当前位置:网站首页>SQL Server - window function - solve the problem of filtering consecutive n records
SQL Server - window function - solve the problem of filtering consecutive n records
2022-06-27 19:53:00 【Lazy Ethan】
Summary
When we are developing an application system to process various reports , Sometimes the temperature is lower than for several consecutive days 0 degree , Similar requirements for continuous login to the system many times in a day . This paper mainly introduces how to use SQL Server Window function in , To solve these complex query problems .
In this paper, two examples will be used to illustrate .
Code and Implementation
Statistics of continuous login in one day 3 Secondary users
Build the predicative sentence as follows :
if object_id('login_details') is not null
drop table login_details;
create table login_details(
login_id int primary key,
user_name varchar(50) not null,
login_date date
);
The login log contains the login Id, User name and login date , among login_id It's the primary key .
See Appendix for data initialization code .
We need to count the user names and dates of those who log in three or more times in a day . Continuous login Id continuity .
The code is as follows :
;WITH DUPICATE_3 AS (
SELECT
ld.[login_id], ld.[user_name], ld.[login_date],
CASE
WHEN
ld.[user_name] = LEAD(ld.[user_name]) OVER(PARTITION BY ld.[login_date] ORDER BY ld.[login_id ])
AND
ld.[user_name] = LEAD(ld.[user_name],2) OVER(PARTITION BY ld.[login_date] ORDER BY ld.[login_id ])
THEN 1
WHEN
ld.[user_name] = LAG(ld.[user_name]) OVER(PARTITION BY ld.[login_date] ORDER BY ld.[login_id ])
AND
ld.[user_name] = LEAD(ld.[user_name]) OVER(PARTITION BY ld.[login_date] ORDER BY ld.[login_id ])
THEN 1
WHEN
ld.[user_name] = LAG(ld.[user_name]) OVER(PARTITION BY ld.[login_date] ORDER BY ld.[login_id ])
AND
ld.[user_name] = LAG(ld.[user_name],2) OVER(PARTITION BY ld.[login_date] ORDER BY ld.[login_id ])
THEN 1
END AS TAG
FROM [login_details] ld
)
,DUPICATE_FILTER AS(
SELECT DISTINCT d.[user_name], d.[login_date]
FROM DUPICATE_3 d WHERE d.TAG = 1
)
SELECT
d4.[user_name],d4.login_date,
COUNT(d4.[user_name]) AS login_time
FROM DUPICATE_FILTER d4
LEFT JOIN DUPICATE_3 d3
ON d4.login_date = d3.login_date AND d4.[user_name] = d3.[user_name]
GROUP BY d4.[user_name],d4.login_date
- Avoid nested queries , Define a DIPICATE_3 Of CTE. The CTE It mainly generates a tag column TAG , If you log in three or more times a day , Then the column is 1, Other cases should be classified as 0.
- Through window analysis function LEAD/LAG, Data analysis . Group by date , Each group is logged in by Id Sort ,
a. If the user name of the current record and the next , The user name of the next item is the same , Then the record is marked as 1;
b. If the current user name and the previous , The user names in the next entry are the same , Then the record is marked as 1;
c. If the current user name and the previous , The user names in the previous item are the same , Then the record is marked as 1; - Total logins , The query results are as follows :
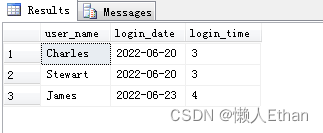
The temperature is less than for three consecutive days 0 Degree record
Build the predicative sentence as follows :
if object_id('weather','U') is not null
drop table weather
create table weather
(
id int primary key,
city varchar(50) not null,
temperature int not null,
day date not null
);
The meteorological information record table contains Id, City name , Temperature and record date , among id It's the primary key , This column is a self incrementing numeric column .
See Appendix for data initialization code .
We need to count the temperature less than... For three consecutive days 0 Degree record .
The solution to this problem is similar to the previous login problem , Give the solution directly
WITH WEATHER_ADD_TAG AS (
SELECT *,
CASE
WHEN
ld.temperature < 0
AND
LEAD(ld.temperature) OVER(PARTITION BY 1 ORDER BY ld.[day]) < 0
AND
LEAD(ld.temperature,2) OVER(PARTITION BY 1 ORDER BY ld.[day]) < 0
THEN 1
WHEN
LAG(ld.temperature) OVER(PARTITION BY 1 ORDER BY ld.[day]) < 0
AND
ld.temperature < 0
AND
LEAD(ld.temperature) OVER(PARTITION BY 1 ORDER BY ld.[day ]) < 0
THEN 1
WHEN
LAG(ld.temperature) OVER(PARTITION BY 1 ORDER BY ld.[day ]) < 0
AND
LAG(ld.temperature,2) OVER(PARTITION BY 1 ORDER BY ld.[day ]) < 0
AND
ld.temperature < 0
THEN 1
END AS TAG
FROM weather ld
)
SELECT * FROM WEATHER_ADD_TAG WHERE TAG = 1
The results are as follows :

Scheme optimization
The purpose of the scheme is to case when Part is too cumbersome , What we need is to find out that the temperature is lower than 0 Degree record , There is no need for strict string matching as in the previous example .
The temperature is less than for three consecutive days or more 0 Degree equivalent to 3 The high temperature within days is less than 0 degree .
The optimization code is as follows :
SELECT Id, City, Temperature, Day
FROM
(
SELECT *,
CASE
WHEN max(w.temperature) OVER(PARTITION BY 1 ORDER BY day ROWS BETWEEN CURRENT ROW and 2 FOLLOWING ) < 0
THEN 1
WHEN max(w.temperature) OVER(PARTITION BY 1 ORDER BY day ROWS BETWEEN 1 PRECEDING and 1 FOLLOWING ) < 0
THEN 1
WHEN max(w.temperature) OVER(PARTITION BY 1 ORDER BY day ROWS BETWEEN 2 PRECEDING and CURRENT ROW ) < 0
THEN 1
END AS TAG
FROM weather w
) x WHERE x.TAG = 1;
The results are as follows :

There was a problem with the result , Two more days to record .
LAG/LEAD If the records do not exist in the two methods , For example, the record before the first record , Records after the last record , This is the NULL To process and participate in operations , Can be filtered out .
This example uses FOLLOWING/PRECEDING To get the previous and subsequent records , For records that don't exist , It doesn't follow NULL To deal with it . Records before the first or after the last do not exist , Will not participate in the operation .1 month 1 Records before No. 1 are not treated as null values , It is not involved in computation , therefore 1 month 1 Number and 2 The temperature of No 0 degree , They are added to the final result .
Solution :
Add two records that do not meet the requirements , As the first and last record ,
The code is as follows :
;WITH APPEND_MIN_MAX_DATE_CTE as (
SELECT * FROM weather w
UNION
SELECT 1, 'London', 0, '2020-01-01'
UNION
SELECT 1, 'London', 0, '2050-01-01'
)
SELECT Id, City, Temperature, Day
FROM
(
SELECT *,
CASE
WHEN max(w.temperature) OVER(PARTITION BY 1 ORDER BY day ROWS BETWEEN CURRENT ROW and 2 FOLLOWING ) < 0
THEN 1
WHEN max(w.temperature) OVER(PARTITION BY 1 ORDER BY day ROWS BETWEEN 1 PRECEDING and 1 FOLLOWING ) < 0
THEN 1
WHEN max(w.temperature) OVER(PARTITION BY 1 ORDER BY day ROWS BETWEEN 2 PRECEDING and CURRENT ROW ) < 0
THEN 1
END AS TAG
FROM APPEND_MIN_MAX_DATE_CTE w
) x WHERE x.TAG = 1;
The results are as follows :

Statistical continuity N The temperature is less than 0 Degree record
The following needs to be upgraded , No more specific days , Instead, the user enters , Control by oneself .
obviously , The existing schemes are based on the known days , Unable to meet new needs . We need to redefine continuity N Heaven is in T-SQL The determination method in .
The implementation code is as follows :
;WITH ADD_ROW_NUMBER_CTE AS (
SELECT *,
ROW_NUMBER() OVER(PARTITION BY 1 ORDER BY [day])AS RN
FROM weather w
),
ADD_ROW_NUMBER_LT_0_CTE AS (
SELECT *,
ROW_NUMBER() OVER(PARTITION BY 1 ORDER BY [day])AS RN_LT_0
FROM ADD_ROW_NUMBER_CTE WHERE temperature < 0
),
ADD_DIFF_CTE AS (
SELECT *,
(c.RN - c.RN_LT_0) AS DIFF
FROM ADD_ROW_NUMBER_LT_0_CTE c
),
ADD_COUNT_CTE AS (
SELECT *,
COUNT(*) OVER (PARTITION BY DIFF ORDER BY DIFF) AS CNT
FROM ADD_DIFF_CTE
)
SELECT * FROM ADD_COUNT_CTE WHERE CNT = 4
- Definition CTE,ADD_ROW_NUMBER_CTE, newly added RN Serial number column , Sort by date .
- Definition CTE,ADD_ROW_NUMBER_LT_0_CTE , newly added RN_LT_0 Serial number column , Sort by date , But the filtered temperature is greater than 0 The record of .
- seek RN and RN_LT_0 Difference , Columns with the same difference , Prove their continuity .
- Definition CTE,ADD_COUNT_CTE , Count the number of the same difference , This number means that the continuous temperature is lower than 0 The number of days , We can set any number , To meet the needs .
appendix
Log in to the log sheet
if object_id('login_details') is not null
drop table login_details;
create table login_details(
login_id int primary key,
user_name varchar(50) not null,
login_date date);
truncate table login_details;
insert into login_details values
(101, 'Michael', GETDATE()),
(102, 'James', GETDATE()),
(103, 'Stewart', DATEADD(DD,1,GETDATE())),
(104, 'Stewart', DATEADD(DD,1,GETDATE())),
(105, 'Stewart', DATEADD(DD,1,GETDATE())),
(106, 'Michael', DATEADD(DD,2,GETDATE())),
(107, 'Michael', DATEADD(DD,2,GETDATE())),
(108, 'Stewart', DATEADD(DD,3,GETDATE())),
(109, 'Stewart', DATEADD(DD,3,GETDATE())),
(110, 'James', DATEADD(DD,4,GETDATE())),
(111, 'James', DATEADD(DD,4,GETDATE())),
(112, 'James', DATEADD(DD,4,GETDATE())),
(113, 'James', DATEADD(DD,4,GETDATE())),
(114, 'James', DATEADD(DD,5,GETDATE())),
(115, 'Charles', DATEADD(DD,1,GETDATE())),
(116, 'Charles', DATEADD(DD,1,GETDATE())),
(117, 'Charles', DATEADD(DD,1,GETDATE()));
Meteorological information table
if object_id('weather','U') is not null
drop table weather
create table weather
(
id int primary key,
city varchar(50) not null,
temperature int not null,
day date not null
);
delete from weather;
insert into weather values
(1, 'London', -1, '2021-01-01'),
(2, 'London', -2, '2021-01-02'),
(3, 'London', 4, '2021-01-03'),
(4, 'London', 1, '2021-01-04'),
(5, 'London', -2, '2021-01-05'),
(6, 'London', -5, '2021-01-06'),
(7, 'London', -7, '2021-01-07'),
(8, 'London', 5, '2021-01-08'),
(9, 'London', -20,'2021-01-09'),
(10, 'London', 20, '2021-01-10'),
(11, 'London', 22,'2021-01-11'),
(12, 'London', -1, '2021-01-12'),
(13, 'London', -2, '2021-01-13'),
(14, 'London', -2, '2021-01-14'),
(15, 'London', -4, '2021-01-15'),
(16, 'London', -9, '2021-01-16'),
(17, 'London', 0, '2021-01-17'),
(18, 'London', -10, '2021-01-18'),
(19, 'London', -11, '2021-01-19'),
(20, 'London', -12, '2021-01-20'),
(21, 'London', -11, '2021-01-21');
边栏推荐
- 指针和结构体
- Doctoral Dissertation of the University of Toronto - training efficiency and robustness in deep learning
- 通过 Cargo 管理 Rust 项目
- 基于STM32F103ZET6库函数跑马灯实验
- 基础数据类型和复杂数据类型
- UE4:Build Configuration和Config的解释
- Adding, deleting, modifying and querying MySQL tables (basic)
- 【help】JVM的CPU资源占用过高问题的排查
- 1028 List Sorting
- # Leetcode 821. 字符的最短距离(简单)
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
Making single test so simple -- initial experience of Spock framework
刷题记录:Easy 数组(持续更新)
What is ICMP? What is the relationship between Ping and ICMP?
What is ssr/ssg/isr? How do I host them on AWS?
OpenSSL client programming: SSL session failure caused by an obscure function
指针和结构体
今晚战码先锋润和赛道第2期直播丨如何参与OpenHarmony代码贡献
可靠的分布式锁 RedLock 与 redisson 的实现
作用域-Number和String的常用Api(方法)
【登录界面】
Crawl national laws and Regulations Database
金鱼哥RHCA回忆录:DO447管理项目和开展作业--创建作业模板并启动作业
Comprehensively analyze the zero knowledge proof: resolve the expansion problem and redefine "privacy security"
1028 List Sorting
Running lantern experiment based on stm32f103zet6 library function
redis集群系列三
UE4-Actor基础知识
多伦多大学博士论文 | 深度学习中的训练效率和鲁棒性
华大单片机KEIL报错_WEAK的解决方案
Leetcode 821. 字符的最短距离(简单) - 续集