当前位置:网站首页>[STL] unordered of associated container_ Map Usage Summary
[STL] unordered of associated container_ Map Usage Summary
2022-06-23 06:58:00 【Shu Yang】
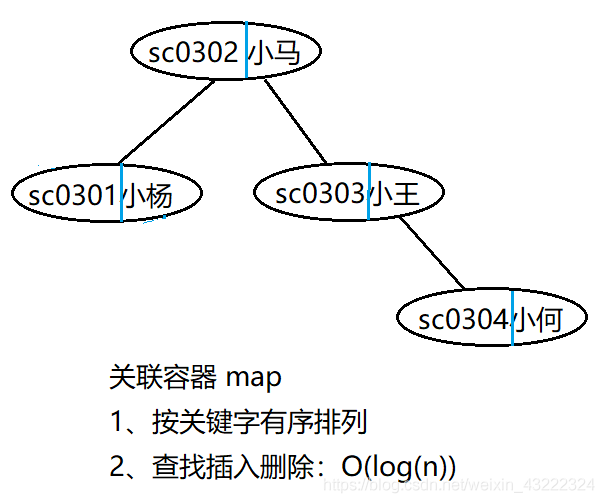
One 、 The basic principle
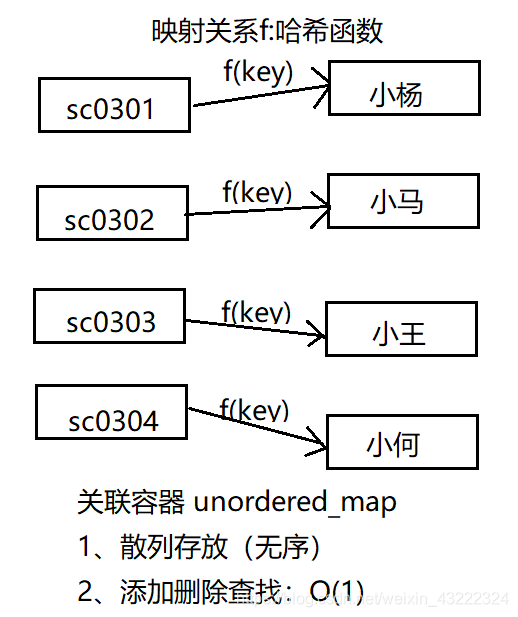
unordered_map yes C++ One of the associated containers provided by the standard library , Save the key value pair (key-value), We can go through key Quickly find the corresponding value.unordered_map The underlying data structure is Hashtable (hash table), So in unordered_map Search for 、 The time complexity of adding or removing elements is Constant time O(1). Besides ,unordered_map The element in is A disorderly .
unordered_map Use scenarios :
Now suppose there is a bedroom 501, The bedroom has 4 A student , We're going to use a container to hold this 4 Student numbers and names of students , The requirement is that I need to find the name corresponding to this student number through the student number .

Now we use a unordered_map To preserve , Student number as key, Name as value, These two messages of a student serve as unordered_map An element of pair(pair Usage Summary ), We can get the corresponding name by student number .
Maybe you have such a question , Why use unordered_map Well , I use a two-dimensional array can not also store the bedroom 4 Student number and name of students ?
Yes , Save can save , But the time complexity of the operation is different , For example, I know the student number "sc0303", I want to find the corresponding name , If you use unordered_map The saved , According to the characteristics of hash table , It only needs O(1) The corresponding name can be found in the time of . If you use a two-dimensional array to save , You need to traverse the first column of the two-dimensional array from the beginning , need O(n) Time to find out . This is the use of unordered_map The meaning of .
Maybe you will have such questions , Why use unordered_map Well , I use one. map Can you also save it ?
use map and unordered_map The difference is that ,map Based on the red black tree , It is ordered by keywords ,unordered_map Based on hash table , It is hashed ( disorder ). When you need to do a range query “ Comparison number sc0302 The name of the big classmate ”, So use map It's more convenient , because map The element in has been in accordance with the student number ( keyword ) It's arranged orderly , But if this scenario is used unordered_map, You can only compare the ranges one by one . When performing an equivalence query unordered_map It only needs O(1) You can find out when , but map But I need O(log(n)) Time for , Therefore, the equivalent query uses unordered_map faster .
Which container to choose depends on the usage scenario , They have their own advantages .

Two 、 usage
unordered_map The elements in are a pair of key value pairs , type pair, For usage, please refer to the blog pair Usage Summary
initialization
| unordered_map<T1,T2> Container name ; | T1、T2 Is the type name , It can be a basic data type int、double etc. , It can also be a class type string etc. |
|---|---|
| unordered_map<T1,T2> m1; | Create a file called m1 Of empty unordered_map,key The type of T1,value The type of T2 |
| unordered_map<T1,T2> m1{p1,p2……}; | m1 The element in is initialized to p1,p2……,p1、p2 yes pair type |
| unordered_map<T1,T2> m1{ {key1,value1},{key2,value2}……}; | m1 The element in is initialized to Key value pair {key1,value1},{key2,value2}…… |
| unordered_map<T1,T2> m2(m1); | m2 Contains and m1 The same elements |
| unordered_map<T1,T2> m2=m1; | m2 Contains and m1 The same elements |
Program example :
pair<string, string> p1("sc0301"," Xiao Yang "); // Mode one , Create a pair be known as p1
pair<string, string> p2 = make_pair("sc0302", " The pony "); // Mode two ,make_pair Function returns a function with "sc0302" and " The pony " The initialization of the pair
pair<string, string> p3("sc0303", " Xiao Wang ");
pair<string, string> p4("sc0304", " Xiao He ");
unordered_map<string, string> m1; // Create an empty unordered_map
unordered_map<string, string> m2{
p1,p2,p3,p4 }; // Create a containing key value pairs p1、p2、p3、p4 Of unordered_map
unordered_map<string, string> m3{
{
"sc0301"," Xiao Yang "},{
"sc0302", " The pony "},{
"sc0303", " Xiao Wang "},{
"sc0304", " Xiao He "} }; // The effect is the same as the previous sentence
unordered_map<string, string> m4(m2); // Create a unordered_map,m4 Contains and m2 The same elements
unordered_map<string, string> m5 = m2; // Create a unordered_map,m5 Contains and m2 The same elements
Access elements
| Access elements | |
|---|---|
| T2 value = m1[key]; | Get keywords key Corresponding value value |
| m1.at(key); | Get keywords key Corresponding value value |
| *iter | Access iterators iter Pointing elements |
| Acquisition iterator | |
|---|---|
| m1.begin(); | Get directions m1 First element The iterator |
| m1.end(); | Get directions m1 The last position of the tail element The iterator |
| m1.rbegin(); | Get directions m1 The previous position of the first element The iterator |
| m1.rend(); | Get directions m1 The tail element The iterator |
| m1.cbegin(); m1.cend(); | The above meaning , But what we get is const_iterator |
| m1.crbegin(); m1.crend(); | The above meaning , But what we get is const_iterator |
Program example :
string p2_name = m2["sc0302"]; // Get student number ( keyword )"sc0302" Corresponding name ( value )
string p3_name = m2.at("sc0303"); // Get student number "sc0303" Corresponding name
unordered_map<string, string>::iterator it1 = m2.begin(); // Get a point to m2 Iterator of the first element
unordered_map<string, string>::iterator it2 = m2.end(); // Get a point to m2 Iterator for the next position of the tail element
pair<string, string> p11 = *it1; // obtain m2 First element of {"sc0301"," Xiao Yang "}
string p1_ID = it1->first; // obtain m2 First element of {"sc0301"," Xiao Yang "} Of fisrt member
string p1_name = it1->second; // obtain m2 First element of {"sc0301"," Xiao Yang "} Of second member
Traversal container
1、 Using Iterators
for (auto it_b = m2.begin(), it_e = m2.end(); it_b != it_e;++it_b) {
pair<string, string> current = *it_b;
cout << " Student number :" << it_b->first << "; full name :" << it_b->second << endl;
// The above sentence is equivalent to the following sentence
cout << " Student number :" << current.first << "; full name :" << current.second << endl;
}
2、 Range for sentence
for (auto p : m2) {
cout << " Student number :" << p.first << "; full name :" << p.second << endl;
}
add to 、 Modifying elements
| m1.insert(p1); | stay unordered_map Insert existing pair |
|---|---|
| m1.insert({key1,value1}); | stay unordered_map Key value pairs are inserted in {key1,value1} |
| m1.insert(pair<T1, T2> (key1, value1)); | // Create an anonymous pair object , And insert into unordered_map in |
| m1.insert(make_pair(key1, value1)); | // Create an anonymous pair object , And insert into unordered_map in |
| m1.insert(unordered_map<T1, T2>::value_type (key1, value1)); | // Create an anonymous pair object , And insert into unordered_map in |
| m1[key] = value; | If key Insert if it doesn't exist The key value pair , If key Modify if it already exists The key Corresponding value |
| m1.emplace(p1); | stay unordered_map Insert existing pair |
| m1.emplace(pair<T1, T2> (key1, value1)); | // Create an anonymous pair object , And insert into unordered_map in |
Program example :
m1.insert(p1); // stay unordered_map Insert existing pair
m1.insert({
"sc0302", " The pony " }); // Insert key-value pairs { "sc0302", " The pony " }
m1.insert(pair<string, string> ("sc0303", " Xiao Wang ")); // Create an anonymous pair object , And insert into unordered_map in
m1.insert(make_pair("sc0303", " Xiao Wang ")); // The keyword to insert is already in the container ,emplace/insert Don't do anything?
m1.insert(unordered_map<string, string>::value_type("sc0303", " Xiao Wang ")); // The keyword to insert is already in the container ,emplace/insert Don't do anything?
m1["sc0304"] = " Xiao He "; // If key If it does not exist, insert the key value pair , If key Modify this if it already exists key Corresponding value.
m1.emplace(p1); // The keyword to insert is already in the container ,emplace/insert Don't do anything?
m1.emplace(pair<string, string>("sc0303", " Xiao Wang ")); // The keyword to insert is already in the container ,emplace/insert Don't do anything?
Remove elements
| m1.erase(key) | Delete the keyword as key The elements of |
|---|---|
| m1.erase(iter); | Delete iterator iter Pointing elements |
| m1.erase(iter1,iter2); | Delete iterator iter1 and ter2 The element in the range pointed to |
| m1.clear(); | Delete m1 Medium all Elements |
Program example :
m1.erase("sc0301"); // Delete the keyword as "sc0301" The elements of
auto iter = m1.begin(); // Point to m2 Iterator of the first element of
m1.erase(iter); // Delete the element that the iterator points to
auto iter1 = m1.begin(), iter2 = m1.end();
m1.erase(iter1, iter2); // Delete iterator iter1、iter2 The element in the range pointed to
m2.clear(); // Delete all elements in the container
unordered_map Size
| m1.szie(); | get m1 Size |
|---|---|
| m1.empty(); | if m1 If NULL, the return value is true, Otherwise, the return value is false |
Program example :
int s = m3.size(); // get m1 Size
bool e = m3.empty(); // if m1 If NULL, the return value is true, Otherwise, the return value is false
lookup
| m1.find(key) | Returns an iterator , Point to the first keyword as key The elements of , if key Not in the container , Then return the post iterator |
|---|---|
| m1.count(key); | The return keyword is equal to key The number of elements . For containers that do not allow duplicate keywords unordered_map, The value returned is 0 or 1 |
Program example :
unordered_map<string, string>::iterator it = m4.find("sc0301"); // Search keywords are "sc0301" The elements of , Returns an iterator
if (it == m4.end()) {
// if "sc0301" Not in the container , be it Equals the trailing iterator
cout << " Not found !" << endl;
}
else {
pair<string, string> result1 = *it; // eureka
}
int result2 = m4.count("sc0305"); // Search keywords are "sc0301" The elements of , The return keyword is equal to "sc0301" The number of elements
if (result2==0) {
cout << " Not found !" << endl;
}
else {
cout << " eureka !" << endl;
}
unordered_map<string, string>::iterator it_up = m4.upper_bound("sc0301"); // Returns an iterator , Point to the first keyword greater than "sc0301" The elements of
pair<string, string> result3 = *it_up;
3、 ... and 、 Program example
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <utility>
#include <unordered_map>
using namespace std;
int main() {
// initialization -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
pair<string, string> p1("sc0301"," Xiao Yang "); // Mode one , Create a pair be known as p1
pair<string, string> p2 = make_pair("sc0302", " The pony "); // Mode two ,make_pair Function returns a function with "sc0302" and " The pony " The initialization of the pair
pair<string, string> p3("sc0303", " Xiao Wang ");
pair<string, string> p4("sc0304", " Xiao He ");
unordered_map<string, string> m1; // Create an empty unordered_map
unordered_map<string, string> m2{
p1,p2,p3,p4 }; // Create a containing key value pairs p1、p2、p3、p4 Of unordered_map
unordered_map<string, string> m3{
{
"sc0301"," Xiao Yang "},{
"sc0302", " The pony "},{
"sc0303", " Xiao Wang "},{
"sc0304", " Xiao He "} }; // The effect is the same as the previous sentence
unordered_map<string, string> m4(m2); // Create a unordered_map,m4 Contains and m2 The same elements
unordered_map<string, string> m5 = m2; // Create a unordered_map,m5 Contains and m2 The same elements
// Access elements -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
string p2_name = m2["sc0302"]; // Get student number ( keyword )"sc0302" Corresponding name ( value )
string p3_name = m2.at("sc0303"); // Get student number "sc0303" Corresponding name
unordered_map<string, string>::iterator it1 = m2.begin(); // Get a point to m2 Iterator of the first element
unordered_map<string, string>::iterator it2 = m2.end(); // Get a point to m2 Iterator for the next position of the tail element
pair<string, string> p11 = *it1; // obtain m2 First element of {"sc0301"," Xiao Yang "}
string p1_ID = it1->first; // obtain m2 First element of {"sc0301"," Xiao Yang "} Of fisrt member
string p1_name = it1->second; // obtain m2 First element of {"sc0301"," Xiao Yang "} Of second member
// Traversal container -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
for (auto it_b = m2.begin(), it_e = m2.end(); it_b != it_e;++it_b) {
pair<string, string> current = *it_b;
cout << " Student number :" << it_b->first << "; full name :" << it_b->second << endl;
// The above sentence is equivalent to the following sentence
cout << " Student number :" << current.first << "; full name :" << current.second << endl;
}
for (auto p : m2) {
cout << " Student number :" << p.first << "; full name :" << p.second << endl;
}
// add to 、 Modifying elements -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
m1.insert(p1); // stay unordered_map Insert existing pair
m1.insert({
"sc0302", " The pony " }); // Insert key-value pairs { "sc0302", " The pony " }
m1.insert(pair<string, string> ("sc0303", " Xiao Wang ")); // Create an anonymous pair object , And insert into unordered_map in
m1.insert(make_pair("sc0303", " Xiao Wang ")); // The keyword to insert is already in the container ,emplace/insert Don't do anything?
m1.insert(unordered_map<string, string>::value_type("sc0303", " Xiao Wang ")); // The keyword to insert is already in the container ,emplace/insert Don't do anything?
m1["sc0304"] = " Xiao He "; // If key If it does not exist, insert the key value pair , If key Modify this if it already exists key Corresponding value.
m1.emplace(p1); // The keyword to insert is already in the container ,emplace/insert Don't do anything?
m1.emplace(pair<string, string>("sc0303", " Xiao Wang ")); // The keyword to insert is already in the container ,emplace/insert Don't do anything?
// Remove elements -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
m1.erase("sc0301"); // Delete the keyword as "sc0301" The elements of
auto iter = m1.begin(); // Point to m2 Iterator of the first element of
m1.erase(iter); // Delete the element that the iterator points to
auto iter1 = m1.begin(), iter2 = m1.end();
m1.erase(iter1, iter2); // Delete iterator iter1、iter2 The element in the range pointed to
m2.clear(); // Delete all elements in the container
// size -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
int s = m3.size(); // get m1 Size
bool e = m3.empty(); // if m1 If NULL, the return value is true, Otherwise, the return value is false
// lookup -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
unordered_map<string, string>::iterator it = m4.find("sc0301"); // Search keywords are "sc0301" The elements of , Returns an iterator
if (it == m4.end()) {
// if "sc0301" Not in the container , be it Equals the trailing iterator
cout << " Not found !" << endl;
}
else {
pair<string, string> result1 = *it; // eureka
}
int result2 = m4.count("sc0305"); // Search keywords are "sc0301" The elements of , The return keyword is equal to "sc0301" The number of elements
if (result2==0) {
cout << " Not found !" << endl;
}
else {
cout << " eureka !" << endl;
}
}
边栏推荐
- cmder
- 746. climbing stairs with minimum cost - Dynamic Planning
- Chrome删除重复书签
- Measurement principle and thickness measurement mode of spectral confocal
- 剑指 Offer 42. 连续子数组的最大和
- Concepts and differences of DQL, DML, DDL and DCL
- redux Actions may not have an undefined “type“ property. Have you misspelled a constant?
- Idea installing the cloudtoolkit plug-in
- mysql 函数
- asp.net文件下载demo与相关问题的处理
猜你喜欢

Usage Summary of item views and item widgets controls in QT

为什么TCP协议是三次握手而不是两次?
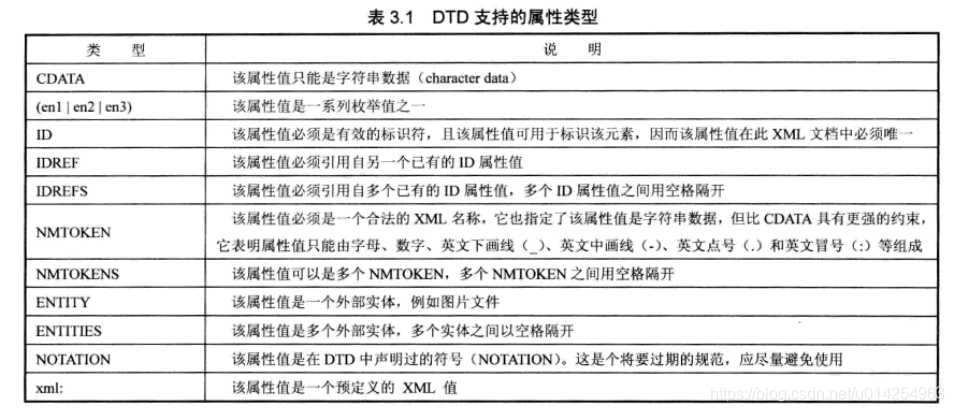
XML DTD record

【日常训练】513. 找树左下角的值

How to realize video call and live interaction in a small program when live broadcasting is so popular?

MySQL重做日志 redo log

【项目实训】多段线扩充为平行线

Linux Installation mysql8.0.25

Influence of steam education on domestic college students

Easy EDA #学习笔记09# | ESP32-WROOM-32E模组ESP32-DevKitC-V4开发板 一键下载电路
随机推荐
/Bin/sh no such file or directory problem
system 权限程序不能访问sd卡问题
Focusing on the smart city, Huawei cooperates with China Science and technology Xingtu to jointly develop a new digital blue ocean
关于职业态度
Drawing and resetting of mars3d point, line and surface
XML schema record
746. climbing stairs with minimum cost - Dynamic Planning
回调函数详解
mysql 优化
xml dtd 记录
Badly placed ()‘s 问题
How to view native IP
English语法_副词 - ever / once
页面嵌入iframe 点击浏览器后退问题
What are the pension financial products in 2022? Low risk
小白投资理财必看:图解基金买入与卖出规则
2.17 haas506 2.0 development tutorial system (only versions above 2.2 are supported)
DQL、DML、DDL、DCL的概念与区别
开源OAuth2框架 实现SSO单点登录
Cloud box is deeply convinced to create a smart dual-mode teaching resource sharing platform for Nanjing No. 1 middle school