当前位置:网站首页>Binary tree non-recursive traversal
Binary tree non-recursive traversal
2022-07-31 22:11:00 【Massachusetts_11】
1. 遍历一棵树
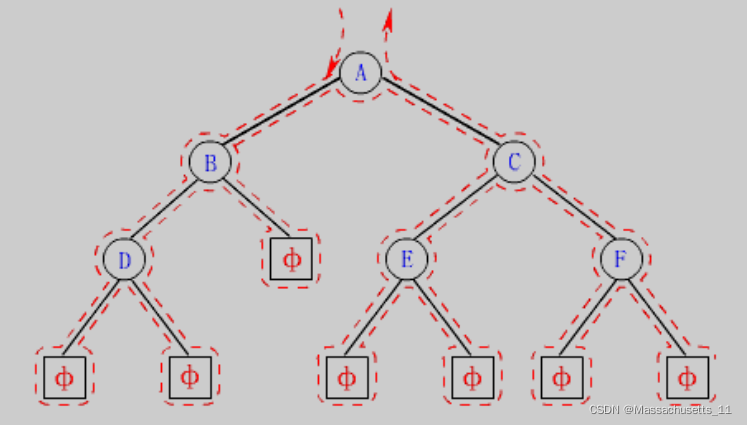
前、中、The path of the post-order traversal is actually the same,They all travel the same way.
前、中、The results of post-order access are different,In fact, the timing of accessing the nodes is different:
前序:Visit a node as soon as you encounter it
中序:After visiting the left tree, go to visit
后序:After visiting the right subtree, visit again
如下是B节点的前、中、Post-order access timing
2. 非递归遍历
2.1 理解
The previous recursive traversal,Think of a tree as a symmetrical structure:左子树根右子树,With the help of recursive functions,You can enter the left and right subtrees for access;
But if you want to do it within the current function迭代访问,The previous left-right subproblem approach is difficult to implement.
Here we might as well take a look at the path graph of this traversal:

Walk down the far left firstA-B-D
然后向上,走D的右子树、B的右子树、A的右子树,走完AThe return of the right subtree means the traversal is over
Here access to the right subtree can be regarded as one子问题——Visit another tree rooted at the right node,Go back to the beginning;
It can be found that the order in which the nodes on the left go for the first time is from top to bottom:A-B-D,The order in which the right subtree is visited at the next encounter is againD-B-A,恰好相反,因此可以用栈的结构,When walking from the left, first save the nodes from top to bottom,When traversing to the end,When it is empty, remove the node at the top of the stack,Use this node to access its right tree;
At the same time by virtue of the stack structure,When entering the right tree,Go to the node of the right tree,Still into this stack,When the right tree is finished walking back,All the pushed nodes of the right tree have also been taken out,Again, only the nodes on the previous trunk are left,Mainline logic can also continue,Similar to the logic of the recursive way——No matter how complicated the logic of recursion is,Complete the branch task and come back,My main quest is still going on as normal.
2.2 实现
注:The following only provides methods for traversing the entire tree non-recursively,前、中、The timing of subsequent access to the node is not written,具体见后.
变量定义:

实现:
Traverse the leftmost node,At the same time, they are pushed onto the stack in turn

Start fetching elements from the stack

Access its right tree through this node
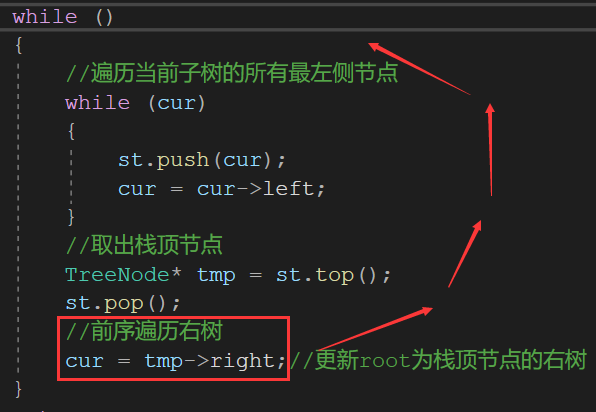
The judgment of the end of the traversal
- The elements in the stack are fetched——栈空
- At the same time, the current root node corresponds to an empty tree
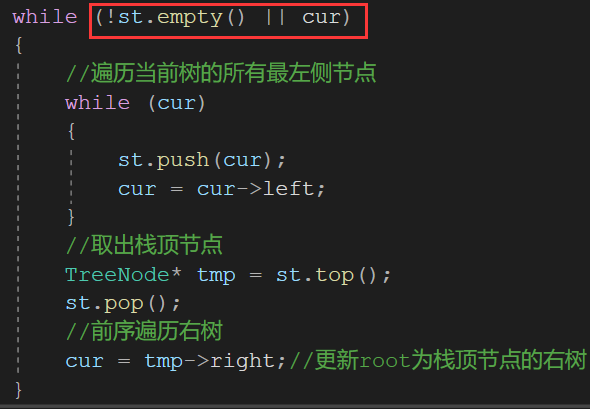
The case where the subtree is empty(Back to the main question):
Skip the traversal of the current tree,Take the next node from the stack
The current logic just works
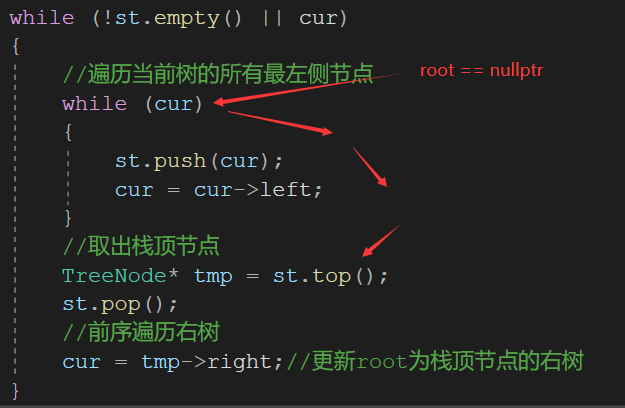
3. 前、中、后序遍历
前、中、The only difference between post-order traversal is the timing of visiting nodes
Each node can be seen as being traversed three times:first encounter,Come back from the left and meet again,Meet again after traversing the right subtree,
These three encounters happened to correspond to the previous ones、中、subsequent access timing,
Just find the corresponding parts of these three encounters in the iterative logic to visit,before you can finish、中、后序遍历.

3.1 前序遍历
访问时机:第一次碰到,That is, when the left traversal is to be pushed into the stack
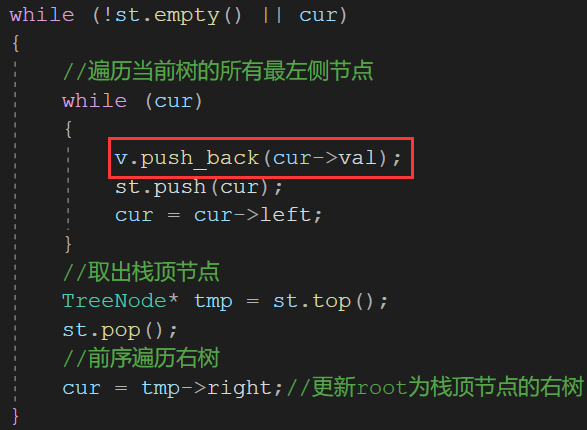
此时访问,You can put it on the stack.
vector<int> preorderTraversal(TreeNode* root)
{
vector<int> v;//Storage accesses out elements
stack<TreeNode*> st;//栈——Temporary storage node
TreeNode* cur = root;//A pointer for traversing the entire tree
while (!st.empty() || cur)
{
//Traverse all leftmost nodes of the current tree
while (cur)
{
v.push_back(cur->val);
st.push(cur);
cur = cur->left;
}
//取出栈顶节点
TreeNode* tmp = st.top();
st.pop();
//前序遍历右树
cur = tmp->right;//更新rootis the right tree of the top node of the stack
}
return v;
}
3.2 中序遍历
访问时机:Left node access is complete,节点出栈,It's about time to enter the right tree for access
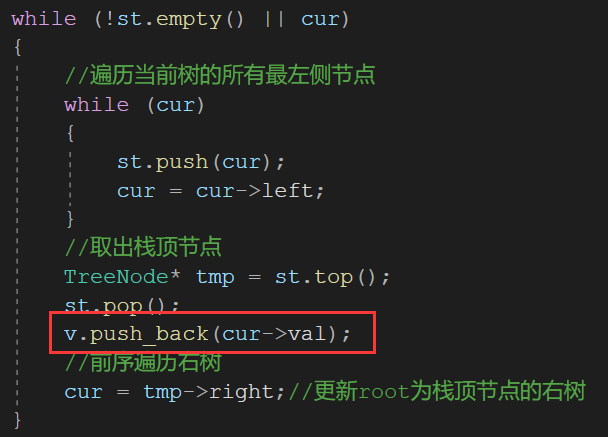
此时访问,You can put it on the stack.
vector<int> inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root)
{
vector<int> v;//Storage accesses out elements
stack<TreeNode*> st;//栈——Temporary storage node
TreeNode* cur = root;//A pointer for traversing the entire tree
while (!st.empty() || cur)
{
//Traverse all leftmost nodes of the current tree
while (cur)
{
st.push(cur);
cur = cur->left;
}
//取出栈顶节点
TreeNode* tmp = st.top();
st.pop();
v.push_back(cur->val);
//前序遍历右树
cur = tmp->right;//更新rootis the right tree of the top node of the stack
}
return v;
}
3.3 后序遍历
Access is done on the entire right tree,Visit when you come back to this node again
Since accessing the right tree is an iterative traversal of multiple layers,The location of the visit cannot be found directly on this single code
观察后,The last node visited in the postorder traversal of the right subtree is the root node of the right tree,The next node after visiting this node is the node to be visited currently

So visit one node at a time,This node is recorded,Before a node is popped from the stack, it must first determine whether the right node corresponding to the top node of the stack is a recorded node
- 若是,则出栈并进行访问,同时Update the node for logging,The right tree does not need to be visited at this time,Direct access to the next top element of the stack
- Otherwise, it indicates that it is currently②的位置,先不出栈,先访问右树,The right tree comes back and pops the stack again
**特殊情况:**When the right tree is empty,This node is also visited
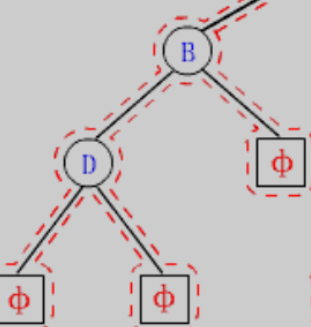
如访问BWhen the right tree is finished,prev是D,但此时Balso have to visit,Therefore, if the right tree is empty, the judgment condition for pop-up access should also be added
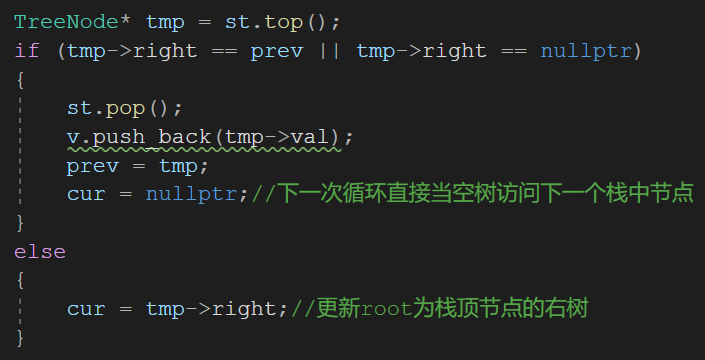
vector<int> postorderTraversal(TreeNode* root)
{
vector<int> v;//Storage accesses out elements
stack<TreeNode*> st;//栈——Temporary storage node
TreeNode* cur = root;//A pointer for traversing the entire tree
TreeNode* prev = nullptr;
while (!st.empty() || cur)
{
//Traverse all leftmost nodes of the current tree
while (cur)
{
st.push(cur);
cur = cur->left;
}
TreeNode* tmp = st.top();
if (tmp->right == prev || tmp->right == nullptr)
{
st.pop();
v.push_back(tmp->val);
prev = tmp;
cur = nullptr;//The next loop directly accesses the next node in the stack as the empty tree
}
else
{
cur = tmp->right;//更新rootis the right tree of the top node of the stack
}
}
return v;
}
边栏推荐
- 角色妆容的实现
- Linux环境redis集群搭建「建议收藏」
- Douyin fetches video list based on keywords API
- Niuke.com brush questions (1)
- cas and spin locks (is lightweight locks spin locks)
- [QNX Hypervisor 2.2用户手册]9.14 set
- Structure of the actual combat battalion module eight operations
- 老牌音乐播放器 WinAmp 发布 5.9 RC1 版:迁移到 VS 2019 完全重建,兼容 Win11
- IDA PRO中汇编结构体识别
- NVIDIA has begun testing graphics products with AD106 and AD107 GPU cores
猜你喜欢

Unity - LineRenderer show a line
NVIDIA已经开始测试AD106和AD107 GPU核心的显卡产品

【论文精读】iNeRF

统计UTF-8字符串中的字符函数

The article you worked so hard to write may not be your original

基于STM32 环形队列来实现串口接收数据
Implementing a Simple Framework for Managing Object Information Using Reflection
Dry goods | 10 tips for MySQL add, delete, change query performance optimization

Realize serial port receiving data based on STM32 ring queue

Unity-LineRenderer显示一条线
随机推荐
Financial profitability and solvency indicators
Structure of the actual combat battalion module eight operations
21. Support Vector Machine - Introduction to Kernel Functions
二叉树非递归遍历
Student management system on the first day: complete login PyQt5 + MySQL5.8 exit the operation logic
Pytest初体验
A shortcut to search for specific character content in idea
What is Thymeleaf?How to use.
Linux环境redis集群搭建「建议收藏」
BM5 merge k sorted linked lists
flowable workflow all business concepts
Document management and tools in the development process
Redis综述篇:与面试官彻夜长谈Redis缓存、持久化、淘汰机制、哨兵、集群底层原理!...
grep command written test questions
NVIDIA has begun testing graphics products with AD106 and AD107 GPU cores
BM3 将链表中的节点每k个一组翻转
ECCV 2022 Huake & ETH propose OSFormer, the first one-stage Transformer framework for camouflaging instance segmentation!The code is open source!...
cas and spin locks (is lightweight locks spin locks)
20. Support vector machine - knowledge of mathematical principles
Several methods for deleting specified elements in Golang slices
