当前位置:网站首页>ThreadLocal夺命11连问
ThreadLocal夺命11连问
2022-07-25 18:41:00 【InfoQ】
前言
ThreadLocal
1. 为什么要用ThreadLocal?
JDKsynchronizedLock原子性JDKThreadLocal线程副本@Service
public class ThreadLocalService {
private static final ThreadLocal<Integer> threadLocal = new ThreadLocal<>();
public void add() {
threadLocal.set(1);
doSamething();
Integer integer = threadLocal.get();
}
}
2. ThreadLocal的原理是什么?
ThreadLocalThreadLocalMappublic class ThreadLocal<T> {
...
public T get() {
//获取当前线程
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
//获取当前线程的成员变量ThreadLocalMap对象
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null) {
//根据threadLocal对象从map中获取Entry对象
ThreadLocalMap.Entry e = map.getEntry(this);
if (e != null) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
//获取保存的数据
T result = (T)e.value;
return result;
}
}
//初始化数据
return setInitialValue();
}
private T setInitialValue() {
//获取要初始化的数据
T value = initialValue();
//获取当前线程
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
//获取当前线程的成员变量ThreadLocalMap对象
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
//如果map不为空
if (map != null)
//将初始值设置到map中,key是this,即threadLocal对象,value是初始值
map.set(this, value);
else
//如果map为空,则需要创建新的map对象
createMap(t, value);
return value;
}
public void set(T value) {
//获取当前线程
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
//获取当前线程的成员变量ThreadLocalMap对象
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
//如果map不为空
if (map != null)
//将值设置到map中,key是this,即threadLocal对象,value是传入的value值
map.set(this, value);
else
//如果map为空,则需要创建新的map对象
createMap(t, value);
}
static class ThreadLocalMap {
...
}
...
}
ThreadLocalgetsetsetInitialValueThreadLocalMapThreadLocalMapstatic class ThreadLocalMap {
static class Entry extends WeakReference<ThreadLocal<?>> {
Object value;
Entry(ThreadLocal<?> k, Object v) {
super(k);
value = v;
}
}
...
private Entry[] table;
...
}
ThreadLocalMapEntryWeakReferenceEntryThreadLocalMapEntryEntryThreadLocalvalueThreadLocalMapThreadpublic class Thread implements Runnable {
...
ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap threadLocals = null;
}

ThreadThreadLocalMapEntry数组EntryGC
弱引用强引用3. 为什么用ThreadLocal做key?
ThreadLocalMapThreadLocalThreadThreadLocalThread@Service
public class ThreadLocalService {
private static final ThreadLocal<Integer> threadLocal = new ThreadLocal<>();
}
Thread@Service
public class ThreadLocalService {
private static final ThreadLocal<Integer> threadLocal1 = new ThreadLocal<>();
private static final ThreadLocal<Integer> threadLocal2 = new ThreadLocal<>();
private static final ThreadLocal<Integer> threadLocal3 = new ThreadLocal<>();
}
Thread
ThreadThreadLocalget
4. Entry的key为什么设计成弱引用?
WeakReference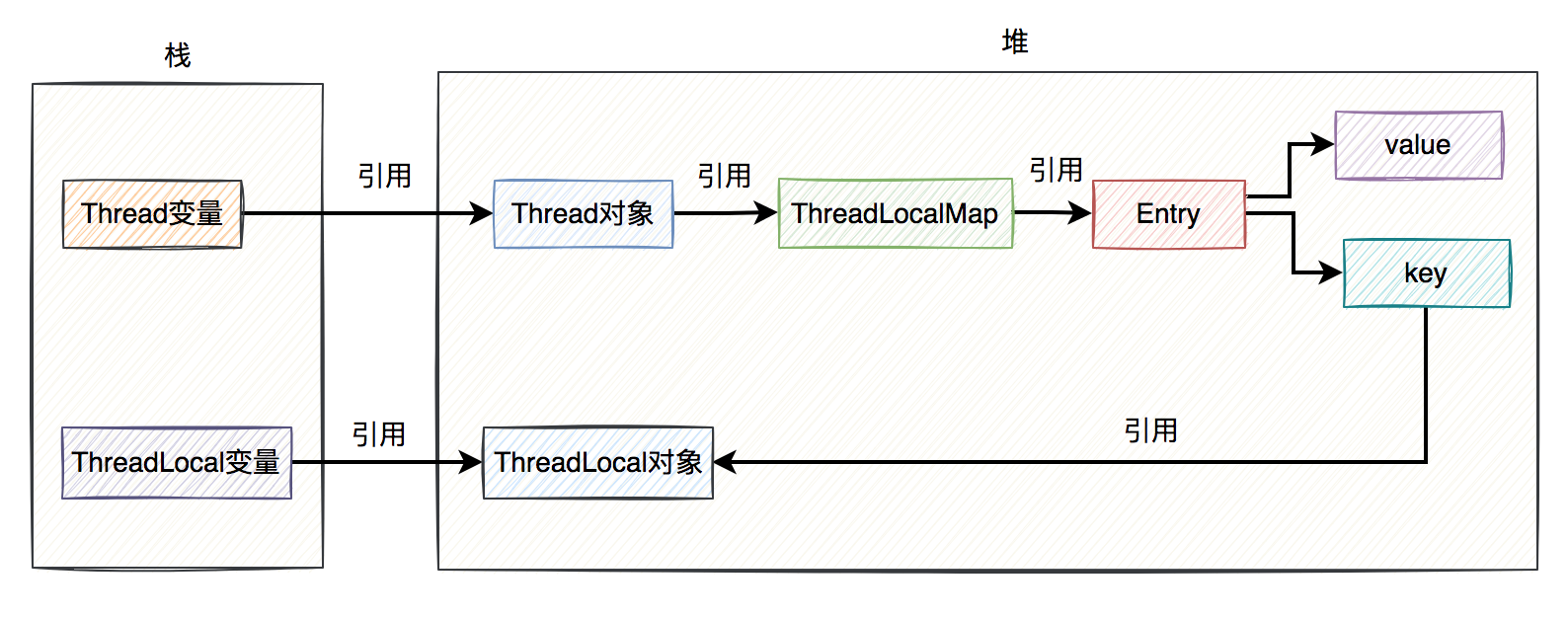
线程线程池强引用链GC内存泄露弱引用弱引用
nullgetsetremove空指针异常getsetremove内存泄露- key为null的条件是,ThreadLocal变量指向
null,并且key是弱引用。如果ThreadLocal变量没有断开对ThreadLocal的强引用,即ThreadLocal变量没有指向null,GC就贸然的把弱引用的key回收了,不就会影响正常用户的使用?
- 如果当前ThreadLocal变量指向
null了,并且key也为null了,但如果没有其他ThreadLocal变量触发get、set或remove方法,也会造成内存泄露。
public static void main(String[] args) {
WeakReference<Object> weakReference0 = new WeakReference<>(new Object());
System.out.println(weakReference0.get());
System.gc();
System.out.println(weakReference0.get());
}
[email protected]
null
public static void main(String[] args) {
Object object = new Object();
WeakReference<Object> weakReference1 = new WeakReference<>(object);
System.out.println(weakReference1.get());
System.gc();
System.out.println(weakReference1.get());
}
[email protected]
[email protected]
public static void main(String[] args) {
Object object = new Object();
WeakReference<Object> weakReference1 = new WeakReference<>(object);
System.out.println(weakReference1.get());
System.gc();
System.out.println(weakReference1.get());
object=null;
System.gc();
System.out.println(weakReference1.get());
}
[email protected]
[email protected]
null
5. ThreadLocal真的会导致内存泄露?
getsetremove
getsetremove强引用链内存泄露6. 如何解决内存泄露问题?
removepublic class CurrentUser {
private static final ThreadLocal<UserInfo> THREA_LOCAL = new ThreadLocal();
public static void set(UserInfo userInfo) {
THREA_LOCAL.set(userInfo);
}
public static UserInfo get() {
THREA_LOCAL.get();
}
public static void remove() {
THREA_LOCAL.remove();
}
}
public void doSamething(UserDto userDto) {
UserInfo userInfo = convert(userDto);
try{
CurrentUser.set(userInfo);
...
//业务代码
UserInfo userInfo = CurrentUser.get();
...
} finally {
CurrentUser.remove();
}
}
finallyremoveremove7. ThreadLocal是如何定位数据的?
int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len-1);
与与取模与运算162hash冲突getEntryprivate Entry getEntry(ThreadLocal<?> key) {
//通过hash算法获取下标值
int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (table.length - 1);
Entry e = table[i];
//如果下标位置上的key正好是我们所需要寻找的key
if (e != null && e.get() == key)
//说明找到数据了,直接返回
return e;
else
//说明出现hash冲突了,继续往后找
return getEntryAfterMiss(key, i, e);
}
getEntryAfterMissprivate Entry getEntryAfterMiss(ThreadLocal<?> key, int i, Entry e) {
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
//判断Entry对象如果不为空,则一直循环
while (e != null) {
ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get();
//如果当前Entry的key正好是我们所需要寻找的key
if (k == key)
//说明这次真的找到数据了
return e;
if (k == null)
//如果key为空,则清理脏数据
expungeStaleEntry(i);
else
//如果还是没找到数据,则继续往后找
i = nextIndex(i, len);
e = tab[i];
}
return null;
}
nextIndexprivate static int nextIndex(int i, int len) {
return ((i + 1 < len) ? i + 1 : 0);
}
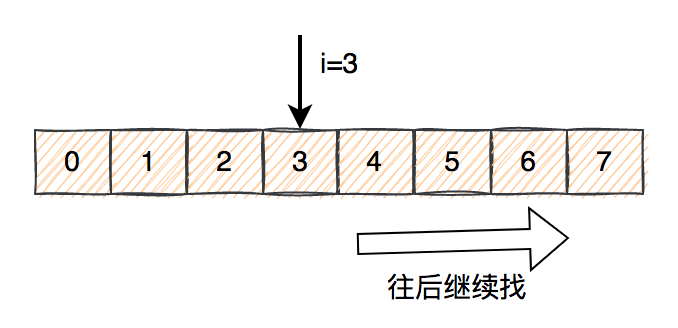

环形- 通过key的hashCode取余计算出一个下标。
- 通过下标,在数组中定位具体Entry,如果key正好是我们所需要的key,说明找到了,则直接返回数据。
- 如果第2步没有找到我们想要的数据,则从数组的下标位置,继续往后面找。
- 如果第3步中找key的正好是我们所需要的key,说明找到了,则直接返回数据。
- 如果还是没有找到数据,再继续往后面找。如果找到最后一个位置,还是没有找到数据,则再从头,即下标为0的位置,继续从前往后找数据。
- 直到找到第一个Entry为空为止。
8. ThreadLocal是如何扩容的?
16setrehashprivate void set(ThreadLocal<?> key, Object value) {
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len-1);
for (Entry e = tab[i];
e != null;
e = tab[i = nextIndex(i, len)]) {
ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get();
if (k == key) {
e.value = value;
return;
}
if (k == null) {
replaceStaleEntry(key, value, i);
return;
}
}
tab[i] = new Entry(key, value);
int sz = ++size;
if (!cleanSomeSlots(i, sz) && sz >= threshold)
rehash();
}
ThreadLocalMap(ThreadLocal<?> firstKey, Object firstValue) {
table = new Entry[INITIAL_CAPACITY];
int i = firstKey.threadLocalHashCode & (INITIAL_CAPACITY - 1);
table[i] = new Entry(firstKey, firstValue);
size = 1;
setThreshold(INITIAL_CAPACITY);
}
private void setThreshold(int len) {
threshold = len * 2 / 3;
}
private void rehash() {
//先尝试回收一次key为null的值,腾出一些空间
expungeStaleEntries();
if (size >= threshold - threshold / 4)
resize();
}
16 * 2 * 4 / 3 * 4 - 16 * 2 / 3 * 4 = 8
1/2private void resize() {
Entry[] oldTab = table;
int oldLen = oldTab.length;
//按2倍的大小扩容
int newLen = oldLen * 2;
Entry[] newTab = new Entry[newLen];
int count = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < oldLen; ++j) {
Entry e = oldTab[j];
if (e != null) {
ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get();
if (k == null) {
e.value = null; // Help the GC
} else {
int h = k.threadLocalHashCode & (newLen - 1);
while (newTab[h] != null)
h = nextIndex(h, newLen);
newTab[h] = e;
count++;
}
}
}
setThreshold(newLen);
size = count;
table = newTab;
}

- 老size + 1 = 新size
- 如果新size大于等于老size的2/3时,需要考虑扩容。
- 扩容前先尝试回收一次key为null的值,腾出一些空间。
- 如果回收之后发现size还是大于等于老size的1/2时,才需要真正的扩容。
- 每次都是按2倍的大小扩容。
9. 父子线程如何共享数据?
一个线程public class ThreadLocalTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadLocal<Integer> threadLocal = new ThreadLocal<>();
threadLocal.set(6);
System.out.println("父线程获取数据:" + threadLocal.get());
new Thread(() -> {
System.out.println("子线程获取数据:" + threadLocal.get());
}).start();
}
}
父线程获取数据:6
子线程获取数据:null
InheritableThreadLocalpublic class ThreadLocalTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
InheritableThreadLocal<Integer> threadLocal = new InheritableThreadLocal<>();
threadLocal.set(6);
System.out.println("父线程获取数据:" + threadLocal.get());
new Thread(() -> {
System.out.println("子线程获取数据:" + threadLocal.get());
}).start();
}
}
父线程获取数据:6
子线程获取数据:6
ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap threadLocals = null;
ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap inheritableThreadLocals = null;
init10. 线程池中如何共享数据?
单独的线程线程池private static void fun1() {
InheritableThreadLocal<Integer> threadLocal = new InheritableThreadLocal<>();
threadLocal.set(6);
System.out.println("父线程获取数据:" + threadLocal.get());
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
threadLocal.set(6);
executorService.submit(() -> {
System.out.println("第一次从线程池中获取数据:" + threadLocal.get());
});
threadLocal.set(7);
executorService.submit(() -> {
System.out.println("第二次从线程池中获取数据:" + threadLocal.get());
});
}
父线程获取数据:6
第一次从线程池中获取数据:6
第二次从线程池中获取数据:6
TransmittableThreadLocal<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>transmittable-thread-local</artifactId>
<version>2.11.0</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
private static void fun2() throws Exception {
TransmittableThreadLocal<Integer> threadLocal = new TransmittableThreadLocal<>();
threadLocal.set(6);
System.out.println("父线程获取数据:" + threadLocal.get());
ExecutorService ttlExecutorService = TtlExecutors.getTtlExecutorService(Executors.newFixedThreadPool(1));
threadLocal.set(6);
ttlExecutorService.submit(() -> {
System.out.println("第一次从线程池中获取数据:" + threadLocal.get());
});
threadLocal.set(7);
ttlExecutorService.submit(() -> {
System.out.println("第二次从线程池中获取数据:" + threadLocal.get());
});
}
父线程获取数据:6
第一次从线程池中获取数据:6
第二次从线程池中获取数据:7
TransmittableThreadLocalTtlExecutors.getTtlExecutorServiceExecutorServiceTransmittableThreadLocalExecutorServiceTtlRunnableTtlCallableRunnablepublic void run() {
Map<TransmittableThreadLocal<?>, Object> copied = (Map)this.copiedRef.get();
if (copied != null && (!this.releaseTtlValueReferenceAfterRun || this.copiedRef.compareAndSet(copied, (Object)null))) {
Map backup = TransmittableThreadLocal.backupAndSetToCopied(copied);
try {
this.runnable.run();
} finally {
TransmittableThreadLocal.restoreBackup(backup);
}
} else {
throw new IllegalStateException("TTL value reference is released after run!");
}
}
- 把当时的ThreadLocal做个备份,然后将父类的ThreadLocal拷贝过来。
- 执行真正的run方法,可以获取到父类最新的ThreadLocal数据。
- 从备份的数据中,恢复当时的ThreadLocal数据。
11. ThreadLocal有哪些用途?
- 在spring事务中,保证一个线程下,一个事务的多个操作拿到的是一个Connection。
- 在hiberate中管理session。
- 在JDK8之前,为了解决SimpleDateFormat的线程安全问题。
- 获取当前登录用户上下文。
- 临时保存权限数据。
- 使用MDC保存日志信息。
- ThreadLocal变量为什么建议要定义成static的?
- Entry数组为什么要通过hash算法计算下标,即直线寻址法,而不直接使用下标值?
- 强引用和弱引用有什么区别?
- Entry数组大小,为什么是2的N次方?
- 使用InheritableThreadLocal时,如果父线程中重新set值,在子线程中能够正确的获取修改后的新值吗?
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢

终极套娃 2.0 | 云原生交付的封装

单臂路由实验演示(Huawei路由器设备配置)

华为年内二度招聘“天才少年”;540万Twitter账号信息泄露,卖价3万美元;谷歌解雇了相信AI有意识的工程师|极客头条

n-queens problem

浏览器内核有几种,浏览器版本过低怎么升级

One week activity express | in simple terms, issue 8; Meetup Chengdu station registration in progress

柔性电流探头选型指南

SQL things
Detailed introduction and application of GaN (comprehensive and complete)
8 年产品经验,我总结了这些持续高效研发实践经验 · 研发篇
随机推荐
How to add EXE file to boot
通讯录(二)
You can change this value on the server by setting the 'Max_ allowed_ Packet 'variable error
Experimental reproduction of image classification (reasoning only) based on caffe resnet-50 network
市值300亿,欧洲十年来最大IPO再冲纽交所
rust多线程安全计数
[QNX Hypervisor 2.2用户手册]9.4 dryrun
Experiment 2 goods purchase and sale management system
Project: serial port receiving RAM storage TFT display (complete design)
Is it true that CITIC Securities' low commission account opening is free of 5? Is it safe
How to create an effective help document?
Analysis of regression problem, modeling and prediction
对迁移学习中域适应的理解和3种技术的介绍
Regex 正则表达式
Register carefully! The number of applicants for these double non-governmental institutions exceeded 10000!
8 年产品经验,我总结了这些持续高效研发实践经验 · 研发篇
Safe operation instructions for oscilloscope probe that must be read by engineers
RTC 性能自动化工具在内存优化场景下的实践
[NOI2015] 软件包管理器
What is the difference between GB and gib disk space units?