当前位置:网站首页>Redis data structure
Redis data structure
2022-06-10 23:10:00 【Let me ride】
Redis data structure
Preface
Rides Why so fast ?
Except it's an in memory database , So that all operations are carried out outside memory , There is another important factor , The data structure it implements , So that when we add, delete, query and modify data ,Redis Efficient handling .
Be careful ,Redis Data structures do not mean String( character string ) object 、List( list ) object 、Hash( Hash ) object 、Set( aggregate ) Objects and Zset( Ordered set ) object , Because these are Redis The data type of the value in the key value pair , That's how the data is stored , The underlying implementation of these objects uses data structures 
One 、 How to implement key value pair database ?
Redis Of key value pairs key It's a string object , and value It can be a string object , It can also be an object of collection data type , such as List object 、Hash object 、Set Objects and Zset object .
for instance , I'll list several Redis Commands for adding key value pairs :
How these key value pairs are saved in Redis What about the middle ?
Redis Is using a 「 Hashtable 」 Save all key value pairs , The biggest advantage of hash table is that we can use O(1) Time complexity to quickly find key value pairs . A hash table is actually an array , The elements in the array are called hash buckets .
Redis How does the hash bucket store key value pair data ?
The hash bucket holds a pointer to the key value pair data (dictEntry*), In this way, the key value pair data can be found through the pointer , Then, because the value of the key value pair can save string objects and objects of collection data types , Therefore, the data structure of key value pairs does not directly store the value itself , But saved void * key and void * value The pointer , Points to the actual key object and value object respectively , thus , Even if the value is aggregate data , It can also be done through void * value Pointer found .
redisDb structure , Express Redis The structure of the database , Stored in the structure points to dict Pointer to structure ;
dict structure , In the structure 2 Hash table , Under normal circumstances, it is used 「 Hashtable 1」.
ditctht structure , Represents the structure of the hash table , Structure stores a hash table array , Each element in the array points to a hash table node structure (dictEntry) The pointer to ;
dictEntry structure , Represents the structure of the hash table node , In the structure **void * key and void * value The pointer , key Pointing to String object , and value You can point to String object , You can also point to objects of collection type , such as List object 、Hash object 、Set Objects and Zset object .
In particular ,void * key and void * value The pointer points to Redis object ,Redis Each object in the is represented by redisObject Structural representation , Here's the picture :
Member variables contained in the object structure :
type, Identifies what type of object the object is (String object 、 List object 、Hash object 、Set Objects and Zset object );
encoding, Identify which underlying data structure is used by the object ;
ptr, Pointer to the underlying data structure .
Two 、SDS
Redis Yes, it is C The realization of language , But it doesn't directly use C Linguistic char* Character array to implement string , Instead, it encapsulates a simple dynamic string (simple dynamic string,SDS) Data structure to represent a string , That is to say Redis Of String The underlying data structure of the data type is SDS.
since Redis Designed SDS Structure to represent a string , Must be C Linguistic char* There are some defects in character arrays .
C Defects in language strings
C The string of language is actually an array of characters , That is, each element in the array is a character in the string .

C The time complexity for language to obtain string length is O(N)( This is a place that can be improved )
And besides the end of the string , String cannot contain “\0” character , Otherwise, it will be read by the program first “\0” The character will be mistaken for the end of the string , This limitation makes C Language strings can only hold text data , Can't save images like 、 Audio 、 Binary data such as video culture ( This is also a place that can be improved )
Okay , Through the above analysis , We can see C Language string deficiencies and areas for improvement :
1. The time complexity of getting the string length is O(N);
2. The string ends with “\0” Character identification , The string cannot contain “\0” character , Therefore, binary data cannot be saved ;
3. String manipulation functions are inefficient and unsafe , For example, there is a risk of buffer overflow , It may cause the program to terminate ;
SDS The structure design
The picture below is Redis 5.0 Of SDS Data structure of :
Each member variable in the structure is introduced separately :
len, The string length is recorded . In this way, when getting the length of the string , Just return the value of the member variable , Time complexity only needs to be O(1).
alloc, The length of space allocated to the character array . In this way, when modifying the string , Can pass alloc - len Calculate the size of the remaining space , It can be used to judge whether the space meets the modification requirements , If not satisfied , Will automatically send SDS
The space of is extended to the size required to perform the modification , The actual modification is then performed , So use SDS There is no need to manually modify SDS Space size of , There will be no buffer overflow problem mentioned earlier .
flags, Used to represent different types of SDS. A total of 5 Types , Namely sdshdr5、sdshdr8、sdshdr16、sdshdr32 and sdshdr64, The differences will be explained later .
buf[], A character array , Used to save actual data . Not only can you save strings , You can also save binary data .
in general ,Redis Of SDS Structure is above the original character array , Added three metadata :len、alloc、flags, Used to solve C Defects in language strings .
3、 ... and 、 Linked list
Redis Of List One of the underlying implementations of an object is a linked list .C The language itself does not have the data structure of linked list , therefore Redis I designed a linked list data structure .
Linked list structure design
typedef struct list {
// Chain header node
listNode *head;
// The end of the list
listNode *tail;
// Node value copy function
void *(*dup)(void *ptr);
// Node value release function
void (*free)(void *ptr);
// Node value comparison function
int (*match)(void *ptr, void *key);
// Number of linked list nodes
unsigned long len;
} list;
list Structure provides a chain header pointer for the linked list head、 The end of the list tail、 Number of linked list nodes len、 And can customize the implementation of dup、free、match function .

Advantages and disadvantages of linked list
Advantages as follows :
listNode The structure of the linked list node has prev and next The pointer , The time complexity of obtaining the pre node or post node of a node only needs O(1), And both pointers can point to NULL, So the linked list is a acyclic linked list ;
list Structure because it provides a header pointer head And footer nodes tail, therefore The time complexity of obtaining the header node and footer node of the linked list only needs O(1);
list Structure because it provides the number of linked list nodes len, therefore The time complexity of obtaining the number of nodes in the linked list only needs O(1);
listNode Linked list links use void* The pointer holds the node value , And through list Structural dup、free、match The function pointer sets the node type specific function for the node , therefore Linked list nodes can store various types of values ;
There are also defects in linked lists :
The memory between each node of the linked list is discontinuous , signify Can't make good use of CPU cache . Can make good use of CPU The cached data structure is an array , Because the memory of the array is continuous , So you can make the most of CPU Cache to speed up access .
And a little bit more , Saving the value of a linked list node requires the allocation of a linked list node structure header , High memory overhead .
therefore ,Redis 3.0 Of List Object in the case of a small amount of data , Will be used 「 Compressed list 」 As the implementation of the underlying data structure , Its advantage is to save memory space , And it is a memory compact data structure .
however , There is a performance problem with compressing the list ( What's the problem , Next I'll say ), therefore Redis stay 3.2 A new data structure is designed in version quicklist, And will List The underlying data structure of the object is changed from quicklist Realization .
And then in Redis 5.0 A new data structure is designed listpack, It follows the compact memory layout of compressed list , Finally, in the latest Redis edition , take Hash Objects and Zset Object's underlying data structure implements one of the compressed lists , Replace with listpack Realization .
Four 、 Compressed list
The biggest feature of compressed list , It is designed as a memory compact data structure , Take up a continuous memory space , Not only can we use CPU cache , And for data of different lengths , Code accordingly , This method can effectively save memory overhead .
however , There are also flaws in compressed lists :
Cannot save too many elements , Otherwise, the query efficiency will be reduced ;
When adding or modifying an element , The memory space occupied by the compressed list needs to be reallocated , It may even cause chain update problems .
therefore ,Redis object (List object 、Hash object 、Zset object ) Contains fewer elements , Or when the element value is small, the compressed list will be used as the underlying data structure .
Compressed list structure design
The compressed list is Redis Developed to save memory , It is A sequential data structure consisting of contiguous memory blocks , It's kind of like arrays .
The compressed list has three fields in the header :
zlbytes, Record the memory bytes occupied by the whole compressed list ;
zltail, Compressed list of records 「 The tail 」 The number of bytes from the node to the starting address , That is, the offset of the end of the list ;
zllen, Record the number of nodes contained in the compressed list ;
zlend, Mark the end point of the compressed list , Fixed value 0xFF( Decimal system 255).
In the compressed list , If we want to locate the first element and the last element , It can be directly located by the length of the three fields in the header , Complexity is O(1). and When looking for other elements , It's not so efficient , Only one by one , The complexity here is O(N) 了 , Therefore, a compressed list is not suitable for saving too many elements .
in addition , Compressed list nodes (entry) The composition of the system is as follows :

The compressed list node contains three parts :
prevlen, Recorded 「 Previous node 」 The length of ;
encoding, It records the type and length of the actual data of the current node ;
data, The actual data of the current node is recorded ;
When we insert data into a compressed list , The compressed list depends on whether the data is a string or an integer , And the size of the data , Will use different space sizes prevlen and encoding The information stored in these two elements , This design idea of different space allocation according to data size and type , It is Redis Used to save memory .
Say separately ,prevlen and encoding How to allocate different space sizes according to the size and type of data .
Compress each node in the list prevlen Properties are recorded 「 The length of the previous node 」, and prevlen The space size of the attribute is related to the length value of the previous node , such as :
If The length of the previous node is less than 254 byte , that prevlen Properties need to use 1 Byte space To save this length value ;
If The length of the previous node is greater than or equal to 254 byte , that prevlen Properties need to use 5 Byte space To save this length value ;
encoding The space size of the attribute depends on whether the data is a string or an integer , And the length of the string :
If The data of the current node is an integer , be encoding Will use 1 Byte space Encoding .
If The data of the current node is a string , According to the length of the string ,encoding Will use 1 byte /2 byte /5 Byte space Encoding .
Chain update
When adding or modifying an element to a compressed list , If there is not enough space , The memory space occupied by the compressed list needs to be reallocated . When the newly inserted element is large , May cause subsequent elements to prevlen The occupied space changes , That cause 「 Chain update 」 problem , Cause the space of each element to be reallocated , The performance of accessing compressed list is degraded .
Mentioned earlier , Compress the list of nodes prevlen Property will allocate different space sizes according to the length of the previous node :
If the previous one The length of the node is less than 254 byte , that prevlen Properties need to use 1 Byte space To save this length value ;
If the previous one The length of the node is greater than or equal to 254 byte , that prevlen Properties need to use 5 Byte space To save this length value ;
This continuous multiple space expansion operation under special circumstances is called 「 Chain update 」
Defects in compressed lists
Space expansion is the reallocation of memory , therefore Once a chain update occurs , This will cause the memory space occupied by the compressed list to be reallocated multiple times , This will directly affect the access performance of the compressed list .
So , Although compressed lists and compact memory layout can save memory overhead , But if the number of saved elements increases , Or the elements get bigger , Will cause memory reallocation , Worst of all, there will be 「 Chain update 」 The problem of .
therefore , The compressed list will only be used for scenes with a small number of saved nodes , As long as the number of nodes is small enough , Even if a chain update occurs , It's also acceptable .
Nevertheless ,Redis For the design deficiency of compressed list , In later versions , Two new data structures are designed :quicklist(Redis 3.2 introduce ) and listpack(Redis 5.0 introduce ). The design objectives of these two data structures , Is to keep the memory saving advantages of compressed lists as much as possible , At the same time, solve the problem of compressed list 「 Chain update 」 The problem of .
5、 ... and 、 Hashtable
The advantage of hash tables is that , it Can be O(1) Fast query data based on Complexity . How to do it ? take key adopt Hash Calculation of function , You can locate the data in the table , Because the hash table is actually an array , So you can quickly query the data through the index value .
But there are also risks , When the hash table size is fixed , As data grows , that Hash Collisions The more likely it will be .
Redis Adopted 「 Chained hash 」 To resolve hash conflicts , Without expanding the hash table , String data with the same hash value , Form a link , So that these data can still be queried in the table .
Hash table structure design

You can see , The hash table is an array (dictEntry **table), Each element of the array is a pointer to 「 Hash table node (dictEntry)」 The pointer to .

The structure of the hash table node is as follows :
dictEntry Structure contains not only pointers to keys and values , It also contains a pointer to the next hash table node , This pointer can link multiple key value pairs with the same hash value , To solve the problem of hash conflict , This is chain hashing .
in addition , Here's another thing for you ,dictEntry The value in the key value pair in the structure is a 「 Consortium v」 Defined , therefore , The value in a key value pair can be a pointer to the actual value , Or an unsigned 64 Bit integer or signed 64 Bit integer or double Value of class . The advantage of this is that you can save memory space , Because when 「 value 」 Is an integer or floating point number , You can embed the data of the value in dictEntry In structure , There is no need to point to the actual value with a pointer , This saves memory space .
Hash Collisions
The hash table is actually an array , Each element in the array is a hash bucket .
rehash
This section of hash table structure design , I've introduced you Redis Use dictht The structure represents the hash table . however , When actually using a hash table ,Redis Define a dict Structure , This structure defines Two hash tables (ht[2])
The reason for defining 2 Hash table , Because of rehash When , Need to use 2 A hash table .
During the normal service request phase , Inserted data , Will be written to 「 Hashtable 1」, At this time 「 Hashtable 2 」 There's no space allocated .
As the data grows , Triggered rehash operation , The process is divided into three steps :
to 「 Hashtable 2」 Allocate space , General comparison 「 Hashtable 1」 Big 2 times ;
take 「 Hashtable 1 」 Data migration to 「 Hashtable 2」 in ;
After migration ,「 Hashtable 1 」 The space will be released , And put 「 Hashtable 2」 Set to 「 Hashtable 1」, And then in 「 Hashtable 2」 Create a new blank hash table , For the next time rehash To prepare for .
The process looks simple , But in fact, the second step is very problematic , If 「 Hashtable 1 」 It's a huge amount of data , Then move to 「 Hashtable 2 」 When , Because it involves a lot of data copies , At this point, it may be possible to Redis Cause obstruction , Unable to service other requests .
Progressive type rehash
for fear of rehash During data migration , Because it takes time to copy data , influence Redis Performance conditions , therefore Redis Adopted Progressive type rehash, That is, the data migration is no longer completed at one time , But migrate multiple times .
Progressive type rehash Steps are as follows :
to 「 Hashtable 2」 Allocate space
stay rehash During the process , Each time a hash table element is added 、 Delete 、 When searching or updating operations ,Redis In addition to performing the corresponding operations , Will also sequentially 「 Hashtable 1 」 All at index position in key-value Migrate to 「 Hashtable 2」 On ;
The more hash table operation requests initiated by the client are processed , Eventually at some point 「 Hashtable 1 」 All of the key-value Migrate to 「 Hashtable 2」, To complete the rehash operation .
In this way, the overhead of a large amount of data migration at one time , Allocated to multiple requests , Avoid one-time rehash Time consuming operation .
It's progressive rehash In the process of , There will be two hash tables , So in progressive rehash During the process , Deletion of hash table elements 、 lookup 、 Update and other operations will be performed in these two hash tables .
such as , Find a key If it's worth it , First of all 「 Hashtable 1」 Search inside , If not , It will continue to the hash table 2 Inside to find .
in addition , In a progressive way rehash During the process , Add a new one key-value when , Will be saved to 「 Hashtable 2 」 Inside , and 「 Hashtable 1」 No more add operations , That's a guarantee 「 Hashtable 1 」 Of key-value The number will only decrease , With rehash Completion of operation , Final 「 Hashtable 1 」 It will become an empty table .
rehash The trigger condition
rehash Trigger conditions of ** Load factor (load factor)** It matters .

Trigger rehash Operating conditions , There are two main ones :
When the load factor is greater than or equal to 1 , also Redis It's not being executed bgsave Order or bgrewiteaof command , That is, there is no implementation RDB Snapshot or not in progress AOF When rewriting , It will rehash operation .
When the load factor is greater than or equal to 5 when , This indicates that the hash conflict is very serious , Whether it's being executed or not RDB Snapshot or AOF rewrite , Will be forced to rehash operation .
6、 ... and 、 Set of integers
The set of integers is Set One of the underlying implementations of objects . When one Set Object contains only integer value elements , And when the number of elements is small , The data structure of integer set will be used as the underlying implementation .
Integer set structure design
An integer set is essentially a contiguous memory space , Its structure is defined as follows :
You can see , The container that holds the elements is a contents Array , although contents Be declared int8_t An array of types , But actually contents The array does not hold anything int8_t Element of type ,contents The real type of array depends on intset In the structure encoding The value of the property . such as :
If encoding The property value is INTSET_ENC_INT16, that contents It's just one. int16_t An array of types , The type of each element in the array is int16_t;
If encoding The property value is INTSET_ENC_INT32, that contents It's just one. int32_t An array of types , The type of each element in the array is int32_t;
If encoding The property value is INTSET_ENC_INT64, that contents It's just one. int64_t An array of types , The type of each element in the array is int64_t;
Different types of contents Array , It means that the size of the array will be different .
Upgrade operation of integer set
The integer set will have an upgrade rule , When we add a new element to the set of integers , If the type of the new element (int32_t) Than the type of all existing elements in the integer set (int16_t) It takes a long time , The integer set needs to be upgraded first , That is, according to the type of new element (int32_t) Expand contents The space size of the array , Then the new element can be added to the integer set , Of course, in the process of upgrading , Also maintain the order of the set of integers .
The process of upgrading an integer set does not reallocate a new type of array , Instead, expand space on the original array , Then divide each element by interval type size , If encoding The property value is INTSET_ENC_INT16, Then the interval between each element is 16 position .
for instance , Suppose there is a set of integers with 3 Types are int16_t The elements of .
Now? , Add a new element to the set of integers 65535, This new element needs to use int32_t Type to hold , Therefore, the integer set needs to be upgraded , First of all, it needs to be contents Array capacity , Expand the capacity more than the size of the original space 80 position (4x32-3x16=80), So you can save 4 Types are int32_t The elements of .
After expansion contents After the array space size , You need to convert the previous three elements to int32_t type , And put the transformed element on the right bit , And you need to keep the order of the underlying array unchanged , The whole conversion process is as follows :
What are the benefits of upgrading integer sets ?
If you want an array to be saved at the same time int16_t、int32_t、int64_t Element of type , The simplest way is to use int64_t An array of types . But in that case , When all the elements are int16_t Type of , It will cause a waste of memory .
Integer set upgrade can avoid this situation , If you keep adding to the set of integers int16_t Element of type , Then the underlying implementation of the integer set has been using int16_t An array of types , Only when we are going to int32_t Type or int64_t When an element of type is added to the collection , Will upgrade the array .
therefore , The benefits of integer set upgrade are Save memory resources .
Does the integer set support demotion ?
Downgrade operation not supported , Once the array is upgraded , Will always remain in the upgraded state . For example, the previous example of upgrade operation , If you delete 65535 Elements , The array of integer sets is still int32_t Type of , It will not be downgraded to int16_t type .
7、 ... and 、 Jump watch
Redis Only in Zset The underlying implementation of the object uses a jump table , The advantage of jump table is that it can support average O(logN) Complex node searching .
Zset Object is the only one that uses two data structures at the same time Redis object , One of the two data structures is the skip table , One is the hash table . This has the advantage of efficient range query , It can also carry out efficient single point query .
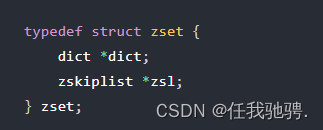
Zset Object can support range query ( Such as ZRANGEBYSCORE operation ), This is because its data structure design adopts jump table , And the element weight can be obtained with constant complexity ( Such as ZSCORE operation ), This is because it also uses a hash table for indexing .
Skip table structure design
When looking up elements in the linked list , Because you need to find it one by one , So the query efficiency is very low , The time complexity is O(N), So there's the jump watch . Jump list is improved on the basis of linked list , A kind of 「 Multi-storey 」 Ordered linked list , The advantage of this is that it can quickly read the positioning data .
What does the jump watch look like ? Let me give you an example , The following figure shows a hierarchy of 3 Jump table of .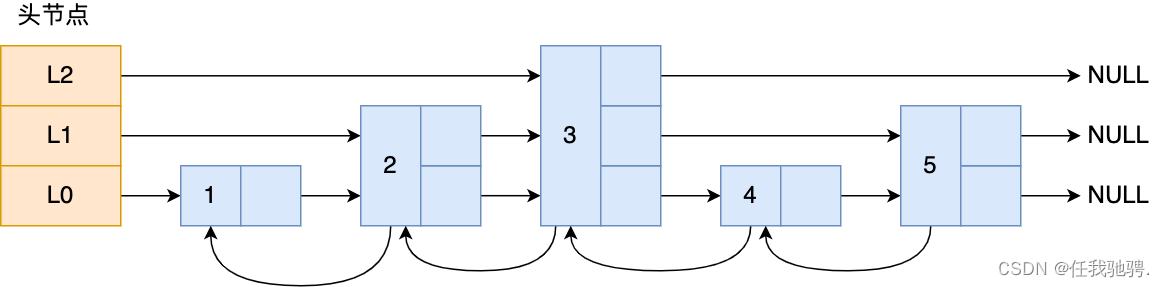
The head node in the figure has L0~L2 Three head pointers , Points to different levels of nodes , Then the nodes of each level are connected by pointers :
L0 Levels share 5 Nodes , They are nodes 1、2、3、4、5;
L1 Levels share 3 Nodes , They are nodes 2、3、5;
L2 There are only 1 Nodes , That is, nodes 3 .
If we want to find nodes in the linked list 4 This element , You can only traverse the linked list from the beginning , Need to find 4 Time , After using the jump table , Just look for 2 You can locate the node once 4, Because you can directly from the header node L2 The hierarchy jumps to the node 3, Then traverse forward to find the node 4.
You can see , This search process is to jump around at multiple levels , Finally, go to the element . When the amount of data is large , The lookup complexity of the jump table is O(logN).
How does the hop table node realize multi-level ? This needs to see 「 Skip table node 」 The data structure of , as follows :

Zset Object to save both elements and their weights , Corresponding to the hop table node structure is sds Type of ele Variables and double Type of score Variable . Each hop table node has a backward pointer , Point to previous node , The purpose is to facilitate access to nodes from the tail node of the hop table , It is convenient to find in reverse order .
A jump list is a linked list with hierarchical relationships , And each level can contain multiple nodes , Each node is connected by a pointer , This feature is implemented by the... In the jump table node structure zskiplistLevel Structure type level Array .
level Each element in the array represents a layer of the skip table , That is, by zskiplistLevel The structure represents , such as leve[0] It means the first floor ,leve[1] It means the second floor .zskiplistLevel The structure defines 「 Pointer to the next hop table node 」 and 「 span 」, Span is used to record the distance between two nodes .
When I first saw the span , Think it's about traversal , It doesn't really matter , The traversal operation only needs a forward pointer to complete .
The span is actually to calculate the ranking of this node in the jump table . How to do it specifically ? Because the nodes in the jump table are arranged in order , When calculating the ranking of a node , The query path from the node to the node , Add up the spans of all layers visited along the way , The result is the ranking of the target node in the hop table .
for instance , Find the nodes in the graph 3 Ranking in the jump table , Find nodes from the beginning 3, The search process only goes through one layer (L3), And the span of the floor is 3, So node 3 The ranking in the jump table is 3.
The problem is coming. , Who defines which hop table node is the head node ? Let's introduce 「 Jump watch 」 Structure. , As shown below :
The jump table structure contains :
The head and tail nodes of the jump table , Easy to do O(1) Access the head node and tail node of the hop table within the time complexity ;
The length of the meter , Easy to do O(1) Time complexity gets the number of hop table nodes ;
The maximum number of layers of the skip table , Easy to do O(1) Time complexity gets the number of layers of the node with the largest layer height in the hop table ;
Skip table node query process
The process of finding a hop table node , The jump table will start from the highest level of the node , Go through each layer one by one . When traversing the hop table node of a layer , Will use... In the hop table node SDS The element of type and the weight of element , There are two criteria :
If the weight of the current node 「 Less than 」 When you want to find the weight of , The jump table will access the next node on the layer .
If the weight of the current node 「 be equal to 」 When you want to find the weight of , And the current node SDS Type data 「 Less than 」 When looking for data , The jump table will access the next node on the layer .
If neither of the above conditions is met , Or when the next node is empty , The jump table will use the current traversal of the node level The next pointer in the array , Then continue to find along the next pointer , This is equivalent to jumping to the next level and looking for .
for instance , There is a 3 Hierarchical jump table .
If you want to find 「 Elements :abcd, The weight :4」 The node of , The search process is like this :
Start from the top of the node ,L2 Yes 「 Elements :abc, The weight :3」 node , The weight of this node is smaller than that of the node to be found , So you need to access the next node on this layer ;
But the next node on this layer is an empty node , So you jump to 「 Elements :abc, The weight :3」 The next level of the node , That is to say leve[1];
「 Elements :abc, The weight :3」 Node leve[1]
The next pointer of points to 「 Elements :abcde, The weight :4」 The node of , Then compare it with the node to be found . although 「 Elements :abcde, The weight :4」 The weight of the node is the same as the weight to be found , But the of the current node
SDS Type data 「 Greater than 」 The data to look for , So I'll continue to jump to 「 Elements :abc, The weight :3」 The next level of the node , That is to say leve[0];「 Elements :abc, The weight :3」 Node leve[0] The next pointer of points to 「 Elements :abcd, The weight :4」 The node of , This node is exactly the node to find , End of query .
Skip table node layer number setting
The proportion of the number of nodes in the adjacent two layers of the hop table will affect the query performance of the hop table .
for instance , The jump table in the figure below , The number of nodes in the second layer is only 1 individual , The number of nodes in the first layer is 6 individual .

At this time , If you want to query nodes 6, That's basically the same as the query complexity of the linked list , You need to find the nodes in the first layer in order , The complexity is O(N) 了 . therefore , To reduce query complexity , We need to maintain the relationship between the number of adjacent nodes .
The optimal ratio of the number of nodes in the adjacent two layers of the hop table is 2:1, The search complexity can be reduced to O(logN).
The jump table below is , The ratio of the number of nodes in two adjacent layers is 2 : 1.
How to maintain the ratio of the number of nodes in two adjacent layers to 2 : 1 Well ?
If you add a node or delete a node , To adjust the hop table node to maintain the proportion , There will be additional costs .
Redis A clever method is , When creating a node, the jump table , Randomly generate the number of layers of each node , The ratio of the number of nodes in two adjacent layers is not strictly maintained 2 : 1 The situation of .
Here's how , When creating a node, the jump table , Will generate a range of [0-1] A random number of , If this random number is less than 0.25( Equivalent to probability 25%), Then the number of layers will increase 1 layer , Then continue to generate the next random number , Until the result of the random number is greater than 0.25 end , Finally determine the number of layers of the node .
The way to do it , It is equivalent that the probability of each additional layer does not exceed 25%, The higher the number of layers , The lower the probability , The maximum floor height limit is 64.
8、 ... and 、quicklist
stay Redis 3.0 Before ,List The underlying data structure of an object is a two-way linked list or a compressed list . And then in Redis 3.2 When ,List The bottom layer of the object is changed from quicklist Data structure implementation .
Actually quicklist Namely 「 Double linked list + Compressed list 」 Combine , Because a quicklist It's just a linked list , And each element in the linked list is a compressed list .
When we talked about compressing the list , I also mentioned the shortcomings of compressed lists , Although compressed lists save memory overhead through a compact memory layout , But because of its structural design , If the number of saved elements increases , Or the element gets bigger , The compressed list will have 「 Chain update 」 The risk of , Once occurred , Will cause performance degradation .
quicklist terms of settlement , By controlling the size of the compressed list or the number of elements in each linked list node , To avoid the problem of chain update . Because the fewer or smaller the compressed list elements , The smaller the impact of chain renewal , This provides better access performance .
quicklist The structure design
quicklist The structure of is similar to that of a linked list , Both include header and footer , The difference lies in quicklist The node of is quicklistNode.
So let's see ,quicklistNode Structure definition of :

You can see ,quicklistNode The structure contains the previous node and the next node pointer , So each of them quicklistNode Form a two-way linked list . However, the elements of linked list nodes are no longer simply saving element values , Instead, a compressed list is saved , therefore quicklistNode There is a pointer to the compressed list in the structure *zl.
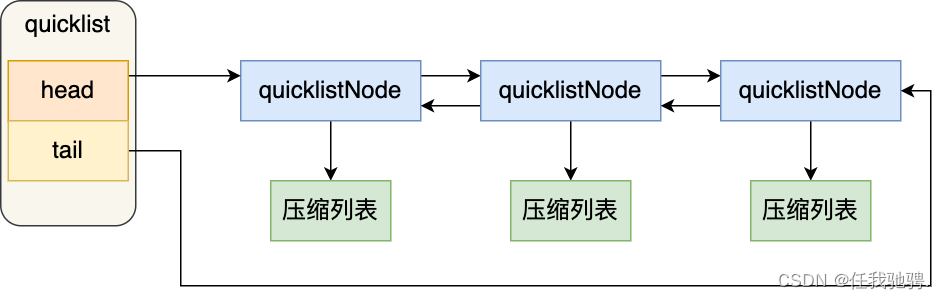
In the quicklist When adding an element , Not like an ordinary linked list , Directly create a linked list node . Instead, it checks whether the compressed list at the insertion position can accommodate the element , If you can hold it, save it directly to quicklistNode Compressed list in structure , If it can't hold , Will create a new one quicklistNode structure .
quicklist Can control quicklistNode The size of the compressed list or the number of elements in the structure , To avoid the risk of potential chain updates , However, this does not completely solve the problem of chain update .
Nine 、listpack
listpack Many excellent designs with compressed lists , For example, a continuous memory space is used to store data compactly , And to save memory overhead ,listpack Nodes use different encoding methods to save data of different sizes .
Let's see listpack structure :
listpack The header contains two properties , We recorded listpack Total bytes and elements , then listpack There is also an end tag at the end . In the picture listpack entry Namely listpack The node .
Every listpack The node structure is as follows :
It mainly includes three aspects :
encoding, Define the encoding type of the element , Will encode integers and strings of different lengths ;
data, Data actually stored ;
len,encoding+data The total length of ;
You can see ,listpack There is no field in the compressed list to record the length of the previous node ,listpack Only record the length of the current node , When we turn to listpack When adding a new element , It will not affect the change of the length field of other nodes , Thus, the chain update problem of compressed list is avoided .
边栏推荐
- Icml2022 | reexamine end-to-end voice to text translation from scratch
- 数据与信息资源共享平台(六)
- 关于String.format(String format, Object... args)
- Display of successful cases of target customer matching data table
- "Draw the bow as strong, use the arrow as long", Manfu technology opens a new track for the data service industry
- Unity code registers events for animation
- [QPSK if] Verilog design of QPSK IF signal generation module based on FPGA
- IPO can't cure Weima's complications?
- Web3技术栈权威指南【2022】
- Locking mechanism
猜你喜欢

Display of successful cases of target customer matching data table
视频融合云服务EasyCVR集群录像事件查询无效是什么原因?

Can Huawei matepad become the secondary screen of your laptop?

Vulnhub练习 DC-1靶机
![[original] analysis of nine price HPV data capture of Yilu app](/img/e0/af4901d119a6e59de02a6786d427dd.png)
[original] analysis of nine price HPV data capture of Yilu app

UE4骨骼动画新手入门

Lenovo explained for the first time the five advantages of hybrid cloud Lenovo xcloud and how to build an intelligent digital base

2022g1 industrial boiler stoker test questions and online simulation test

关于idea中src下 无法new一个package

软件测试入门之软件测试的概念与过程(精辟内容)
随机推荐
[raise bar C #] how to call the base of the interface
Html+php+mysql login registration page
项目实训12——解析建表的SQL语句
Keras deep learning practice (8) -- using data enhancement to improve neural network performance
Vulnhub's DC3
Simulated 100 questions and simulated examination of G2 utility boiler stoker examination in 2022
Creation of thread pool
0223 summary
Laravel8 enables alicloud file upload
Untiy reset animation
Custom view: graphics and image processing (I): using simple pictures
样板小作坊
Open source project PM how to design official website
That's great. The Ministry of industry and information technology has launched an internet account with a "one click unbinding" mobile phone number, which can be called an artifact
How about opening an account with flush? Is it safe to open an account?
中银证券开户有什么风险吗?安全的吗?
What are the common methods of object
Thread pool: a magic weapon for managing threads
电子协会 C语言 1级 7 、画矩形
爬虫学习知识
