当前位置:网站首页>二叉树相关问题2
二叉树相关问题2
2022-06-27 18:05:00 【无敌的神龙战士】
文章目录
105. 从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
给定两个整数数组 preorder 和 inorder ,其中 preorder 是二叉树的先序遍历, inorder 是同一棵树的中序遍历,请构造二叉树并返回其根节点。
示例 1:
输入: preorder = [3,9,20,15,7], inorder = [9,3,15,20,7]
输出: [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
unordered_map<int, int> map;
public:
TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& preorder, vector<int>& inorder) {
for(int i = 0; i < inorder.size(); ++i){
map[inorder[i]] = i;
}
int len = preorder.size();
return help(preorder, inorder, 0, len - 1, 0, len - 1);
}
TreeNode *help(vector<int> &preorder, vector<int> &inorder, int p_left, int p_right, int i_left, int i_right){
if(p_left > p_right){
return nullptr;
}
//前序遍历根节点的位置
int p_root = p_left;
//中序遍历根节点的位置
int i_root = map[preorder[p_root]];
//构造根节点
TreeNode *root = new TreeNode(inorder[i_root]);
//左边子树的长度
int left_size = i_root - i_left;
root->left = help(preorder, inorder, p_left + 1, p_root + left_size, i_left, i_root - 1);
root->right = help(preorder, inorder, p_root + left_size + 1, p_right, i_root + 1, i_right);
return root;
}
};
106. 从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
给定两个整数数组 inorder 和 postorder ,其中 inorder 是二叉树的中序遍历, postorder 是同一棵树的后序遍历,请你构造并返回这颗 二叉树 。
示例 1:
输入:inorder = [9,3,15,20,7], postorder = [9,15,7,20,3]
输出:[3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
unordered_map<int, int> map;
public:
TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& inorder, vector<int>& postorder) {
for(int i = 0; i < inorder.size(); ++i){
map[inorder[i]] = i;
}
int len = inorder.size();
return help(inorder, postorder, 0, len - 1, 0, len - 1);
}
TreeNode* help(vector<int> &inorder, vector<int> &postorder, int i_left, int i_right, int p_left, int p_right){
if(i_left > i_right || p_left > p_right){
return nullptr;
}
int p_root = p_right;
int i_root = map[postorder[p_root]];
int left_size = i_root - i_left;
TreeNode *root = new TreeNode(inorder[i_root]);
root->left = help(inorder, postorder, i_left, i_root - 1, p_left, p_left + left_size -1);
root->right = help(inorder, postorder, i_root + 1, i_right, p_left + left_size, p_right - 1);
return root;
}
};
654. 最大二叉树
给定一个不重复的整数数组 nums 。 最大二叉树 可以用下面的算法从 nums 递归地构建:
创建一个根节点,其值为 nums 中的最大值。
递归地在最大值 左边 的 子数组前缀上 构建左子树。
递归地在最大值 右边 的 子数组后缀上 构建右子树。
返回 nums 构建的 最大二叉树 。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [3,2,1,6,0,5]
输出:[6,3,5,null,2,0,null,null,1]
解释:递归调用如下所示:
- [3,2,1,6,0,5] 中的最大值是 6 ,左边部分是 [3,2,1] ,右边部分是 [0,5] 。
- [3,2,1] 中的最大值是 3 ,左边部分是 [] ,右边部分是 [2,1] 。
- 空数组,无子节点。
- [2,1] 中的最大值是 2 ,左边部分是 [] ,右边部分是 [1] 。
- 空数组,无子节点。
- 只有一个元素,所以子节点是一个值为 1 的节点。
- [0,5] 中的最大值是 5 ,左边部分是 [0] ,右边部分是 [] 。
- 只有一个元素,所以子节点是一个值为 0 的节点。
- 空数组,无子节点。
- [3,2,1] 中的最大值是 3 ,左边部分是 [] ,右边部分是 [2,1] 。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* constructMaximumBinaryTree(vector<int>& nums) {
int len = nums.size();
return help(nums, 0, len);
}
TreeNode *help(vector<int> &nums, int left, int right){
if(left >= right){
return nullptr;
}
int max_value_index = left;
for(int i = left; i < right; ++i){
if(nums[i] > nums[max_value_index]){
max_value_index = i;
}
}
TreeNode *node = new TreeNode(nums[max_value_index]);
node->left = help(nums, left, max_value_index);
node->right = help(nums, max_value_index + 1, right);
return node;
}
};
617. 合并二叉树
给你两棵二叉树: root1 和 root2 。
想象一下,当你将其中一棵覆盖到另一棵之上时,两棵树上的一些节点将会重叠(而另一些不会)。你需要将这两棵树合并成一棵新二叉树。合并的规则是:如果两个节点重叠,那么将这两个节点的值相加作为合并后节点的新值;否则,不为 null 的节点将直接作为新二叉树的节点。
返回合并后的二叉树。
注意: 合并过程必须从两个树的根节点开始。
示例 1:
输入:root1 = [1,3,2,5], root2 = [2,1,3,null,4,null,7]
输出:[3,4,5,5,4,null,7]
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* mergeTrees(TreeNode* root1, TreeNode* root2) {
if(root1 == nullptr){
return root2;
}
if(root2 == nullptr){
return root1;
}
root1->val += root2->val;
root1->left = mergeTrees(root1->left, root2->left);
root1->right = mergeTrees(root1->right, root2->right);
return root1;
}
};
700. 二叉搜索树中的搜索
给定二叉搜索树(BST)的根节点 root 和一个整数值 val。
你需要在 BST 中找到节点值等于 val 的节点。 返回以该节点为根的子树。 如果节点不存在,则返回 null 。
示例 1:
输入:root = [4,2,7,1,3], val = 2
输出:[2,1,3]
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
TreeNode *node = new TreeNode;
public:
TreeNode* searchBST(TreeNode* root, int val) {
if(root == nullptr){
return root;
}
if(root->val == val){
return root;
}
if(root->val > val){
return searchBST(root->left, val);
} else if(root->val < val){
return searchBST(root->right, val);
}
return nullptr;
}
};
98. 验证二叉搜索树
给你一个二叉树的根节点 root ,判断其是否是一个有效的二叉搜索树。
有效 二叉搜索树定义如下:
节点的左子树只包含 小于 当前节点的数。
节点的右子树只包含 大于 当前节点的数。
所有左子树和右子树自身必须也是二叉搜索树。
示例 1:
输入:root = [2,1,3]
输出:true
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
vector<int> res;
public:
bool isValidBST(TreeNode* root) {
help(root);
for(int i = 0; i < res.size() - 1; ++i){
if(res[i] >= res[i + 1]){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
void help(TreeNode *root){
if(!root){
return;
}
help(root->left);
res.push_back(root->val);
help(root->right);
return;
}
};
530. 二叉搜索树的最小绝对差
给你一个二叉搜索树的根节点 root ,返回 树中任意两不同节点值之间的最小差值 。
差值是一个正数,其数值等于两值之差的绝对值。
示例 1:
输入:root = [4,2,6,1,3]
输出:1
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
vector<int> res;
public:
int getMinimumDifference(TreeNode* root) {
help(root);
int _min = INT_MAX;
for(int i = 0; i < res.size() - 1; ++i){
if(res[i + 1] - res[i] < _min){
_min = res[i + 1] - res[i];
}
}
return _min;
}
void help(TreeNode *root){
if(root == nullptr){
return;
}
help(root->left);
res.push_back(root->val);
help(root->right);
}
};
501. 二叉搜索树中的众数
给你一个含重复值的二叉搜索树(BST)的根节点 root ,找出并返回 BST 中的所有 众数(即,出现频率最高的元素)。
如果树中有不止一个众数,可以按 任意顺序 返回。
假定 BST 满足如下定义:
结点左子树中所含节点的值 小于等于 当前节点的值
结点右子树中所含节点的值 大于等于 当前节点的值
左子树和右子树都是二叉搜索树
示例 1:
输入:root = [1,null,2,2]
输出:[2]
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
unordered_map<int, int> map;
public:
bool static cmp(const pair<int, int> &a, const pair<int, int> &b){
return a.second > b.second;
}
vector<int> findMode(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> res;
help(root, res);
// for(auto it = map.begin())
vector<pair<int, int>> vec(map.begin(), map.end());
sort(vec.begin(), vec.end(), cmp);
res.push_back(vec[0].first);
for(int i = 1; i < vec.size(); ++i){
if(vec[i].second == vec[0].second){
res.push_back(vec[i].first);
}
}
return res;
}
void help(TreeNode *root, vector<int> &res){
if(root == nullptr){
return;
}
help(root->left, res);
// res.push_back(root->val);
map[root->val]++;
help(root->right, res);
}
};
236. 二叉树的最近公共祖先
给定一个二叉树, 找到该树中两个指定节点的最近公共祖先。
百度百科中最近公共祖先的定义为:“对于有根树 T 的两个节点 p、q,最近公共祖先表示为一个节点 x,满足 x 是 p、q 的祖先且 x 的深度尽可能大(一个节点也可以是它自己的祖先)。”
示例 1:
输入:root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], p = 5, q = 1
输出:3
解释:节点 5 和节点 1 的最近公共祖先是节点 3 。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {
//如果找到p节点或者q节点就返回
if(root == q || root == p || root == NULL){
return root;
}
TreeNode *left = lowestCommonAncestor(root->left, p, q);
TreeNode *right = lowestCommonAncestor(root->right, p, q);
if(left != NULL && right != NULL){
return root;
}
if(left == NULL && right != NULL){
return right;
} else if(left != NULL && right == NULL){
return left;
} else {
return NULL;
}
}
};
235. 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先
给定一个二叉搜索树, 找到该树中两个指定节点的最近公共祖先。
百度百科中最近公共祖先的定义为:“对于有根树 T 的两个结点 p、q,最近公共祖先表示为一个结点 x,满足 x 是 p、q 的祖先且 x 的深度尽可能大(一个节点也可以是它自己的祖先)。”
例如,给定如下二叉搜索树: root = [6,2,8,0,4,7,9,null,null,3,5]
示例 1:
输入: root = [6,2,8,0,4,7,9,null,null,3,5], p = 2, q = 8
输出: 6
解释: 节点 2 和节点 8 的最近公共祖先是 6。
示例 2:
输入: root = [6,2,8,0,4,7,9,null,null,3,5], p = 2, q = 4
输出: 2
解释: 节点 2 和节点 4 的最近公共祖先是 2, 因为根据定义最近公共祖先节点可以为节点本身。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {
if(root == p || root == q || root == NULL){
return root;
}
TreeNode *left = lowestCommonAncestor(root->left, p, q);
TreeNode *right = lowestCommonAncestor(root->right, p, q);
if(left != NULL && right != NULL){
return root;
}
if(left == NULL && right != NULL){
return right;
} else if(left != NULL && right == NULL){
return left;
} else {
return NULL;
}
}
};
701. 二叉搜索树中的插入操作
给定二叉搜索树(BST)的根节点 root 和要插入树中的值 value ,将值插入二叉搜索树。 返回插入后二叉搜索树的根节点。 输入数据 保证 ,新值和原始二叉搜索树中的任意节点值都不同。
注意,可能存在多种有效的插入方式,只要树在插入后仍保持为二叉搜索树即可。 你可以返回 任意有效的结果 。
示例 1:
输入:root = [4,2,7,1,3], val = 5
输出:[4,2,7,1,3,5]
解释:另一个满足题目要求可以通过的树是:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* insertIntoBST(TreeNode* root, int val) {
if(root == nullptr){
TreeNode *node = new TreeNode(val);
return node;
}
if(val < root->val){
root->left = insertIntoBST(root->left, val);
}
if(val > root->val){
root->right = insertIntoBST(root->right, val);
}
return root;
}
};
边栏推荐
- Longitude and latitude analysis
- 1028 List Sorting
- Batch insert data using MySQL bulkloader
- 网络上开户买股票是否安全呢?刚接触股票,不懂求指导
- Bit. Store: long bear market, stable stacking products may become the main theme
- Cdga | what is the core of digital transformation in the transportation industry?
- Function key input experiment based on stm32f103zet6 Library
- Manage rust project through cargo
- 刷题记录:Easy 数组(持续更新)
- 1023 Have Fun with Numbers
猜你喜欢

数组练习 后续补充

Connection integration development theme month | drivers of enterprise master data governance

SQL Server - window function - solve the problem of filtering consecutive n records

【bug】联想小新出现问题,你的PIN不可用。

Array exercises follow up
GIS遥感R语言学习看这里
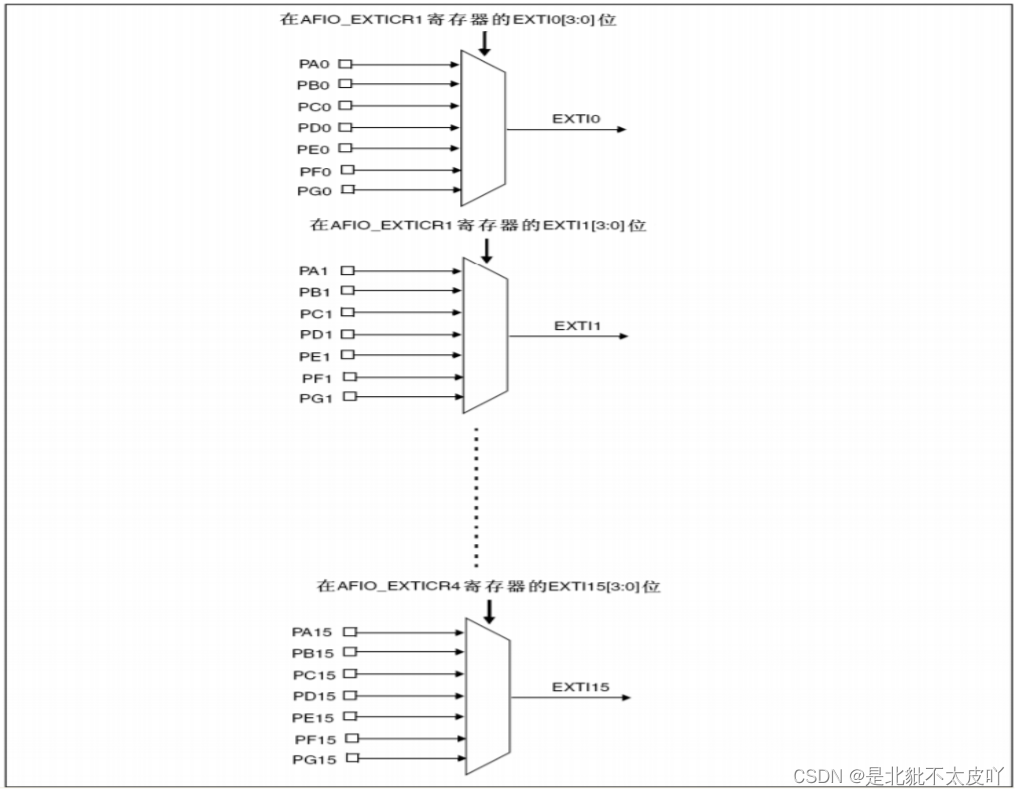
External interrupt experiment based on stm32f103zet6 library function

GIS remote sensing R language learning see here

MySQL beginner benefits

UE4:Build Configuration和Config的解释
随机推荐
Rust 中的枚举和控制流运算
Determine whether a variable is an array or an object?
External interrupt experiment based on stm32f103zet6 library function
The Fifth Discipline: the art and practice of learning organization
UE4:Build Configuration和Config的解释
这个是和数据采集一样,可以定义一个参数为上个月或者前一天,然后在sql中使用这个参数吗?
1028 List Sorting
数组练习 后续补充
Observable, reliable: the first shot of cloudops series Salon of cloud automation operation and maintenance
GIS remote sensing R language learning see here
运算符的基础知识
Manage rust project through cargo
MASS幸运哈希游戏系统开发丨冲突解决方法(代码分析)
shell脚本常用命令(三)
【云驻共创】 什么是信息化?什么是数字化?这两者有什么联系和区别?
Code and principle of RANSAC
OpenSSL client programming: SSL session failure caused by an obscure function
指针和结构体
华大单片机KEIL报错_WEAK的解决方案
Doctoral Dissertation of the University of Toronto - training efficiency and robustness in deep learning