当前位置:网站首页>用栈实现队列、用队列实现栈(C语言_leetcode_232+225)
用栈实现队列、用队列实现栈(C语言_leetcode_232+225)
2022-07-01 13:42:00 【Brant_zero】
前两天实现了栈和队列,现在做两道经典的例题来巩固所学的知识。
题目链接:
目录
一、用栈实现队列
思路:
①构建两个栈实现队列。一个栈为input栈,只存入数据;一个栈为output栈,只负责出数据。
②当出数据时,先判断output栈是否为空(StackEmpty(&output)),如果为空,要把input栈中的数据全部导入到output栈中,然后再出output栈顶元素,再删除一个output栈中的数据。
这时我们来分析为什么要让output为空时才倒数据。

注意了!栈是先进后出哦!只有当output为空的时候才能倒数据,要不然后插入的数据会将出栈的顺序打乱。

因为我们是使用C语言做这道题,我们要自己创建栈,这点是比较麻烦的,好在是前两天我们实现了一个栈,直接拿来使用即可。
源码较长,我放在最后,可以通过目录跳转。
二、用队列实现栈
思路:
①一个队列存放输入的数据,一个队列专门为空,在出数据时用于保存数据。这两个队列每出一次数据时会进行功能的倒换。
②出数据时,要将存数据的队列中数据导入到空队列中,直到只留下一个数据。然后将此数据输出,如果是Pop型,输出后则将数据删除,如果是Top型,则将数据输出后再插入到倒数据队列。
步骤:
一、插入数据
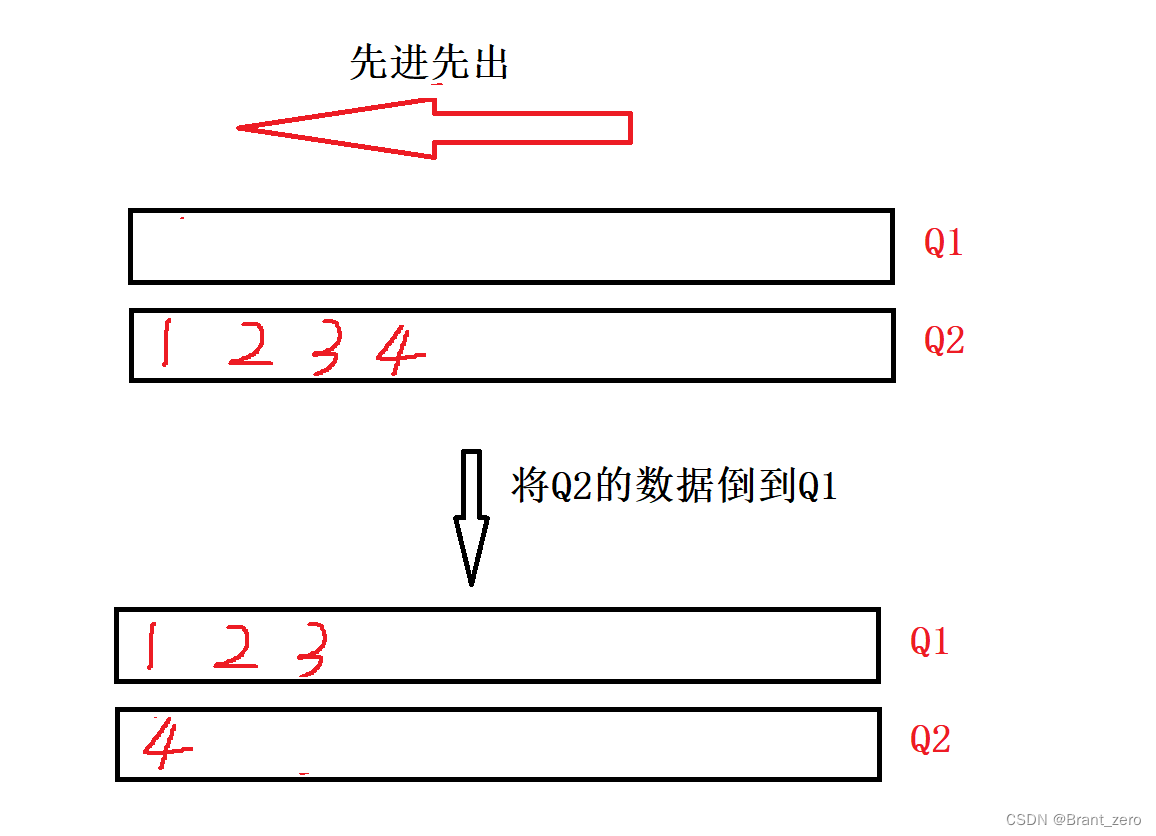
如果q1为空,则q1是用于倒数据的队列,所以放入q2,反之亦然,q2为空放数据插入q1。
二、取数据
1.将除了最后一个数据之外的剩下数据全部导入到倒数据队列,然后将剩下这最后一个数据输出。
2.如果要求是Pop型,输出后则将该数据删除;如果是Top型,则将数据输出后再插入到倒数据队列。
三、源码
因为C语言没有这些结构的库,我们只能手搓出栈和队列,好在前两天我们实现过栈和队列,这时我们直接将其拷贝过来然后套用既可,所以代码有点多。
3.1 栈-->队列 源码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef int STDateType;
typedef struct Stack
{
STDateType* a;
int top; //标识栈顶的数据
int capacity; //动态性的 可以扩容
}ST;
void StackInit(ST* ps);
void StackDestory(ST* ps);
void StackPush(ST* ps, STDateType x);
void StackPop(ST* ps);
STDateType StackTop(ST* ps); //取栈顶的元素
bool StackEmpty(ST* ps); //判断栈是否为空
int StackSize(ST* ps); //得知栈的大小
void StackInit(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->top = 0;
ps->capacity = 0;
}
void StackDestory(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
free(ps->a);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->top = ps->capacity = 0;
}
void StackPush(ST* ps, STDateType x)
{
assert(ps);
if (ps->capacity == ps->top)
{
int NewCapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : ps->capacity * 2;
STDateType* temp = (STDateType * )realloc(ps->a, sizeof(STDateType) * NewCapacity);
if (temp == NULL)
{
printf("realloc fail");
exit(-1);
}
ps->a = temp;
ps->capacity = NewCapacity;
}
ps->a[ps->top] = x;
ps->top++;
}
void StackPop(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(!StackEmpty(ps));
ps->top--;
}
STDateType StackTop(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(!StackEmpty(ps));
return ps->a[ps->top - 1];
}
bool StackEmpty(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top == 0;
}
int StackSize(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top;
}
typedef struct {
ST input; //input栈
ST output; //output栈
} MyQueue;
//将队列创建好 并返回
MyQueue* myQueueCreate() {
//开辟一个结构体变量的空间
//表示我们自己创建的结构体 MyQueue
MyQueue* obj =(MyQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyQueue));
//注意,在创建一个MyQueue中,我们是创建了一个栈,如果我们调用了栈的函数,是需要将该栈的地址传入函数才能符合其类型
StackInit(&obj->input);
StackInit(&obj->output);
return obj;
}
void myQueuePush(MyQueue* obj, int x) {
//将数据放入input栈
StackPush(&obj->input,x);
}
int myQueuePop(MyQueue* obj) {
//将数据弹出
//如果output空,则表示出数据栈为空,则要导数据
if(StackEmpty(&obj->output))
{
//直到input为空
while(!StackEmpty(&obj->input))
{
//将input的数据放入output
//插入一个 Pop一个
StackPush(&obj->output,StackTop(&obj->input));
StackPop(&obj->input);
}
}
int ret=StackTop(&obj->output);
StackPop(&obj->output);
return ret;
}
bool myQueueEmpty(MyQueue* obj) {
//两个栈为空,即队列为空
return (StackEmpty(&obj->input)&& StackEmpty(&obj->output));
}
int myQueuePeek(MyQueue* obj) {
//如果队列为空
if (myQueueEmpty(obj))
{
return -1;
}
if(StackEmpty(&obj->output))
{
while(!StackEmpty(&obj->input))
{
//将input的数据放入output
StackPush(&obj->output,StackTop(&obj->input));
StackPop(&obj->input);
}
}
return StackTop(&obj->output);
}
void myQueueFree(MyQueue* obj) {
StackDestory(&obj->input);
StackDestory(&obj->output);
free(obj);
}3.2 队列-->栈 源码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
typedef int QDataType;
typedef struct QueueNode
{
struct QueueNode* next;
QDataType data;
}QNode;
typedef struct Queue
{
QNode* head;
QNode* tail;
}Queue;
void QueueInit(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
}
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* Dest = pq->head;
while (Dest)
{
QNode* temp = Dest->next;
free(Dest);
Dest = temp;
}
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
}
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x)
{
assert(pq);
//创建一个节点
QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if (newnode == NULL)
{
printf("malloc fail\n");
exit(-1);
}
newnode->data = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
//判断pq是不是一个空结点
//如果是 则将newnode置为当前队列的第一个结点
//如果不是 则将newnode链接到pq的下一个位置
if (pq->tail == NULL)
{ //两个节点都指向newnode 表示此时队列中就一个元素
pq->head = pq->tail = newnode;
}
else
{
//1.将newnode链接到tail的后面
pq->tail->next = newnode;
//2.将newnode置换为新的tail
pq->tail = newnode;
}
}
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->head == NULL;
}
void QueuePop(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
//额外判断一下,解决如果仅剩一个结点了,pop的话导致tail为野指针
if (pq->head->next == NULL)
{
free(pq->head);
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
}
else
{
QNode* next = pq->head->next;
free(pq->head);
pq->head = next;
}
}
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
return pq->head->data;
}
QDataType QueueBck(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
return pq->tail ->data;
}
int QueueSize(Queue *pq)
{
assert(pq);
int count = 0;
QNode* cur = pq->head;
while (cur)
{
cur = cur->next;
count++;
}
return count;
}
typedef struct {
Queue q1; //队列1
Queue q2; //队列2
} MyStack;
MyStack* myStackCreate() {
MyStack* obj = (MyStack*)malloc(sizeof(MyStack));
if (obj == NULL)
{
return 0;
}
//初始化这两个队列
QueueInit(&obj->q1);
QueueInit(&obj->q2);
return obj;
}
bool myStackEmpty(MyStack* obj) {
return QueueEmpty(&obj->q1) && QueueEmpty(&obj->q2);
}
void myStackPush(MyStack* obj, int x) {
//如果q1为空,则往q2里放数据
if (QueueEmpty(&obj->q1))
{
QueuePush(&obj->q2, x);
}
else
{
QueuePush(&obj->q1, x);
}
}
int myStackPop(MyStack* obj) {
//如果q1为空,就要从q2往q1里导数据
if (QueueEmpty(&obj->q1))
{
while (!((&obj->q2)->head->next == NULL))
{
QueuePush(&obj->q1, QueueFront(&obj->q2));
QueuePop(&obj->q2);
}
int ret = QueueFront(&obj->q2);
QueuePop(&obj->q2);
return ret;
}
else
{
while (!((&obj->q1)->head->next == NULL))
{
QueuePush(&obj->q2, QueueFront(&obj->q1));
QueuePop(&obj->q1);
}
int ret = QueueFront(&obj->q1);
QueuePop(&obj->q1);
return ret;
}
}
int myStackTop(MyStack* obj) {
//如果q1为空,则是存放除栈顶数据的位置
if (QueueEmpty(&obj->q1))
{
while (!((&obj->q2)->head->next == NULL))
{
QueuePush(&obj->q1, QueueFront(&obj->q2));
QueuePop(&obj->q2);
}
int ret = QueueFront(&obj->q2);
QueuePush(&obj->q1,ret);
QueuePop(&obj->q2);
return ret;
}
else
{
while (!((&obj->q1)->head->next == NULL))
{
QueuePush(&obj->q2, QueueFront(&obj->q1));
QueuePop(&obj->q1);
}
int ret = QueueFront(&obj->q1);
QueuePush(&obj->q2,ret);
QueuePop(&obj->q1);
return ret;
}
}
void myStackFree(MyStack* obj) {
QueueDestroy(&obj->q1);
QueueDestroy(&obj->q2);
free(obj);
}边栏推荐
- 介绍一种对 SAP GUI 里的收藏夹事务码管理工具增强的实现方案
- Uni app realizes advertisement scroll bar
- 一文读懂TDengine的窗口查询功能
- 04 redis source code data structure dictionary
- Application of 5g industrial gateway in scientific and technological overload control; off-site joint law enforcement for over limit, overweight and overspeed
- Solution to 0xc000007b error when running the game [easy to understand]
- Apache-atlas-2.2.0 independent compilation and deployment
- 关于佛萨奇2.0“Meta Force原力元宇宙系统开发逻辑方案(详情)
- French Data Protection Agency: using Google Analytics or violating gdpr
- 新手准备多少钱可以玩期货?农产品可以吗?
猜你喜欢

Explain IO multiplexing, select, poll, epoll in detail

QT社团管理系统

陈宇(Aqua)-安全-&gt;云安全-&gt;多云安全

6年技术迭代,阿里全球化出海&合规的挑战和探索

Google Earth Engine(GEE)——全球人类居住区网格数据 1975-1990-2000-2014 (P2016)

Station B was scolded on the hot search..

A Fletter version of Notepad

SAP intelligent robot process automation (IRPA) solution sharing

Kongsong (Xintong Institute) - cloud security capacity building and trend in the digital era

一款Flutter版的记事本
随机推荐
Solution to 0xc000007b error when running the game [easy to understand]
uni-app实现广告滚动条
Research Report on China's software outsourcing industry investment strategy and the 14th five year plan Ⓡ 2022 ~ 2028
Google Earth engine (GEE) - Global Human Settlements grid data 1975-1990-2000-2014 (p2016)
French Data Protection Agency: using Google Analytics or violating gdpr
B站被骂上了热搜。。
当你真的学会DataBinding后,你会发现“这玩意真香”!
微机原理与接口技术知识点整理复习–纯手打
单工,半双工,全双工区别以及TDD和FDD区别
Investment analysis and prospect prediction report of global and Chinese p-nitrotoluene industry Ⓙ 2022 ~ 2027
1.8 new features list
Application of 5g industrial gateway in scientific and technological overload control; off-site joint law enforcement for over limit, overweight and overspeed
分布式事务简介(seata)
Several models of IO blocking, non blocking, IO multiplexing, signal driven and asynchronous IO
10. Page layout, guess you like it
【剑指Offer】54. 二叉搜索树的第k大节点
介绍一种对 SAP GUI 里的收藏夹事务码管理工具增强的实现方案
Some summary of pyqt5 learning (overview of the general meaning of some signals and methods)
清华章毓晋老师新书:2D视觉系统和图像技术(文末送5本)
[anwangbei 2021] Rev WP