜索插入位置
2 pcs share a set of keyboard and mouse
Brute force method / adjacency table depth first directed weighted graph undirected weighted graph
蛮力法/任务分配