当前位置:网站首页>2022.7.2 模拟赛
2022.7.2 模拟赛
2022-07-03 05:28:00 【lAWTYl】
T1 counting
小清新 T 1 T1 T1 。个一个数列,没有修改,每次询问问大于等于 x x x 的数的个数。直接每次询问 l o w e r b o u n d ( ) lower_bound() lowerbound() 就搞定了。
考场上 5 5 5 分钟敲完 qwq。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define in read()
#define MAXN 200200
inline int read(){
int x = 0; char c = getchar();
while(c < '0' or c > '9') c = getchar();
while('0' <= c and c <= '9'){
x = x * 10 + c - '0'; c = getchar();
}
return x;
}
int a[MAXN] = {
0 };
int n = 0; int q = 0;
int main(){
freopen("counting.in", "r", stdin);
freopen("counting.out", "w", stdout);
n = in; q = in;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) a[i] = in;
sort(a + 1, a + n + 1);
while(q--){
int x = in;
cout << n - (lower_bound(a + 1, a + n + 1, x) - a) + 1 << '\n';
}
return 0;
}
T2 graph
也是送分题。按照题目意思直接模拟就行了(最暴力的同构图 qwq)。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define MAXN 101
int n = 0; int m = 0;
int mmap1[MAXN][MAXN] = {
0 };
int mmap2[MAXN][MAXN] = {
0 };
bool flag = 0;
bool chk(int a[]){
bool temp = true;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for(int j = 1; j < i; j++){
int x = a[i], y = a[j];
if(mmap1[i][j])
if(!mmap2[x][y]) temp = false;
}
return temp;
}
int a[MAXN] = {
0 };
bool vis[MAXN] = {
0 };
void dfs(int x){
if(x == n + 1){
if(chk(a)) flag = 1;
return;
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
if(vis[i]) continue;
vis[i] = 1; a[x] = i;
dfs(x + 1);
vis[i] = 0; a[x] = 0;
}
}
int main(){
freopen("graph.in", "r", stdin);
freopen("graph.out", "w", stdout);
cin >> n >> m;
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++){
int x = 0, y = 0;
cin >> x >> y;
mmap1[x][y] = mmap1[y][x] = 1;
}
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++){
int x = 0, y = 0;
cin >> x >> y;
mmap2[x][y] = mmap2[y][x] = 1;
}
dfs(1);
flag ? cout << "Yes" << '\n' : cout << "No" << '\n';
return 0;
}
T3 dishes
一开始把题目意思理解错了,想成了字典序最小的拓扑序。打完之后发现样例错了,然后又看了好久的题目才看懂。
让你求的是满足拓扑序且依次让编号小的尽可能在前面。然后就会发现字典序最小显然是不对的。那么我们考虑倒着做。
具体来说我们要让编号小的依次尽可能排在最前面,就可以理解成我们要让编号大的尽可能排在拓扑序的后面。于是我们可以想到反向建图,然后在反图上跑字典序最大的拓扑序,最后再把拓扑序反过来就是要求的答案 (本质就是贪心,但是正确性我不会证,题过了就行 qwq)。
u p d upd upd:这种方法的正确性证明:
首先我们反着求出了字典序最大的拓扑序,所以 1 1 1 所在的位置肯定是最靠后的,因为如果往前挪一点那么字典序就会变小。那么反过来之后 1 1 1 就在最前面,所以 1 1 1 的位置一定是正确的。
然后我们运用数学归纳法,假设前 k k k 个数的位置都是正确的,那么我们需要证明第 k + 1 k + 1 k+1 个数也是正确的。这个证明的方法就和刚刚证明 1 1 1 的位置是正确的的方法一模一样了。
于是这个做法就一定是正确的。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define in read()
#define MAXN 100100
#define MAXM MAXN << 2
inline int read(){
int x = 0; char c = getchar();
while(c < '0' or c > '9') c = getchar();
while('0' <= c and c <= '9'){
x = x * 10 + c - '0'; c = getchar();
}
return x;
}
int t = 0;
int n = 0; int m = 0;
int a[MAXN] = {
0 };
int tot = 0; int cnt = 0;
int first[MAXN] = {
0 };
int nxt[MAXM] = {
0 };
int to[MAXM] = {
0 };
int deg[MAXN] = {
0 };
inline void add(int x, int y){
nxt[++tot] = first[x];
first[x] = tot; to[tot] = y; deg[y]++;
}
void init(){
tot = cnt = 0;
memset(a, 0, sizeof(a));
memset(to, 0, sizeof(to));
memset(nxt, 0, sizeof(nxt));
memset(deg, 0, sizeof(deg));
memset(first, 0, sizeof(first));
}
priority_queue<int> q;
void topsort(){
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) if(!deg[i]) q.push(i);
while(!q.empty()){
int x = q.top(); q.pop();
a[++cnt] = x;
for(int e = first[x]; e; e = nxt[e]){
int y = to[e];
if(!(--deg[y])) q.push(y);
}
}
}
int main(){
freopen("dishes.in", "r", stdin);
freopen("dishes.out", "w", stdout);
t = in;
while(t--){
init();
n = in; m = in;
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++){
int x = in, y = in;
add(y, x);
} topsort();
if(cnt < n) cout << "Impossible!\n";
else {
for(int i = n; i >= 1; i--) cout << a[i] << ' '; puts(""); }
}
return 0;
}
T4 network
传送门:HNOI2016 网络
前 30 p t s 30pts 30pts 可以用一个 O ( m 2 log n ) O(m^2\log n) O(m2logn) 的暴力打过去,具体来说是这样的。
显然我们可以 O ( n log n ) O(n\log n) O(nlogn) 预处理过后 O ( log n ) O(\log n) O(logn) 求 l c a ( x , y ) lca(x, y) lca(x,y),于是我们就能在 O ( log n ) O(\log n) O(logn) 的时间内求出 d i s ( x , y ) dis(x, y) dis(x,y)。于是现在我们就只需要知道一个点 m m m 是否在 p a t h ( x , y ) path(x, y) path(x,y) 的路径上就好了。
如果 m m m 在路径 p a t h ( x , y ) path(x, y) path(x,y) 上,那么显然有 d i s ( x , m ) + d i s ( m , y ) = d i s ( x , y ) dis(x, m) + dis(m, y) = dis(x, y) dis(x,m)+dis(m,y)=dis(x,y)。所以通过这个就能判断 m m m 是否在 p a t h ( x , y ) path(x, y) path(x,y) 上了。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define in read()
#define MAXN 200200
#define MAXM MAXN << 2
inline int read(){
int x = 0; char c = getchar();
while(c < '0' or c > '9') c = getchar();
while('0' <= c and c <= '9'){
x = x * 10 + c - '0'; c = getchar();
}
return x;
}
int n = 0; int m = 0;
int tot = 0;
int first[MAXN] = {
0 };
int nxt[MAXM] = {
0 };
int to[MAXM] = {
0 };
void add(int x, int y){
nxt[++tot] = first[x];
first[x] = tot; to[tot] = y;
}
int dep[MAXN] = {
0 };
int f[MAXN][35] = {
0 };
void prework(int x, int fa){
dep[x] = dep[fa] + 1;
for(int i = 0; i <= 30; i++)
f[x][i + 1] = f[f[x][i]][i];
for(int e = first[x]; e; e = nxt[e]){
int y = to[e];
if(y == fa) continue;
f[y][0] = x; prework(y, x);
}
}
int query(int x, int y){
if(dep[x] < dep[y]) swap(x, y);
for(int i = 30; i >= 0; i--){
if(dep[f[x][i]] >= dep[y]) x = f[x][i];
if(x == y) return x;
}
for(int i = 30; i >= 0; i--)
if(f[x][i] != f[y][i]) x = f[x][i], y = f[y][i];
return f[x][0];
}
int cnt = 0;
struct Tpath{
int t;
int x, y, v;
bool isd;
}path[MAXN];
int main(){
n = in; m = in;
for(int i = 1; i < n; i++){
int x = in, y = in;
add(x, y), add(y, x);
} prework(1, 0);
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++){
int op = in;
if(op == 0){
int a = in, b = in, v = in;
path[++cnt].x = a, path[cnt].y = b, path[cnt].t = i, path[cnt].v = v;
}
else if(op == 1){
int t = in;
for(int j = 1; j <= cnt; j++) if(path[j].t == t) path[j].isd = 1;
}
else if (op == 2){
int k = in; int ans = -1;
for(int j = 1; j <= cnt; j++){
if(path[j].isd) continue;
int x = path[j].x, y = path[j].y;
int lcaxy = query(x, y), lcaxk = query(x, k), lcaky = query(k, y);
int disxy = dep[x] + dep[y] - 2 * dep[lcaxy];
int disxk = dep[x] + dep[k] - 2 * dep[lcaxk];
int disky = dep[k] + dep[y] - 2 * dep[lcaky];
if(disxy != disxk + disky) ans = max(ans, path[j].v);
}
cout << ans << '\n';
}
}
return 0;
}
然后我们发现还有 20 p t s 20pts 20pts 是整棵树变成链的情况。而这种情况题目就变成了一道比较简单的数列上的操作问题。现在显然这个问题就转化成了一个树套树的板子 (考试的时候打板子调了一个多小时没调出来所以就不贴代码了 qwq)。
边栏推荐
- Chapter II program design of circular structure
- [practical project] autonomous web server
- es7创建索引容易犯的错误
- Go practice -- generate and read QR codes in golang (skip2 / go QRcode and boombuilder / barcode)
- (subplots usage) Matplotlib how to draw multiple subgraphs (axis field)
- Making coco datasets
- Can altaro back up Microsoft teams?
- Webrtc native M96 version opening trip -- a reading code download and compilation (Ninja GN depot_tools)
- Obtenir et surveiller les journaux du serveur distant
- Self introduction and objectives
猜你喜欢

Shanghai daoning, together with American /n software, will provide you with more powerful Internet enterprise communication and security component services

Detailed explanation of yolov5 training own data set
3dslam with 16 line lidar and octomap

Primary school campus IP network broadcasting - Design of primary school IP digital broadcasting system based on campus LAN

穀歌 | 蛋白序列的深度嵌入和比對

求质数的方法

【实战项目】自主web服务器
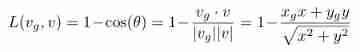
Training method of grasping angle in grasping detection

Altaro o365 total backup subscription plan

ES7 easy mistakes in index creation
随机推荐
(subplots usage) Matplotlib how to draw multiple subgraphs (axis field)
BIO、NIO、AIO区别
Technical analysis of qianyuantong multi card aggregation router
The IntelliJ platform completely disables the log4j component
Go practice -- use redis in golang (redis and go redis / redis)
2022.7.2day594
Introduction to deep learning (II) -- univariate linear regression
Latest version of source insight
今天很多 CTO 都是被幹掉的,因為他沒有成就業務
Installing altaro VM backup
How to install and configure altaro VM backup for VMware vSphere
Azure file synchronization of altaro: the end of traditional file servers?
es7创建索引容易犯的错误
Skip table: principle introduction, advantages and disadvantages of skiplist
Redis 入門和數據類型講解
6.23 warehouse operation on Thursday
Redis breakdown penetration avalanche
JS dynamic table creation
Jetson AGX Orin 平台移植ar0233-gw5200-max9295相机驱动
appium1.22.x 版本后的 appium inspector 需单独安装