当前位置:网站首页>Introduction to guava cache usage
Introduction to guava cache usage
2022-06-11 08:12:00 【Thinking practitioner】
Catalog
3、 ... and 、 Set maximum storage
7、 ... and 、 Remove the action listener
8、 ... and 、 Automatic loading
One 、 background
In daily development , There are many such occasions : Some of the data is not very large , It doesn't change very often , And the visits are very frequent ; however , Limited by hard disk IO Performance of , Or remote network , Getting can be time consuming , Our program is very slow . This is intolerable in some businesses ! Cache is the artifact to solve this kind of problem ! The main function of cache is : Temporarily save the data processing results of the business system in memory , Wait for the next visit .
Caching is widely used in many systems and architectures , for example :
- CPU cache
- Operating system cache
- HTTP cache
- Database cache
- Static file cache
- Local cache
- Distributed cache
In the field of computer and network , Caching is everywhere . As long as there are hardware performance inequities , Where network transmission is involved , There will be a cache .
There are two types of caching in general : Centralized caching and Distributed cache .
“ Centralized caching " And " Distributed cache " The difference is that “ focus ” And " Decentralization " The concept of , The object may be the server 、 Memory module 、 Hard disk, etc. . such as :
1. Server version :
- The cache is concentrated on a single server , For centralized caching .
- The cache is distributed on different servers , For distributed caching .
2. Memory module version :
- The cache is concentrated on one memory module of a server , For centralized caching .
- The cache is distributed on different memory modules of a server , For distributed caching .
3. Hard disk version :
- The cache is concentrated on a hard disk of a server , For centralized caching .
- The cache is distributed on different hard disks of a server , For distributed caching .
Guava cache It belongs to centralized memory cache .
Guava Cache And ConcurrentMap Very similar , But it's not exactly the same . The basic difference is :ConcurrentMap All added elements will always be saved , Until you explicitly remove . relatively ,Guava Cache To limit memory usage , It's usually set to automatically recycle elements . In some cases , Even though LoadingCache Do not recycle elements , It's also useful , Because it automatically loads the cache .Guava Cache It's caching data in memory , Compared to a database or redis Storage , Accessing data in memory is more efficient .
Guava website , The following situations can be considered Guava Cache:
Willing to consume some memory space to improve speed .
Some keys are expected to be queried multiple times .
The total amount of data stored in the cache will not exceed the memory capacity .
therefore , Can be “ A small amount of data frequently used by programs ” Store in Guava Cache in , To improve program performance . Following pair Guava Cache The usage of .
Two 、 Building cache objects
Interface Cache Represents a cache , It has the following methods :
public interface Cache<K, V> {
V get(K key, Callable<? extends V> valueLoader) throws ExecutionException;
ImmutableMap<K, V> getAllPresent(Iterable<?> keys);
void put(K key, V value);
void putAll(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m);
void invalidate(Object key);
void invalidateAll(Iterable<?> keys);
void invalidateAll();
long size();
CacheStats stats();
ConcurrentMap<K, V> asMap();
void cleanUp();
}Can pass CacheBuilder Class to build a cache object ,CacheBuilder Class USES the builder Design patterns , Each of its methods returns CacheBuilder In itself , until build Method is called . The code to build a cache object is as follows :
public class StudyGuavaCache {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Cache<String,String> cache = CacheBuilder.newBuilder().build();
cache.put("word","Hello Guava Cache");
System.out.println(cache.getIfPresent("word"));
}
}The above code passes through CacheBuilder.newBuilder().build() sentence Created One Cache Cache object , And stored in the cache object key by word、value by Hello Guava Cache A record of . You can see ,Cache Very similar to JDK Medium Map, But compared to Map,Guava Cache Provides a lot more powerful features .
from LoadingCache The normal way to query is to use get(K) Method . This method either returns the cached value , Or use CacheLoader Load new values atomically into the cache ( adopt load(String key) Method loading ). because CacheLoader An exception may be thrown ,LoadingCache.get(K) Also declare to throw out ExecutionException abnormal . If you define CacheLoader No check exceptions declared , You can use the getUnchecked(K) Find cache . Must pay attention to , once CacheLoader Declared a check exception , You can't call getUnchecked(K).
LoadingCache<Key, Value> cache = CacheBuilder.newBuilder()
.build(
new CacheLoader<Key, Value>() {
public Value load(Key key) throws AnyException {
return createValue(key);
}
});
###...
try {
return cache.get(key);
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
throw new OtherException(e.getCause());
}3、 ... and 、 Set maximum storage
Guava Cache You can specify the maximum number of records that the cache can store when building a cache object . When Cache After the number of records in reaches the maximum , Call again put Method to add objects to it ,Guava It will first delete one of the object records in the current cache , After making room , Then store the new object in Cache in .
public class StudyGuavaCache {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Cache<String,String> cache = CacheBuilder.newBuilder()
.maximumSize(2)
.build();
cache.put("key1","value1");
cache.put("key2","value2");
cache.put("key3","value3");
System.out.println(" The first value is :" + cache.getIfPresent("key1"));
System.out.println(" Second value :" + cache.getIfPresent("key2"));
System.out.println(" Third values :" + cache.getIfPresent("key3"));
}
}The above code constructs the cache object , adopt CacheBuilder Class maximumSize Method Appoint Cache Up to storage 2 Data , And then call Cache Of put Method Added 3 Objects . The program execution result is shown in the figure below , You can see the insertion of the third object record , Caused the first object record to be deleted .

Four 、 Set expiration time
In the build Cache Object time , Can pass CacheBuilder Class expireAfterAccess and expireAfterWrite Two methods specify the expiration time for objects in the cache , Use CacheBuilder Built cache will not “ Automatically ” Perform cleanup and eviction values , It does not execute or evict any type immediately after the value has expired . contrary , It performs a small amount of maintenance during write operations , Or occasionally read with very few writes . among ,expireAfterWrite Method specifies how long an object will expire after it is written to the cache ,expireAfterAccess Method specifies how long the object has not expired after being accessed .
The following code uses expireAfterWrite Examples of methods .
public class StudyGuavaCache {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Cache<String,String> cache = CacheBuilder.newBuilder()
.maximumSize(2)
.expireAfterWrite(3,TimeUnit.SECONDS)
.build();
cache.put("key1","value1");
int time = 1;
while(true) {
System.out.println(" The first " + time++ + " Take... For the next time key1 The value of is :" + cache.getIfPresent("key1"));
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
}
} The code above is constructing Cache Object time , adopt CacheBuilder Of expireAfterWrite Method , Appoint “ write in Cache Objects in the ” stay 3 It will expire in seconds . stay Cache After storing an object record in an object , every other 1 Read this record every second . The results of the program are shown in the following figure , You can see , front 3 Seconds can be from Cache Get the object from , exceed 3 Seconds later , Objects from Cache Is automatically deleted .
The following code uses expireAfterAccess Examples of methods .
public class StudyGuavaCache {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Cache<String,String> cache = CacheBuilder.newBuilder()
.maximumSize(2)
.expireAfterAccess(3,TimeUnit.SECONDS)
.build();
cache.put("key1","value1");
int time = 1;
while(true) {
Thread.sleep(time*1000);
System.out.println(" sleep " + time++ + " In seconds key1 The value of is :" + cache.getIfPresent("key1"));
}
}
}adopt CacheBuilder Of expireAfterAccess Method , Specify if Cache More than... Objects are stored in 3 Seconds not accessed , It will expire .while The code in every sleep A span , Will visit once Cache Objects stored in the key1; Each visit key1 after , The next time sleep It's going to take a second longer . The results of the program are shown in the following figure , As can be seen from the results , When more than 3 Seconds not read key1 After object , The object will be automatically Cache Delete .

It can also be used at the same time expireAfterAccess and expireAfterWrite Method to specify the expiration time , In this case, as long as the object satisfies one of the two conditions , It will be automatically expired and deleted .
Guava Cache After the cache expires , It doesn't have to be cleaned up right away , Usually in Cache The whole is read a certain number of times and then cleaned up . This strategy is good for performance , If you want to force cleanup , You can manually call `Cache.cleanup()` Or use `ScheduledExecutorService` To complete regular cleaning .
5、 ... and 、 Weak reference
adopt weakKeys and weakValues Method , You can specify Cache Save only “ For cache records key and value The weak references ”. such , When no other strong reference points to key and value when ,key and value The object will be recycled by the garbage collector .
public class StudyGuavaCache {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Cache<String,Object> cache = CacheBuilder.newBuilder()
.maximumSize(2)
.weakValues()
.build();
Object value = new Object();
cache.put("key1",value);
value = new Object();// The original object no longer has a strong reference
System.gc();
System.out.println(cache.getIfPresent("key1"));
}
}The output of the above code is null. structure Cache when , adopt weakValues Method specification Cache Save only a weak reference to the record value . When value After the reference assigns a new object , There is no longer any strong reference to the original object .System.gc() After triggering garbage collection , The original object is removed .
6、 ... and 、 Show clear cache
call Cache Of invalidateAll or invalidate Method , Can display delete Cache Records in .invalidate Methods can only be deleted at a time Cache A record in , The received parameter is to delete the record key.invalidateAll Methods can be deleted in batches Cache Records in ; When no parameters are passed ,invalidateAll Method will clear Cache All the records in .invalidateAll You can also receive a Iterable Parameters of type , Parameter contains all the records to be deleted key value . The following code illustrates this .
public class StudyGuavaCache {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Cache<String,String> cache = CacheBuilder.newBuilder().build();
Object value = new Object();
cache.put("key1","value1");
cache.put("key2","value2");
cache.put("key3","value3");
List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();
list.add("key1");
list.add("key2");
cache.invalidateAll(list); // To remove in bulk list Middle all key Corresponding records
System.out.println(cache.getIfPresent("key1"));
System.out.println(cache.getIfPresent("key2"));
System.out.println(cache.getIfPresent("key3"));
}
}It can be seen that , The code constructs a collection list Used to save the record to be deleted key value , And then call invalidateAll Method batch delete key1 and key2 Corresponding records , only key3 The corresponding record has not been deleted .
7、 ... and 、 Remove the action listener
It can be for Cache Object to add a remove listener . such , When a record is deleted , This event can be sensed .
The following code is an example of using the remove action listener .
public class StudyGuavaCache {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
RemovalListener<String, String> listener = new RemovalListener<String, String>() {
public void onRemoval(RemovalNotification<String, String> notification) {
System.out.println("[" + notification.getKey() + ":" + notification.getValue() + "] is removed!");
}
};
Cache<String,String> cache = CacheBuilder.newBuilder()
.maximumSize(3)
.removalListener(listener)
.build();
Object value = new Object();
cache.put("key1","value1");
cache.put("key2","value2");
cache.put("key3","value3");
cache.put("key4","value3");
cache.put("key5","value3");
cache.put("key6","value3");
cache.put("key7","value3");
cache.put("key8","value3");
}
}removalListener Method is Cache A listener has been designated to remove , When there are records from Cache When it is deleted , Monitor listener You'll feel the event . The results of the program are shown in the following figure .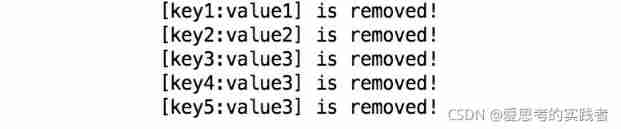
8、 ... and 、 Automatic loading
Cache Of get Method has two parameters , The first parameter is from Cache Get the record in key, The second record is a Callable object . When the cache already exists key The corresponding record is ,get Method directly returns key Corresponding records . If the cache does not contain key Corresponding records ,Guava Will start a thread to execute Callable Object call Method ,call The return value of the method will be used as “key Corresponding value ” Stored in the cache , And be get Method returns .
Here is a multi-threaded application Cache Examples of automatic loading :
public class StudyGuavaCache {
private static Cache<String,String> cache = CacheBuilder.newBuilder()
.maximumSize(3)
.build();
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
new Thread(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
System.out.println("thread1");
try {
String value = cache.get("key", new Callable<String>() {
public String call() throws Exception {
System.out.println("load1"); // Load data thread execution flag
Thread.sleep(1000); // Simulation load time
return "auto load by Callable";
}
});
System.out.println("thread1 " + value);
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}).start();
new Thread(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
System.out.println("thread2");
try {
String value = cache.get("key", new Callable<String>() {
public String call() throws Exception {
System.out.println("load2"); // Load data thread execution flag
Thread.sleep(1000); // Simulation load time
return "auto load by Callable";
}
});
System.out.println("thread2 " + value);
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}).start();
}
}In this code , Two threads share the same Cache object , Two threads call at the same time get Method to get the same key Corresponding value . because key The corresponding value does not exist , So both threads are in get Method block . Here in call Call in method Thread.sleep(1000), Simulation program from the external memory load data time consumption . The execution result of the code is shown in the figure below :

As can be seen from the results , Although two threads call at the same time get Method , But there's only one get Methods Callable Will be performed ( It didn't print out load2).Guava It can guarantee that when multiple threads access at the same time Cache One of them key when , If key The corresponding record does not exist ,Guava Only one thread will be started to execute get In the method Callable The task corresponding to the parameter , Load data to cache . When the data is loaded , In any thread get Methods will get key Corresponding value .
Nine 、 Statistics
It can be done to Cache shooting 、 Load data time and other information for statistics . In the build Cache Object time , adopt CacheBuilder Of recordStats Method , You can turn on the statistical information switch . When the switch is on ,Cache It will automatically count various operations of the cache , call Cache Of stats Method to view the statistical information .
The following code uses Cache Examples of Statistics .
public class StudyGuavaCache {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Cache<String,String> cache = CacheBuilder.newBuilder()
.maximumSize(3)
.recordStats() // Turn on the statistics switch
.build();
cache.put("key1","value1");
cache.put("key2","value2");
cache.put("key3","value3");
cache.put("key4","value4");
cache.getIfPresent("key1");
cache.getIfPresent("key2");
cache.getIfPresent("key3");
cache.getIfPresent("key4");
cache.getIfPresent("key5");
cache.getIfPresent("key6");
System.out.println(cache.stats()); // Get statistics
}
} The program execution result is shown in the figure below :![]() These statistics are crucial for adjusting cache settings . In applications with high performance requirements , These data should be closely watched .
These statistics are crucial for adjusting cache settings . In applications with high performance requirements , These data should be closely watched .
Ten 、LoadingCache
LoadingCache yes Cache Sub interface of , Compared with Cache, When from LoadingCache Read a specified key When recording , If the record does not exist , be LoadingCache The data loaded into the cache can be operated automatically .LoadingCache The interface is defined as follows :
public interface LoadingCache<K, V> extends Cache<K, V>, Function<K, V> {
V get(K key) throws ExecutionException;
V getUnchecked(K key);
ImmutableMap<K, V> getAll(Iterable<? extends K> keys) throws ExecutionException;
V apply(K key);
void refresh(K key);
@Override
ConcurrentMap<K, V> asMap();
}And build Cache Objects of type are similar to ,LoadingCache Objects of type are also passed through CacheBuilder Build . The difference is , Calling CacheBuilder Of build When the method is used , You have to pass a CacheLoader Parameters of type ,CacheLoader Of load Methods require us to provide concrete implementations . When calling LoadingCache Of get When the method is used , If there is no corresponding cache key The record of , be CacheLoader Medium load Method will be called automatically to load data from external storage ,“load Return value of method ” Will act as “key Corresponding value” Store in LoadingCache in , And from get Method returns .
The following code uses LoadingCache Examples of Statistics .
public class StudyGuavaCache {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException {
CacheLoader<String, String> loader = new CacheLoader<String, String> () {
public String load(String key) throws Exception {
Thread.sleep(1000); // Sleep 1s, Simulate loading data
System.out.println(key + " is loaded from a cacheLoader!");
return key + "'s value";
}
};
LoadingCache<String,String> loadingCache = CacheBuilder.newBuilder()
.maximumSize(3)
.build(loader);// Specify autoloader at build time
loadingCache.get("key1");
loadingCache.get("key2");
loadingCache.get("key3");
}
} The program execution result is shown in the figure below :
Reference resources :
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢

A detailed explanation of one of the causes of dead loop caused by array out of bounds in C language

Crawl Baidu Baipin dynamic page
Tutoriel de démarrage bladed (vidéo)

Solve cannot import name 'multiheadattention' from 'tensorflow keras. layers‘

How CSDN reports plagiarized articles

用 Keras/TensorFlow 2.9 创建深度学习模型的方法总结
空间几何

TypeScript-头文件使用细节

Training yolov4 CSP model using coco dataset

Development of sylixos SD device driver
随机推荐
Clipping and overlapping of YUV data
(resolved) pychart debug error -unicode decodeerror: 'UTF-8' codec can't decode byte 0xe8 in position 1023
Socket [5] - struct linker usage
TypeScript-类和接口、类和泛型、接口合并现象
Typescript interface and type alias similarities and differences
安卓初中级开发基础知识整理(面试自用)
Session and session management technology
TypeScript-类型保护
Storage of floating point in memory
Dameng database startup and shutdown
Process control: process waiting (recycling child processes)
Collation of open source modulation identification data set
C. Managing history (greedy / hashing / thinking / good questions)
DAMENG 用户管理
【 史上最全的ENSP【安装图解】!】
TypeScript-声明合并
JS learning basics document Write write a line of text in the page
860. 柠檬水找零
Study the Analects of entanglement
使用POSTMAN 测试firebase