当前位置:网站首页>Four common methods of copying object attributes (summarize the highest efficiency)
Four common methods of copying object attributes (summarize the highest efficiency)
2022-07-04 09:21:00 【Vogat meets grapefruit】
When get/set When it's too cumbersome ; When BeanUtils When the collection cannot be copied ; When ... Probably , You need to take a good look at this article , A complete example code is attached at the end of the article .
In doing business , To isolate change , We will DAO Found out DO And on the front end DTO Isolate . Probably 90% When , They all have similar structures ; But we don't like to write a lot of lengthy ==b.setF1(a.getF1())== This code , So we need to simplify the way objects are copied .
One 、 background
1.1 Object copy concept
Java in , Data types are divided into value types ( Basic data type ) And reference types , Value types include int、double、byte、boolean、char And so on , Reference types include classes 、 Interface 、 Complex types such as arrays .
Object copy is divided into Shallow copy ( Shallow clone ) And Deep copy ( A deep clone ).
The difference between shallow copy and deep copy 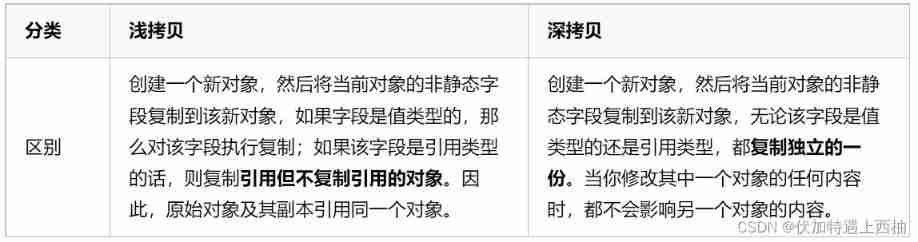
Reference article :Java Deep and shallow copies
1.2 Why do I need to copy objects
- Entity The corresponding data structure of persistence layer ( Generally, it is the mapping model of database tables );
- Model It corresponds to the data structure of the business layer ;
- VO Namely Controller Data structure to interact with the client .
for example : The user information found in the database ( The mapping model for tables ) yes UserDO, But what we need to pass to the client is UserVO, At this time, we need to UserDO The properties of the instance are assigned one by one to UserVO In the example .
A large part of these data structures may have the same properties , It could be different .
1.3 What are the copy methods
- org.springframework.beans.BeanUtils ;
- org.springframework.cglib.beans.BeanCopier;
- ma.glasnost.orika ;
- org.mapstruct( Strongly recommend ).
The complete code in the case
Two 、BeanUtils
Spring Medium BeanUtils, The way to achieve it is very simple , It's a simple way to make attributes with the same name in two objects get/set, Only check the accessibility of properties .
You can see , Member variable assignment is based on the member list of the target object , And will skip ignore And what doesn't exist in the source object , So this method is safe , No errors due to structural differences between two objects , But you have to make sure that two member variables of the same name have the same type .
UserDO
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
@Builder
@Data
public class UserDO {
private Long userId;
private String userName;
private Integer age;
private Integer sex;
}
UserVO
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
@Builder
@Data
public class UserVO {
private Long userId;
private String userName;
private Integer age;
private String sex;
}
2.1、 Single object copy
We found out the database UserDO.java copy to UserVO.java. Use it directly BeanUtils.copyProperties() Method .
/** * Single object copy * @author xlwang55 * @date 2022/1/27 */
@Test
public void commonCopy() {
UserDO userDO = new UserDO(1L, "Van", 18, 1);
UserVO userVO = new UserVO();
BeanUtils.copyProperties(userDO, userVO);
System.out.println("userVO = " + userVO);
// result : userVO = UserVO(userId=1, userName=Van, age=18, sex=null)
}
2.2、 Set copy
What I just copied is an object , But sometimes we want to copy a group of UerDO.java, When it's a set, it can't be assigned directly . If we still follow this logic , as follows :
/** * Set copy * @author xlwang55 * @date 2022/1/27 */
@Test
public void listCopyFalse() {
List<UserDO> userDOList = new ArrayList();
userDOList.add(new UserDO(1L, "Van", 18, 1));
userDOList.add(new UserDO(2L, "VanVan", 18, 2));
List<UserVO> userVOList = new ArrayList();
BeanUtils.copyProperties(userDOList, userVOList);
System.out.println("userVOList = " + userVOList);
// result : userVOList = []
}
Through the log, we can find , The direct copy set is invalid , So how to solve it ?
2.3 Violent copy ( Not recommended )
Will need to copy the collection traversal , Violent copy .
/** * Violent copy ( Not recommended ) Will need to copy the collection traversal , Violent copy * Although this way can solve , But it's not elegant at all , Especially when it's hard to write * @author xlwang55 * @date 2022/1/27 */
@Test
public void listCopyCommon() {
List<UserDO> userDOList = new ArrayList();
userDOList.add(new UserDO(1L, "Van", 18, 1));
userDOList.add(new UserDO(2L, "VanVan", 20, 2));
List<UserVO> userVOList = new ArrayList();
userDOList.forEach(userDO -> {
UserVO userVO = new UserVO();
BeanUtils.copyProperties(userDO, userVO);
userVOList.add(userVO);
});
System.out.println("userVOList = " + userVOList);
// result : userVOList = [UserVO(userId=1, userName=Van, age=18, sex=null), UserVO(userId=2, userName=VanVan, age=20, sex=null)]
}
Although this way can solve , But it's not elegant at all , Especially when it's hard to write .
2.4 Elegant copy ( This article recommends )
adopt JDK 8 The functional interface encapsulation of org.springframework.beans.BeanUtils
2.4.1 Define a functional interface
A functional interface can contain default methods , Here we define the default callback method .
@FunctionalInterface
public interface BeanUtilCopyCallBack <S, T> {
/** * Define the default callback method * @param t * @param s */
void callBack(S t, T s);
}
2.4.2 Encapsulate a tool class == BeanUtilCopy.java==
public class BeanUtilCopy extends BeanUtils {
/** * Copy of collection data * * @param sources: The data source class * @param target: Target class ::new(eg: UserVO::new) * @return */
public static <S, T> List<T> copyListProperties(List<S> sources, Supplier<T> target) {
return copyListProperties(sources, target, null);
}
/** * Copy of collection data with callback function ( You can customize the field copy rules ) * * @param sources: The data source class * @param target: Target class ::new(eg: UserVO::new) * @param callBack: Callback function * @return */
public static <S, T> List<T> copyListProperties(List<S> sources, Supplier<T> target,
BeanUtilCopyCallBack<S, T> callBack) {
List<T> list = new ArrayList<>(sources.size());
for (S source : sources) {
T t = target.get();
copyProperties(source, t);
list.add(t);
if (callBack != null) {
// Callback
callBack.callBack(source, t);
}
}
return list;
}
}
2.4.3 Simple copy test
@Test
public void listCopyUp() {
List<UserDO> userDOList = new ArrayList();
userDOList.add(new UserDO(1L, "Van", 18, 1));
userDOList.add(new UserDO(2L, "VanVan", 20, 2));
List<UserVO> userVOList = BeanUtilCopy.copyListProperties(userDOList, UserVO::new);
System.out.println("userVOList = " + userVOList);
// result : userVOList = [UserVO(userId=1, userName=Van, age=18, sex=null), UserVO(userId=2, userName=VanVan, age=20, sex=null)]
}
By the above method , We basically implemented a copy of the collection , But from the results we can see that : Fields with different properties cannot be copied .
Be careful :
UserDO.java and UserVO.java The last field sex Different types , Namely :Integer/String
Optimize it
- Add gender enumeration class
public enum SexEnum {
UNKNOW(" Not set ", 0),
MEN(" schoolboy ", 1),
WOMAN(" girl student ", 2);
private String desc;
private int code;
SexEnum(String desc, int code) {
this.desc = desc;
this.code = code;
}
public static SexEnum getDescByCode(int code) {
SexEnum[] typeEnums = values();
for (SexEnum value : typeEnums) {
if (code == value.getCode()) {
return value;
}
}
return null;
}
public String getDesc() {
return desc;
}
public void setDesc(String desc) {
this.desc = desc;
}
public int getCode() {
return code;
}
public void setCode(int code) {
this.code = code;
}
- A copy of a set with a specific transformation
@Test
public void listCopyUpWithCallback() {
List<UserDO> userDOList = new ArrayList();
userDOList.add(new UserDO(1L, "Van", 18, 1));
userDOList.add(new UserDO(2L, "VanVan", 20, 2));
List<UserVO> userVOList = BeanUtilCopy.copyListProperties(userDOList, UserVO::new, (userDO, userVO) -> {
// Here you can define specific transformation rules
userVO.setSex(SexEnum.getDescByCode(userDO.getSex()).getDesc());
});
System.out.println("userVOList = " + userVOList);
// result : userVOList = [UserVO(userId=1, userName=Van, age=18, sex= schoolboy ), UserVO(userId=2, userName=VanVan, age=20, sex= girl student )]
}
By printing the results, we can find ,UserDO.java in Integer Type of sex Copied to the UserVO.java a String Type of boy / girl student .
2.5 Summary
This method is the scheme we use most , Here is a simple package , It can facilitate the copy of collection type objects , It is basically enough for normal use , For reference only .
3、 ... and 、BeanCopier
UserDO
@Data
public class UserDO {
private int id;
private String userName;
private int sex;
/** * The following two fields are user analog custom conversion */
private LocalDateTime gmtBroth;
private BigDecimal balance;
public UserDO(Integer id, String userName, int sex, LocalDateTime gmtBroth, BigDecimal balance) {
this.id = id;
this.userName = userName;
this.sex = sex;
this.gmtBroth = gmtBroth;
this.balance = balance;
}
}
UserDomain
@Data
public class UserDomain {
private Integer id;
private String userName;
/** * The following two fields are user analog custom conversion */
private String gmtBroth;
private String balance;
}
BeanCopier Is used in two bean Copy the attributes between .BeanCopier Two ways are supported :
One is not to use Converter The way , Only for two bean Copy variables with the same property name and type ;
The other introduces Converter, You can perform special operations on certain property values .
3.1 Regular use
@Test
public void normalCopy() {
// Simulate and query the data
UserDO userDO = new UserDO(1L, "Van", 18, 1);
System.out.println(" Before copying :userDO:{}" + userDO);
// The first parameter : Source object , The second parameter : Target audience , The third parameter : Use custom converter or not ( We'll talk about that ), The same below
BeanCopier b = BeanCopier.create(UserDO.class, UserVO.class, false);
UserVO userVO = new UserVO();
b.copy(userDO, userVO, null);
System.out.println(" After copying :userDTO:{}" + userVO);
// Before copying :userDO:{}UserDO(userId=1, userName=Van, age=18, sex=1)
// After copying :userDTO:{}UserVO(userId=1, userName=Van, age=18, sex=null)
}
And it turns out that :UserDO Of int Type of sex Can't copy to UserDTO Of Integer Of sex.
namely :BeanCopier Only copy properties with the same name and type .
Even if the source type is primitive (int, short and char etc. ), The target type is its packaging type (Integer, Short and Character etc. ), Or vice versa : Will not be copied .
3.2 Custom converter
adopt 3.1 You know , When the attribute types of source and target classes are different , This property cannot be copied , At this time, we can achieve Converter Interface from definition Converter
- Target object property class
@Data
public class UserDomain {
private Integer id;
private String userName;
/** * The following two fields are user analog custom conversion */
private String gmtBroth;
private String balances;
}
- Realization Converter The interface comes from defining property transformations
public class UserDomainConverter implements Converter {
/** * Time conversion format */
DateTimeFormatter dtf = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
/** * Custom attribute conversion * @param value Source object property class * @param target The attributes in the target object correspond to set Method name ,eg.setId * @param context Target object property class * @return */
@Override
public Object convert(Object value, Class target, Object context) {
if (value instanceof Integer) {
return value;
} else if (value instanceof LocalDateTime) {
LocalDateTime date = (LocalDateTime) value;
return dtf.format(date);
} else if (value instanceof BigDecimal) {
BigDecimal bd = (BigDecimal) value;
return bd.toPlainString();
}
// For more type conversion, please customize
return value;
}
}
- The test method
/** * Different types , Use Converter */
@Test
/** * Different types , Use Converter */
@Test
public void converterTest() {
// Simulate and query the data
UserDO userDO = DataUtil.createData();
log.info(" Before copying :userDO:{}", userDO);
BeanCopier copier = BeanCopier.create(UserDO.class, UserDomain.class, true);
UserDomainConverter converter = new UserDomainConverter();
UserDomain userDomain = new UserDomain();
copier.copy(userDO, userDomain, converter);
log.info(" After copying :userDomain:{}", userDomain);
// Before copying :userDO:UserDO(id=1, userName=Van, sex=0, gmtBroth=2022-02-10T10:32:25.803, balance=100)
// After copying :userDomain:UserDomain(id=1, userName=Van, gmtBroth=2022-02-10 10:32:25, balance=100)
}
- Be careful
Once the use
Converter,BeanCopierUse onlyConverterDefine rules to copy attributes , So inconvert()All attributes should be considered in the method ;without doubt , Use
ConverterIt will slow down the object copying speed .
3.3 cache BeanCopier Instance improves performance
BeanCopier Copy fast , Performance bottlenecks arise in the creation of BeanCopier In the process of instance . therefore , Put the created BeanCopier The instance is put into the cache , You can get it directly next time , Lifting performance .
- Test code
@Test
public void beanCopierWithCache() {
List<UserDO> userDOList = DataUtil.createDataList(10000);
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
List<UserDTO> userDTOS = new ArrayList<>();
userDOList.forEach(userDO -> {
UserDTO userDTO = new UserDTO();
copy(userDO, userDTO);
userDTOS.add(userDTO);
});
}
/** * cache BeanCopier */
private static final ConcurrentHashMap<String, BeanCopier> BEAN_COPIERS = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
public void copy(Object srcObj, Object destObj) {
String key = genKey(srcObj.getClass(), destObj.getClass());
BeanCopier copier = null;
if (!BEAN_COPIERS.containsKey(key)) {
copier = BeanCopier.create(srcObj.getClass(), destObj.getClass(), false);
BEAN_COPIERS.put(key, copier);
} else {
copier = BEAN_COPIERS.get(key);
}
copier.copy(srcObj, destObj, null);
}
private String genKey(Class<?> srcClazz, Class<?> destClazz) {
return srcClazz.getName() + destClazz.getName();
}
3.3 BeanCopier summary
- When the source class and the target class property name 、 All of them are of the same type , No problem copying .
- When the property names of the source and target objects are the same 、 Different types , Properties with the same name but different types will not be copied . Be careful , The original type (
int,short,char) and
Their packing type , It's all treated as a different type here , So it won't be copied . - Of the source or target class
setterThangetterLess , No problem copying , here setter redundant , But there is no error . - The source class and the target class have the same properties ( Of the two
getterAll exist ), But the target classsetternon-existent , This will throwNullPointerException. - Adding cache can improve the copy speed .
Four 、Orika
Orika yes Java Bean Mapping framework , You can copy data recursively from one object to another . Its advantages are : The same name and different types can also be copied directly .
4.1 The required depend on
<dependency>
<groupId>ma.glasnost.orika</groupId>
<artifactId>orika-core</artifactId>
<version>1.5.4</version>
</dependency>
4.2 Mapping tool class
Create a mapping tool class using the singleton pattern of enumeration implementation , To facilitate the test .
public enum MapperUtils {
/** * example */
INSTANCE;
/** * Default field factory */
private static final MapperFactory MAPPER_FACTORY = new DefaultMapperFactory.Builder().build();
/** * Default field instance */
private static final MapperFacade MAPPER_FACADE = MAPPER_FACTORY.getMapperFacade();
/** * Default field instance collection */
private static Map<String, MapperFacade> CACHE_MAPPER_FACADE_MAP = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
/** * Mapping entities ( Default fields ) * * @param toClass Mapping class objects * @param data data ( object ) * @return Mapping class objects */
public <E, T> E map(Class<E> toClass, T data) {
return MAPPER_FACADE.map(data, toClass);
}
/** * Mapping entities ( Custom configuration ) * * @param toClass Mapping class objects * @param data data ( object ) * @param configMap Custom configuration * @return Mapping class objects */
public <E, T> E map(Class<E> toClass, T data, Map<String, String> configMap) {
MapperFacade mapperFacade = this.getMapperFacade(toClass, data.getClass(), configMap);
return mapperFacade.map(data, toClass);
}
/** * Mapping set ( Default fields ) * * @param toClass Mapping class objects * @param data data ( aggregate ) * @return Mapping class objects */
public <E, T> List<E> mapAsList(Class<E> toClass, Collection<T> data) {
return MAPPER_FACADE.mapAsList(data, toClass);
}
/** * Mapping set ( Custom configuration ) * * @param toClass Mapping class * @param data data ( aggregate ) * @param configMap Custom configuration * @return Mapping class objects */
public <E, T> List<E> mapAsList(Class<E> toClass, Collection<T> data, Map<String, String> configMap) {
T t = data.stream().findFirst().orElseThrow(() -> new ExceptionInInitializerError(" Mapping set , Data set is empty "));
MapperFacade mapperFacade = this.getMapperFacade(toClass, t.getClass(), configMap);
return mapperFacade.mapAsList(data, toClass);
}
/** * Get custom mapping * * @param toClass Mapping class * @param dataClass Data mapping class * @param configMap Custom configuration * @return Mapping class objects */
private <E, T> MapperFacade getMapperFacade(Class<E> toClass, Class<T> dataClass, Map<String, String> configMap) {
String mapKey = dataClass.getCanonicalName() + "_" + toClass.getCanonicalName();
MapperFacade mapperFacade = CACHE_MAPPER_FACADE_MAP.get(mapKey);
if (Objects.isNull(mapperFacade)) {
MapperFactory factory = new DefaultMapperFactory.Builder().build();
ClassMapBuilder classMapBuilder = factory.classMap(dataClass, toClass);
configMap.forEach(classMapBuilder::field);
classMapBuilder.byDefault().register();
mapperFacade = factory.getMapperFacade();
CACHE_MAPPER_FACADE_MAP.put(mapKey, mapperFacade);
}
return mapperFacade;
}
}
There are mainly four methods in this tool class :
map(Class toClass, T data):Ordinary mapping entities , The primary mapping name is the same ( The types can be different ) Field of ;map(Class toClass, T data, Map<String, String>configMap): Custom configuration mapping , Different mapping names , The corresponding name of the custom mapping ;mapAsList(Class toClass, Collection data): Mapping of ordinary sets ;mapAsList(Class toClass, Collection data, Map<String, String>configMap): Custom set mapping , The corresponding name of the custom mapping .
4.3 A simple test
UserDO
@Data
public class UserDO {
private int id;
private String userName;
private int sex;
/** * The following two fields are user analog custom conversion */
private LocalDateTime gmtBroth;
private BigDecimal balance;
public UserDO(Integer id, String userName, int sex, LocalDateTime gmtBroth, BigDecimal balance) {
this.id = id;
this.userName = userName;
this.sex = sex;
this.gmtBroth = gmtBroth;
this.balance = balance;
}
}
UserDTO
@Data
public class UserDTO {
private int id;
private String userName;
private Integer sex;
}
The same type of copy name can have different properties
@Test
public void normalCopy() {
// Simulate and query the data
UserDO userDO = DataUtil.createData();
log.info(" Before copying :userDO:{}", userDO);
// The first parameter : Source object , The second parameter : Target audience , The third parameter : Use custom converter or not ( We'll talk about that ), The same below
UserDTO userDTO = MapperUtils.INSTANCE.map(UserDTO.class, userDO);;
log.info(" After copying :userDTO:{}", userDTO);
// Before copying :userDO:UserDO(id=1, userName=Van, sex=0, gmtBroth=2022-02-10T14:50:16.670, balance=100)
// After copying :userDTO:UserDTO(id=1, userName=Van, sex=0)
}
Different field names , With a translator
@Test
public void converterTest() {
// Simulate and query the data
UserDO userDO = DataUtil.createData();
Map<String, String> config = new HashMap<>();
// Custom configuration (balance turn balances)
config.put("balance", "balances");
log.info(" Before copying :userDO:{}", userDO);
UserDomain userDomain = MapperUtils.INSTANCE.map(UserDomain.class, userDO, config);
log.info(" After copying :userDomain:{}", userDomain);
// Before copying :userDO:UserDO(id=1, userName=Van, sex=0, gmtBroth=2022-02-10T14:53:41.568, balance=100)
// After copying :userDomain:UserDomain(id=1, userName=Van, gmtBroth=2022-02-10T14:53:41.568, balances=100)
}
Copy set
@Test
public void beanCopierWithCache() {
List<UserDO> userDOList = DataUtil.createDataList(3);
log.info(" Before copying :userDOList:{}", userDOList);
List<UserDTO> userDTOS = MapperUtils.INSTANCE.mapAsList(UserDTO.class,userDOList);
log.info(" After copying :userDTOS:{}", userDTOS);
// Before copying :userDOList:[UserDO(id=1, userName=Van, sex=1, gmtBroth=2022-02-10T14:54:51.368, balance=100),
// UserDO(id=2, userName=Van, sex=1, gmtBroth=2022-02-10T14:54:51.369, balance=100),
// UserDO(id=3, userName=Van, sex=1, gmtBroth=2022-02-10T14:54:51.369, balance=100)]
// After copying :userDTOS:[UserDTO(id=1, userName=Van, sex=1),
// UserDTO(id=2, userName=Van, sex=1),
// UserDTO(id=3, userName=Van, sex=1)]
}
5、 ... and 、MapStruct
MapStruct It's an automatic generation bean Code generator for mapping classes .MapStruct It can also transform between different data types .
5.1 The required depend on
mapstruct-jdk8
Include the required comments , for example @Mapping.
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mapstruct</groupId>
<artifactId>mapstruct-jdk8</artifactId>
<version>1.3.0.Final</version>
</dependency>
mapstruct-processor
Compiling , Generate the annotation processor implemented by the mapper .
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mapstruct</groupId>
<artifactId>mapstruct-processor</artifactId>
<version>1.3.0.Final</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
5.2 How to use ?
All you have to do is define a mapper Interface , This interface declares any required mapping methods . During compilation ,MapStruct An implementation of this interface will be generated . This implementation uses ordinary Java Method calls to map between source and target objects .
- establish Mapper
utilize @Mapper Annotation marks the interface / Abstract classes are defined by MapStruct Automatically mapped , Only when this annotation exists will the internal interface methods be implemented automatically .
- obtain Mapper
MapStruct It provides us with a variety of access Mapper The way , Get used to using the default configuration : use Mappers Through the dynamic factory internal reflection mechanism Mapper Achieve class acquisition .
UserConvertUtils INSTANCE = Mappers.getMapper(UserConvertUtils.class);
A complete converter demo:
@Mapper
public interface UserConvertUtils {
UserConvertUtils INSTANCE = Mappers.getMapper(UserConvertUtils.class);
/** * Ordinary mapping * * @param userDO UserDO Data persistence layer class * @return Data transmission class */
UserDTO doToDTO(UserDO userDO);
/** * Mapping of type conversions * * @param userDO UserDO Data persistence layer class * @return Data transmission class */
@Mappings({
@Mapping(target = "gmtBroth", source = "gmtBroth", dateFormat = "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"),
@Mapping(target = "balances", source = "balance"),
})
UserDTO doToDtoWithConvert(UserDO userDO);
}
test
/** * General copy */
@Test
public void normalCopy() {
// Simulate and query the data
UserDO userDO = DataUtil.createData();
log.info(" Before copying :userDO:{}", userDO);
UserDTO userDTO = UserConvertUtils.INSTANCE.doToDTO(userDO);
log.info(" After copying :userDTO:{}", userDTO);
}
/** * Contains a copy of the type cast */
@Test
public void doToDtoWithConvert() {
// Simulate and query the data
UserDO userDO = DataUtil.createData();
log.info(" Before copying :userDO:{}", userDO);
UserDTO userDTO = UserConvertUtils.INSTANCE.doToDtoWithConvert(userDO);
log.info(" After copying :userDTO:{}", userDTO);
}
Print mapping results
General copy :
... Before copying :userDO:UserDO(id=1, userName=Van, gmtBroth=2020-04-21T21:38:39.376, balance=100)
... After copying :userDTO:UserDTO(id=1, userName=Van, gmtBroth=2020-04-21T21:38:39.376, balances=null)
Contains a copy of the type cast :
... Before copying :userDO:UserDO(id=1, userName=Van, gmtBroth=2020-04-21T21:05:19.282, balance=100)
... After copying :userDTO:UserDTO(id=1, userName=Van, gmtBroth=2020-04-21 21:05:19, balances=100)
By printing the results, we can find : Compared with the former , Including the copy of type conversion, you can customize the conversion properties and time format .
5.3 MapStruct Keywords of annotation
@Mapper: Only add this annotation to the interface , MapStruct To implement the interface ;@Mappings: Configure multiple @Mapping;@Mapping: Property mapping , If the source object attribute is consistent with the target object name , The corresponding attributes are mapped automatically :source: Source properties ;target: Target properties ;dateFormat: Conversion between string and date ;ignore: Ignore this , An attribute does not want to be mapped , You can add ignore=true;
5.4 For one more
MapStruct You can map several types of objects to another type , For example, multiple DO Object to DTO.
See :
UserDTO doAndInfoToDto(UserDO userDO, UserInfoDO userInfoDO);
5.5 Why use MapStruct
Compared to writing mapping code by hand ,MapStruct Save time by generating tedious and easy to write code . Follow conventions over configuration methods ,MapStruct Use reasonable defaults , But measures will be taken when configuring or implementing special behaviors .
Compared with the dynamic mapping framework ,MapStruct It has the following advantages :
- Fast execution by using normal method calls rather than reflection
- Compile time type safety : Only objects and attributes that map to each other can be mapped , No unexpected mapping of order entities to customers DTO etc. .
- Clear error reports at build time , If the mapping is incomplete ( Not all target attributes are mapped ) The mapping is not correct ( No suitable mapping method or type conversion found )
5.6 Sample code
6、 ... and 、 more
By copying four attributes , Add your own manual get/set, Only the following suggestions are given :
- Simple copy is used directly get/set;
- Copy with too many attribute values and already used Spring Under the circumstances , Use BeanUtils;
- Attribute copying is troublesome , Use when translation exists and copy speed is required MapStruct( Performance is almost equal to direct get/set).
Specific performance , Reference article :Java Bean Copy Performance competition
边栏推荐
- Reading notes on how to connect the network - hubs, routers and routers (III)
- Global and Chinese market of wheel hubs 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
- Investment analysis and prospect prediction report of global and Chinese high purity tin oxide Market Ⓞ 2022 ~ 2027
- Awk from entry to soil (5) simple condition matching
- How does idea withdraw code from remote push
- [untitled] forwarding least square method
- Global and Chinese market of sampler 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
- Launpad | 基础知识
- Some points needing attention in PMP learning
- Launpad | basic knowledge
猜你喜欢

Some points needing attention in PMP learning

2022-2028 research and trend analysis report on the global edible essence industry
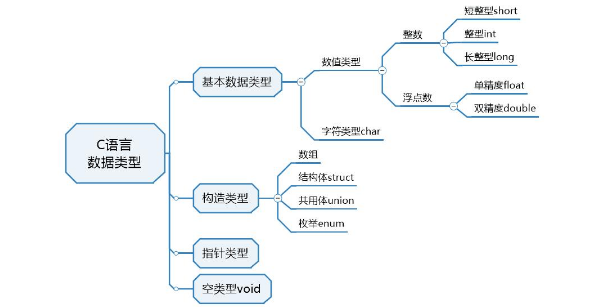
C language - Introduction - Foundation - syntax - data type (4)

Codeforces Round #793 (Div. 2)(A-D)

26. Delete duplicates in the ordered array (fast and slow pointer de duplication)
Implementation principle of redis string and sorted set
![C language - Introduction - Foundation - syntax - [variable, constant light, scope] (V)](/img/dc/5c8077c10cdc7ad6e6f92dedfbe797.png)
C language - Introduction - Foundation - syntax - [variable, constant light, scope] (V)

Awk from entry to earth (12) awk can also write scripts to replace the shell
![C language - Introduction - Foundation - syntax - [main function, header file] (II)](/img/5a/c6a3c5cd8038d17c5b0ead2ad52764.png)
C language - Introduction - Foundation - syntax - [main function, header file] (II)

2022-2028 global protein confectionery industry research and trend analysis report
随机推荐
Analysis report on the development status and investment planning of China's modular power supply industry Ⓠ 2022 ~ 2028
C language - Introduction - Foundation - syntax - data type (4)
Reload CUDA and cudnn (for tensorflow and pytorch) [personal sorting summary]
Lauchpad X | 模式
What is uid? What is auth? What is a verifier?
Review of last week's hot spots (6.27-7.3)
Report on the development trend and prospect trend of high purity zinc antimonide market in the world and China Ⓕ 2022 ~ 2027
《网络是怎么样连接的》读书笔记 - FTTH
Jianzhi offer 09 realizes queue with two stacks
Analysis report on the production and marketing demand and investment forecast of tellurium dioxide in the world and China Ⓣ 2022 ~ 2027
如何编写单元测试用例
Development trend and market demand analysis report of high purity tin chloride in the world and China Ⓔ 2022 ~ 2027
【leetcode】540. A single element in an ordered array
2022-2028 global probiotics industry research and trend analysis report
Investment analysis and prospect prediction report of global and Chinese high purity tin oxide Market Ⓞ 2022 ~ 2027
C语言-入门-基础-语法-数据类型(四)
Target detection -- intensive reading of yolov3 paper
Fatal error in golang: concurrent map writes
C语言-入门-基础-语法-[运算符,类型转换](六)
Reading notes of how the network is connected - understanding the basic concepts of the network (I)