当前位置:网站首页>LeetCode·23.合并K个升序链表·递归·迭代
LeetCode·23.合并K个升序链表·递归·迭代
2022-07-30 21:05:00 【小迅想变强】
链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/merge-k-sorted-lists/solution/by-xun-ge-v-huf8/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
题目
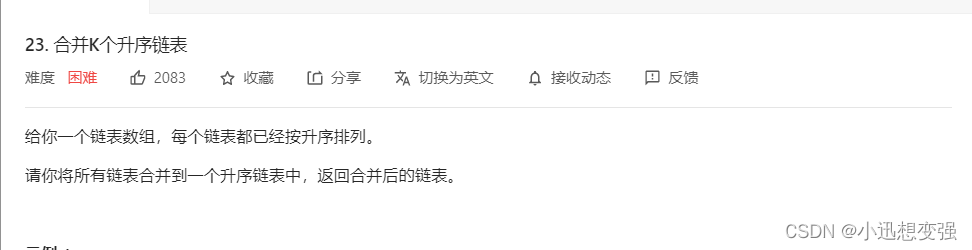
示例

思路
解题思路
- 暴力解法
正所谓暴力永不过时,没有暴力解决不了的问题,只有硬件不行,超时就是过
对于本题,需要合并多个链表,对于链表相关问题,将链表转换为用数组存储基本上都能解决问题,我们将链表所有元素用数组进行存储,然后将数组进行排序,再将数组元素转换到链表中存储即可
- 逐一比较
对于暴力求解,显然看着不高级,那就稍微改进一下
题目给我们的链表已经是升序的了,对于所有链表来说第一个元素都是相对于最小的元素,那么我们按行进行比较,每次取第一行最小的元素加入返回链表中即可。
接下来的解法就存在两种情况,使用递归实现,还是使用迭代,使用递归对我们自己来说简单易写,但是坏处就是程序资源开销大,迭代就和递归相反了。
- 对于多个链表合并,可以转换为同一个子问题
- 任意两个链表合并
对于任意多个链表,我们都可以对其中两个进行合并,然后在对其中任意两个合并。比如4个链表,先合并其中任意两个 -> 3 个再任意两个合并 -> 2 个再任意两个合并 -> 1个即为所求
对于任意两个链表合并可以使用迭代和递归实现,对于转换子问题也可以使用递归和迭代两种方法
迭代可以封装为函数,也可以不需要
- 递归
任意两个链表合并递归实现,直接上代码吧
struct ListNode * dfs(struct ListNode * l1, struct ListNode * l2)
{
if(l1 == NULL)
{
return l2;
}
if(l2 == NULL)
{
return l1;
}
if(l1->val < l2->val)//比较两个链表元素大小,将小的作为头结点
{
l1->next = dfs(l1->next, l2);
return l1;
}
l2->next = dfs(l1, l2->next);
return l2;
}
转换子问题递归实现 -> 其实就是归并排序思路 或者分治思路,看下面代码
- 迭代
任意两个链表合并迭代实现,直接上代码吧
struct ListNode * iterate(struct ListNode * l1, struct ListNode * l2)
{
struct ListNode * head = malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
struct ListNode * tail = head;
while(l1 && l2){
if (l1->val <= l2->val){
tail->next = l1;
l1 = l1->next;
}
else{
tail->next = l2;
l2 = l2->next;
}
tail = tail->next;
}
tail->next = l1 ? l1 : l2;
return head->next;
}
对于转换子问题迭代实现,看下面代码
代码
- 暴力解法
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
int cmp(const void * a, const void * b)//升序子函数
{
return *(int *)a - *(int *)b;
}
struct ListNode* mergeKLists(struct ListNode** lists, int listsSize){
if(listsSize == 0 )
{
return NULL;
}
int ans[10000];//临时保存链表值
int node = 0;
for(int i = 0; i <listsSize; i++)//保存所有链表值
{
while(lists[i])
{
ans[node++] = lists[i]->val;
lists[i] = lists[i]->next;
}
}
qsort(ans, node, sizeof(int), cmp);//排序
struct ListNode * h = NULL;
struct ListNode * root = NULL;
for(int i = 0; i < node; i++)//转换为链表存储
{
struct ListNode * r = malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
r->val = ans[i];
r->next = NULL;
if(root == NULL)
{
h = r;
root = r;
}
else
{
h->next = r;
h = r;
}
}
return root;
}- 逐一比较
struct ListNode* mergeKLists(struct ListNode** lists, int listsSize){
int i = 0, j = 0, m = 0;
struct ListNode *head = malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode)); //头结点
head->next = NULL;
struct ListNode *tail = head, *min = head;
while(1){
for(i = 0; (i < listsSize) && !lists[i]; i++){
//找到链表数组里第一个非空的元素
}
if(i < listsSize){
min = lists[i];
m = i;
}
else{ //链表全空,退出循环
break;
}
for(j=i+1; j<listsSize; j++){ //记录链表最小结点的位置
if(lists[j] && (lists[j]->val < min->val)){
min = lists[j];
m = j;
}
}
tail->next = min; //将最小结点加入head链表
tail = tail->next;
lists[m] = lists[m]->next;
}
return head->next;
}- 转换子问题递归实现 -> 其实就是归并排序思路 或者分治思路
//递归实现
struct ListNode * dfs(struct ListNode * l1, struct ListNode * l2)
{
if(l1 == NULL)
{
return l2;
}
if(l2 == NULL)
{
return l1;
}
if(l1->val < l2->val)
{
l1->next = dfs(l1->next, l2);
return l1;
}
l2->next = dfs(l1, l2->next);
return l2;
}
struct ListNode* TwoLists(struct ListNode** lists, int l, int r){//递归分治
if(l == r) return lists[l];
if(l > r) return NULL;
int mid = l + (r - l)/2;
struct ListNode *l1 = TwoLists(lists, l, mid);//任意两个链表之一
struct ListNode *l2 = TwoLists(lists, mid+1, r);//任意两个链表之一
/*
//迭代方法
struct ListNode * head = malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
struct ListNode * tail = head;
while(l1 && l2){
if (l1->val <= l2->val){
tail->next = l1;
l1 = l1->next;
}
else{
tail->next = l2;
l2 = l2->next;
}
tail = tail->next;
}
tail->next = l1 ? l1 : l2;
return head->next;
*/
//递归方法
return dfs(l1, l2);
}
struct ListNode* mergeKLists(struct ListNode** lists, int listsSize){
if(!listsSize) return NULL;
return TwoLists(lists, 0, listsSize-1);//将多个链表合并转换为任意两个链表合并,转换子问题
}- 转换子问题迭代实现
//递归方法
struct ListNode * dfs(struct ListNode * l1, struct ListNode * l2)
{
if(l1 == NULL)
{
return l2;
}
if(l2 == NULL)
{
return l1;
}
if(l1->val < l2->val)
{
l1->next = dfs(l1->next, l2);
return l1;
}
l2->next = dfs(l1, l2->next);
return l2;
}
//迭代方法
struct ListNode * bfs(struct ListNode * l1, struct ListNode * l2)
{
struct ListNode * head = malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
struct ListNode * tail = head;
while(l1 && l2){
if (l1->val <= l2->val){
tail->next = l1;
l1 = l1->next;
}
else{
tail->next = l2;
l2 = l2->next;
}
tail = tail->next;
}
tail->next = l1 ? l1 : l2;
return head->next;
}
struct ListNode* mergeKLists(struct ListNode** lists, int listsSize){
if(!listsSize) return NULL;
struct ListNode * head = NULL;
for(int i = 0; i < listsSize; i++)
{
//递归实现
head = dfs(head, lists[i]);
//迭代实现
//head = bfs(head, lists[i]);
}
return head;
}
时间空间复杂度

边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
365天挑战LeetCode1000题——Day 044 按公因数计算最大组件大小 并查集
KEIL problem: [keil Error: failed to execute 'C:\Keil\ARM\ARMCC']
Quick Master QML Chapter 6 Animation
2.网络资源访问工具:requests
Mysql 回表
Mysql索引特性(重要)
flowable工作流所有业务概念
Android Studio 实现登录注册-源代码 (连接MySql数据库)
[Nuxt 3] (十四) Nuxt 生命周期
@WebServlet注解(Servlet注解)
@RequestParam使用
文字的选择与排版
触摸屏状态机
服务器不稳定因素
如何解决gedit 深色模式下高亮文本不可见?
What is the common factor
MySQL group_concat()详解
深入浅出边缘云 | 3. 资源配置
第03章 用户和权限管理【1.MySQL架构篇】【MySQL高级】
MySql 创建索引