当前位置:网站首页>system_error错误处理库学习
system_error错误处理库学习
2022-08-02 09:07:00 【班公湖里洗过脚】
在程序开发时,我们有时遇到程序出错了,但不知道具体的原因,莫名其妙的就崩溃了,其实标准库提供了一个系统错误的库,我们可以使用这个system_error库来了解错误的提示。它不仅提供错误码code(),还提供错误类别category(),错误信息message()等相关接口。
成员函数
| 构造一个 error_code (公开成员函数) | |
| 赋值为另一 error_code (公开成员函数) | |
| 赋值为另一 error_code (公开成员函数) | |
修改器 | |
| 设 error_code 为 system_category 中的值 0 (公开成员函数) | |
观察器 | |
| 获得 error_code 的值 (公开成员函数) | |
| 获得此 error_code 的 error_category (公开成员函数) | |
| 获得此 error_code 的 error_condition (公开成员函数) | |
| 获得此 error_code 的解释性字符串 (公开成员函数) | |
| 检查值是否非零 (公开成员函数) | |
下面是具体的示例:
//error_code observers: value, category and message
#include <iostream> //std::cout, std::ios
#include <system_error> //std::system_error
#include <fstream> //std::ifstream
#include <string> //std::string
using std::cout;
using std::ios;
using std::endl;
using std::system_error;
using std::ifstream;
using std::string;
int main()
{
std::error_code code;
cout << "Code: " << code.value() << endl;
cout << "Category: " << code.category().name() << endl;
cout << "Message: " << code.message() << endl;
cout << "default_error_condition: " << code.default_error_condition().message() << endl;
cout << "bool: " << code.operator bool() << endl;
cout << "Hello World!" << endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果:

上面是创建一个error_code 对象,程序正常运行,根据上面的结果可以看没程序正常没有错误。
下面我们来看一个异常的程序。
//error_code observers: value, category and message
#include <iostream> //std::cout, std::ios
#include <system_error> //std::system_error
#include <fstream> //std::ifstream
#include <string> //std::string
using std::cout;
using std::ios;
using std::endl;
using std::system_error;
using std::ifstream;
using std::string;
int main()
{
ifstream is;
is.exceptions(std::ios::failbit);
try {
is.open("unexistent.txt");
} catch (const std::system_error &e) {
cout << "Exception caught (system_error):\n" << endl;
cout << "Error: " << e.what() << endl;
cout << "Code: " << e.code().value() << endl;
cout << "Category: " << e.code().category().name() << endl;
cout << "Message: " << e.code().message() << endl;
cout << "default_error_condition: " << e.code().default_error_condition().message() << endl;
cout << "bool: " << e.code().operator bool() << endl;
cout << endl;
}
cout << "Hello World!" << endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果:

打开一个不存在的文件,出现了异常,从上面的异常提示我们知道这是输入输出流错误。
接着,我们把这个错误对象赋给第一个程序创建的一个空的错误类对象。查看他的信息。
//error_code observers: value, category and message
#include <iostream> //std::cout, std::ios
#include <system_error> //std::system_error
#include <fstream> //std::ifstream
#include <string> //std::string
using std::cout;
using std::ios;
using std::endl;
using std::system_error;
using std::ifstream;
using std::string;
int main()
{
std::error_code code;
cout << "Code: " << code.value() << endl;
cout << "Category: " << code.category().name() << endl;
cout << "Message: " << code.message() << endl;
cout << "default_error_condition: " << code.default_error_condition().message() << endl;
cout << "bool: " << code.operator bool() << endl;
cout << endl;
ifstream is;
is.exceptions(std::ios::failbit);
try {
is.open("unexistent.txt");
} catch (const std::system_error &e) {
cout << "Exception caught (system_error):\n" << endl;
cout << "Error: " << e.what() << endl;
cout << "Code: " << e.code().value() << endl;
cout << "Category: " << e.code().category().name() << endl;
cout << "Message: " << e.code().message() << endl;
cout << "default_error_condition: " << e.code().default_error_condition().message() << endl;
cout << "bool: " << e.code().operator bool() << endl;
cout << endl;
// operator= 操作
code = e.code();
cout << "Code: " << code.value() << endl;
cout << "Category: " << code.category().name() << endl;
cout << "Message: " << code.message() << endl;
cout << "default_error_condition: " << code.default_error_condition().message() << endl;
cout << "bool: " << code.operator bool() << endl;
cout << endl;
}
cout << "Hello World!" << endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果:

e和code两个错误对象的信息相同,接下来再调用clear函数,把信息内容清空
//error_code observers: value, category and message
#include <iostream> //std::cout, std::ios
#include <system_error> //std::system_error
#include <fstream> //std::ifstream
#include <string> //std::string
using std::cout;
using std::ios;
using std::endl;
using std::system_error;
using std::ifstream;
using std::string;
int main()
{
std::error_code code;
cout << "Code: " << code.value() << endl;
cout << "Category: " << code.category().name() << endl;
cout << "Message: " << code.message() << endl;
cout << "default_error_condition: " << code.default_error_condition().message() << endl;
cout << "bool: " << code.operator bool() << endl;
cout << endl;
ifstream is;
is.exceptions(std::ios::failbit);
try {
is.open("unexistent.txt");
} catch (const std::system_error &e) {
cout << "Exception caught (system_error):\n" << endl;
cout << "Error: " << e.what() << endl;
cout << "Code: " << e.code().value() << endl;
cout << "Category: " << e.code().category().name() << endl;
cout << "Message: " << e.code().message() << endl;
cout << "default_error_condition: " << e.code().default_error_condition().message() << endl;
cout << "bool: " << e.code().operator bool() << endl;
cout << endl;
// operator= 操作
code = e.code();
cout << "Code: " << code.value() << endl;
cout << "Category: " << code.category().name() << endl;
cout << "Message: " << code.message() << endl;
cout << "default_error_condition: " << code.default_error_condition().message() << endl;
cout << "bool: " << code.operator bool() << endl;
cout << endl;
//调用clear()
code.clear();
cout << "Code: " << code.value() << endl;
cout << "Category: " << code.category().name() << endl;
cout << "Message: " << code.message() << endl;
cout << "default_error_condition: " << code.default_error_condition().message() << endl;
cout << "bool: " << code.operator bool() << endl;
cout << endl;
}
cout << "Hello World!" << endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果:
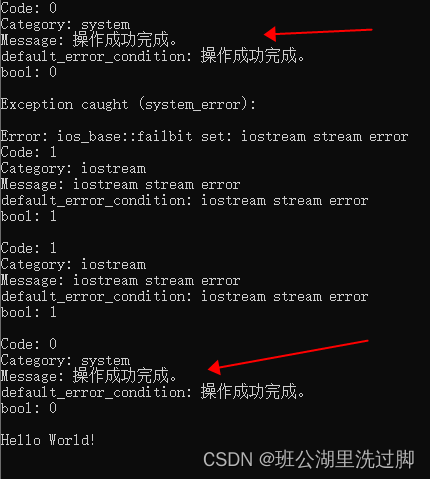
code对象又恢复到初始状态了。
我们也可以对错误码对像进行hash:
//error_code observers: value, category and message
#include <iostream> //std::cout, std::ios
#include <system_error> //std::system_error
#include <fstream> //std::ifstream
#include <string> //std::string
using std::cout;
using std::ios;
using std::endl;
using std::system_error;
using std::ifstream;
using std::string;
int main()
{
ifstream is;
is.exceptions(std::ios::failbit);
try {
is.open("unexistent.txt");
} catch (const std::system_error &e) {
cout << "Exception caught (system_error):\n" << endl;
cout << "Error: " << e.what() << endl;
cout << "Code: " << e.code().value() << endl;
cout << "Category: " << e.code().category().name() << endl;
cout << "Message: " << e.code().message() << endl;
cout << "default_error_condition: " << e.code().default_error_condition().message() << endl;
cout << "bool: " << e.code().operator bool() << endl;
cout << endl;
std::hash<std::error_code> hashErrorCode;
cout << "hash(error_code): " << hashErrorCode(e.code()) << endl;
}
cout << "Hello World!" << endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果:
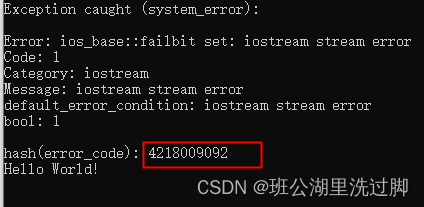
hash这是一个结构体模板,它不仅可以对错误码对象进行hash也可以对数值进行hash,比如int, long long, float, double,string等,下面来看一个示例:
//error_code observers: value, category and message
#include <iostream> //std::cout, std::ios
#include <system_error> //std::system_error
#include <fstream> //std::ifstream
#include <string> //std::string
using std::cout;
using std::ios;
using std::endl;
using std::system_error;
using std::ifstream;
using std::string;
int main()
{
ifstream is;
is.exceptions(std::ios::failbit);
try {
is.open("unexistent.txt");
} catch (const std::system_error &e) {
cout << "Exception caught (system_error):\n" << endl;
cout << "Error: " << e.what() << endl;
cout << "Code: " << e.code().value() << endl;
cout << "Category: " << e.code().category().name() << endl;
cout << "Message: " << e.code().message() << endl;
cout << "default_error_condition: " << e.code().default_error_condition().message() << endl;
cout << "bool: " << e.code().operator bool() << endl;
cout << endl;
std::hash<std::error_code> hashErrorCode;
cout << "hash(error_code): " << hashErrorCode(e.code()) << endl;
string str = "hello world!";
std::hash<string> hashStr;
cout << "hash(string): " << hashStr(str) << endl;
int n = 100;
std::hash<int> hashN;
cout << "hash(int): " << hashN(n) << endl;
long long ln = 100;
std::hash<long long> hashLn;
cout << "hash(long long): " << hashLn(ln) << endl;
double dou = 100;
std::hash<double> hashD;
cout << "hash(double): " << hashD(dou) << endl;
float f = 100;
std::hash<float> hashF;
cout << "hash(float): " << hashF(f) << endl;
}
cout << "Hello World!" << endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果:
参考:
边栏推荐
- Analysis of software testing technology How far is Turing test from us
- PyCharm usage tutorial (more detailed, picture + text)
- 天地图给多边形加标注
- 中国发布丨滴滴因违反网络安全法等被罚80.26亿元!调查细节公布
- Tencent T8 architect, teach you to learn small and medium R&D team architecture practice PDF, senior architect shortcut
- 初学者怎么快速学会SQL
- leetcode:81. 搜索旋转排序数组 II
- AI目标分割能力,无需绿幕即可实现快速视频抠图
- Gorilla Mux 和 GORM 的使用方法
- Spend 2 hours a day to make up for Tencent T8, play 688 pages of SSM framework and Redis, and successfully land on Meituan
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
YugaByte adds Voyager migration service in its 2.15 database update
ORBSLAM代码阅读
JSP页面中page指令有哪些属性及方法可使用呢?
稳定币:对冲基金做空 Tether 的结局会是什么?
HCIA动态主机配置协议实验(dhcp)
JSP中page指令的import命令具有什么功能呢?
RestTemlate源码分析及工具类设计
next permutation
恋爱十不要
node制作一个视频帧长图生成器
postman下载安装汉化及使用
【论文阅读】Distilling the Knowledge in a Neural Network
EdrawMax Crack,多合一的图表应用程序
每天花2小时恶补腾讯T8纯手打688页SSM框架和Redis,成功上岸美团
day_05模块
EPSANet: An Efficient Pyramid Split Attention Block on Convolutional Neural Network
CFdiv2-The Number of Imposters-(两种点集图上染色问题总结)
PyCharm usage tutorial (more detailed, picture + text)
js函数防抖和函数节流及其使用场景
Jenkins--基础--6.3--Pipeline--语法--脚本式