当前位置:网站首页>What is the forkjoin framework in the concurrent programming series?
What is the forkjoin framework in the concurrent programming series?
2022-07-01 15:43:00 【51CTO】
What is concurrent programming ForkJoin frame ?
1、 What is? ForkJoin frame
ForkJoin The frame is java Of JUC It's in the bag , Used to handle some heavy tasks , Will divide this big task into several small tasks , After multiple small tasks are processed, the results will be summarized to Result, It embodies a kind of “ Divide and rule ” Thought . First step , Split fork Mission , Divide large tasks into small tasks ; The second step , Merger join, The processing results of small tasks will be merged into one result .
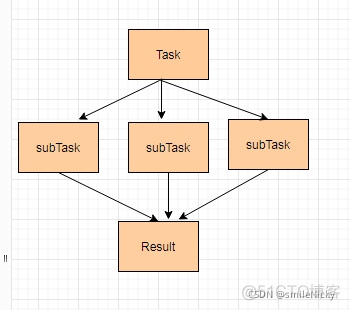
Insert picture description here
2、ForkJoinTask
ForkJoinTask yes ForkJoin Tasks provided by the framework API,ForkJoinTask Is an abstract class , There are two main implementation classes ,RecursiveTask and RecursiveAction, among RecursiveTask and RecursiveAction The main difference is ,RecursiveAction no return value , and RecursiveTask There is a return value

Insert picture description here
3、ForkJoinPool
ForkJoinPool Class is forkjoin The thread pool implementation of the framework , be based on ExecutorService Interface . This thread pool is jdk1.7 Just joined in , For managing threads , perform forkjoin The task of . For the use of thread pools , We use ThreadPoolExecutor More , Can be in idea Take a look inside uml Class diagram , It can be seen that ForkJoinPool and ThreadPoolExecutor Achieve almost .

Insert picture description here
Several important parameters :
- parallelism: Parallelism , Parallel execution threads , You can specify , Or not , Not specified , It's based on cpu The core creates available threads
- ForkJoinWorkerThreadFactory: Create a factory implementation of threads
- UncaughtExceptionHandler : Callback processing for unknown exception interrupt
- asyncMode: Asynchronous or not , The default is false
When using , Can be created directly ForkJoinPool, It's OK not to pass on the parameters , If you don't pass the parameters , The number of thread parallelism specified by default is Runtime.getRunTime().availableProcessors();, Express basis cpu Number of threads available for core creation
It can also be used to pass parameters , Specifies the degree of parallelism public ForkJoinPool(int parallelism), parallelism Parallelism , Execute several threads in parallel
take forkjoin Add tasks to FrokJoinPool There are several ways to thread pool
- execute(): Call its fork Method splits work between multiple threads .
- invoke(): stay ForkJoinPool Call... On the thread pool invoke Method
- submit(): Return to one Future object ,Future Can be monitored , After the task is completed, the result is returned
4、 Print Fibonacci series
ForkJoin The framework can be used in some recursive traversal scenarios , For Fibonacci series , You can be familiar with , Because sometimes I often ask , The characteristic of Fibonacci sequence is that the result of the last term is equal to the sum of the first two terms
package com.example.concurrent.forkjoin;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.ForkJoinPool;
import java.util.concurrent.ForkJoinTask;
import java.util.concurrent.RecursiveTask;
/**
* <pre>
* Fibonacci sequence
* </pre>
* <p>
* <pre>
* @author nicky.ma
* Modify the record
* Revised version : Modifier : modification date : 2021/10/12 16:22 Modify the content :
* </pre>
*/
public class Fibonacci extends RecursiveTask<Integer>{
private int n;
public Fibonacci(int n) {
this.n = n;
}
@Override
protected Integer compute() {
if (n <= 1)
return n;
Fibonacci f1 = new Fibonacci(n - 1);
f1.fork();
Fibonacci f2 = new Fibonacci(n - 2);
f2.fork();
return f1.join() + f2.join();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
ForkJoinPool pool = new ForkJoinPool();
for (int i = 0; i< 10; i++) {
ForkJoinTask task = pool.submit(new Fibonacci(i));
System.out.println(task.get());
}
}
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
- 29.
- 30.
- 31.
- 32.
- 33.
- 34.
- 35.
- 36.
- 37.
- 38.
- 39.
- 40.
- 41.
- 42.
- 43.
- 44.
- 45.
5、ForkJoin Merge sort
Interview questions : Quickly sort an array with a length of millions
difficulty : You can use merge sort , How do multithreads organize and implement merge sorting
package com.example.concurrent.forkjoin;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.ForkJoinPool;
import java.util.concurrent.RecursiveAction;
/**
* <pre>
* Large array sort
* </pre>
* <p>
* <pre>
* @author mazq
* Modify the record
* Revised version : Modifier : modification date : 2021/10/12 17:04 Modify the content :
* </pre>
*/
public class ArraySortTask extends RecursiveAction{
final long[] array; final int lo, hi;
ArraySortTask(long[] array, int lo, int hi) {
this.array = array; this.lo = lo; this.hi = hi;
}
ArraySortTask(long[] array) { this(array, 0, array.length); }
@Override
protected void compute() {
if (hi - lo < THRESHOLD)
// Less than threshold , Use Arrays.sort Quick line up
sortSequentially(lo, hi);
else {
/* Merge sort */
// Median value
int mid = (lo + hi) >>> 1;
// Split the task
invokeAll(new ArraySortTask(array, lo, mid),
new ArraySortTask(array, mid, hi));
// The result of amalgamation
merge(lo, mid, hi);
}
}
// implementation details follow:
static final int THRESHOLD = 1000;
void sortSequentially(int lo, int hi) {
Arrays.sort(array, lo, hi);
}
void merge(int lo, int mid, int hi) {
long[] buf = Arrays.copyOfRange(array, lo, mid);
for (int i = 0, j = lo, k = mid; i < buf.length; j++)
array[j] = (k == hi || buf[i] < array[k]) ?
buf[i++] : array[k++];
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
int size = 10_000;
long[] array = new long[size];
Random random = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i< size; i++) {
array[i] = random.nextInt();
}
ForkJoinPool forkJoinPool = new ForkJoinPool();
ArraySortTask task = new ArraySortTask(array , 0 , size);
forkJoinPool.submit(task);
task.get();
for (long a : array) {
System.out.println(a);
}
}
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
- 29.
- 30.
- 31.
- 32.
- 33.
- 34.
- 35.
- 36.
- 37.
- 38.
- 39.
- 40.
- 41.
- 42.
- 43.
- 44.
- 45.
- 46.
- 47.
- 48.
- 49.
- 50.
- 51.
- 52.
- 53.
- 54.
- 55.
- 56.
- 57.
- 58.
- 59.
- 60.
- 61.
- 62.
- 63.
- 64.
- 65.
- 66.
- 67.
- 68.
- 69.
- 70.
- 71.
- 72.
- 73.
- 74.
- 75.
Reference material
边栏推荐
- Wechat applet 01 bottom navigation bar settings
- 微服务追踪SQL(支持Isto管控下的gorm查询追踪)
- [stm32-usb-msc problem help] stm32f411ceu6 (Weact) +w25q64+usb-msc flash uses SPI2 to read out only 520kb
- Zhang Chi's class: several types and differences of Six Sigma data
- 她就是那个「别人家的HR」|ONES 人物
- 跨平台应用开发进阶(二十四) :uni-app实现文件下载并保存
- 工厂高精度定位管理系统,数字化安全生产管理
- SAP s/4hana: one code line, many choices
- 微信小程序02-轮播图实现与图片点击跳转
- 【300+精选大厂面试题持续分享】大数据运维尖刀面试题专栏(三)
猜你喜欢

Survey of intrusion detection systems:techniques, datasets and challenges

《QT+PCL第六章》点云配准icp系列2

【STM32-USB-MSC问题求助】STM32F411CEU6 (WeAct)+w25q64+USB-MSC Flash用SPI2 读出容量只有520KB

求求你们,别再刷 Star 了!这跟“爱国”没关系!
《性能之巅第2版》阅读笔记(五)--file-system监测
STM32ADC模拟/数字转换详解
Raytheon technology rushes to the Beijing stock exchange and plans to raise 540million yuan
![[one day learning awk] conditions and cycles](/img/e6/c96a4fd6ced9b492e70a06004f5159.png)
[one day learning awk] conditions and cycles
Don't ask me again why MySQL hasn't left the index? For these reasons, I'll tell you all

微信小程序02-轮播图实现与图片点击跳转
随机推荐
【目标跟踪】|模板更新 时间上下文信息(UpdateNet)《Learning the Model Update for Siamese Trackers》
三星率先投产3nm芯片,上海应届硕士生可直接落户,南开成立芯片科学中心,今日更多大新闻在此...
张驰咨询:家电企业用六西格玛项目减少客户非合理退货案例
Some abilities can't be learned from work. Look at this article, more than 90% of peers
SAP CRM organization Model(组织架构模型)自动决定的逻辑分析
综述 | 激光与视觉融合SLAM
go-zero实战demo(一)
做空蔚来的灰熊,以“碰瓷”中概股为生?
Phpcms background upload picture button cannot be clicked
华为发布HCSP-Solution-5G Security人才认证,助力5G安全人才生态建设
将ABAP On-Premises系统连接到中央检查系统以进行自定义代码迁移
vim 从嫌弃到依赖(22)——自动补全
入侵检测模型(An Intrusion-Detection Model)
#夏日挑战赛# HarmonyOS canvas实现时钟
Returning to the top of the list, the ID is still weak
Tableapi & SQL and MySQL grouping statistics of Flink
Redis seckill demo
Don't ask me again why MySQL hasn't left the index? For these reasons, I'll tell you all
张驰课堂:六西格玛数据的几种类型与区别
TensorFlow团队:我们没被抛弃
