当前位置:网站首页>LeetCode · 23. Merge K ascending linked lists · recursion · iteration
LeetCode · 23. Merge K ascending linked lists · recursion · iteration
2022-07-30 21:06:00 【Xiao Xun wants to become stronger】
链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/merge-k-sorted-lists/solution/by-xun-ge-v-huf8/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有.商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处.
题目
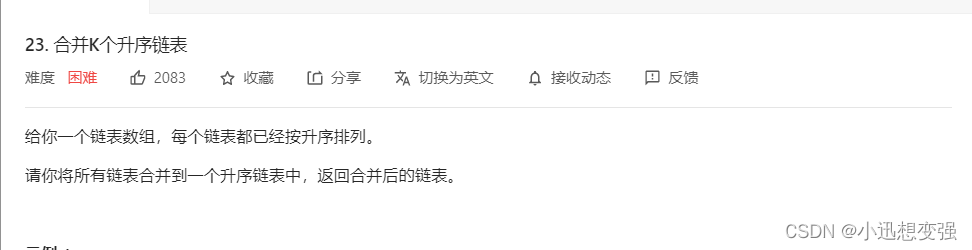
示例

思路
解题思路
- 暴力解法
As the saying goes, violence never goes out of style,There is no problem that violence cannot solve,Only hardware doesn't work,Timeout is over
对于本题,Need to merge multiple linked lists,For linked list related issues,Converting the linked list to storing it in an array basically solves the problem,We store all elements of the linked list in arrays,然后将数组进行排序,Then convert the array elements to the linked list for storage
- 逐一比较
Solving for violence,Obviously not looking high class,Then improve it a bit
The linked list given to us by the title is already in ascending order,For all linked lists the first element is relative to the smallest element,Then we compare row by row,Take the smallest element of the first row each time and add it to the return list.
There are two cases for the next solution,使用递归实现,Still use iteration,Using recursion is simple and easy to write on our own,But the disadvantage is that the program resource overhead is large,Iteration is the opposite of recursion.
- For merging multiple linked lists,Can be transformed into the same subproblem
- Any two linked lists are merged
for any number of linked lists,We can both merge two of them,Then merge any two of them.比如4个链表,Merge any two of them first -> 3 and then any two are combined -> 2 and then any two are combined -> 1One is what is desired
Iterative and recursive implementations can be used to merge any two linked lists,Both recursive and iterative approaches can also be used for transforming subproblems
Iterations can be encapsulated as functions,也可以不需要
- 递归
Any two linked lists are merged recursively,直接上代码吧
struct ListNode * dfs(struct ListNode * l1, struct ListNode * l2)
{
if(l1 == NULL)
{
return l2;
}
if(l2 == NULL)
{
return l1;
}
if(l1->val < l2->val)//Compare the element sizes of two linked lists,Use the small one as the head node
{
l1->next = dfs(l1->next, l2);
return l1;
}
l2->next = dfs(l1, l2->next);
return l2;
}
The transformation subproblem is implemented recursively -> In fact, it is the idea of merge sort Or divide and conquer ideas,看下面代码
- 迭代
Any two linked lists are merged iteratively,直接上代码吧
struct ListNode * iterate(struct ListNode * l1, struct ListNode * l2)
{
struct ListNode * head = malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
struct ListNode * tail = head;
while(l1 && l2){
if (l1->val <= l2->val){
tail->next = l1;
l1 = l1->next;
}
else{
tail->next = l2;
l2 = l2->next;
}
tail = tail->next;
}
tail->next = l1 ? l1 : l2;
return head->next;
}
Iterative implementation for the transformation subproblem,看下面代码
代码
- 暴力解法
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
int cmp(const void * a, const void * b)//升序子函数
{
return *(int *)a - *(int *)b;
}
struct ListNode* mergeKLists(struct ListNode** lists, int listsSize){
if(listsSize == 0 )
{
return NULL;
}
int ans[10000];//Temporarily save linked list values
int node = 0;
for(int i = 0; i <listsSize; i++)//Save all linked list values
{
while(lists[i])
{
ans[node++] = lists[i]->val;
lists[i] = lists[i]->next;
}
}
qsort(ans, node, sizeof(int), cmp);//排序
struct ListNode * h = NULL;
struct ListNode * root = NULL;
for(int i = 0; i < node; i++)//Convert to linked list storage
{
struct ListNode * r = malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
r->val = ans[i];
r->next = NULL;
if(root == NULL)
{
h = r;
root = r;
}
else
{
h->next = r;
h = r;
}
}
return root;
}- 逐一比较
struct ListNode* mergeKLists(struct ListNode** lists, int listsSize){
int i = 0, j = 0, m = 0;
struct ListNode *head = malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode)); //头结点
head->next = NULL;
struct ListNode *tail = head, *min = head;
while(1){
for(i = 0; (i < listsSize) && !lists[i]; i++){
//Find the first non-empty element in the linked list array
}
if(i < listsSize){
min = lists[i];
m = i;
}
else{ //The linked list is completely empty,退出循环
break;
}
for(j=i+1; j<listsSize; j++){ //Record the position of the smallest node in the linked list
if(lists[j] && (lists[j]->val < min->val)){
min = lists[j];
m = j;
}
}
tail->next = min; //Add the smallest nodehead链表
tail = tail->next;
lists[m] = lists[m]->next;
}
return head->next;
}- The transformation subproblem is implemented recursively -> In fact, it is the idea of merge sort Or divide and conquer ideas
//递归实现
struct ListNode * dfs(struct ListNode * l1, struct ListNode * l2)
{
if(l1 == NULL)
{
return l2;
}
if(l2 == NULL)
{
return l1;
}
if(l1->val < l2->val)
{
l1->next = dfs(l1->next, l2);
return l1;
}
l2->next = dfs(l1, l2->next);
return l2;
}
struct ListNode* TwoLists(struct ListNode** lists, int l, int r){//递归分治
if(l == r) return lists[l];
if(l > r) return NULL;
int mid = l + (r - l)/2;
struct ListNode *l1 = TwoLists(lists, l, mid);//One of any two linked lists
struct ListNode *l2 = TwoLists(lists, mid+1, r);//One of any two linked lists
/*
//迭代方法
struct ListNode * head = malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
struct ListNode * tail = head;
while(l1 && l2){
if (l1->val <= l2->val){
tail->next = l1;
l1 = l1->next;
}
else{
tail->next = l2;
l2 = l2->next;
}
tail = tail->next;
}
tail->next = l1 ? l1 : l2;
return head->next;
*/
//递归方法
return dfs(l1, l2);
}
struct ListNode* mergeKLists(struct ListNode** lists, int listsSize){
if(!listsSize) return NULL;
return TwoLists(lists, 0, listsSize-1);//Convert multiple linked list merges to any two linked list merges,Transform subproblems
}- The transformation subproblem is implemented iteratively
//递归方法
struct ListNode * dfs(struct ListNode * l1, struct ListNode * l2)
{
if(l1 == NULL)
{
return l2;
}
if(l2 == NULL)
{
return l1;
}
if(l1->val < l2->val)
{
l1->next = dfs(l1->next, l2);
return l1;
}
l2->next = dfs(l1, l2->next);
return l2;
}
//迭代方法
struct ListNode * bfs(struct ListNode * l1, struct ListNode * l2)
{
struct ListNode * head = malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
struct ListNode * tail = head;
while(l1 && l2){
if (l1->val <= l2->val){
tail->next = l1;
l1 = l1->next;
}
else{
tail->next = l2;
l2 = l2->next;
}
tail = tail->next;
}
tail->next = l1 ? l1 : l2;
return head->next;
}
struct ListNode* mergeKLists(struct ListNode** lists, int listsSize){
if(!listsSize) return NULL;
struct ListNode * head = NULL;
for(int i = 0; i < listsSize; i++)
{
//递归实现
head = dfs(head, lists[i]);
//迭代实现
//head = bfs(head, lists[i]);
}
return head;
}
时间空间复杂度

边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
mpls简介
HJ85 longest palindrome substring
Swift RegexBuilder Vs. Raku Grammar
Babbitt | Metaverse Daily Must Read: The shuffling is coming, will the digital Tibetan industry usher in a new batch of leaders in the second half?Will there be new ways to play?...
【回归预测-lssvm分类】基于最小二乘支持向量机lssvm实现数据分类代码
Network layer protocol------IP protocol
Redis数据更新,是先更新数据库还是先更新缓存?
MySQL笔记2(函数,约束,多表查询,事务)
【深度学习】目标检测|SSD原理与实现
Deep Kalman Filter Network for Video Compression Artifact Removal
C language: detailed explanation of operators
Enhancing Quality for HEVC Compressed Videos
MySQL (2)
QUALITY-GATED CONVOLUTIONAL LSTM FOR ENHANCING COMPRESSED VIDEO
2022年SQL经典面试题总结(带解析)
C语言中指针没那么难~ (1)【文章结尾有资料】
How to make a deb package
DPW-SDNet: Dual Pixel-Wavelet Domain Deep CNNsfor Soft Decoding of JPEG-Compressed Images
[Deep Learning] Target Detection | SSD Principle and Implementation
IDEA2018.3.5取消双击Shift快捷键