当前位置:网站首页>Getting started with microservices: gateway gateway
Getting started with microservices: gateway gateway
2022-07-04 08:37:00 【Mm writes bugs every day】
List of articles
Introduction to microservice :Gateway gateway
One 、 Why do I need a gateway
Gateway It is equivalent to the goalkeeper in microservice , It can help us complete :
- Authentication and permission verification
- Service routing and load balancing
- Request current limiting
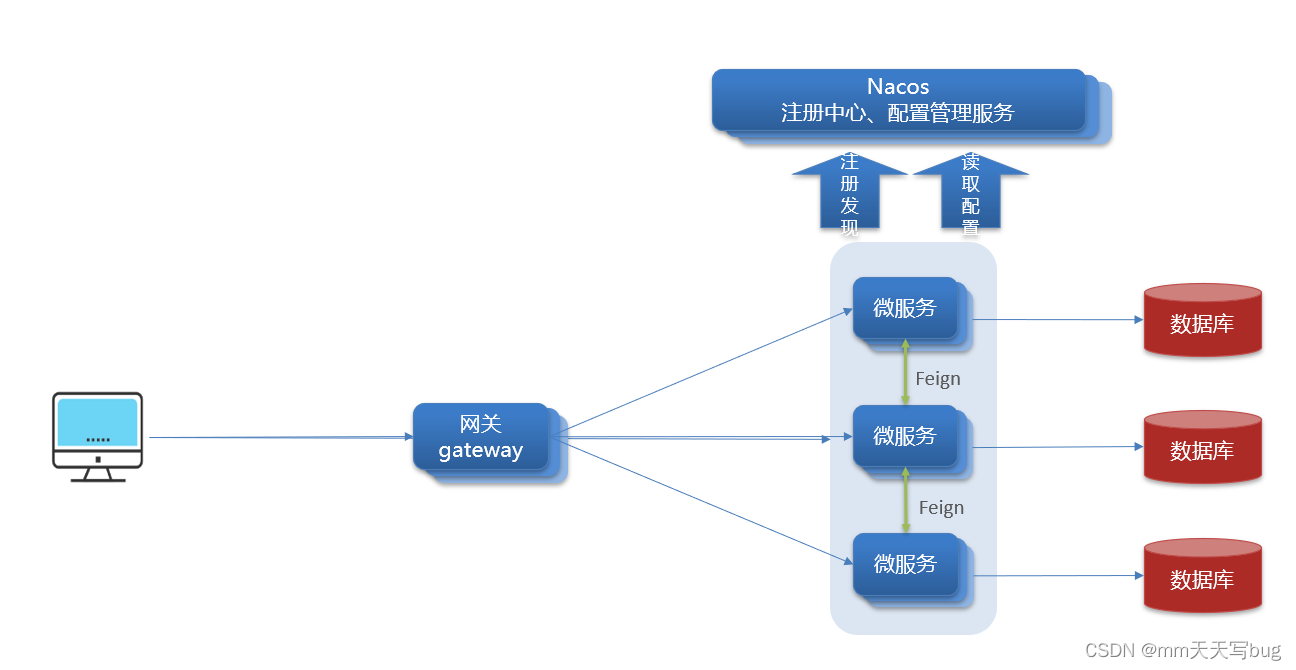
stay SpringCloud There are two ways to implement the gateway in :
- gateway
- zuul
The main use of gateway, because Zuul Is based on Servlet Realized , It belongs to blocking programming .
and SpringCloudGateway Is based on Spring5 Provided in WebFlux, It belongs to the implementation of responsive programming , Better performance
Two 、 Build gateway service
Build gateway service , First we need to create a Maven modular , It is recommended to select an empty module , Do not use SpringBoot Template creation , Otherwise, unknown errors will occur ( Because the first time I used SpringBoot Created by template , Then there are dependencies that cannot be imported Bug)
Create an empty Maven After the project , stay pom.xml Import the following dependencies
<!--nacos Service discovery depends on -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-nacos-discovery</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- introduce gateway gateway -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-gateway</artifactId>
</dependency>
After importing dependencies , Manually add GatewayApplication as well as yml file
@SpringBootApplication
public class GatewayApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(GatewayApplication.class,args);
}
}
And then in yml Configure gateways and routes
Routing configuration includes :
1. route id: The unique identifier of the route
2. Routing destination (uri): The destination address of the route ,http Represents a fixed address ,lb Represents load balancing based on service name
3. Route assertion (predicates): Rules for judging routing ,
4. Routing filter (filters): To process a request or response
server:
port: 10010
spring:
application:
name: gateway # The service name
cloud:
nacos:
server-addr: localhost:8848 #nacos Address
gateway:
routes:
- id: user-service # route id, Customize , As long as it's the only one
uri: lb://userservice # The destination address of the route lb It's load balancing , Followed by the service name
predicates: # Route assertion , That is, judge whether the request meets the conditions of routing rules
- Path=/user/** # This is matched according to the path , As long as /user/ Meet the requirements at the beginning
- id: order-service
uri: lb://orderservice
predicates:
- Path=/order/**
If we add multiple services to , Then write more id that will do
This completes the construction of the gateway
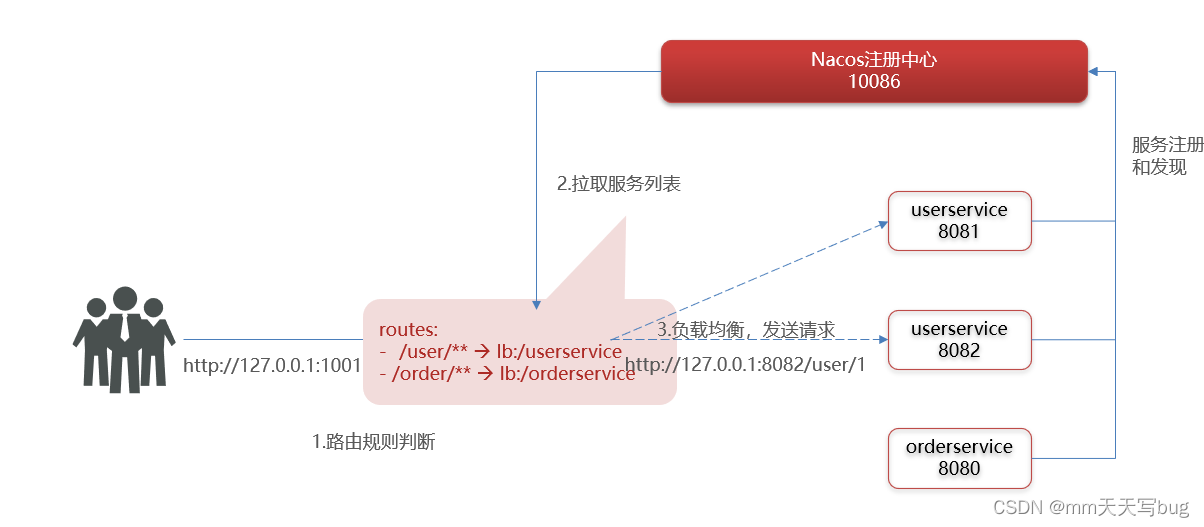
The completed gateway will play the role of goalkeeper , When we ask /user/** This url When , It will judge which service it is according to the reason rule , Then load balance and send the request .
For example, we access the gateway http://localhost:10010/user/1, Then meet /user/** The rules , Request forwarding to uri:http://userservice/user/1, Got the result :

3、 ... and 、 Route assertion factory
In the above yml Configuration in progress , You can see there's one predicates
This predicates Route assertion , Determine whether the request meets the rules , If it meets the rules, it will be forwarded to the routing destination
The assertion rules written in the configuration file are just strings , These strings will be Predicate Factory Read and process , The condition for changing to routing judgment
for example :Path=/user/** Is to match according to the path , This rule is made by org.springframework.cloud.gateway.handler.predicate.PathRoutePredicateFactory Class to handle
Assertion factories like this are SpringCloudGateway There are more than a dozen
| name | explain | Example |
|---|---|---|
| After | It's a request after a certain point in time | - After=2037-01-20T17:42:47.789-07:00[America/Denver] |
| Before | It's a request before a certain point in time | - Before=2031-04-13T15:14:47.433+08:00[Asia/Shanghai] |
| Between | It's a request before two points in time | - Between=2037-01-20T17:42:47.789-07:00[America/Denver], 2037-01-21T17:42:47.789-07:00[America/Denver] |
| Cookie | The request must contain some cookie | - Cookie=chocolate, ch.p |
| Header | The request must contain some header | - Header=X-Request-Id, \d+ |
| Host | The request must be to access a host( domain name ) | - Host=.somehost.org,.anotherhost.org |
| Method | The request method must be the specified method | - Method=GET,POST |
| Path | The request path must comply with the specified rules | - Path=/red/{segment},/blue/** |
| Query | The request parameter must contain the specified parameter | - Query=name, Jack perhaps - Query=name |
| RemoteAddr | Requestor's ip Must be the specified range | - RemoteAddr=192.168.1.1/24 |
| Weight | Weight processing |
Four 、 Routing filter
GatewayFilter It is a filter provided in the gateway , You can process the request to enter the gateway and the response returned by the microservice
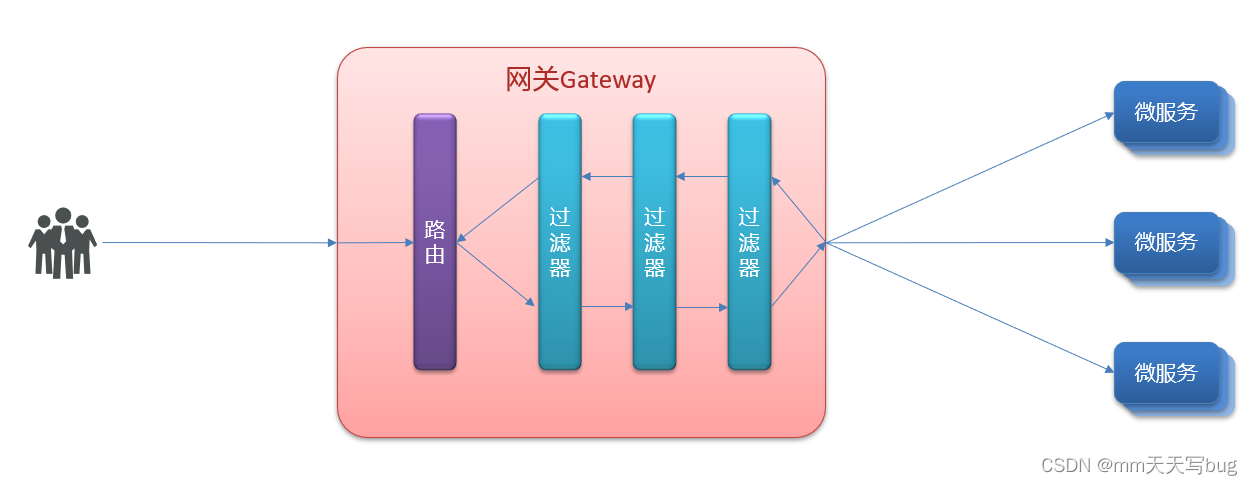
Spring Provides 31 Different routing filter factories in , Here are several displays
| name | explain |
|---|---|
| AddRequestHeader | Add a request header to the current request |
| RemoveRequestHeader | Remove a request header from the request |
| AddResponseHeader | Add a response header to the response result |
| RemoveResponseHeader | Remove a response header from the response result |
| RequestRateLimiter | Limit the requested traffic |
4.1 Add filter GatewayFilter
stay Gateway Modular yml Add filter
The following case is to add a request header
server:
port: 10010
spring:
application:
name: gateway # The service name
cloud:
nacos:
server-addr: localhost:8848 #nacos Address
gateway:
routes:
- id: user-service # route id, Customize , As long as it's the only one
uri: lb://userservice # The destination address of the route lb It's load balancing , Followed by the service name
predicates: # Route assertion , That is, judge whether the request meets the conditions of routing rules
- Path=/user/** # This is matched according to the path , As long as /user/ Meet the requirements at the beginning
filters: # filter
- AddRequestHeader=Truth,Itcast is freaking aowsome!
- id: order-service
uri: lb://orderservice
predicates:
- Path=/order/**
default-filters: # Default filter , It will take effect for all routing requests
- AddRequestHeader=Truth,Itcast is freaking aowsome!
filters It's a local filter , As shown in the above code , It's only in user-service Work
and default-filters Is the default filter , All services in routing work
4.2 Global filter GlobalFilter
The global filter is also used to handle all requests and microservice responses entering the gateway , And GatewayFilter It does the same thing .
The difference lies in GatewayFilter Defined by configuration , The processing logic is fixed . and GlobalFilter You need to write your own code to implement your logic .
The definition is to implement GlobalFilter Interface .
First of all we have Gateway Module adds a Java class
// @Order(-1)
@Component
public class AuthorizeFilter implements GlobalFilter, Ordered {
@Override
public Mono<Void> filter(ServerWebExchange exchange, GatewayFilterChain chain) {
//1. Get request parameters
ServerHttpRequest request = exchange.getRequest();
//2. Get all parameters
MultiValueMap<String, String> queryParams = request.getQueryParams();
//3. obtain Authorization Parameters
String first = queryParams.getFirst("Authorization");
//4. Judge whether the parameter is admin
if ("admin".equals(first)){
//5. Yes, release
return chain.filter(exchange);
}
//6. Set status code
exchange.getResponse().setStatusCode(HttpStatus.UNAUTHORIZED);
//7. Intercept request
return exchange.getResponse().setComplete();
}
@Override
public int getOrder() {
return -1;
}
}
The main function of this class is to realize GlobalFilter, Judge the sent request Authorization Is the parameter admin, If so, release , If not, set the status code to 401 Then intercept the request
Pay attention to is , This interceptor requires @Component Annotation to Spring trusteeship
And we can set the priority of the interceptor ( The smaller the number is. , The higher the priority )
For example, using @Order(-1) set priority
You can also choose to implement Ordered Interface getOrder Method , Return a number , That number determines the priority of interceptors
4.3 Filter execution sequence
The request to enter the gateway will encounter three types of filters : Filter for the current route 、DefaultFilter、GlobalFilter
After request routing , The current route filter and DefaultFilter、GlobalFilter, Merge into a filter chain ( aggregate ) in , After sorting, execute each filter in turn
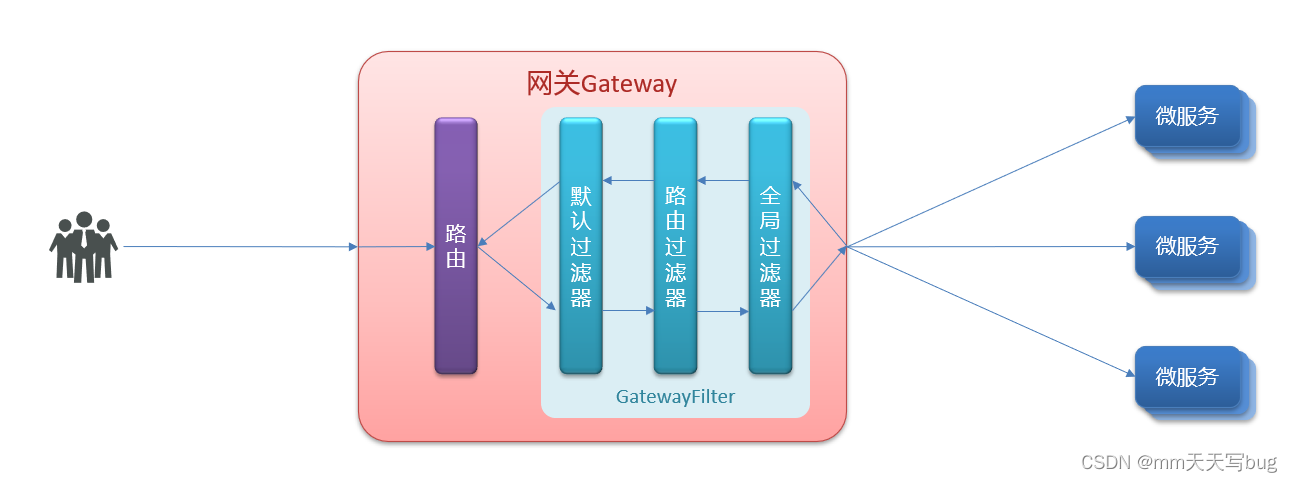
- Each filter must specify a int Type of order value ,order The smaller the value. , The higher the priority , The higher the order of execution .
- GlobalFilter By implementing Ordered Interface , Or add @Order Note to specify order value , It's up to us to designate
- Routing filters and defaultFilter Of order from Spring Appoint , The default is from... In the order of declaration 1 Increasing .
- When the filter order When the value is the same , According to defaultFilter > Routing filter > GlobalFilter Sequential execution .
5、 ... and 、 Cross domain problem solving
What is cross domain problem ?
Developed before SpringBoot+vue When it comes to the project , If the cross domain problem is not solved , I use axios Sending a request to the backend will result in an error
This is because the port numbers of the front end and the back end are different , The browser prohibits cross domain communication between the initiator of the request and the server ajax request
So the cross domain problem is The browser prohibits cross domain communication between the initiator of the request and the server ajax request , The request is blocked by the browser
Except that different ports will cause cross domain problems , If the domain name is different , It can also lead to cross domain problems
Solution :CORS
server:
port: 10010
spring:
application:
name: gateway # The service name
cloud:
nacos:
server-addr: localhost:8848 #nacos Address
gateway:
globalcors: # Global cross domain processing
add-to-simple-url-handler-mapping: true # solve options The request is blocked
corsConfigurations:
'[/**]':
allowedOrigins: # Allow cross domain requests for which websites
- "http://127.0.0.1:5500"
- "http://www.leyou.com"
allowedMethods: # Allowed cross domain ajax Request method of
- "GET"
- "POST"
- "DELETE"
- "PUT"
- "OPTIONS"
allowedHeaders: "*" # Header information allowed to be carried in the request
allowCredentials: true # Is it allowed to carry cookie
maxAge: 360000 # The validity period of this cross domain detection
stay gateway Configure the above configuration in the gateway module , To solve cross domain problems
边栏推荐
- 一文了解數據异常值檢測方法
- [BSP video tutorial] stm32h7 video tutorial phase 5: MDK topic, system introduction to MDK debugging, AC5, AC6 compilers, RTE development environment and the role of various configuration items (2022-
- Sort by item from the list within the list - C #
- 2022 gas examination registration and free gas examination questions
- Unity-写入Word
- 广和通高性能4G/5G无线模组解决方案全面推动高效、低碳智能电网
- What should I do if there is a problem with the graphics card screen on the computer
- Flutter integrated amap_ flutter_ location
- Using the rate package for data mining
- C # implements a queue in which everything can be sorted
猜你喜欢
Newh3c - routing protocol (RIP, OSPF)
Common components of flask
snipaste 方便的截图软件,可以复制在屏幕上
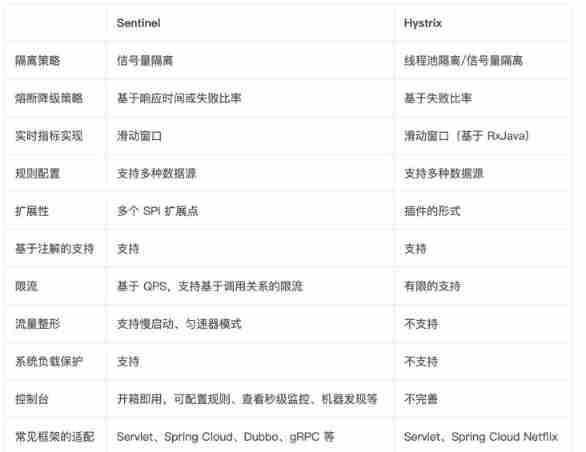
Comparison between sentinel and hystrix
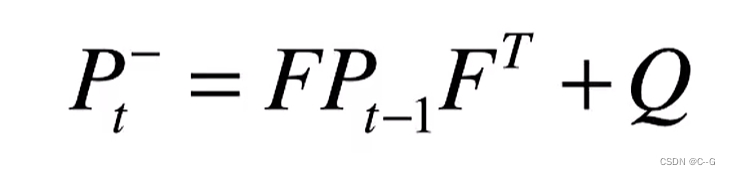
1、卡尔曼滤波-最佳的线性滤波器
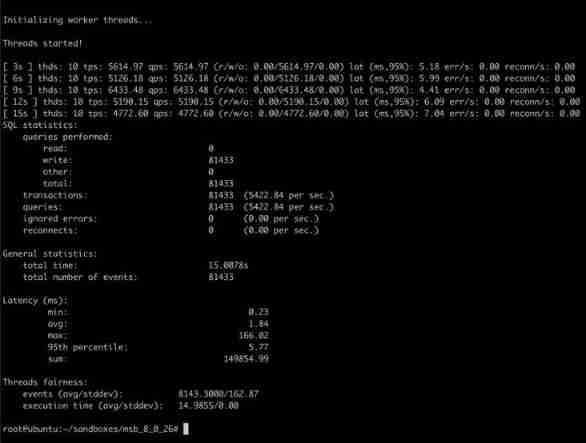
Question 49: how to quickly determine the impact of IO latency on MySQL performance
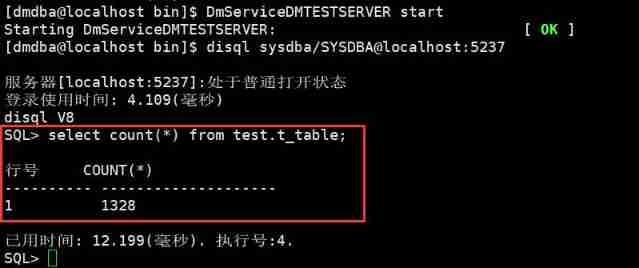
DM8 database recovery based on point in time
From scratch, use Jenkins to build and publish pipeline pipeline project
User login function: simple but difficult
![Leetcode topic [array] -136- numbers that appear only once](/img/6d/f2e4b812e5dd872fbeb43732d6f27f.jpg)
Leetcode topic [array] -136- numbers that appear only once
随机推荐
Basic operations of databases and tables ----- view data tables
How to solve the problem that computers often flash
[Chongqing Guangdong education] National Open University spring 2019 455 logistics practice reference questions
Sports [running 01] a programmer's half horse challenge: preparation before running + adjustment during running + recovery after running (experience sharing)
Do you know about autorl in intensive learning? A summary of articles written by more than ten scholars including Oxford University and Google
[gurobi] establishment of simple model
Common components of flask
埃氏筛+欧拉筛+区间筛
根据数字显示中文汉字
R language uses cforest function in Party package to build random forest based on conditional inference trees, uses varimp function to check feature importance, and uses table function to calculate co
How to solve the problem of computer jam and slow down
Conversion of yolov5 XML dataset to VOC dataset
Unity-Text上标平方表示形式+text判断文本是否为空
manjaro安装微信
一文了解數據异常值檢測方法
FOC控制
Sort by item from the list within the list - C #
Webapi interview question summary 01
Leetcode 146. LRU 缓存
Flutter 集成 amap_flutter_location