当前位置:网站首页>C language - Introduction - Foundation - syntax - [operators, type conversion] (6)
C language - Introduction - Foundation - syntax - [operators, type conversion] (6)
2022-07-04 08:49:00 【Hu Anmin】
Operator basic concepts
Like operators in Mathematics , C An operator in a language is a symbol that tells a program to perform a specific arithmetic or logical operation
What is an expression : Expressions are meaningful expressions linked together by operators , Statements with results ; for example : a + b; Is an arithmetic expression , Its meaning is to add two numbers , The result of adding two numbers is the result of the expression Be careful : The expression must have a result
Operator classification
By function :
- Arithmetic operator
- Assignment operator
- Relational operator
- Logical operators
- An operator
Divide according to the number of operands involved in the operation :
- Monocular operations , There is only one operand Such as : i++;
- Binocular operation , There are two operands Such as : a + b;
- Three mesh operation , C The only one in the language , Also known as question mark expression Such as : a>b ? 1 : 0;
Precedence and associativity of operators
As early as in the mathematics textbook of primary school , We learned about it " From left to right , First multiply, then divide, then add or subtract , In parentheses ", This sentence implies the problem of priority and combination
C In language , The operation priority of operators is divided into 15 level .1 Highest level ,15 Lowest level
- stay C In language expressions , Operators with different priorities , The operation order is from high to low
- stay C In language expressions , Operators of the same priority , The operation sequence shall be executed in the direction specified by the associativity
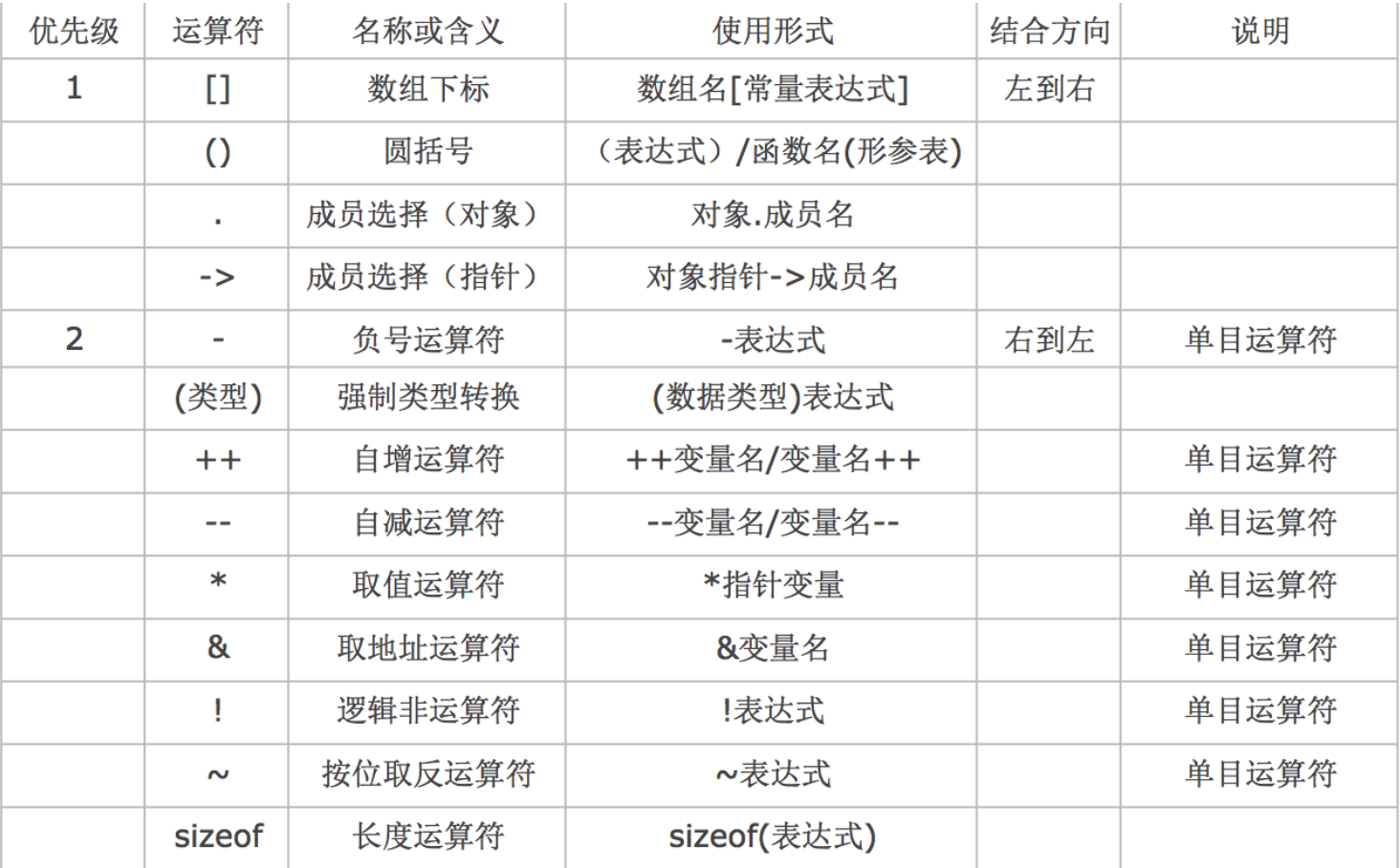
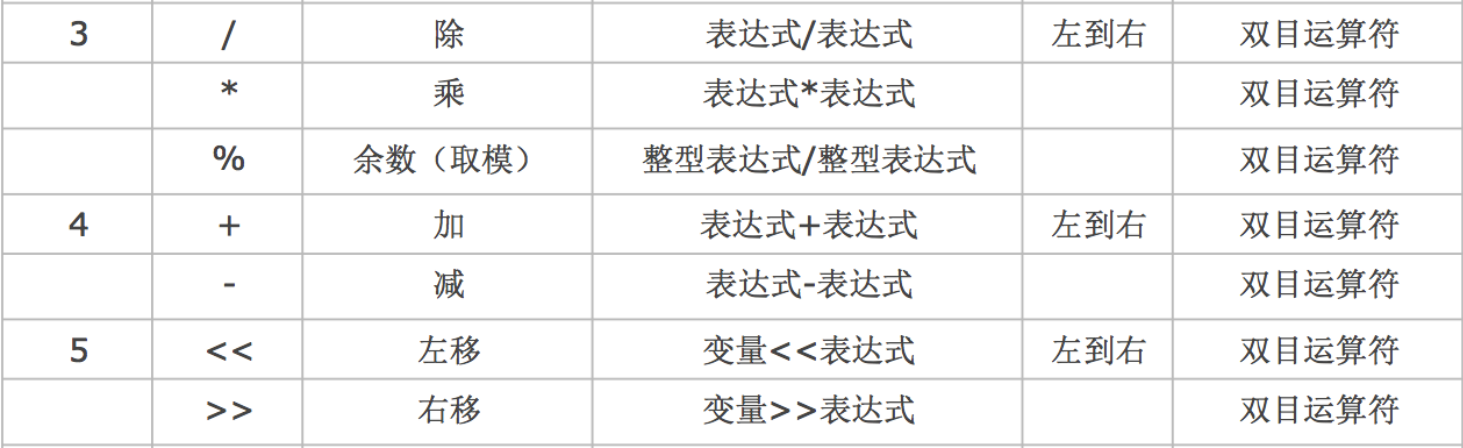
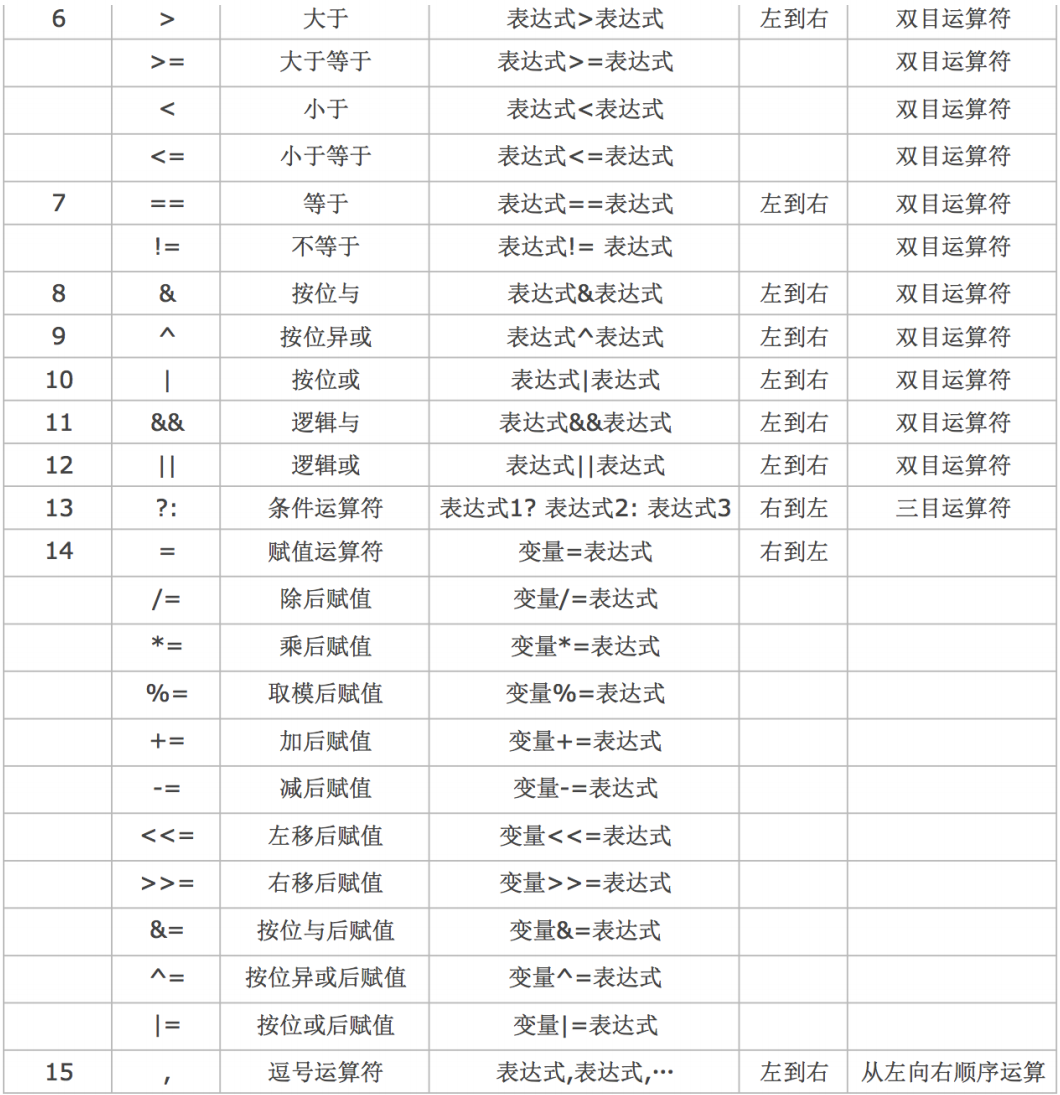
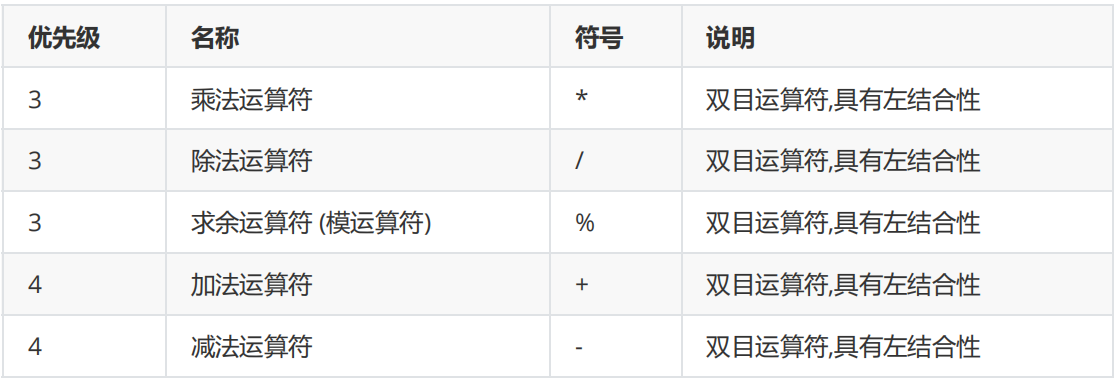
Arithmetic operator
matters needing attention
- If both operands involved in the operation are integers , Then the result is an integer
- If one of the two operands involved in the operation is a floating point number , Then the result must be a floating point number
- The remainder operator , In essence, it is the quotient and remainder of mathematics , The remainder in
- The remainder operator , Both operands participating in the operation must be integers , Cannot contain floating point numbers
- The remainder operator , Divisor less than divisor , So the result is the divisor
- The remainder operator , The negativity of the result depends on the divisor , It has nothing to do with divisor , The divisor is a positive number, and the result is a positive number , Divisor
- If it is negative, the result is negative
- The remainder operator , The divisor is 0, The result is 0
- The remainder operator , Divisor is 0, It makes no sense ( Don't write like this )



Assignment operator
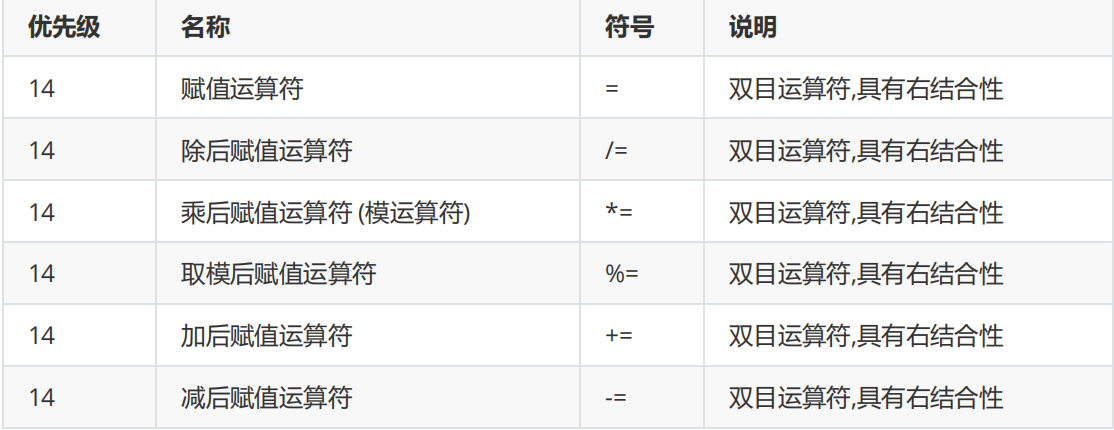
Simple assignment operator

Compound assignment operator

Combination and priority

Auto increment and auto decrement operator
In programming , I often meet “i=i+1” and “i=i-1” These two very common operations .C Language provides two more concise operators for this operation , namely ++ and --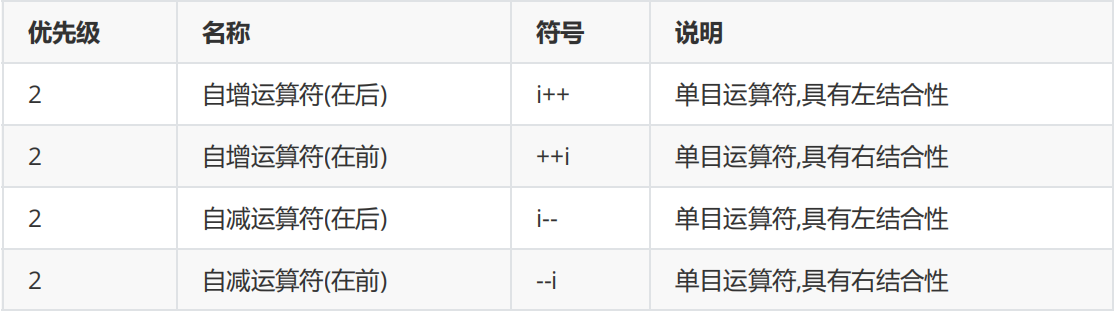
If it appears in an expression , Then the symbols written in front of and after will be different
Prefix expression :
++x, --x;among x Represents the variable name , First complete the self increase and self decrease of variables 1 operation , Reuse x As the value of the expression
value ; namely “ First change and then use. ”, That is, the value of the variable changes first , Then use the value of the variable to participate in the operationPostfix expression :
x++, x--;First use x As the value of the expression , Then self increase and self decrease 1 operation . namely “ Use first and then change. ”, also
That is, first use the value of the variable to participate in the operation , The value of the variable increases and decreases automatically
Self increasing :
If there is only a single variable , No matter what ++ Variables will be written before or after +1 operation 
If autoincrement participates in the operation 

Self reduction 

Be careful :
- Self increasing 、 Self subtraction can only be used for a single variable , As long as it is a standard type variable , Whether it's an integer 、 Real type , Or character variables
etc. , But not for expressions or constants , Incorrect usage :++(a+b); - Try to make
++ --alone , Try not to mix with other operators
Please replace with the following code
C Language standards are not clearly defined , How to operate after the same variable increases or decreases in the same expression , Different compilers get different results , Never write this in enterprise development
sizeof Operator
sizeof Can be used to calculate a variable or constant 、 Number of memory bytes occupied by data type
A standard format : sizeof( Constant or Variable );
sizeof() and +=、*= The same is a compound operator , from sizeof and () Two parts , But it represents a whole
therefore sizeof Not a function , Is an operator , The priority of this operator is 2
sizeof Several forms of :
// sizeof( Variable \ Constant );
sizeof(10);
char c = 'a';
sizeof(c);
//sizeof Variable \ Constant ;
sizeof 10;
char c = 'a';
sizeof c;
// sizeof( data type );
sizeof(float); // If it is a data type, you cannot omit parentheses

The comma operator
- stay C Commas in language “,” It's also an operator , It's called the comma operator . Its function is to connect multiple expressions to form an expression , It's called a comma expression
- The comma operator takes the value of each expression from left to right , The value of the last comma expression is equal to that of the last expression
value - Format :
expression 1, expression 2,… …, expression n;
#include <stdio.h>
int main(){
int a=2,b=4,x,y;
y=(x=a+b,b+x); // In a comma expression , The last operation is the final value , And then assign it to y
printf("y=%d, x=%d \n",y,x);// y=10, x=6
return 0;
}
Relational operator
By default , Every correct code we write in the program is executed . But a lot of times , We want to execute a piece of code only when a certain condition holds , In this case, you can use conditional statements to complete , But before learning conditional statements , Let's first look at some more basic knowledge :
How to judge whether a condition is true , C Authenticity in language , stay C In language , The condition is called “ really ”, If the condition does not hold, it is called “ false ”, therefore , Judge whether the conditions are true , Is to judge the conditions “ True and false ”
How to judge true and false ?C Language policy , Any value is true or false , Anything that is not 0 Values are “ really ”, Only 0 Only then “ false ”. in other words ,108、-18、4.5、-10.5 Are all “ really ”,0 It is “ false
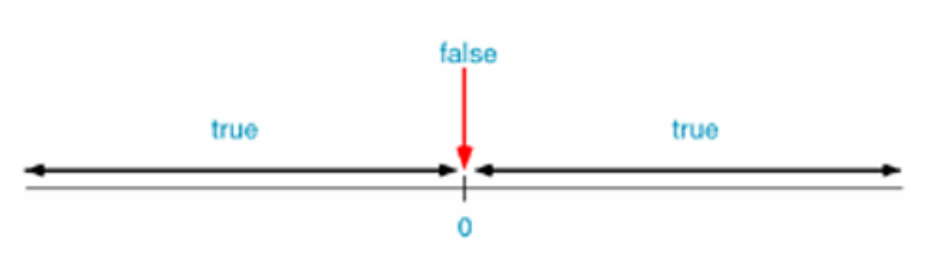
The result of a relational operator is 2 Kind of : If the condition holds , The results for 1, That is to say “ really ”; If the conditions don't hold , result for 0, That is to say “ false 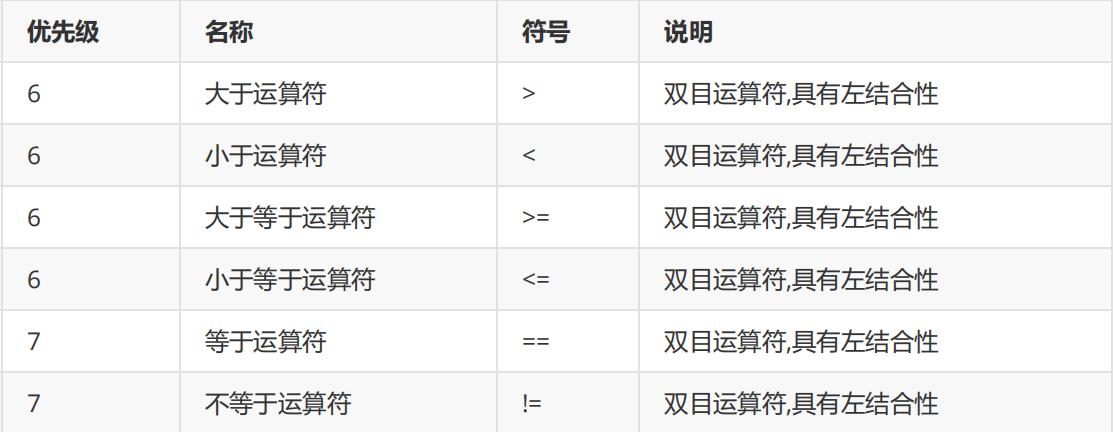
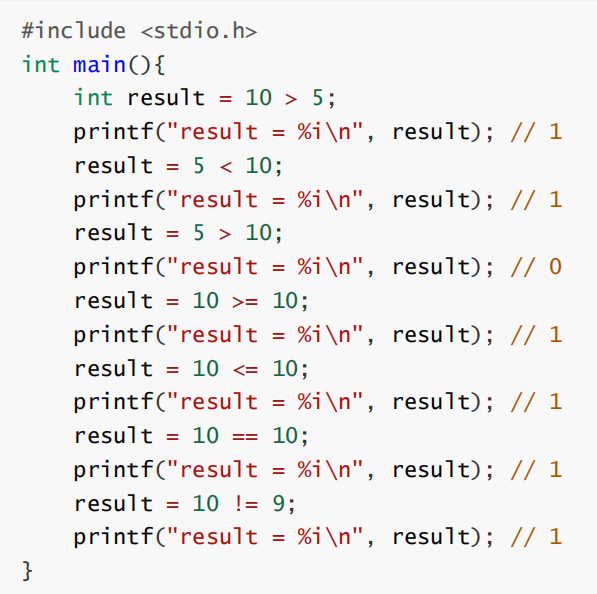
Priority and combination 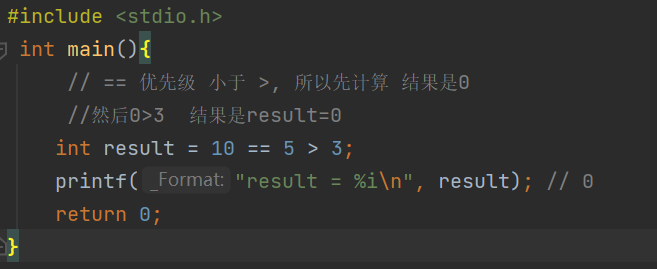
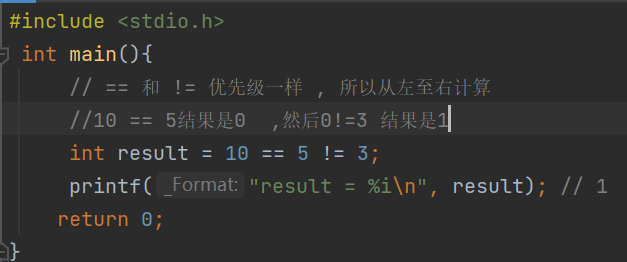
Be careful : Whether it's float still double There are accuracy problems , So be sure to avoid using == Determine whether floating point numbers are equal 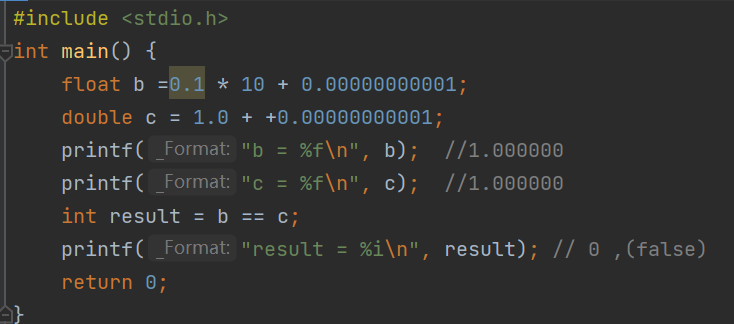
Logical operators
| priority | name | Symbol | explain |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | Logical nonoperator | ! | Monocular operator , Right binding |
| 11 | Logic and operators | && | Binocular operator , It has left binding property |
| 12 | Logical or operator | || | Binocular operator , It has left binding property |
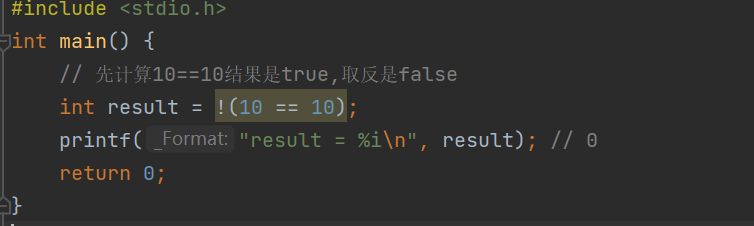
Logic is not
Format : ! Conditions A; ( True to false , False to true )
Logic and
Format : Conditions A && Conditions B;
Calculation results : A false is a false , That is to say, if it is true, then it is true
The calculation process :
- Always judge first " Conditions A" Is it true , If " Conditions A" establish , Then judge " Conditions B" Is it true , If " Conditions B" It was also established , The results for 1, namely “ really ”
- If " Conditions A" establish ," Conditions B" Don't set up , The results for 0, namely “ false ”
- If " Conditions A" Don't set up , No more judgment " Conditions B" Is it true , Because logic and as long as one is not true, the result is not true
Use caution : Conditions A" For false , " Conditions B" Will not be executed


Logic or
Format : Conditions A || Conditions B;
Calculation results : When it's true, it's true
The calculation process :
- First judge " Conditions A" Is it true
- If " Conditions A" Don't set up , Then judge " Conditions B" Is it true , If " Conditions B" establish , The results for 1, namely “ really ”
- If " Conditions A" Don't set up ," Conditions B" Nor does it hold true , The results for 0, namely “ false ”
- If " Conditions A" establish , No more judgment " Conditions B" Is it true , Because logic or as long as one is true, the result is true
Use caution : " Conditions A" It's true , " Conditions B" Will not be executed


Ternary operator
Ternary operator , It needs to 3 A data or expression constitutes a conditional expression
Format 1: expression 1?( result A):( result B)
Format 2: expression 1? expression 2: expression 3
Example : Pass the exam ? pass : fail, ;
Evaluation rules : If " expression 1" It's true , The result of the ternary operator is ( result A), Otherwise ( result B)
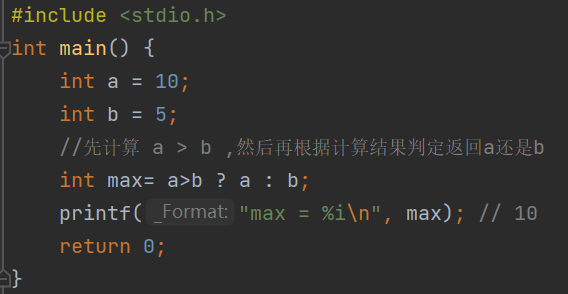
We can also do more complicated int res = a>b?a:(c>d?c:d);
Type conversion
Data type conversion is data type conversion ( Variable 、 The number 、 The result of the expression, etc ) Conversion from one type to another .
Automatic type conversion
Automatic type conversion is when the compiler silently 、 Implicitly 、 Data type conversion secretly , This transformation does not require programmer intervention , It happens automatically . Automatic type conversion occurs when one type of data is assigned to another type of variable , for example :
//100 yes int Data of type , It needs to be converted to float Type can be assigned to a variable f.
float f = 100;
// Again :f yes float Data of type , It needs to be converted to int Type can be assigned to a variable n.
int n = f;
In assignment operations , The data types on both sides of the assignment number are different , You need to convert the type of the expression on the right to the type of the variable on the left , This may cause data distortion , Or the accuracy is reduced ; So , Automatic type conversion is not necessarily safe . For unsafe type conversions , Compilers usually give warnings .
In different types of mixed operations , The compiler also automatically converts data types , Convert all data involved in the operation to the same type first , And then calculate . The rules of transformation are as follows :
- The conversion proceeds in the direction of increasing data length , To ensure that the value is not distorted , Or the accuracy is not reduced . for example ,int and long When participating in the operation , The first int Type of data into long Type and then calculate .
- All floating-point operations are performed with double precision , Even if there is only float type , Also convert to double type , In order to do the calculation .
- char and short When participating in the operation , It must be converted to int type .
The following figure describes this transformation rule more vividly :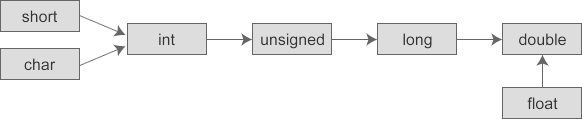
unsigned That is to say unsigned int, You can omit int, Just write unsigned.
Example of automatic type conversion :
#include<stdio.h>
int main(){
float PI = 3.14159;
int s1, r = 5;
double s2;
s1 = r * r * PI;
s2 = r * r * PI;
printf("s1=%d, s2=%f\n", s1, s2);
return 0;
}
When evaluating an expression r*r*PI when ,r and PI Are converted into double type , The result of the expression is also double type . But because of s1 Is an integer , So the result of the assignment operation is still integer , The decimal part is omitted , Cause data distortion .
Cast
Automatic type conversion is the result of the compiler's own judgment according to the context of the code , Sometimes it's not so “ intelligence ”, Can't meet all the needs . if necessary , Programmers can also explicitly propose type conversion in their own code , This is called cast .
Automatic type conversion is the compiler silently 、 An implicit type conversion , It doesn't need to be reflected in the code ; Mandatory type conversion is explicitly proposed by programmers 、 A type conversion that needs to be specified by code in a specific format . let me put it another way , Automatic type conversion requires no programmer intervention , Casts must have programmer intervention .
The format of the cast is : (type_name) expression
type_name Name the new type ,expression Expression for . for example :
(float) a; // Put the variable a Convert to float type
(int)(x+y); // Put the expression x+y The result of is converted to int integer
(float) 100; // Numerical value 100( The default is int type ) Convert to float type
The following is a classic example that requires cast :
#include <stdio.h>
int main(){
int sum = 103; // total
int count = 7; // number
double average; // The average
average = (double) sum / count;
printf("Average is %lf!\n", average); //Average is 14.714286!
return 0;
}
sum and count All are int type , Without intervention , that sum / count The result of the operation is also int type , The decimal part will be discarded ; Although it is average yes double type , Can receive decimal parts , But the heart has spare power and insufficient strength , The decimal part is written in advance “ castration ” 了 , It can only receive integer parts , This leads to serious distortion of the result of division operation .
since average yes double type , Why not make full use of , Try to improve the accuracy of the calculation results ? To achieve this goal , We just need to sum perhaps count One of them is converted to double The type is enough . In the above code , We will sum Cast to double type , such sum / count The result will also become double type , You can keep the decimal part ,average The received value will also be more accurate .
In this code , There are two points to note :
- For division operations , If both divisor and dividend are integers , Then the result of the operation is also an integer , The decimal part will be discarded directly ; If one of the divisor and the divisor is a decimal , So it's also going to be a decimal .
- ( ) Has a higher priority than /, For the expression (double) sum / count, Will execute first (double) sum, take sum Convert to double type , And then we do Division , So the result is double type , Able to retain decimal parts . Be careful not to write (double) (sum / count), The result of this operation will be 3.000000, Still can't keep the decimal part .
Type conversion is only temporary
Whether it's automatic type conversion or forced type conversion , It's just a temporary conversion for this operation , The result of the conversion will also be saved to the temporary memory space , It will not change the original type or value of data . Please see the following example :
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
double total = 400.8; // The total price
int count = 5; // number
double unit; // The unit price
int total_int = (int)total; //400
unit = total / count; // 80.160000
printf("total=%lf, total_int=%d, unit=%lf\n", total, total_int, unit); //total=400.800000, total_int=400, unit=80.160000
return 0;
}
Through the code above , We can see ,total Although the type is converted to total_int , however total The original data type has not changed , So the final calculation is still decimal , That means that type conversion only takes time and only acts on the current calculation
Automatic type conversion VS Cast
stay C In language , Some types can be converted automatically , You can also cast , for example int To double,float To int etc. ; Some types can only be cast , Can't switch automatically , For example, what will be learned later void * To int *,int To char * etc. .
Types that can be automatically converted must be cast , however , Types that need to be cast may not be automatically cast . Now we've learned about data types , It can automatically convert , It can also be forced to convert , In the future, we will also learn some types that can only be cast but not automatically cast .
Automatic type conversions are generally less risky , There will be no serious consequences for the program , for example ,int To double No shortcomings ,float To int At best, it's numerical distortion . Type conversions that can only be forced are generally risky , Or act strangely , for example ,char * To int * It's a strange transformation , This leads to strange values , Again ,int To char * It's a very risky conversion , It usually causes the program to crash . When using cast , Programmers themselves should be aware of the potential risks .

边栏推荐
- Codeforces Round #793 (Div. 2)(A-D)
- 到底什么才是DaaS数据即服务?别再被其他DaaS概念给误导了
- Newh3c - network address translation (NAT)
- Xcode 6 swift code completion does not work properly - Xcode 6 swift code completion not working
- A single element in an ordered array
- Sequence model
- Li Kou today's question -1200 Minimum absolute difference
- Awk from getting started to digging in (9) circular statement
- FRP intranet penetration, reverse proxy
- What exactly is DAAS data as a service? Don't be misled by other DAAS concepts
猜你喜欢
SSRF vulnerability exploitation - attack redis
ctfshow web255 web 256 web257
![[CV] Wu Enda machine learning course notes | Chapter 9](/img/de/41244904c8853b8bb694e05f430156.jpg)
[CV] Wu Enda machine learning course notes | Chapter 9
Turn: excellent managers focus not on mistakes, but on advantages

How to solve the problem of computer jam and slow down
Basic operations of databases and tables ----- view data tables
](/img/dc/5c8077c10cdc7ad6e6f92dedfbe797.png)
C语言-入门-基础-语法-[变量,常亮,作用域](五)

Codeforces Round #803 (Div. 2)(A-D)
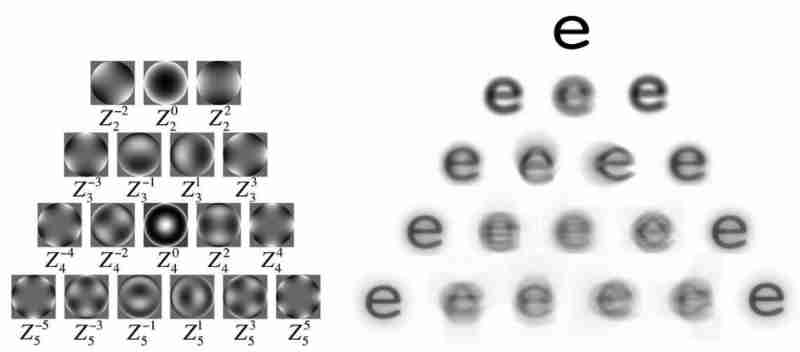
High order phase difference such as smear caused by myopic surgery
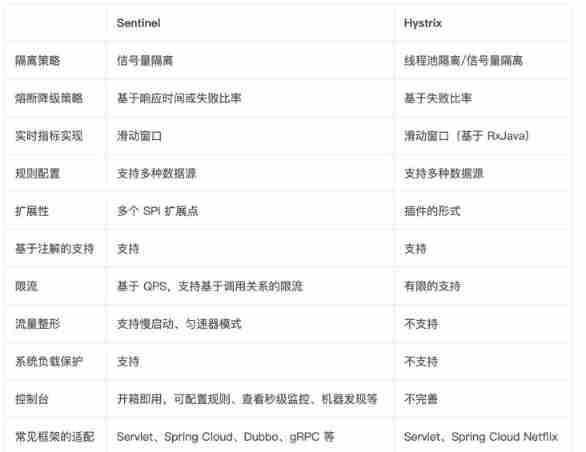
Comparison between sentinel and hystrix
随机推荐
到底什么才是DaaS数据即服务?别再被其他DaaS概念给误导了
Sequence model
HMS core helps baby bus show high-quality children's digital content to global developers
There are 100 people eating 100 apples, one adult eating 4 apples, and four children eating 1 apple. How can they eat exactly 100 apples? Use any high-level language you are familiar with
A single element in an ordered array
awk从入门到入土(7)条件语句
How to play dapr without kubernetes?
Collections in Scala
C, Numerical Recipes in C, solution of linear algebraic equations, Gauss Jordan elimination method, source code
Take you to master the formatter of visual studio code
上周热点回顾(6.27-7.3)
High order phase difference such as smear caused by myopic surgery
小程序容器技术与物联网 IoT 可以碰撞出什么样的火花
Leetcode topic [array] - 121 - the best time to buy and sell stocks
awk从入门到入土(18)gawk线上手册
Conversion of yolov5 XML dataset to VOC dataset
Educational Codeforces Round 115 (Rated for Div. 2)
How to solve the problem of computer jam and slow down
Codeforces Round #750 (Div. 2)(A,B,C,D,F1)
awk从入门到入土(8)数组