当前位置:网站首页>m-way search trees
m-way search trees
2022-06-11 23:42:00 【Run after XX】
Binary tree and B Trees
The problem analysis of binary tree
The operation efficiency of binary tree is high , But there are also problems , Look at the binary tree below
- Binary trees need to be loaded into memory , If the binary tree has fewer nodes , No problem , But if the binary tree has many nodes ( such as 1 Billion ), Just The following problems exist :
- problem 1: When building a binary tree , It needs to be done many times i/o operation ( Massive data exists in databases or files ), Massive nodes , When building a binary tree , Speed has an effect .
- problem 2: Massive nodes , It also causes the height of the binary tree to be very high , It will reduce the operation speed .
Multiforked tree
- In a binary tree , Each node has data items , Up to two child nodes . If each node is allowed to have more data items and more children , It's a multi branched tree (multiway tree)
- We'll talk about it later 2-3 Trees ,2-3-4 A tree is a multi branched tree , By reorganizing nodes , Reduce the height of the tree , Can optimize the binary tree .
- Illustrate with examples ( below 2-3 A tree is a multi branched tree )

B A basic introduction to trees
B By reorganizing the nodes , Lower the height of the tree , And reduce i/o Read and write times to improve efficiency .
- Pictured B By reorganizing the nodes , Lowered the height of the tree .
- The designers of file system and database system make use of the principle of disk read ahead , Set the size of a node equal to a page ( Page size is usually 4k), In this way, each node only needs one time I/O You can load it completely .
- The degree of the tree M Set to 1024, stay 600 Of the billion elements, you only need 4 Time I/O Operation can read the desired element , B Trees (B+) widely Applied to file storage system and database system
2-3 Trees
2-3 Trees are the simplest B Tree structure , It has the following characteristics :
- 2-3 All the leaf nodes of the tree are on the same layer .( As long as it is B Trees all satisfy this condition )
- A node with two child nodes is called a two node node , Two nodes or no child nodes , Either there are two child nodes .
- A node with three child nodes is called a three node , Three nodes or no child nodes , Or there are three child nodes .
- 2-3 A tree is a tree composed of two nodes and three nodes .
2-3 Tree application case
Will be in series {16, 24, 12, 32, 14, 26, 34, 10, 8, 28, 38, 20} To build a 2-3 Trees , And ensure the order of data insertion .( Show me how to build 2-3 Tree process .)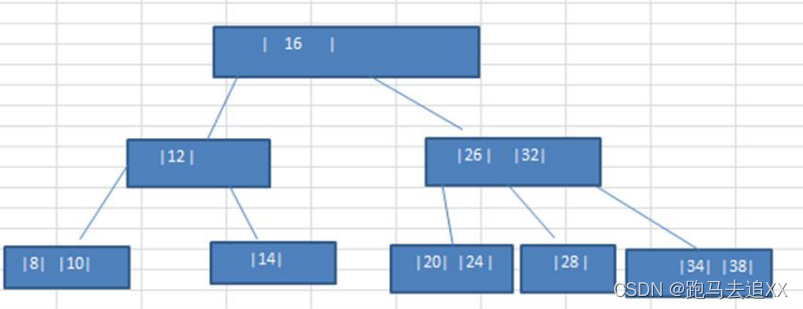
Insert rules :
- 2-3 All the leaf nodes of the tree are on the same layer .( As long as it is B Trees all satisfy this condition )
- A node with two child nodes is called a two node node , Two nodes or no child nodes , Either there are two child nodes .
- A node with three child nodes is called a three node , Three nodes or no child nodes , Or there are three child nodes
- When a number is inserted into a node according to the rules , Can't meet the above three requirements , You need to dismantle , Take it up first , If the upper floor is full of , Remove this layer , It still needs to meet the above requirements after dismantling 3 Conditions .
- For a three node subtree, the value size still follows (BST Binary sort tree ) The rules of
Other instructions
except 23 Trees , also 234 Trees, etc , Concepts and 23 Trees are like , It is also a kind of B Trees . Pictured :
B Trees 、B+ Trees and B* Trees
B Introduction to the tree
B-tree A tree is a tree B Trees ,B namely Balanced, Balance means . Someone put B-tree Translate into B- Trees , It's easy to misunderstand . Would think B- A tree is a kind of tree , and B A tree is another kind of tree . actually ,B-tree It means B Trees .
I've already introduced 2-3 Trees and 2-3-4 Trees , They are B Trees ( English :B-tree It's also written as B- Trees ), Here's another explanation , We are learning xi Mysql when , It is often said that a certain type of index is based on B Trees or B+ Treelike , Pictured :
For the illustration above :
- B The steps of the tree : The maximum number of child nodes of a node . such as 2-3 The steps of the tree are 3,2-3-4 The steps of the tree are 4
- B- Tree search , Start at root , For keywords in nodes ( Orderly ) Sequence binary search , If it hits, it ends , Otherwise, enter the query The child node of the range to which the keyword belongs ; repeat , Until the corresponding son pointer is null , Or it's already a leaf node
- The keyword set is distributed throughout the tree , That is, leaf nodes and non leaf nodes both store data .
- The search may end at a non leaf node
- Its search performance is equivalent to a binary search in the keyword set
B+ Introduction to the tree
B+ Trees are B A variation of a tree , It's also a multi-path search tree .
For the illustration above :
- B+ Tree search and B Trees are basically the same , The difference is that B+ A tree hits only when it reaches the leaf node (B Trees can hit at non leaf nodes ), Its nature Can also be equivalent to doing a binary search in the complete set of keywords
- All keywords appear in the linked list of leaf nodes ( That is, data can only be stored in leaf nodes 【 Also called dense index 】), And the keywords in the linked list ( data ) It happens to be orderly .
- It's impossible to hit at a non leaf node
- The non leaf node is equivalent to the index of the leaf node ( Sparse index ), Leaf node is equivalent to storage ( keyword ) Data layer of data
- More suitable for file index system
- B Trees and B+ Each tree has its own application scenarios , Can't say B+ Trees are more than B Good tree , vice versa .
B* Introduction to the tree
B Trees are B+ A variation of a tree , stay B+ The non root and non leaf nodes of the tree increase the pointer to the brother .
B Description of the tree :
- B* The tree defines that the number of keywords of non leaf nodes is at least (2/3)*M, That is, the minimum utilization rate of the block is 2/3, and B+ The minimum usage of tree blocks is 1/2.
- From 1 We can see that ,B* The probability ratio of a tree to allocate new nodes B+ Trees should be low , More space use
边栏推荐
- On the knowledge points of cookie attributes and the differences between webstorage and cookies?
- 图及图的遍历
- Handwritten simple promise
- Les produits antigéniques entrent dans la famille et les entreprises chinoises de dispositifs médicaux accueillent un nouvel océan bleu
- New Year Countdown JS case
- 二叉排序树
- Read the logstash principle
- require. context
- El scrollbar display horizontal scroll bar
- 2022年高处安装、维护、拆除操作证考试题库模拟考试平台操作
猜你喜欢

(dp+ longest common subsequence) acwing 897 Longest common subsequence

Wechat applet Bluetooth development

2022年安全员-A证考题模拟考试平台操作

2022 safety officer-b certificate theoretical question bank and simulation test

Jenkins of the integrate tool

Two ways of using reuqests in RF

帝国理工等最新《胶囊网络综述》论文,29页pdf阐述胶囊的概念、方法与应用

Test case design method

Procédures d'introduction et d'installation de sonarqube

多路查找树
随机推荐
(counting class +dp) acwing 900 Integer partition
删除收货地址【项目 商城】
双向带头循环链表(C语言)
Meet o & M (I) common questions for O & M interview
【delphi】判断文件的编码方式(ANSI、Unicode、UTF8、UnicodeBIG)
How to construct PostgreSQL error codes
Fonctionnement de la plate - forme d'examen de simulation pour les agents de sécurité - Questions d'examen de certificat a en 2022
Wireless communication comparison of si4463, si4438 and Si4432 schemes of wireless data transmission module
Read the logstash principle
HMS core shows the latest open capabilities in mwc2022, helping developers build high-quality applications
loading
(linear DP) acwing 898 Number triangle
2022年起重机司机(限桥式起重机)考试题模拟考试题库及模拟考试
产品力进阶新作,全新第三代荣威RX5盲订开启
2022年安全员-B证理论题库及模拟考试
Top selling commodities 【 project mall 】
Jetpack架构组件学习(3)——Activity Results API使用
Test case design method
Figure overview of neural network
What are the pitfalls of redis's current network: using a cache and paying for disk failures?