当前位置:网站首页>typeScript的介绍与变量定义的基本类型
typeScript的介绍与变量定义的基本类型
2022-06-23 07:49:00 【wendyTan10】
(一)TypeScript的简介
认识typeScript
TypeScript官网:TypeScript is a typed superset of JavaScript that compiles to plain JavaScript.
GitHub说法:TypeScript is a superset of JavaScript that compiles to clean JavaScript output.
翻译一下:TypeScript是拥有类型的JavaScript超集,它可以编译成普通、干净、完整的JavaScript代码
理解官网的这句话:
- 就相对于
TypeScript(简称ts)是JavaScript(简称js)的加强版; - js所拥有的所有特性,ts全部支持;它紧随ECMAScript的标准,所以ES6、ES7、ES8等新语法标准,它都是支持的;
- 并且在语言层面上,不仅仅增加了类型约束,而且包括一些语法的扩展,比如枚举类型(Enum)、元组类型(Tuple)等;
- TypeScript在实现新特性的同时,总是保持和ES标准的同步甚至是领先;
- 并且TypeScript最终会被编译成JavaScript代码,所以你并不需要担心它的兼容性问题,在编译时也不需要借助于Babel这样的工具;
- 所以,我们可以把TypeScript理解成更加强大的JavaScript,不仅让JavaScript更加安全,而且给它带来了诸多好用的好用特性;
TypeScript的编译环境
TypeScript最终会被编译成JavaScript来运行,所以我们需要搭建对应的环境;
我们需要在电脑上安装TypeScript,这样就可以通过TypeScript的Compiler将其编译成JavaScript;
# 安装命令 npm install typescript -g
# 查看版本 tsc --version
TypeScript的运行环境
俩种解决方案来配置查看运行:
- 方式一:webpack的配置:点击翻看 coderwhy作者所写的文章
- 方式二:使用ts-node,直接运行;
安装ts-node:npm install ts-node -g
另外ts-node需要依赖 tslib 和 @types/node 两个包:npm install tslib @types/node -g
现在,我们可以直接通过 ts-node 来运行TypeScript的代码:ts-node math.ts
(二)变量的声明
在TypeScript中定义变量需要指定 标识符 的类型。 所以完整的声明格式如下:
// 根据定义的数据类型赋值
var/let/const 标识符: 数据类型 = 赋值;
const name:string = 'wendy';
上面说过是支持JavaScript的模式定义,也可不进行数据类型的添加,但typescript本身的特性帮助我们推断出对应的变量类型;
如下方的name起初赋值string类型后,不可更改为非string类型
(二)JavaScript和TypeScript的数据类型
JavaScript和TypeScript的数据类型之间的包含关系: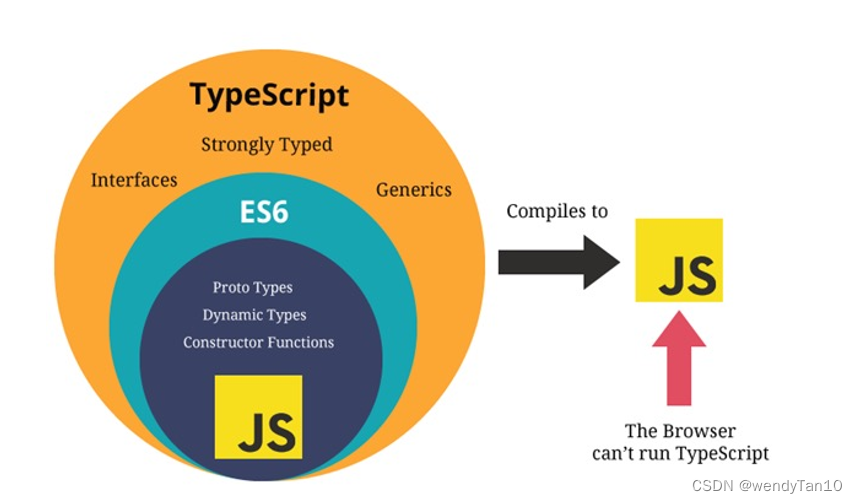
(1)基本的数据类型与定义:
- number类型;
- boolean类型;
- string类型;
- Array类型;
const list1:string[] = ['1', '22']; // 推荐使用 const list2:Array<string> = ['1', '22']; // 在react中时常会有<div></div>的写法,以免冲突 - Object类型;
- Symbol类型;
- null和undefined类型;
- any类型;
// any类型有点像一种讨巧的TypeScript手段,就是不定义类型,任何类型都可实现 let name:any = 'wendy'; name = 'Bond'; name = 14555; name = true; - unknown类型
在没有对它进行类型检查之前,// unknown是TypeScript中比较特殊的一种类型,它用于描述类型不确定的变量; // 相对于any ,只有在针对unknown进行类型安全检测之后,才可以允许执行特定的操作。 let score: unknown = 98; let num = Math.round(score); //errorubnknow类型的变量是不能进行任何操作的。
只有在针对unknown进行类型安全检测之后,才可以允许执行特定的操作;let score: unknown = 98; if(typeof score === "number") { let num = Math.round(score); // ok } - void类型
// 函数没有返回值的类型; function sum(num1: number, num2: number): void { console.log(num1 + num2); } - never类型
never 表示永远不会发生值的类型,比如一个无限循环或抛出错误的函数:// 提前 // 封装一个核心函数 function handleMessage(message: string | number | boolean) { switch (typeof message) { case 'string': console.log("string处理方式处理message") break; case 'number': console.log("number处理方式处理message") break case 'boolean': console.log("boolean处理方式处理message") break default: const check: never = message } } // 抛出错误的函数 function loopErr(): never { throw new Error(); } - tuple类型 - 元组类型
const tInfo: [string, number, number] = ["why", 18, 18]; const item1 = tInfo[0]; // why,并可知类型是string类型 const item2 = tInfo[1]; // 18,并可知类型是numbertuple和Array数组的区别:const info:(string|number)[] = ["why", 18, 18]; const item1 = info[0]; // 不能确定类型 const tInfo: [string, number, number] = ["why", 18, 18]; const item2 = tInfo[0]; // 一定时string类型
(2)类型定义的补充
自动推导类型:
// 给参数加上类型注解: num1: number, num2: number
// 给返回值加上类型注释: (): number
// 在开发中,通常情况下可以不写返回值的类型(自动推导)
function sum(num1: number, num2: number) {
return num1 + num2
}
sum(123, 321); // 推导出的类型是number
const names = ["abc", "cba", "nba"]
// item根据上下文的环境推导出来的, 这个时候可以不添加的类型注解
// 上下文中的函数: 可以不添加类型注解
names.forEach(function(item) {
console.log(item.split(""))
})
类型推导出item是string类型: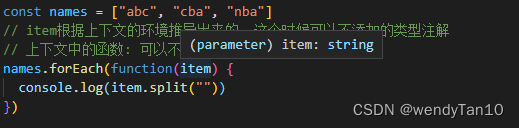
对象类型的定义:
// Point: x/y -> 对象类型
// {x: number, y: number}
function printPoint(point: {
x: number, y: number}) {
console.log(point.x);
console.log(point.y)
}
printPoint({
x: 123, y: 321})
可选类型的使用:?
// Point: x/y/z -> 对象类型
// {x: number, y: number, z?: number}
function printPoint(point: {
x: number, y: number, z?: number}) {
console.log(point.x)
console.log(point.y)
console.log(point.z)
}
printPoint({
x: 123, y: 321})
printPoint({
x: 123, y: 321, z: 111})
联合类型的使用: |
// number|string 联合类型
function printID(id: number|string|boolean) {
// 使用联合类型的值时, 需要特别的小心
// narrow: 缩小
if (typeof id === 'string') {
// TypeScript帮助确定id一定是string类型
console.log(id.toUpperCase())
} else {
console.log(id)
}
}
printID(123)
printID("abc")
printID(true)
可选类型与对象类型的关系:
// 当一个参数一个可选类型的时候, 这个参数等价于:类型|undefined 的联合类型
// message?: string 等同于 message: string | undefined
function foo(message?: string) {
console.log(message)
}
类型别名的使用,使用type的关键字去定义:
// type用于定义类型别名(type alias)
type IDType = string | number | boolean
type PointType = {
x: number
y: number
z?: number
}
function printId(id: IDType) {
}
function printPoint(point: PointType) {
}
(3)类型的断言使用:
- 类型断言
as();
类型断言用于将一个变量在编译阶段进行类型的强制改变,通常用于联合类型,any,及父子类之间的断言,通常这会发生在你清楚地知道一个实体具有比它现有类型更确切的类型;有两种书写的形式:value as type<type>value
let data : any = "Hello";
let len : number = (<string>data).length;
console.log(len);//输出5
len = (data as string).length;
console.log(len);//输出5
使用示例:
// 1.类型断言 as
const el = document.getElementById("why") as HTMLImageElement
el.src = "url地址"
// 2.另外案例: Person是Student的父类
class Person {
}
class Student extends Person {
studying() {
}
}
function sayHello(p: Person) {
(p as Student).studying()
}
const stu = new Student()
sayHello(stu)
// 3.了解: as any/unknown
const message = "Hello World"
const num: number = (message as unknown) as number
- 非空类型断言的使用:
!
// message? -> undefined | string
function printMessageLength(message?: string) {
// if (message) {
// console.log(message.length)
// }
// vue3源码
console.log(message!.length)
}
printMessageLength("aaaa")
printMessageLength("hello world")
- 可选链的使用:
?
// ? 代码非必传选项
type Person = {
name: string
friend?: {
name: string
age?: number,
girlFriend?: {
name: string
}
}
}
const info: Person = {
name: "why",
friend: {
name: "kobe",
girlFriend: {
name: "lily"
}
}
}
console.log(info.name)
// console.log(info.friend!.name)
console.log(info.friend?.name)
console.log(info.friend?.girlFriend?.name)
边栏推荐
- PHP file contains -ctf
- Deep learning ----- different methods to realize vgg16
- Markdown learning
- 【Try to Hack】ip地址
- Acwing第 56 场周赛【完结】
- openni.utils.OpenNIError: (OniStatus.ONI_STATUS_ERROR, b‘DeviceOpen using default: no devices found‘
- Using jetpack datastore for data storage
- Set接口和Set子实现类
- Hackers use new PowerShell backdoors in log4j attacks
- Acwing game 56 [End]
猜你喜欢

Implementation principle and source code analysis of ThreadPoolExecutor thread pool

Check the file through the port

Tensorboard的使用

开源软件、自由软件、Copyleft、CC都是啥,傻傻分不清楚?
![Vulnhub | DC: 4 | [combat]](/img/33/b7422bdb18f39e9eb55855dbf1d584.png)
Vulnhub | DC: 4 | [combat]

INT 104_ LEC 06

Openvino series 19 Openvino and paddleocr for real-time video OCR processing

AVL树的实现

值得反复回味的81句高人高语

QT project error: -1: error: cannot run compiler 'clang++' Output:mingw32-make. exe
随机推荐
List接口三个子实现类
深度学习------不同方法实现vgg16
Moodle e-learning platform fixes the session hijacking error that leads to pre authorized rce
Gif verification code analysis
生产环境服务器环境搭建+项目发布流程
transform的结构及用法
Using jetpack datastore for data storage
Acwing game 56 [End]
Quick sort + bubble sort + insert sort + select sort
Do not put files with garbled names into the CFS of NFS protocol
imperva-查找正则匹配超时的方法
配置ASMX无法访问
QT reading XML files using qdomdocument
11 字符串函数
openni.utils.OpenNIError: (OniStatus.ONI_STATUS_ERROR, b‘DeviceOpen using default: no devices found‘
For loop of go language foundation
[cross border e-commerce solutions] lighthouse will be used for pure IP expansion of new business - continuous efforts!
Hackers use new PowerShell backdoors in log4j attacks
vtk. JS left mouse button sliding to change window level and window width
Quickly delete the node in the code_ modules