当前位置:网站首页>C language pointer classic interview question - the first bullet
C language pointer classic interview question - the first bullet
2022-07-04 09:38:00 【Hair is not as much as code】
Catalog
sizeof() and char Type one-dimensional array
strlen and char Type one-dimensional array
Character pointer and sizeof()
Character pointer and strlen()
Two dimensional arrays and sizeof()
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a[] = { 1,2,3,4 };
printf("%d\n", sizeof(a));
// The result is 16, Here is the whole array
printf("%d\n", sizeof(a + 0));
// The result is 4 or 8, Here is the size of the first address
printf("%d\n", sizeof(*a));
// The result is 4, Here is the size of the first element
printf("%d\n", sizeof(a + 1));
// The result is 4 or 8, Here is the size of the second address
printf("%d\n", sizeof(a[1]));
// The result is 4, Here is the size of the second element
printf("%d\n", sizeof(&a));
// The result is 4 or 8, Here is the address size of the entire array
printf("%d\n", sizeof(*&a));
// The result is 16, Here we first take out the entire array address , Then dereference the entire array , That is, the size of the entire array is calculated
printf("%d\n", sizeof(&a + 1));
// The result is 4 or 8, The entire array is skipped here , Calculate the address size after the array , So it is 4 or 8,&a The type is int(*)[4]
printf("%d\n", sizeof(&a[0]));
// The result is 4 or 8, Here is the address size of the first element
printf("%d\n", sizeof(&a[0] + 1));
// The result is 4 or 8, Here is the address size of the second element
return 0;
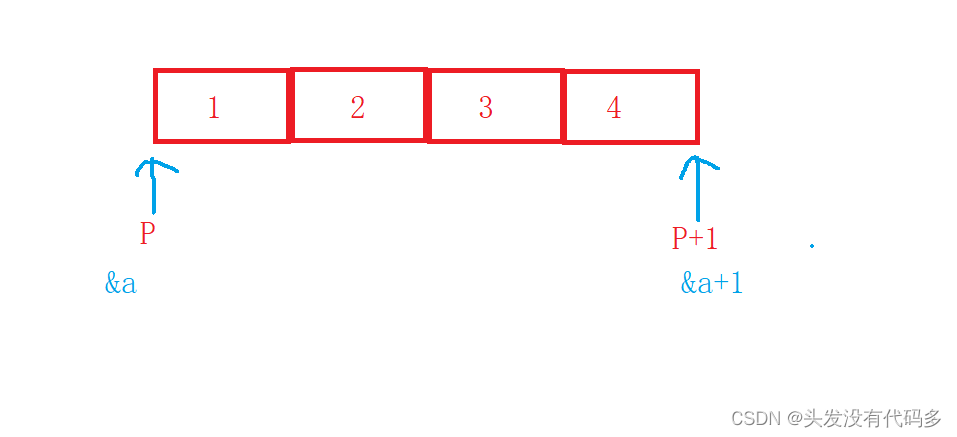
}Be careful : here &a The type is int(*)[4], Array pointer ,
&a+1 Is to skip the entire array
sizeof() and char Type one-dimensional array
char arr[] = { 'a','b','c','d','e','f' };
printf("%d\n", sizeof(arr));
//6, Here we calculate the whole array
printf("%d\n", sizeof(arr + 0));
//4 or 8, Here we calculate the address of the first element
printf("%d\n", sizeof(*arr));
//1, Here we calculate the size of the first element
printf("%d\n", sizeof(arr[1]));
//1, Philosophy calculates the size of the second element
printf("%d\n", sizeof(&arr));
//4 or 8, Here we calculate the address size of the whole array
printf("%d\n", sizeof(&arr + 1));
// still 4 or 8, The calculation here is after skipping the entire array , The size of the entire address
printf("%d\n", sizeof(&arr[0] + 1));
// still 4 or 8, Here we calculate the address size of the second element strlen and char Type one-dimensional array
char arr[] = { 'a','b','c','d','e','f' };
printf("%d\n", strlen(arr));
// Random value , Here we calculate the whole array , That is, calculate from the first element to find \0 Location , The random value is because there is no \0
printf("%d\n", strlen(arr + 0));
// Random value , here strlen Is counting back from the first element , The value of random value is the same as the above value
printf("%d\n", strlen(*arr));
// Report errors , Here is the first element , The first element is a value ,strlen() What is in brackets must be char * Pointer variable of type , And the elements in it are char The type is not char * type , If the 'a' Transfer the past , It is equivalent to 97 As a pointer through
printf("%d\n", strlen(arr[1]));
// Report errors , The second element is passed , Same as the above value
printf("%d\n", strlen(&arr));
// Random value , It's the same as before , It's the whole address , The entire address starts with the address of the first element , Random values will be generated at random , Because it starts from the first element , So the result will be the same as the first
printf("%d\n", strlen(&arr + 1));
// Random value , Here is skipping the entire array , Then start calculating , encounter \0 Then stop , It is different from the first random value 6
printf("%d\n", strlen(&arr[0] + 1));
// Random value , Calculate from the address of the second element , encounter \0 stop it , It is different from the first random value 1sizeof() And string arrays
char arr[] = "abcdef";
printf("%d\n", sizeof(arr));
//7, Yes \0
printf("%d\n", sizeof(arr + 0));
//4 or 8, The address size is calculated , Start with the address of the first element
printf("%d\n", sizeof(*arr));
//1, What we calculate is the size of the first element
printf("%d\n", sizeof(arr[1]));
//1, It calculates the size of the second element
printf("%d\n", sizeof(&arr));
//4 or 8, The whole address is calculated
printf("%d\n", sizeof(&arr + 1));
//4 or 8, After skipping this array , Calculate the size of the following address
printf("%d\n", sizeof(&arr[0] + 1));
//4 or 8, After skipping the first element , Calculate the size of the following address , Instead of the size of the contents in the array sizeof And string arrays
char arr[] = "abcdef"; printf("%d\n", sizeof(arr)); //7, Yes \0 printf("%d\n", sizeof(arr + 0)); //4 or 8, The address size is calculated , Start with the address of the first element printf("%d\n", sizeof(*arr)); //1, What we calculate is the size of the first element printf("%d\n", sizeof(arr[1])); //1, It calculates the size of the second element printf("%d\n", sizeof(&arr)); //4 or 8, The whole address is calculated printf("%d\n", sizeof(&arr + 1)); //4 or 8, After skipping this array , Calculate the size of the following address printf("%d\n", sizeof(&arr[0] + 1)); //4 or 8, After skipping the first element , Calculate the size of the following address , Instead of the size of the contents in the array
strlen And string
char arr[] = "abcdef";
printf("%d\n", strlen(arr));
//6, encounter \0 Stop printing
printf("%d\n", strlen(arr + 0));
//6, encounter \0 Stop printing
printf("%d\n", strlen(*arr));
// Report errors , It's not char * type
printf("%d\n", strlen(arr[1]));
// Report errors , Not wearing char* type
printf("%d\n", strlen(&arr));
//6, The address of the whole array is passed , Start with the address of the first element
printf("%d\n", strlen(&arr + 1));
// Random value , After spanning the entire array , Starting calculation encountered \0 stop it
printf("%d\n", strlen(&arr[0] + 1));
//5, Start with the second element , encounter \0 stop it Character pointer and sizeof()
char* p = "abcdef";
printf("%d\n", sizeof(p));
//4 or 8, there p Is a pointer ,p Inside the village is the address of the first element ,
printf("%d\n", sizeof(p + 1));
//4 or 8, Point to the address of the second element
printf("%d\n", sizeof(*p));
//1, The size of the first element
printf("%d\n", sizeof(p[0]));
//1, The size of the first element
printf("%d\n", sizeof(&p));
//4 or 8,&p It's a secondary pointer
printf("%d\n", sizeof(&p + 1));
//4 or 8, Across the entire array
printf("%d\n", sizeof(&p[0] + 1));
//4 or 8, Calculate the size of the address from the second element Character pointer and strlen()
char* p = "abcdef";
printf("%d\n", strlen(p));
//6,p It's the first element address
printf("%d\n", strlen(p + 1));
//5, Start with the second element
printf("%d\n", strlen(*p));
// Report errors , Because what you wear is a value , No char * Type of
printf("%d\n", strlen(p[0]));
// Report errors , It passes a value , No char * Type of
printf("%d\n", strlen(&p));
// Random value ,p Is a first level pointer ,&p It's just a secondary pointer , That is to say, here strlen It's from p The address of starts counting backwards \0 stop it
printf("%d\n", strlen(&p + 1));
// Random value , Across the entire array , Then start to calculate the encounter \0 Location
printf("%d\n", strlen(&p[0] + 1));
// Random value , Calculate from the first element encountered \0 until , The number that differs from the above is also a random value , Not a definite number , Because they met \0 The situation is different
// The value of the difference between the penultimate and the penultimate , It's a random value , because &p It's from p Starting number of addresses , When not &p[0]+1 when , There may be \0 It may not happen \0, and &p[0]+1, Start counting from the address of the second element , When did you meet \0 It's impossible 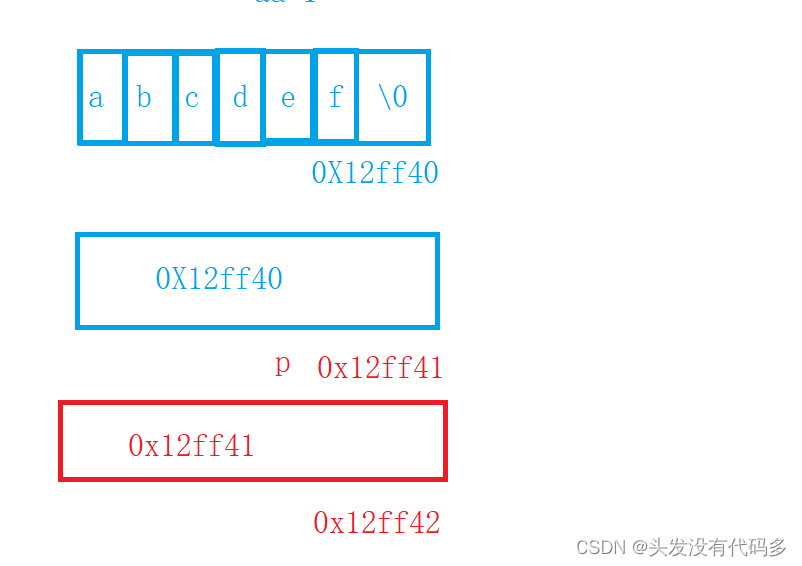

&p+1 and &p[0]+1 The reason why the difference of results is random , Are likely to p[0]+1 Move to the right and don't reach &p+1 When I met \0, It may also be with &p+1 Meet the same \0, Because of the \0 With uncertainty , So the difference between them is a random value .
Two dimensional arrays and sizeof()
int a[3][4] = { 0 };
printf("%d\n", sizeof(a));
//48, Here is the size of the entire array
printf("%d\n", sizeof(a[0][0]));
//4, Here we calculate the size of the first element
printf("%d\n", sizeof(a[0]));
//16,a[0] The size of the first line of elements
printf("%d\n", sizeof(a[0] + 1));
//4/8, there a[0] No longer put it alone () Inside , Yes +1 The operation of , So here a[0] Represents the address of the first element ,+1 It means the size of the address of the second element , So here is the address
printf("%d\n", sizeof(*(a[0] + 1)));
//4, This is the first line , The size of the second element
printf("%d\n", sizeof(a + 1));
//4/8,a Yes +1 The operation of , therefore a Represents the address of the first element , The first line ,a+1 It's the address on the second line , Because it's an address, it's 4/8
printf("%d\n", sizeof(*(a + 1)));
//16, The size of the element in the second line
printf("%d\n", sizeof(&a[0] + 1));
//4/8, The address on the second line
printf("%d\n", sizeof(*(&a[0] + 1)));
//16, The array size of the second row
printf("%d\n", sizeof(*a));
//16,a Represents the address of the first element ,*a Is to dereference , So it is 16
printf("%d\n", sizeof(a[3]));summary
The meaning of array names :
1. sizeof( Array name ), The array name here represents the entire array , It calculates the size of the entire array .2. & Array name , The array name here represents the entire array , It takes out the address of the entire array .3. In addition, all array names represent the address of the first element .
边栏推荐
- Kotlin:集合使用
- Summary of the most comprehensive CTF web question ideas (updating)
- Global and Chinese market of planar waveguide optical splitter 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
- The child container margin top acts on the parent container
- Analysis report on the production and marketing demand and investment forecast of tellurium dioxide in the world and China Ⓣ 2022 ~ 2027
- Trim leading or trailing characters from strings- Trim leading or trailing characters from a string?
- H5 audio tag custom style modification and adding playback control events
- Golang Modules
- Global and Chinese market of wheel hubs 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
- mmclassification 标注文件生成
猜你喜欢

智能网关助力提高工业数据采集和利用

HMS core helps baby bus show high-quality children's digital content to global developers
How to batch change file extensions in win10

C # use gdi+ to add text with center rotation (arbitrary angle)
C # use ffmpeg for audio transcoding
How should PMP learning ideas be realized?
ASP. Net to access directory files outside the project website
Kubernetes CNI 插件之Fabric
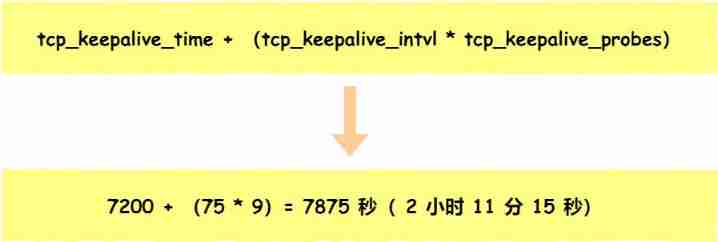
After unplugging the network cable, does the original TCP connection still exist?
Logstack configuration details -- elasticstack (elk) work notes 020
随机推荐
Hands on deep learning (34) -- sequence model
Flutter tips: various fancy nesting of listview and pageview
回复评论的sql
UML sequence diagram [easy to understand]
Hands on deep learning (33) -- style transfer
If you can quickly generate a dictionary from two lists
品牌连锁店5G/4G无线组网方案
查看CSDN个人资源下载明细
PHP personal album management system source code, realizes album classification and album grouping, as well as album image management. The database adopts Mysql to realize the login and registration f
技术管理进阶——如何设计并跟进不同层级同学的绩效
Global and Chinese PCB function test scale analysis and development prospect planning report Ⓑ 2022 ~ 2027
2022-2028 global optical transparency industry research and trend analysis report
Reading notes on how to connect the network - hubs, routers and routers (III)
Global and Chinese market of planar waveguide optical splitter 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
Reload CUDA and cudnn (for tensorflow and pytorch) [personal sorting summary]
Summary of small program performance optimization practice
Write a jison parser from scratch (4/10): detailed explanation of the syntax format of the jison parser generator
Global and Chinese markets of water heaters in Saudi Arabia 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
HMS core helps baby bus show high-quality children's digital content to global developers
Ultimate bug finding method - two points