当前位置:网站首页>Understanding and learning of code blocks
Understanding and learning of code blocks
2022-07-27 01:37:00 【Daxiong who loves learning】
List of articles
Basic introduction
A code block belongs to a member of a class , It's similar to the method , Encapsulate logical statements in the method body , adopt {} Surrounded .
But different from the method , No method name , No return , No parameters , Only the method body , And you don't have to call... Explicitly through objects or classes , But when loading classes , Or implicitly call... When creating an object
Basic grammar
Modifier {
Code };
Note description :
1. Modifier can be written or not , What to write , I can only write static
2. If you use static Modifiers are called static code blocks , If there is no static The modification is called ordinary code block
3 A logical statement can be any logical statement ( Input and output , Method call , Cycle, etc )
4; The number can be written , You can omit it
The benefits of code blocks
1. Equivalent to another form of constructor ( Complementary mechanisms to constructors ), You can do initialization
2. scene : If there are repeated statements in multiple constructors , It can be extracted into the initialization block , Improve code reuse
Code case :
class Movie {
private String name;
private double price;
private String director;
//3 Constructor -> heavy load
{
System.out.println(" The movie screen opens ...");
System.out.println(" Advertising begins ...");
System.out.println(" The film is just the beginning ...");
};
public Movie(String name) {
System.out.println("Movie(String name) Called ...");
this.name = name;
}
public Movie(String name, double price) {
this.name = name;
this.price = price;
}
public Movie(String name, double price, String director) {
System.out.println("Movie(String name, double price, String director) Called ...");
this.name = name;
this.price = price;
this.director = director;
}
}
** explain :** The three constructors consist of the same statement , In order to avoid excessive redundancy of code , We use code blocks to initialize the constructor , Then we can put the same sentence , Put it into a code block , So when we call any constructor , Create objects , Will call the contents of the code block first , Last , Remember that the order of code block calls takes precedence over constructors .
Code block usage details
When is it implemented
static The function of the code block is to initialize the class , And it executes as the class loads , And only once . If it's a normal code block , Every time an object is created, it executes .
When the class is loaded **【 a key 】**
When creating an object instance (new When an object )
Create subclass object instances , The parent class is also loaded
Here is an explanation of why the parent class is also loaded , When we create subclass objects , Will contain a constructor , The default is parameterless constructor , There is an implicit super Point to the parent class , So if the parent class is also composed of static code blocks , Will load first
When using static members of a class ( Static attribute , Static methods )
eg:A class extends B class The static block of
Common code block , When creating an object instance , Will be called , To create a , Call once .
If you only use members of a class , Ordinary blocks of code do not execute
class BB {
{
System.out.println("BB Common code blocks 2 Be performed ...");
}
// Static code block
static {
System.out.println("BB Static code 1 Be performed ...");//1
}
}
class AA extends BB {
// Static code block
static {
System.out.println("AA Static code 1 Be performed ...");//2
}
{
System.out.println("AA Common code blocks 2 Be performed ...");
}
}
// Class is loaded, for example
// 1. When creating an object instance (new)
AA aa = new AA();
//2. Create subclass object instances , The parent class is also loaded , and , The parent class is loaded first , Subclasses are loaded
AA aa2 = new AA();

The execution order of the two code blocks
Here we first remember Static code blocks are executed before ordinary code blocks , The order of execution will be described in detail later
When creating an object , When a class is called in sequence ( No inheritance ):( a key )
- Call static code block and static attribute initialization ( Static code blocks have the same priority as static attribute initialization calls , Call according to their defined properties
- Call the initialization of common code blocks and common attributes ( The priority of ordinary code block and ordinary attribute initialization call together , Call in the order they define )
- Call constructor
class C02 {
private int n1 = 100;
private static int n2 = 200;
private static int n3 = 300;
public C02() {
System.out.print("C02 The constructor is called ...");
}
private void m1() {
System.out.println("m1 Method is called ...");
}
private static void m2() {
System.out.println("m2 Method is called ...");
}
static {
// Static code block , Only static members can be called
//System.out.println(n1); error
System.out.println(n2);//ok
//m1();// error
m2();
}
{
// Common code block , You can use any member
System.out.println(n1);
System.out.println(n2);//ok
m1();
m2();
}
}
new C02();
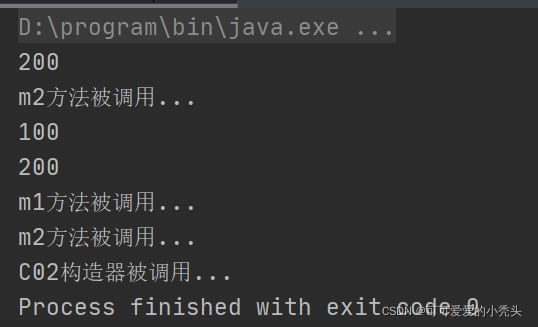
The execution order of the two code blocks in the class
When creating a subclass object , The calling order when calling a class :
- Static code blocks and static attributes of the parent class ( The priority is the same , In order of definition )
- Static code and static attributes of subclasses ( The priority is the same , In order of definition )
- Parent class common code and common attributes ( The priority is the same , In order of definition )
- Parent class constructor
- Common code blocks and common attributes of subclasses ( The priority is the same , In order of definition )
- Subclass construction method
class A02 {
// Parent class
private static int n1 = getVal01();
static {
System.out.println("A02 A static block of code ..");//(2)
}
{
System.out.println("A02 The first common block of code ..");//(5)
}
public int n3 = getVal02();// Initialization of common properties
public static int getVal01() {
System.out.println("getVal01");//(1)
return 10;
}
public int getVal02() {
System.out.println("getVal02");//(6)
return 10;
}
public A02() {
// Constructors
// hide
//super()
// Initialization of common code and common properties ......
System.out.println("A02 Constructor ");//(7)
}
}
class B02 extends A02 {
//
private static int n3 = getVal03();
static {
System.out.println("B02 A static block of code ..");//(4)
}
public int n5 = getVal04();
{
System.out.println("B02 The first common block of code ..");//(9)
}
public static int getVal03() {
System.out.println("getVal03");//(3)
return 10;
}
public int getVal04() {
System.out.println("getVal04");//(8)
return 10;
}
// Be sure to taste it slowly ..
public B02() {
// Constructors
// Hide the
//super()
// Initialization of common code blocks and common attributes ...
System.out.println("B02 Constructor ");//(10)
}
}
new B02();
Here is an explanation of why static code blocks are executed first , Because statically related code blocks , Property initialization , When the class loads , It's done , Therefore, it takes precedence over constructors and ordinary code blocks
Member permission requirements in code
Code blocks can only call static members directly , Ordinary code blocks can call any member
summary
I'm reviewing recently java Basic knowledge of , When learning the code block of Tao, I found that I was not familiar with it , So keep notes for future review .
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
Buuctf casual note, exec, easysql, secret file
Iptables firewall (I)
Esp8266 --- JSON data exchange format
Summary of heap sorting related knowledge
[ctf attack and defense world] questions about cookies in the web area
Unity screenshot widget
Shell(11)括号的用法
Web服务(02)——Web服务器中间件
Web服务(07)——LNMP一键部署
十二、正则表达式
Li Kou brushes 300 record posts
Web服务器(01)——介绍web服务器
Some simple extension methods commonly used by unity
Shell(10)数组和冒泡排序
MTCNN
OJ question of sequence table
Unity ugui text text box adaptation
Mqtt---- bottom (precautions)
Question making notes 1
正则表达式
![[ctf real question] 2018 WANGDING cup web unfinish](/img/d8/a367c26b51d9dbaf53bf4fe2a13917.png)








