当前位置:网站首页>Realizing deep learning framework from zero -- LSTM from theory to practice [practice]
Realizing deep learning framework from zero -- LSTM from theory to practice [practice]
2022-07-05 19:17:00 【Angry coke】
introduction
In line with “ Everything I can't create , I can't understand ” Thought , This series The article will be based on pure Python as well as NumPy Create your own deep learning framework from zero , The framework is similar PyTorch It can realize automatic derivation .
Deep understanding and deep learning , The experience of creating from scratch is very important , From an understandable point of view , Try not to use an external complete framework , Implement the model we want . This series The purpose of this article is through such a process , Let us grasp the underlying realization of deep learning , Instead of just being a switchman .
Last article in , We learned LSTM Theoretical part . And in RNN The actual combat part of , We saw how to achieve multi tier RNN And two way RNN. Again , What is achieved here LSTM It also supports multilayer and bidirectional .
LSTMCell
class LSTMCell(Module):
def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size: int, bias: bool = True) -> None:
super(LSTMCell, self).__init__()
# Combined x->input gate; x-> forget gate; x-> g ; x-> output gate Linear transformation of
self.input_trans = Linear(hidden_size, 4 * hidden_size, bias=bias)
# Combined h->input gate; h-> forget gate; h-> g ; h-> output gate Linear transformation of
self.hidden_trans = Linear(input_size, 4 * hidden_size, bias=bias)
def forward(self, x: Tensor, h: Tensor, c: Tensor) -> Tuple[Tensor, Tensor]:
# i: input gate
# f: forget gate
# o: output gate
# g: g_t
ifgo = self.input_trans(h) + self.hidden_trans(x)
ifgo = F.chunk(ifgo, 4, -1)
# Calculate three doors at one time And g_t
i, f, g, o = ifgo
c_next = F.sigmoid(f) * c + F.sigmoid(i) * F.tanh(g)
h_next = F.sigmoid(o) * F.tanh(c_next)
return h_next, c_next
In the implementation, I refer to the last reference article , take x and h Related linear transformations separate :
i t = Linear x i ( x t ) + Linear h i ( h t − 1 ) f t = Linear x f ( x t ) + Linear h f ( h t − 1 ) g t = Linear x g ( x t ) + Linear h g ( h t − 1 ) o t = Linear x o ( x t ) + Linear h o ( h t − 1 ) (1) \begin{aligned} i_t &= \text{Linear}^i_x(x_t) + \text{Linear}^i_h(h_{t-1}) \\ f_t &= \text{Linear}^f_x(x_t) + \text{Linear}^f_h(h_{t-1}) \\ g_t &= \text{Linear}^g_x(x_t) + \text{Linear}^g_h(h_{t-1}) \\ o_t &= \text{Linear}^o_x(x_t) + \text{Linear}^o_h(h_{t-1}) \\ \end{aligned} \tag{1} itftgtot=Linearxi(xt)+Linearhi(ht−1)=Linearxf(xt)+Linearhf(ht−1)=Linearxg(xt)+Linearhg(ht−1)=Linearxo(xt)+Linearho(ht−1)(1)
For example, formula ( 3 ) (3) (3) Of i t = σ ( U i h t − 1 + W i x t ) i_t = \sigma(U_ih_{t-1} + W_ix_t) it=σ(Uiht−1+Wixt) in σ \sigma σ The parameter part of can be changed to :
U i h t − 1 + W i x t ⇒ i t = Linear x i ( x t ) + Linear h i ( h t − 1 ) U_ih_{t-1} + W_ix_t \Rightarrow i_t = \text{Linear}^i_x(x_t) + \text{Linear}^i_h(h_{t-1}) Uiht−1+Wixt⇒it=Linearxi(xt)+Linearhi(ht−1)
Then we can combine similar linear transformations , For example, combination x t x_t xt Related linear transformation : Linear x i ( x t ) , Linear x f ( x t ) , Linear x g ( x t ) , Linear x o ( x t ) \text{Linear}^i_x(x_t),\text{Linear}^f_x(x_t),\text{Linear}^g_x(x_t),\text{Linear}^o_x(x_t) Linearxi(xt),Linearxf(xt),Linearxg(xt),Linearxo(xt) by :
self.input_trans = Linear(hidden_size, 4 * hidden_size, bias=bias)
Similarly ,hidden_trans Empathy . The reason for this is to speed up the calculation , We only need to do one linear operation , You can get four results .
adopt
ifgo = self.input_trans(h) + self.hidden_trans(x) \tag 2
The results of these four important values are obtained , But they are spliced into a tensor . And then use it
ifgo = F.chunk(ifgo, 4, -1)
Split them into tuples containing four values ,
i, f, g, o = ifgo
In this way, we get the parameter value in the corresponding function , Add the corresponding Sigmoid Function or Tanh Function can get the value we want .
Next, calculate c t c_t ct:
c t = σ ( f t ) ⊙ c t − 1 + σ ( i t ) ⊙ tanh ( g t ) (3) c_t = \sigma(f_t) \odot c_{t-1} + \sigma(i_t) \odot \tanh(g_t) \tag 3 ct=σ(ft)⊙ct−1+σ(it)⊙tanh(gt)(3)
The corresponding code :
c_next = F.sigmoid(f) * c + F.sigmoid(i) * F.tanh(g)
And then according to o t o_t ot and c t c_t ct Calculate hidden state h t h_t ht:
h t = σ ( o t ) ⊙ tanh ( c t ) (4) h_t = \sigma(o_t) \odot \tanh(c_t) \tag 4 ht=σ(ot)⊙tanh(ct)(4)
The corresponding code :
h_next = F.sigmoid(o) * F.tanh(c_next)
LSTM
With LSTMCell You can achieve complete LSTM 了 .
class LSTM(Module):
def __init__(self, input_size: int, hidden_size: int, batch_first: bool = False, num_layers: int = 1,
bidirectional: bool = False, dropout: float = 0):
super(LSTM, self).__init__()
self.num_layers = num_layers
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
self.batch_first = batch_first
self.bidirectional = bidirectional
# Multi tier support
self.cells = ModuleList([LSTMCell(input_size, hidden_size)] +
[LSTMCell(hidden_size, hidden_size) for _ in range(num_layers - 1)])
if self.bidirectional:
# Support two-way
self.back_cells = copy.deepcopy(self.cells)
self.dropout = dropout
if dropout:
# Dropout layer
self.dropout_layer = Dropout(dropout)
def _one_directional_op(self, input, cells, n_steps, hs, cs, reverse=False):
''' Args: input: Input [n_steps, batch_size, input_size] cells: Forward or reverse RNNCell Of ModuleList hs: cs: n_steps: step reverse: true reverse Returns: '''
output = []
for t in range(n_steps):
inp = input[t]
for layer in range(self.num_layers):
hs[layer], cs[layer] = cells[layer](inp, hs[layer], cs[layer])
inp = hs[layer]
if self.dropout and layer != self.num_layers - 1:
inp = self.dropout_layer(inp)
# Collect the output of the final layer
output.append(hs[-1])
output = F.stack(output) # (n_steps, batch_size, num_directions * hidden_size)
if reverse:
output = F.flip(output, 0) # Reverse the output time step dimension , Make time step t=0 On , It's the result of looking at the whole sequence .
if self.batch_first:
output = output.transpose((1, 0, 2))
h_n = F.stack(hs)
c_n = F.stack(cs)
return output, (h_n, c_n)
def forward(self, input: Tensor, state: Optional[Tuple[Tensor, Tensor]] = None):
''' Args: input: shape [n_steps, batch_size, input_size] if batch_first=False ; Otherwise shape [batch_size, n_steps, input_size] state: Tuples (h,c) num_directions = 2 if self.bidirectional else 1 h: [num_directions * num_layers, batch_size, hidden_size] c: [num_directions * num_layers, batch_size, hidden_size] Returns: num_directions = 2 if self.bidirectional else 1 output: (n_steps, batch_size, num_directions * hidden_size) if batch_first=False or (batch_size, n_steps, num_directions * hidden_size) if batch_first=True Contains the last layer of each time step ( Multi-storey RNN) Output h_t h_n: (num_directions * num_layers, batch_size, hidden_size) Contains the final hidden state c_n: (num_directions * num_layers, batch_size, hidden_size) Contains the final hidden state '''
h_0, c_0 = None, None
if state is not None:
h_0, c_0 = state
is_batched = input.ndim == 3
batch_dim = 0 if self.batch_first else 1
if not is_batched:
# Convert to batch size 1 The input of
input = input.unsqueeze(batch_dim)
if state is not None:
h_0 = h_0.unsqueeze(1)
c_0 = c_0.unsqueeze(1)
if self.batch_first:
batch_size, n_steps, _ = input.shape
input = input.transpose((1, 0, 2)) # take batch Put it in the middle dimension
else:
n_steps, batch_size, _ = input.shape
if state is None:
num_directions = 2 if self.bidirectional else 1
h_0 = Tensor.zeros((self.num_layers * num_directions, batch_size, self.hidden_size), dtype=input.dtype,
device=input.device)
c_0 = Tensor.zeros((self.num_layers * num_directions, batch_size, self.hidden_size), dtype=input.dtype,
device=input.device)
# Get the state of each layer
hs, cs = list(F.split(h_0)), list(F.split(c_0))
if not self.bidirectional:
# If it's one-way
output, (h_n, c_n) = self._one_directional_op(input, self.cells, n_steps, hs, cs)
else:
output_f, (h_n_f, c_n_f) = self._one_directional_op(input, self.cells, n_steps, hs[:self.num_layers],
cs[:self.num_layers])
output_b, (h_n_b, c_n_b) = self._one_directional_op(F.flip(input, 0), self.back_cells, n_steps,
hs[self.num_layers:], cs[self.num_layers:],
reverse=True)
output = F.cat([output_f, output_b], 2)
h_n = F.cat([h_n_f, h_n_b], 0)
c_n = F.cat([c_n_f, c_n_b], 0)
return output, (h_n, c_n)
In the implementation of multi-layer and bi-directional, and RNN Is essentially the same , Its input and output are somewhat different . This is from LSTM It's decided by the architecture of .
Part of speech tagging practice
Based on the above implementation LSTM To implement the part of speech tagging classification model , It is also called LSTM:
class LSTM(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, vocab_size: int, embedding_dim: int, hidden_dim: int, output_dim: int, n_layers: int,
dropout: float, bidirectional: bool = False):
super(LSTM, self).__init__()
self.embedding = nn.Embedding(vocab_size, embedding_dim)
self.rnn = nn.LSTM(embedding_dim, hidden_dim, batch_first=True, num_layers=n_layers, dropout=dropout,
bidirectional=bidirectional)
num_directions = 2 if bidirectional else 1
self.output = nn.Linear(num_directions * hidden_dim, output_dim)
def forward(self, input: Tensor, hidden: Tensor = None) -> Tensor:
embeded = self.embedding(input)
output, _ = self.rnn(embeded, hidden) # pos tag The task takes advantage of all the time steps output
outputs = self.output(output)
log_probs = F.log_softmax(outputs, axis=-1)
return log_probs
Process and RNN Similar to , The training code is as follows :
embedding_dim = 128
hidden_dim = 128
batch_size = 32
num_epoch = 10
n_layers = 2
dropout = 0.2
# Load data
train_data, test_data, vocab, pos_vocab = load_treebank()
train_dataset = RNNDataset(train_data)
test_dataset = RNNDataset(test_data)
train_data_loader = DataLoader(train_dataset, batch_size=batch_size, collate_fn=train_dataset.collate_fn, shuffle=True)
test_data_loader = DataLoader(test_dataset, batch_size=batch_size, collate_fn=test_dataset.collate_fn, shuffle=False)
num_class = len(pos_vocab)
# Load model
device = cuda.get_device("cuda:0" if cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
model = LSTM(len(vocab), embedding_dim, hidden_dim, num_class, n_layers, dropout, bidirectional=True)
model.to(device)
# Training process
nll_loss = NLLLoss()
optimizer = SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.1)
model.train() # Make sure that... Is applied dropout
for epoch in range(num_epoch):
total_loss = 0
for batch in tqdm(train_data_loader, desc=f"Training Epoch {
epoch}"):
inputs, targets, mask = [x.to(device) for x in batch]
log_probs = model(inputs)
loss = nll_loss(log_probs[mask], targets[mask]) # adopt bool choice ,mask Part does not need to be calculated
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
total_loss += loss.item()
print(f"Loss: {
total_loss:.2f}")
# Testing process
acc = 0
total = 0
model.eval() # Unwanted dropout
for batch in tqdm(test_data_loader, desc=f"Testing"):
inputs, targets, mask = [x.to(device) for x in batch]
with no_grad():
output = model(inputs)
acc += (output.argmax(axis=-1).data == targets.data)[mask.data].sum().item()
total += mask.sum().item()
# The accuracy of the output on the test set
print(f"Acc: {
acc / total:.2f}")
Output :
Loss: 102.51
Acc: 0.70
Same configuration , The accuracy on the test set is also 70%, Do you need more batches .
Here's a demonstration , Only trained. 10 Lots .
Reference resources
边栏推荐
- Applet modification style (placeholder, checkbox style)
- #夏日挑战赛#数据库学霸笔记,考试/面试快速复习~
- Can Leica capture the high-end market offered by Huawei for Xiaomi 12s?
- You can have both fish and bear's paw! Sky wing cloud elastic bare metal is attractive!
- Mathematical modeling of oil pipeline layout MATLAB, mathematical model of oil pipeline layout
- JS解力扣每日一题(十二)——556. 下一个更大元素 III(2022-7-3)
- How to quickly advance automated testing? Listen to the personal feelings of the three bat test engineers
- 100million single men and women supported an IPO with a valuation of 13billion
- Debezium系列之:postgresql从偏移量加载正确的最后一次提交 LSN
- Go语言学习教程(十五)
猜你喜欢
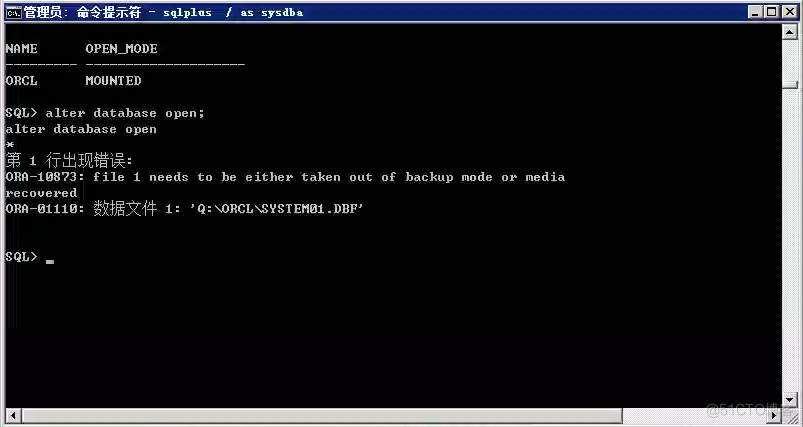
Oracle故障处理:Ora-10873:file * needs to be either taken out of backup or media recovered
Why can't Bi software do correlation analysis? Take you to analyze

Oracle fault handling: ora-10873:file * needs to be either taken out of backup or media recovered
Analysis of postman core functions - parameterization and test report
Hiengine: comparable to the local cloud native memory database engine

14、用户、组和权限(14)
Fuzor 2020軟件安裝包下載及安裝教程
Password reset of MariaDB root user and ordinary user
Tianyi cloud understands enterprise level data security in this way

Fuzor 2020 software installation package download and installation tutorial
随机推荐
Debezium系列之:解析默认值字符集
Explain in detail the functions and underlying implementation logic of the groups sets statement in SQL
Mathematical modeling of oil pipeline layout MATLAB, mathematical model of oil pipeline layout
2022 the most complete Tencent background automation testing and continuous deployment practice in the whole network [10000 words]
uniapp获取微信头像和昵称
After the company went bankrupt, the blackstones came
Go语言 | 01 WSL+VSCode环境搭建避坑指南
How MySQL queries and modifies JSON data
How to convert word into PDF? Word to PDF simple way to share!
Android面试,android音视频开发
The easycvr authorization expiration page cannot be logged in. How to solve it?
JAD installation, configuration and integration idea
HiEngine:可媲美本地的云原生内存数据库引擎
Oracle date format conversion to_ date,to_ char,to_ Timestamp mutual conversion
从零实现深度学习框架——LSTM从理论到实战【实战】
数据库 逻辑处理功能
Shang Silicon Valley Shang preferred project tutorial release
Oracle故障处理:Ora-10873:file * needs to be either taken out of backup or media recovered
#夏日挑战赛#数据库学霸笔记,考试/面试快速复习~
Django使用mysqlclient服务连接并写入数据库的操作过程