当前位置:网站首页>Kube scheduler source code analysis (1) - initialization and startup analysis
Kube scheduler source code analysis (1) - initialization and startup analysis
2022-06-25 07:18:00 【InfoQ】
kube-scheduler Source code analysis (1)- Initialize and start analysis
kube-scheduler brief introduction
kube-scheduler Architecture diagram
sched.scheduleOne
1.kube-scheduler Initialize and start analysis
be based on tag v1.17.4
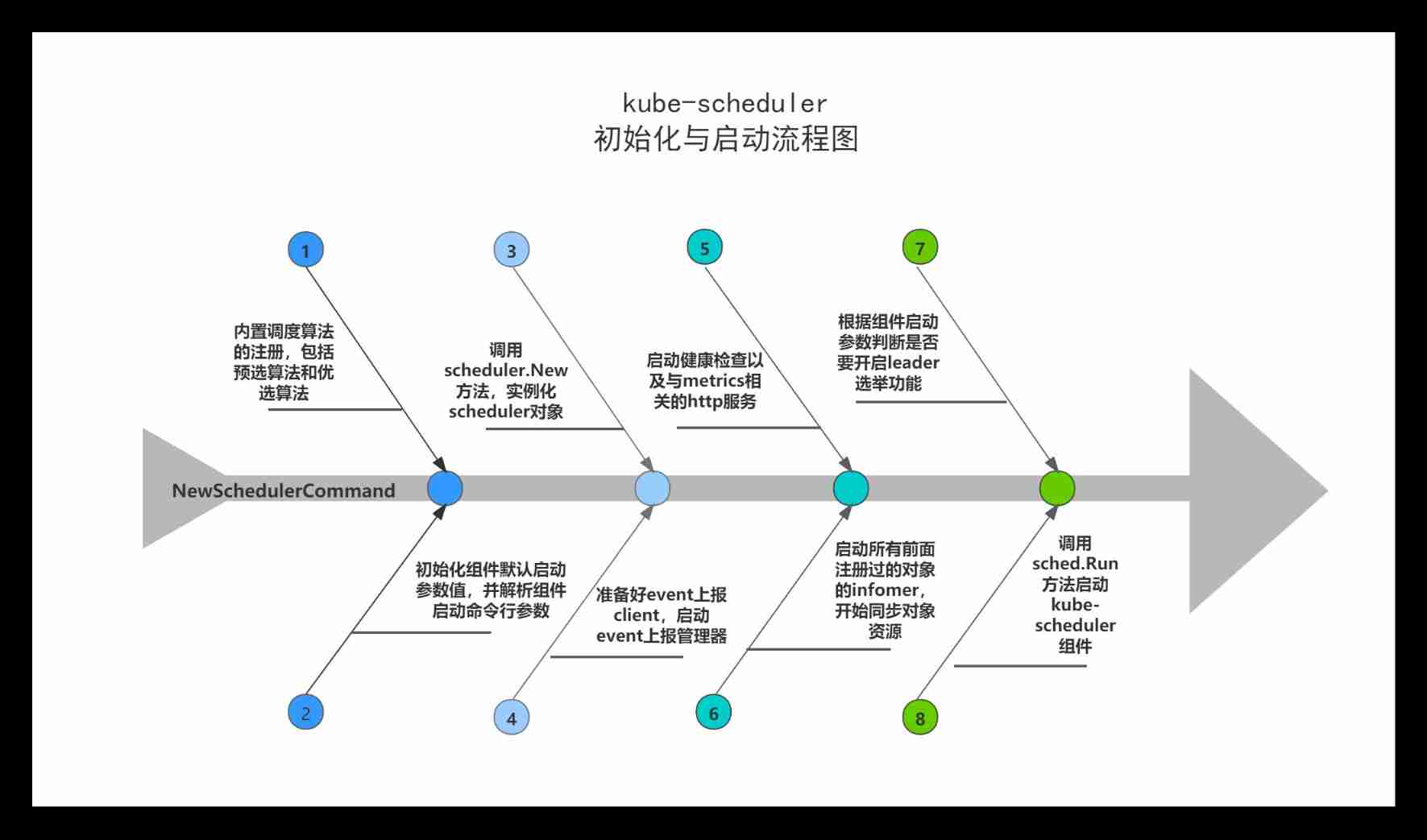
NewSchedulerCommand
// cmd/kube-scheduler/app/server.go
func NewSchedulerCommand(registryOptions ...Option) *cobra.Command {
// 1. Initialize the default startup parameter value of the component
opts, err := options.NewOptions()
if err != nil {
klog.Fatalf("unable to initialize command options: %v", err)
}
// 2. Definition kube-scheduler Method of running command of component , namely runCommand function
cmd := &cobra.Command{
Use: "kube-scheduler",
Long: `The Kubernetes scheduler is a policy-rich, topology-aware,
workload-specific function that significantly impacts availability, performance,
and capacity. The scheduler needs to take into account individual and collective
resource requirements, quality of service requirements, hardware/software/policy
constraints, affinity and anti-affinity specifications, data locality, inter-workload
interference, deadlines, and so on. Workload-specific requirements will be exposed
through the API as necessary.`,
Run: func(cmd *cobra.Command, args []string) {
if err := runCommand(cmd, args, opts, registryOptions...); err != nil {
fmt.Fprintf(os.Stderr, "%v\n", err)
os.Exit(1)
}
},
}
// 3. Component command line starts parameter resolution
fs := cmd.Flags()
namedFlagSets := opts.Flags()
verflag.AddFlags(namedFlagSets.FlagSet("global"))
globalflag.AddGlobalFlags(namedFlagSets.FlagSet("global"), cmd.Name())
for _, f := range namedFlagSets.FlagSets {
fs.AddFlagSet(f)
}
...
}
runCommand
// cmd/kube-scheduler/app/server.go
// runCommand runs the scheduler.
func runCommand(cmd *cobra.Command, args []string, opts *options.Options, registryOptions ...Option) error {
...
// Apply algorithms based on feature gates.
// TODO: make configurable?
algorithmprovider.ApplyFeatureGates()
// Configz registration.
if cz, err := configz.New("componentconfig"); err == nil {
cz.Set(cc.ComponentConfig)
} else {
return fmt.Errorf("unable to register configz: %s", err)
}
ctx, cancel := context.WithCancel(context.Background())
defer cancel()
return Run(ctx, cc, registryOptions...)
}
1.1 algorithmprovider.ApplyFeatureGates
// pkg/scheduler/algorithmprovider/plugins.go
import (
"k8s.io/kubernetes/pkg/scheduler/algorithmprovider/defaults"
)
func ApplyFeatureGates() func() {
return defaults.ApplyFeatureGates()
}
1.1.1 init
// pkg/scheduler/algorithmprovider/defaults/defaults.go
func init() {
registerAlgorithmProvider(defaultPredicates(), defaultPriorities())
}
// pkg/scheduler/algorithmprovider/defaults/defaults.go
func defaultPredicates() sets.String {
return sets.NewString(
predicates.NoVolumeZoneConflictPred,
predicates.MaxEBSVolumeCountPred,
predicates.MaxGCEPDVolumeCountPred,
predicates.MaxAzureDiskVolumeCountPred,
predicates.MaxCSIVolumeCountPred,
predicates.MatchInterPodAffinityPred,
predicates.NoDiskConflictPred,
predicates.GeneralPred,
predicates.PodToleratesNodeTaintsPred,
predicates.CheckVolumeBindingPred,
predicates.CheckNodeUnschedulablePred,
)
}
// pkg/scheduler/algorithmprovider/defaults/defaults.go
func defaultPriorities() sets.String {
return sets.NewString(
priorities.SelectorSpreadPriority,
priorities.InterPodAffinityPriority,
priorities.LeastRequestedPriority,
priorities.BalancedResourceAllocation,
priorities.NodePreferAvoidPodsPriority,
priorities.NodeAffinityPriority,
priorities.TaintTolerationPriority,
priorities.ImageLocalityPriority,
)
}
// pkg/scheduler/algorithmprovider/defaults/defaults.go
func registerAlgorithmProvider(predSet, priSet sets.String) {
// Registers algorithm providers. By default we use 'DefaultProvider', but user can specify one to be used
// by specifying flag.
scheduler.RegisterAlgorithmProvider(scheduler.DefaultProvider, predSet, priSet)
// Cluster autoscaler friendly scheduling algorithm.
scheduler.RegisterAlgorithmProvider(ClusterAutoscalerProvider, predSet,
copyAndReplace(priSet, priorities.LeastRequestedPriority, priorities.MostRequestedPriority))
}
// pkg/scheduler/algorithm_factory.go
// RegisterAlgorithmProvider registers a new algorithm provider with the algorithm registry.
func RegisterAlgorithmProvider(name string, predicateKeys, priorityKeys sets.String) string {
schedulerFactoryMutex.Lock()
defer schedulerFactoryMutex.Unlock()
validateAlgorithmNameOrDie(name)
algorithmProviderMap[name] = AlgorithmProviderConfig{
FitPredicateKeys: predicateKeys,
PriorityFunctionKeys: priorityKeys,
}
return name
}
// pkg/scheduler/algorithm_factory.go
var (
...
algorithmProviderMap = make(map[string]AlgorithmProviderConfig)
...
)
// pkg/scheduler/algorithmprovider/defaults/register_predicates.go
func init() {
...
// Fit is defined based on the absence of port conflicts.
// This predicate is actually a default predicate, because it is invoked from
// predicates.GeneralPredicates()
scheduler.RegisterFitPredicate(predicates.PodFitsHostPortsPred, predicates.PodFitsHostPorts)
// Fit is determined by resource availability.
// This predicate is actually a default predicate, because it is invoked from
// predicates.GeneralPredicates()
scheduler.RegisterFitPredicate(predicates.PodFitsResourcesPred, predicates.PodFitsResources)
...
// pkg/scheduler/algorithmprovider/defaults/register_priorities.go
func init() {
...
// Prioritize nodes by least requested utilization.
scheduler.RegisterPriorityMapReduceFunction(priorities.LeastRequestedPriority, priorities.LeastRequestedPriorityMap, nil, 1)
// Prioritizes nodes to help achieve balanced resource usage
scheduler.RegisterPriorityMapReduceFunction(priorities.BalancedResourceAllocation, priorities.BalancedResourceAllocationMap, nil, 1)
...
}
// pkg/scheduler/algorithm_factory.go
var (
...
fitPredicateMap = make(map[string]FitPredicateFactory)
...
priorityFunctionMap = make(map[string]PriorityConfigFactory)
...
)
1.1.2 defaults.ApplyFeatureGates
// pkg/scheduler/algorithmprovider/defaults/defaults.go
func ApplyFeatureGates() (restore func()) {
...
// Only register EvenPodsSpread predicate & priority if the feature is enabled
if utilfeature.DefaultFeatureGate.Enabled(features.EvenPodsSpread) {
klog.Infof("Registering EvenPodsSpread predicate and priority function")
// register predicate
scheduler.InsertPredicateKeyToAlgorithmProviderMap(predicates.EvenPodsSpreadPred)
scheduler.RegisterFitPredicate(predicates.EvenPodsSpreadPred, predicates.EvenPodsSpreadPredicate)
// register priority
scheduler.InsertPriorityKeyToAlgorithmProviderMap(priorities.EvenPodsSpreadPriority)
scheduler.RegisterPriorityMapReduceFunction(
priorities.EvenPodsSpreadPriority,
priorities.CalculateEvenPodsSpreadPriorityMap,
priorities.CalculateEvenPodsSpreadPriorityReduce,
1,
)
}
// Prioritizes nodes that satisfy pod's resource limits
if utilfeature.DefaultFeatureGate.Enabled(features.ResourceLimitsPriorityFunction) {
klog.Infof("Registering resourcelimits priority function")
scheduler.RegisterPriorityMapReduceFunction(priorities.ResourceLimitsPriority, priorities.ResourceLimitsPriorityMap, nil, 1)
// Register the priority function to specific provider too.
scheduler.InsertPriorityKeyToAlgorithmProviderMap(scheduler.RegisterPriorityMapReduceFunction(priorities.ResourceLimitsPriority, priorities.ResourceLimitsPriorityMap, nil, 1))
}
...
}
1.2 Run
// cmd/kube-scheduler/app/server.go
func Run(ctx context.Context, cc schedulerserverconfig.CompletedConfig, outOfTreeRegistryOptions ...Option) error {
// To help debugging, immediately log version
klog.V(1).Infof("Starting Kubernetes Scheduler version %+v", version.Get())
outOfTreeRegistry := make(framework.Registry)
for _, option := range outOfTreeRegistryOptions {
if err := option(outOfTreeRegistry); err != nil {
return err
}
}
// 1. Get ready event Report client, Is used to kube-scheduler All kinds of event Report to api-server
// Prepare event clients.
if _, err := cc.Client.Discovery().ServerResourcesForGroupVersion(eventsv1beta1.SchemeGroupVersion.String()); err == nil {
cc.Broadcaster = events.NewBroadcaster(&events.EventSinkImpl{Interface: cc.EventClient.Events("")})
cc.Recorder = cc.Broadcaster.NewRecorder(scheme.Scheme, cc.ComponentConfig.SchedulerName)
} else {
recorder := cc.CoreBroadcaster.NewRecorder(scheme.Scheme, v1.EventSource{Component: cc.ComponentConfig.SchedulerName})
cc.Recorder = record.NewEventRecorderAdapter(recorder)
}
// 2. call scheduler.New Method , Instantiation scheduler object
// Create the scheduler.
sched, err := scheduler.New(cc.Client,
cc.InformerFactory,
cc.PodInformer,
cc.Recorder,
ctx.Done(),
scheduler.WithName(cc.ComponentConfig.SchedulerName),
scheduler.WithAlgorithmSource(cc.ComponentConfig.AlgorithmSource),
scheduler.WithHardPodAffinitySymmetricWeight(cc.ComponentConfig.HardPodAffinitySymmetricWeight),
scheduler.WithPreemptionDisabled(cc.ComponentConfig.DisablePreemption),
scheduler.WithPercentageOfNodesToScore(cc.ComponentConfig.PercentageOfNodesToScore),
scheduler.WithBindTimeoutSeconds(cc.ComponentConfig.BindTimeoutSeconds),
scheduler.WithFrameworkOutOfTreeRegistry(outOfTreeRegistry),
scheduler.WithFrameworkPlugins(cc.ComponentConfig.Plugins),
scheduler.WithFrameworkPluginConfig(cc.ComponentConfig.PluginConfig),
scheduler.WithPodMaxBackoffSeconds(cc.ComponentConfig.PodMaxBackoffSeconds),
scheduler.WithPodInitialBackoffSeconds(cc.ComponentConfig.PodInitialBackoffSeconds),
)
if err != nil {
return err
}
// 3. start-up event Escalation Manager
// Prepare the event broadcaster.
if cc.Broadcaster != nil && cc.EventClient != nil {
cc.Broadcaster.StartRecordingToSink(ctx.Done())
}
if cc.CoreBroadcaster != nil && cc.CoreEventClient != nil {
cc.CoreBroadcaster.StartRecordingToSink(&corev1.EventSinkImpl{Interface: cc.CoreEventClient.Events("")})
}
// 4. Set up kube-scheduler Component health check , And start a health check and communicate with metrics dependent http service
// Setup healthz checks.
var checks []healthz.HealthChecker
if cc.ComponentConfig.LeaderElection.LeaderElect {
checks = append(checks, cc.LeaderElection.WatchDog)
}
// Start up the healthz server.
if cc.InsecureServing != nil {
separateMetrics := cc.InsecureMetricsServing != nil
handler := buildHandlerChain(newHealthzHandler(&cc.ComponentConfig, separateMetrics, checks...), nil, nil)
if err := cc.InsecureServing.Serve(handler, 0, ctx.Done()); err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("failed to start healthz server: %v", err)
}
}
if cc.InsecureMetricsServing != nil {
handler := buildHandlerChain(newMetricsHandler(&cc.ComponentConfig), nil, nil)
if err := cc.InsecureMetricsServing.Serve(handler, 0, ctx.Done()); err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("failed to start metrics server: %v", err)
}
}
if cc.SecureServing != nil {
handler := buildHandlerChain(newHealthzHandler(&cc.ComponentConfig, false, checks...), cc.Authentication.Authenticator, cc.Authorization.Authorizer)
// TODO: handle stoppedCh returned by c.SecureServing.Serve
if _, err := cc.SecureServing.Serve(handler, 0, ctx.Done()); err != nil {
// fail early for secure handlers, removing the old error loop from above
return fmt.Errorf("failed to start secure server: %v", err)
}
}
// 5. Start the of all previously registered objects informer, Start synchronizing object resources
// Start all informers.
go cc.PodInformer.Informer().Run(ctx.Done())
cc.InformerFactory.Start(ctx.Done())
// 6. Wait for all informer The synchronization of objects is complete , Make the locally cached data and etcd The data in is consistent
// Wait for all caches to sync before scheduling.
cc.InformerFactory.WaitForCacheSync(ctx.Done())
// 7. Judge whether to start according to the component startup parameters leader Election function
// If leader election is enabled, runCommand via LeaderElector until done and exit.
if cc.LeaderElection != nil {
cc.LeaderElection.Callbacks = leaderelection.LeaderCallbacks{
OnStartedLeading: sched.Run,
OnStoppedLeading: func() {
klog.Fatalf("leaderelection lost")
},
}
leaderElector, err := leaderelection.NewLeaderElector(*cc.LeaderElection)
if err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("couldn't create leader elector: %v", err)
}
leaderElector.Run(ctx)
return fmt.Errorf("lost lease")
}
// 8. call sched.Run Method start up kube-scheduler Components
// Leader election is disabled, so runCommand inline until done.
sched.Run(ctx)
return fmt.Errorf("finished without leader elect")
}
1.2.1 scheduler.New
// pkg/scheduler/scheduler.go
func New(client clientset.Interface,
informerFactory informers.SharedInformerFactory,
podInformer coreinformers.PodInformer,
recorder events.EventRecorder,
stopCh <-chan struct{},
opts ...Option) (*Scheduler, error) {
stopEverything := stopCh
if stopEverything == nil {
stopEverything = wait.NeverStop
}
options := defaultSchedulerOptions
for _, opt := range opts {
opt(&options)
}
// 1. Instantiation node、pvc、pv Wait for the object infomer
schedulerCache := internalcache.New(30*time.Second, stopEverything)
volumeBinder := volumebinder.NewVolumeBinder(
client,
informerFactory.Core().V1().Nodes(),
informerFactory.Storage().V1().CSINodes(),
informerFactory.Core().V1().PersistentVolumeClaims(),
informerFactory.Core().V1().PersistentVolumes(),
informerFactory.Storage().V1().StorageClasses(),
time.Duration(options.bindTimeoutSeconds)*time.Second,
)
registry := options.frameworkDefaultRegistry
if registry == nil {
registry = frameworkplugins.NewDefaultRegistry(&frameworkplugins.RegistryArgs{
VolumeBinder: volumeBinder,
})
}
registry.Merge(options.frameworkOutOfTreeRegistry)
snapshot := nodeinfosnapshot.NewEmptySnapshot()
configurator := &Configurator{
client: client,
informerFactory: informerFactory,
podInformer: podInformer,
volumeBinder: volumeBinder,
schedulerCache: schedulerCache,
StopEverything: stopEverything,
hardPodAffinitySymmetricWeight: options.hardPodAffinitySymmetricWeight,
disablePreemption: options.disablePreemption,
percentageOfNodesToScore: options.percentageOfNodesToScore,
bindTimeoutSeconds: options.bindTimeoutSeconds,
podInitialBackoffSeconds: options.podInitialBackoffSeconds,
podMaxBackoffSeconds: options.podMaxBackoffSeconds,
enableNonPreempting: utilfeature.DefaultFeatureGate.Enabled(kubefeatures.NonPreemptingPriority),
registry: registry,
plugins: options.frameworkPlugins,
pluginConfig: options.frameworkPluginConfig,
pluginConfigProducerRegistry: options.frameworkConfigProducerRegistry,
nodeInfoSnapshot: snapshot,
algorithmFactoryArgs: AlgorithmFactoryArgs{
SharedLister: snapshot,
InformerFactory: informerFactory,
VolumeBinder: volumeBinder,
HardPodAffinitySymmetricWeight: options.hardPodAffinitySymmetricWeight,
},
configProducerArgs: &frameworkplugins.ConfigProducerArgs{},
}
metrics.Register()
// 2. call configurator.CreateFromConfig, According to the previously registered built-in scheduling algorithm ( Or according to the scheduling policy provided by the user ), Instantiation scheduler
var sched *Scheduler
source := options.schedulerAlgorithmSource
switch {
case source.Provider != nil:
// Create the config from a named algorithm provider.
sc, err := configurator.CreateFromProvider(*source.Provider)
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("couldn't create scheduler using provider %q: %v", *source.Provider, err)
}
sched = sc
case source.Policy != nil:
// Create the config from a user specified policy source.
policy := &schedulerapi.Policy{}
switch {
case source.Policy.File != nil:
if err := initPolicyFromFile(source.Policy.File.Path, policy); err != nil {
return nil, err
}
case source.Policy.ConfigMap != nil:
if err := initPolicyFromConfigMap(client, source.Policy.ConfigMap, policy); err != nil {
return nil, err
}
}
sc, err := configurator.CreateFromConfig(*policy)
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("couldn't create scheduler from policy: %v", err)
}
sched = sc
default:
return nil, fmt.Errorf("unsupported algorithm source: %v", source)
}
// Additional tweaks to the config produced by the configurator.
sched.Recorder = recorder
sched.DisablePreemption = options.disablePreemption
sched.StopEverything = stopEverything
sched.podConditionUpdater = &podConditionUpdaterImpl{client}
sched.podPreemptor = &podPreemptorImpl{client}
sched.scheduledPodsHasSynced = podInformer.Informer().HasSynced
// 3. to infomer Object registration eventHandler
AddAllEventHandlers(sched, options.schedulerName, informerFactory, podInformer)
return sched, nil
}
summary
kube-scheduler brief introduction
kube-scheduler Architecture diagram
sched.scheduleOne
kube-scheduler Initialization and startup analysis flow chart
边栏推荐
- Torchserve pit avoidance Guide
- Too beautiful promise because too young
- Shell命令学习
- 弱大数定理的意义与证明
- Qcom--lk phase I2C interface configuration scheme -i2c6
- Shell command learning
- 【C语言】给字符串增加分隔符
- Jameswebb Space Telescope goes into operation to help study interstellar objects
- 1W words | 40 pictures | hard core es actual combat
- Google extender address
猜你喜欢

MCU IO explanation (pull-up pull-down quasi bidirectional input / output push-pull open drain)

ES can finally find brother Wukong!

破万,我用了六年!

joda. Time get date summary

Streamnational platform version 1.5 is released, integrating istio and supporting openshift deployment

Three laws of go reflection
Navicat prevent new query from being deleted by mistake

Make enough money to go back home
![[he doesn't mention love, but every word is love]](/img/28/0c3ddad3dc9b1ef8d0618164f39e53.png)
[he doesn't mention love, but every word is love]

5g private network market is in full swing, and it is crucial to solve deployment difficulties in 2022
随机推荐
Message queue table structure for storing message data
CTFHub-Web-信息泄露-目錄遍曆
Clearing Magento log data - clearing Magento log data
Design of PWM breathing lamp based on FPGA
Kubernetes 集群中流量暴露的几种方案
太美的承诺因为太年轻
全局变量&局部变量
ES can finally find brother Wukong!
Blue Bridge Cup SCM module code (timer) (code + comments)
活动报名|Apache Pulsar x KubeSphere 在线 Meetup 火热报名中
[tool sharing] a software that pays equal attention to appearance and skills
Too beautiful promise because too young
lotus v1.16.0-rc2 Calibration-net
高效探索|ES地理位置查询的一次应用实践
The king scheme in distributed locks - redisson
Finally, when you open source the applet ~
Rotation vector (rotation matrix) and Euler angle
How to recover redis data from snapshot(rdb file) copied from another machine?
【C语言】给字符串增加分隔符
破万,我用了六年!