当前位置:网站首页>Detailed explanation of the underlying data structure of redis
Detailed explanation of the underlying data structure of redis
2022-07-27 19:49:00 【Lin Musen^~^】
redis The underlying data structure has a total of 6 Kind of :
- Simple dynamic string
- Dictionaries
- list
- Compressed list
- Skip list
- Set of integers
Next, let's take a look at several data structures in turn :
1. Simple dynamic string
Redis No direct use C The traditional string representation of the language ( An array of characters ending in empty characters , hereinafter referred to as C character string ), Instead, I built a simple dynamic string (simple dynamic string,SDS) Abstract type of , And will SDS Used as a Redis The default string representation of .
When Redis You need more than just a literal string , It's a string value that can be modified ,Redis Will use SDS To represent a string value , For example Redis In the database of , The key value pairs containing string values are all created by SDS Realized .
that Redis A new key-value pair will be created in the database , among :
- The key of a key-value pair is a string object , The underlying implementation of the object is a holding string "msg" Of SDS.
- The value of a key-value pair is also a string object , The underlying implementation of the object is a holding string "hello world" Of SDS.
And such as , If the client executes the command :
that Redis A new key-value pair will be created in the database , among :
- The key of a key-value pair is a string object , The underlying implementation of the object is a saved string "fruits" Of SDS.
- The value of a key value pair is a list object , The list object contains three string objects , These three string objects are composed of three SDS Realization : first SDS Save the string "apple", the second SDS Save the string "banana", Third SDS Save the string "cherry".
In addition to storing string values in the database ,SDS It is also used as a buffer (buffer):AOF Module AOF buffer , And the input buffer in the client state , It's all by SDS Realized , After that, I will introduce AOF Persistence and client state , We'll see SDS Application in these two modules .
1.1 SDS The definition of
Every sds.h/sdshdr The structure represents a SDS value :
struct sdshdr {
// Record buf The number of bytes used in an array
// be equal to SDS The length of the saved string
int len;
// Record buf The number of unused bytes in an array
int free;
// Byte array , To hold strings
char buf[];
};

- free The value of the property is 0, Express this SDS No unused space has been allocated .
- len The value of the property is 5, Express this SDS Saved a five byte string .
- buf Property is a char An array of types , The first five bytes of the array are saved separately ’R’、‘e’、‘d’、 ‘i’、‘s’ Five characters , And the last byte holds the null character ’\0’.
1.2 Binary security
1.3 Space preallocation
Space is pre-allocated for optimization SDS String growth operation : When SDS Of API To a SDS Make changes , And you need to SDS When you do spatial expansion , Not only will the program be SDS Allocate the necessary space for modification , Also for the SDS Allocate additional unused space .
among , The amount of unused space allocated is determined by :
- If the SDS After modification ,SDS The length of ( That is to say len The value of the property ) Will be less than 1MB, So the program allocates the sum len Property of the same size of unused space , At this time SDS len The value of the property will be sum free The value of the property is the same . for instance , If after modification ,SDS Of len Will become 13 byte , So the program will also assign 13 Unused space for bytes ,SDS Of buf The actual length of the array will be 13+13+1=27 byte ( An extra byte is used to store empty words
- If the SDS After modification ,SDS The length of will be greater than or equal to 1MB, So the program will allocate 1MB Of unused space . for instance , If after modification ,SDS Of len Will become 30MB, So the program will allocate 1MB Of unused space ,SDS Of buf The actual length of the array will be 30 MB + 1MB + 1byte.
Redis Only use C String as literal , in the majority of cases ,Redis Use SDS(Simple Dynamic String, Simple dynamic string ) As a string .
summary : Compared with C character string ,SDS Has the following advantages :
- Constant complexity gets the string length .
- Prevent buffer overflow .
- Reduce the number of memory reallocations required to modify string length .
- Binary security .
- Compatible with the part C String function .
SDS And C Language string comparison :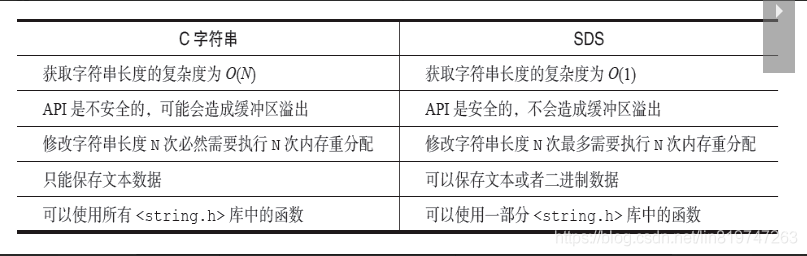
2. Linked list
Linked list provides efficient node rearrangement capability , And sequential node access , And you can adjust the length of the linked list flexibly by adding or deleting nodes .
As a common data structure , Linked lists are built into many advanced programming languages , because Redis The use of C The language doesn't have this data structure built in , therefore Redis Build your own linked list implementation .
The list is in Redis It is widely used in , For example, one of the underlying implementations of the list key is the linked list . When a list key contains a large number of elements , Or when the elements in the list are long strings ,Redis Will use the linked list as the underlying implementation of the list key .
3.1 The realization of linked list and linked list node
Each linked list node uses one adlist.h/listNode Structure to express :
typedef struct listNode {
// Front node
struct listNode * prev;
// Post node
struct listNode * next;
// The value of the node
void * value;
}listNode;
Redis The features of the linked list implementation can be summarized as follows :
- Two ends : Link list nodes with prev and next The pointer , The complexity of obtaining the pre node and post node of a node is O(1).
- acyclic : Of the header node prev Pointer and tail node next The hands all point to NULL, Access to the linked list NULL End point .
- With head pointer and tail pointer : adopt list Structural head Pointers and tail The pointer , The complexity of getting the header node and the tail node of the linked list is O(1).
- Counter with chain length : Program usage list Structural len Attribute to list Count the number of linked list nodes held , The complexity of getting the number of nodes in the list is O(1).
- polymorphic : Link list node use void* Pointer to save the node value , And through list Structural dup、free
3. Dictionaries
Dictionaries , Also known as the symbol table (symbol table)、 Associative array (associative array) Or map (map), It is used to save key value pairs (key-value pair) The abstract data structure of .
In the dictionary , One key (key) It can be combined with a value (value) Association ( Or map keys to values ), These associated keys and values are called key value pairs .
4. Skip list
5. Set of integers
6. Compressed list
7. object
Redis There is no direct use of these data structures to implement key value pair databases , Instead, an object system is created based on these data structures , This system contains string objects 、 List objects 、 Hash object 、 There are five types of objects: collection objects and ordered collection objects , Each object uses at least one of the data structures we described earlier .
Redis Each object in is represented by a redisObject Structural representation , The three attributes of this structure related to data preservation are type attribute 、encoding Properties and ptr attribute :
typedef struct redisObject {
// type
unsigned type:4;
// code
unsigned encoding:4;
// Pointer to the underlying implementation data structure
void *ptr;
// ...
} robj;
type 

Object's ptr The pointer points to the underlying implementation data structure of the object , And these data structures are made up of encoding Attribute decision .
encoding Property records the encoding used by the object , That is to say, what data structure is used as the underlying implementation of the object , The value of this property can be a table 8-3 One of the constants listed .
Each type of object uses at least two different encodings , surface 8-4 Lists the encoding that can be used for each type of object 
Use OBJECT ENCODING Command to view the value object code of a database key :
边栏推荐
- C language: 11. Pipeline
- 二叉搜索树
- C language: 6. Simple use and precautions of pointer
- [basic knowledge of deep learning - 47] Bayesian networks and naive Bayes
- 记一次无准备的实习面试
- BroadcastReceiver(广播)
- ToggleButton(按钮开关)
- [daily accumulation - 06] view CUDA and cudnn versions
- A lock faster than read-write lock. Don't get to know it quickly
- Publish your own NPM component library
猜你喜欢

GestureDetector(手势识别)

C language: 5. Multidimensional array

C language: 13. Pointer and memory

C language: 8. Makefile preparation

一种比读写锁更快的锁,还不赶紧认识一下

SystemService(系统服务)

influxDB系列(四)TSM引擎(存储原理)

A lock faster than read-write lock. Don't get to know it quickly

Release Samsung 3J1 sensor: the code implies that the safety of pixel 7 face recognition will be greatly increased

C language: 10. Input stream, output stream, error stream
随机推荐
二叉搜索树
【深度学习基础知识 - 37】解决正负样本不均衡 Focal Loss
[basic knowledge of deep learning - 39] comparison of BN, LN and WN
27、golang基础-互斥锁、读写锁
golang设置国内镜像,vscode配置golang开发环境,vscode调试golang代码
Transaction log full problem handling in sqlserver 2008
嵌入式C语言对次数不定的循环的优化
[basic knowledge of deep learning - 37] solve the imbalance between positive and negative samples
Ericsson admitted bribery in China and other five countries and paid a fine of $1.06 billion to the United States
Release Samsung 3J1 sensor: the code implies that the safety of pixel 7 face recognition will be greatly increased
[basic knowledge of deep learning - 48] characteristics of Bayesian network
C language: 13. Pointer and memory
[deep learning target detection series - 01] what is target detection
redis底层数据结构详解
TSMC 5nm is about to mass produce: Apple A14 monopolizes 70% of the production capacity, and Huawei Kirin 1020 takes 30%
记一次无准备的实习面试
GestureDetector(手势识别)
【深度学习基础知识 - 43】优势比的概念
Optimization of embedded C language for indefinite cycles
传苹果计划以2亿美元购买JDI部分工厂