当前位置:网站首页>[function explanation (Part 1)] | | knowledge sorting + code analysis + graphic interpretation
[function explanation (Part 1)] | | knowledge sorting + code analysis + graphic interpretation
2022-07-03 05:38:00 【Sobtemesa】
“ The boy looked back Laugh, I'm not fast enough to keep up .”
Catalog
4. The parameters of the function
7. Nested calls and chained access to functions
1. What is a function
A program may be used many times , If you write such a repeated piece of code every time , It's not only time-consuming and laborious 、 It's easy to make mistakes , And it's troublesome to give it to others , therefore C Language provides a function , It allows us to encapsulate common code into a separate module in a fixed format , As long as you know the name of this module, you can reuse it , This module is called function (Function). Function compared to other code , With relative independence .
Generally, there will be input parameters and return values , Provide encapsulation of the process and hiding of details . These codes are usually integrated into Software library .
2. Library function
C Function classification in language :
1. Library function
2. Custom function
Why are there library functions ?
Before we learn C In language programming , It's a little bit like scanf,printf,strcpy,strlen And other basic functions , They are not business code , In the process of development, every programmer will use , in order to Support portability and improve program efficiency , therefore C The language base library provides a series of similar library functions , It is convenient for programmers to develop software .

notes : Use library functions , must #include The corresponding header file .
Take a chestnut :
1.

int main()
{
char arr1[] = "#####################";
char arr2[] = "hello world";
strcpy(arr1, arr2);
printf("%s\n", arr1);
return 0;
} 
2.
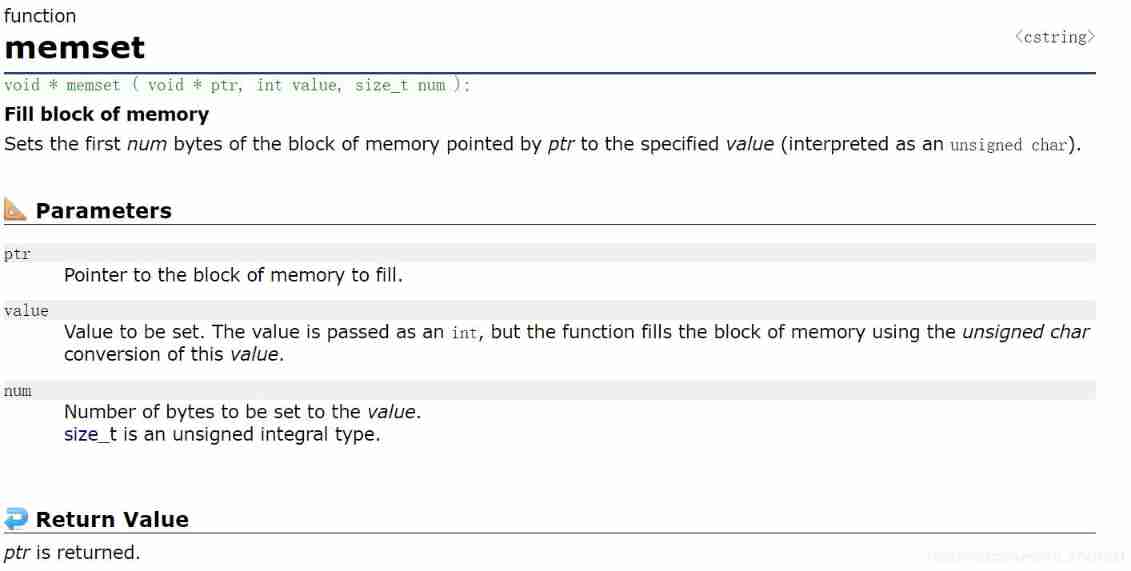
int main()
{
char arr2[] = "hello world";
memset(arr2, 'x', 5);
printf("%s\n", arr2);
return 0;
}
notes :memset It is initialized in bytes .

3. Custom function
Except for library functions , We can still Write your own functions , Expand the function of the program . The function written by yourself is called user-defined function . Custom functions and library functions are written and used in exactly the same way , It's just written by different institutions .
ret_type fun_name ( para1 )
{ statement;// Statement item }
ret_type Return type fun_name Function name para1 Function parameter
Take a chestnut :
int Max(int a, int b)
{
return (a > b ? a : b);
}
int main()
{
int a = 0;
int b = 0;
scanf("%d%d", &a, &b);
int max=Max(a, b);
printf("%d", max);
return 0;
}void Change(int *a, int *b)
{
int tmp = 0;
tmp = *a;
*a =*b;
*b = tmp;
}
int main()
{
int a = 0;
int b = 90;
printf("a:%db:%d\n", a, b);
Change(&a,&b);
printf("a:%db:%d\n", a, b);
return 0;
}4. The parameters of the function
Actual parameters :
The parameters that are actually passed to the function . It can be : Constant , Variable , expression , Functions, etc . When you make a function call , They all have to have certain values , In order to pass these values to the parameter .
Shape parameter :
When you define a function , Variables in parentheses after function names , because Formal parameters are instantiated only when called ( Allocate space ), So it's called formal parameter . Formal parameters will be destroyed after the function is called , Therefore, formal parameters are only valid in functions .
5. Function call
Value transfer call :
Function parameters and arguments occupy different memory blocks , Changes to formal parameters do not affect arguments . After the formal parameter is instantiated, it is actually equivalent to a temporary copy of the argument .
Address call :
Address calling is a calling method that passes the memory address of the variable created outside the function to the function parameters .
This way of parameter transfer can establish a real connection between the function and the variables outside the function . In other words, the variables outside the function can be directly manipulated inside the function .

6. practice
1. Write a function to determine whether a number is a prime .
int is_prime(int i)
{
for (int j = 2; j <= sqrt(i); j++)
{
if (i%j == 0)
{
return 0;
}
}
return 1;
}
int main()
{
for (int i = 100; i <= 200; i++)
{
if (is_prime(i))
{
printf("%d ", i);
}
}
return 0;
}2. Write a function to determine whether a year is a leap year .
int is_leap_year(int y)
{
return((y % 4 == 0) && (y % 100 != 0) || (y % 400 == 0));
}
int main()
{
int y = 0;
int i = 0;
scanf("%d", &y);
if (is_leap_year(y))
{
printf(" It's a leap year ");
}else
printf(" It's not a leap year ");
return 0;
}3. Write a function , To realize binary search of an ordered array .
int binary_search(int k,int arr[], int sz)
{
int left = 0;
int right = sz - 1;
while (left <= right)
{
int mid = (left + right) / 2;
if (arr[mid] < k)
{
left = mid + 1;
}
else if (arr[mid]>k)
{
right = mid - 1;
}
else if (arr[mid] == k)
{
return mid;
}
}
return -1;
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10 };
int k = 7;
int sz = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
int tmp=binary_search(k,arr, sz);
if (tmp == -1)
{
printf(" Can't find ");
}
else
{
printf(" eureka , Subscript to be %d\n", tmp);
}
return 0;
}4. Write a function , Every time you call this function , Will be num The value of the increase 1.
int Count(int* pnum)
{
(*pnum)++;
}
int main()
{
int num = 0;
Count(&num);
Count(&num);
Count(&num);
Count(&num);
printf("%d", num);
return 0;
}7. Nested calls and chained access to functions
Nested calls
void Print()
{
printf("hello world\n1");
}
void test()
{
Print();
}
int main()
{
test();
return 0;
}Functions can be called nested, but not defined nested .
// Error model
void Print()
{
printf("hello world\n1");
}
int main()
{
void test()
{
Print();
}
return 0;
}Chained access
Chained access is a function of Return value As Parameters of another function .
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
printf("%d", printf("%d", printf("%d", 43)));
// The result is what ?
return 0;
}

analysis : 1. Execute first printf("%d", 43), Its return value is 2
1. Execute first printf("%d", 43), Its return value is 2
2. Re execution printf("%d",2), Its return value is 1
3. Re execution printf("%d",1)
边栏推荐
- The request database reported an error: "could not extract resultset; SQL [n/a]; needed exception is org.hibernate.exception.sqlgram"
- [Shangshui Shuo series together] day 10
- 今天很多 CTO 都是被干掉的,因为他没有成就业务
- Differences among bio, NiO and AIO
- Final review (Day2)
- Talk about how to use p6spy for SQL monitoring
- ROS Compilation Principle
- Robot capture experiment demonstration video
- Deploy crawl detection network using tensorrt (I)
- Installing altaro VM backup
猜你喜欢

Win10 install pytullet and test

Export the altaro event log to a text file

Map的扩容机制
How to use source insight

求质数的方法

How do I migrate my altaro VM backup configuration to another machine?

谷歌 | 蛋白序列的深度嵌入和比对

Webrtc native M96 version opening trip -- a reading code download and compilation (Ninja GN depot_tools)
College campus IP network broadcasting - manufacturer's design guide for college campus IP broadcasting scheme based on campus LAN

Simpleitk learning notes
随机推荐
2022.6.30DAY591
Troubleshooting of 32GB Jetson Orin SOM failure to brush
Making coco datasets
Capacity expansion mechanism of map
Get and monitor remote server logs
中职网络子网划分例题解析
大二困局(复盘)
2022.7.2 模拟赛
2022.6.30DAY591
2022.7.2 simulation match
EMD distance - example of use
Altaro o365 total backup subscription plan
【无标题】
Go practice -- factory mode of design patterns in golang (simple factory, factory method, abstract factory)
Source insight License Activation
Robot capture experiment demonstration video
一起上水硕系列】Day 9
Redis expiration elimination mechanism
Interview question -- output the same characters in two character arrays
Calculation method of AUC