当前位置:网站首页>Conditional statements of shell programming
Conditional statements of shell programming
2022-07-03 21:57:00 【Human shadow】
1. File test and integer test
2. String testing and logic testing
Two .if sentence
1.if Single branch statements
2.if Two branch statements
3.if Multi branch statement
3、 ... and .case Branch statement
One . Conditions for testing
( One ). Conditional test operation
1.test command
Test whether the expression holds , Return if established 0, Otherwise, other values are returned
Format 1: test Conditional expression
Format 2:【 Conditional expression 】
To make shell The script program has certain " intelligence ", The first problem is how to distinguish between different situations to determine what to do . for example , When disk utilization exceeds 95% when , Send alarm information ; When the backup directory does not exist , Can automatically create : When the source code compiles the program , If the configuration fails, the installation will not continue Shell The environment returns the status value according to the command execution ($?〉 To judge whether the execution is successful , When the return value is o Time means success , otherwise ( Not О value ) Indicates failure or exception .
Use special testing tools —test command , You can test specific conditions , And judge whether the condition is true according to the return value ( The return value is 0 Indicates that the condition is true ).
Grammar format :
Format l test Conditional expression
Format 2〔 Conditional expression ]# Note that you need to separate a space or... Between the brackets and the expression
[[ Conditional expression ]]
2. File test
[ Operator file or directory ]
Common test operators
File testing refers to testing based on a given path name , Determine whether the corresponding file or directory , Or judge whether the file is
Can be read 、 Can write 、 Executable, etc . Common operation options for file testing are as follows , When using, put the test object after the operation option .
-d: Test whether it's a directory (Directory) .
-e: Test whether the directory or file exists (Exist ) .
-f: Whether the test is a file ( File ) .
-r: Test whether the current user has permission to read (Read).
-w: Test whether the current user has permission to write (write ) .
-x: Test if executable (Excute) jurisdiction .
-b: Test whether it is a device file
-c: Test whether it is a character device file
-s: The test exists and the file size is empty
-L: Test whether it is a linked file
After performing the conditional test operation , Through predefined variables $? You can get the return status value of the test command , So as to judge whether the condition is true . for example , Do the following to test the directory /media/ Whether there is , If the return value $? by 0,
Indicates that this directory exists , Otherwise, it means that it does not exist or although it exists, it is not a directory
example 1
test -d letcl sysconfig/
test -f letc/ sysconfig/
test -e letcl sysconfig/
example 2
[ -f / home / humajun/ ]
[ -d / home / humajun/ ] & & echo "YES"
[ ! -e /opt/ kgc ] & & mkdir /opt/ kgc
3. Integer comparison
[ Integers 1 Operator integer 2]
Common test operators
-eq: be equal to (Equal)
-ne: It's not equal to (Not Equal)
-gt: Greater than (Greater Than)
-lt: Less than (Lesser Than)
-le: Less than or equal to (Lesser or Equal)
-ge: Greater than or equal to (Greater or Equal)
1.2 Integer comparison
Integer value comparison refers to the comparison between two given integer values , Judge the relationship between the first number and the second number , If it is greater than 、 be equal to 、 Less than the second number . Common operation options for integer value comparison are as follows , When using, put the operation options to
Compare between two integers .
Common test operators
-eq: The first number equals (Equal) The second number .
-ne: The first number is not equal to (Not Equal) The second number .-gt: The first number is greater than (Greater Than) The second number .-lt: The first number is less than (Lesser Than) The second number .
-le: The first number is less than or equal to (Lesser or Equal) The second number .-ge: The first number is greater than or equal to ( Greater or Equal) The second number
example 1
who lwc -l
[ $ (who | wc -l) -le 5 ] &&echo " Too few users "
[ $(who / wc -l) -ge 10 ] && echo "> = 10. "
example 2
FreecC=$ (free -m l grep "Mem: " | awk '{print $6} ')
[$Freecc -lt 4096 ]&& echo ${FreecC}MB
mem_size=$ (free -m | grep "Mem: " | awk '{print $4} ')
[$mem_size -ge 1024 ]&& echo
" because 192.168.10.17 The server system has insufficient memory resources , Please handle the fault as soon as possible ."
1.3 String comparison
String comparisons are often used to check user input 、 Whether the system environment meets the conditions , In providing interactive operation shell Script , It can also be used to judge whether the position parameters entered by the user meet the requirements . The common operation options for string comparison are as follows .
-: The first Ningfu string is the same as the second string .
!=: The first string is not the same as the second string , among "!" The sign means reverse .
-z Check if the string is empty (zero), Variables that are undefined or given null values are treated as empty strings .
example 1
echo $LANGzh_CN.UTF-8
[ $LANG!="en. us" ]& & echo "Not en.us"
example 2
read -p " Overwrite existing file ( yes/ no ) ?"
ACK Overwrite existing file
( yes/no ) ?yes
[$ACK = "yes" ]&& echo" Cover "
1.4 Logic test
Logical testing refers to judging the dependency between two or more conditions . When the system task depends on several different conditions , According to these
Whether the conditions are true at the same time or as long as one of them is true , There needs to be a testing process .
Common logic test operations, such as ” Next , Put it between different test statements or commands .
&&: Logic and , Express " and ”, Only when the last two conditions are true , The return value of the entire test command is by
0 ( It turns out that ). Use test Command test ,“&&” Can be changed to "-a”.
●11: Logic or , Express " perhaps ”, As long as one of the two conditions “ One set up , The return value of the entire test command is 0 ( It turns out that ). Use test Command test ,“11” Can be changed to "-o”.
●!: Logical not , Express " No ”, Only when the specified conditions are not true , The return value of the entire test command is 0 ( It turns out that ).
example 1
[ -d /etc ] && [ -r /etc ] && echo "You can open it"
[ -d /etc ] || [ -d /home ] && echo "ok"
In the operation options of the above logic test ,"&&" and “11" It is also commonly used for command operations with different intervals , Its function is similar . In fact, I have been in contact with “&&" Application of operation , Such as “make && make install" Compilation of Installation operation .
for example , To judge the current Linux Whether the kernel version of the system is greater than 3.4, You can do the following . among ,
The kernel version number passes uname and awk Command to get
example 2
uname - r
// check Look at the kernel version information 3.10.0-514.e17.x86_ 64 I
Mnum=$ (uname -r I awk -F. ' {print $1}') // Take the major version number
Snum=$ (uname -r | awk -F. '{print $2}') // Take the secondary version number
[ $Mnum-ge3 ] && [ $Snum-gt4 ] && echo" Meet the requirements "
Two .if Statement single branch
( One ). Single branch if sentence
Actually use "&&" and “11" Logic test can complete simple judgment and perform corresponding operations , But when you need to choose the life to execute
Make more sentences , This approach will make the execution of the code very complex , Hard to understand . And use a dedicated if
Conditional statements , You can better organize the script structure , Make layers clear ,
Clear and easy to understand
( Two ). Single branch if
sentence : For single branch selection structure , Only in “ Conditions established ” The corresponding code will be executed , Otherwise, nothing will be done .
Grammar format :
1)
if Conditional test operation
then
Command sequence
fi
# Notice that there's an end , Make a pair at the beginning and end, otherwise you will report a syntax error
2)
if Conditional test operation ; then
Command sequence
fi
if[3 -gt 2]; then .
echo "ok""
fi
[3-gt2] & &echo"ok"
example 1 Determine whether the directory exists
#! /bin/bash
if ls /mnt
then
echo "it's ok"
fi
example 2
Determine the mount point , If it doesn't exist, it will be created automatically
#! /bin/bash
MOUNT_ DIR= "/media/ cdrom/”
#2. If you don't have this directory, create a directory
if[ !-d$MOUNTDIR ]
then
mkdir -P $MOUNT_DIR
fi
example 3 Determine whether the end of the input is .sh
#!/bin/bash
read -p " Please enter filename :”file
If [ [ $file == *.sh ] ]; then
echo " This is a shell Foot wood "
fi
Double branch if The statement is only on a single branch basis for " Conditions not established ” To perform another operation , instead of
“ Sit idly by ” Without doing anything
example 1 Determine whether the target host is alive or not , Print if you live is up, If it doesn't survive, print is down
C ping The number of times
-1 How long each time ping- once , The unit is seconds
-W Time for feedback , If it doesn't work, you can speed up the feedback time , The unit is seconds
#! /bin/bash
ip=192.168.10.10
ping -c 2 -i 0.2 -W 3 $ip &> /dev/null
if[$?-eq0];then
echo "$ip is up "
else
echo "$ip is down"
fi
Judge by . sh The script at the end is a shell Script ( Use of brackets : Can pattern match )
[abc==abc]
[[ abc == abc* ]]
example 4
#! /bin/bash .
read -p " Check that the directory exists , Please enter the directory :”
aaa
if ls $aaa > /dev/null
then
echo” Directory exists "
else
echo " Please enter the correct path "
fi
example 5
#! /bin/bash
netstat -natup I grep ":80" &> /dev/nu1l
if[$?-eq0];then
echo " The website service is already running !”
else
echo " start-up httpd service " .
yum install -y httpd > /dev/null
systemctl start httpd
fi
( 3、 ... and ). nesting if sentence
example 1. Judge httpd Did the service start
Judge whether to start
If you start ------ Output started
If it doesn't start ---- Determine whether to install --- If installed --- start-up
If not installed ---- install --- If the installation is successful --- start-up
If the installation is not successful --—-- Report errors
ps aux l grep httpd l grep -v grep
if [ $? -ne o ] ;then
if [ "$ (rpm -q httpd) " == " Package not installed httpd " ];then
yum -y install httpd
systemctl start httpd
else
systemctl start httpd
fi
else
echo "httpd is running"
fi
example 2. Determine whether a user has a home directory , Printing is normal , Did not ask if you need to delete , If yes, delete it, and judge that the system has incomparable users ---- Yes --- Determine whether there is a home directory ---- Yes ---- Output normal user
nothing ----- Ask if you want to delete this user ---- yes ---- Delete
no ---- Exit script
nothing ---- Prompt that there is no such user
example 1 Users of the system :
There are users and home directories
There are users but no home directories
No users but home directory
read -p " Please enter a user name :"user
if grep $user fetc/passwd &> / dev/null;then
if[ -d f home/ suser ] ;then
echo" The user status is normal "
else
read -p " The user does not have a home directory , Delete this user , Please enter [yes/no]: " ask
if [ $ask == yes ] ; then
echo " Deleting user ..."
userdel $user_6>_ldev/null; sleep 2
echo" The user has been removed "
elif [ $ask == no ] ;then
exit
fi
fi
else
echo" The user does not exist "
fi
( Four ).case sentence
case
Statement can make the structure of the script program clearer 、 distinct , Commonly used for service startup 、 restart 、 Stopped script , Some services do not provide such control scripts , Need to use case Statement writing
case Statement is mainly applicable to the following situations : There are many values for a variable , Each of these needs to be Each value executes different command sequences . This is the case with multi - branched
if The sentences are very similar , It's just if Statements need to judge multiple different conditions , and case The statement just judges the different values of a variable
case A variable's value in
Pattern 1)
Command sequence 1
;;
Pattern 2)
Command sequence 1
;;
*
Default command sequence
esac
case Line ending must be a word "in", Every time - The pattern must be enclosed with a closing parenthesis ")” end .
Double a semicolon “;;” Indicates the end of the command sequence .
In pattern string , You can use square brackets to indicate a continuous range , Such as “[0-9]"; You can also use the vertical bar symbol “|" Represents or , Such as “A | B".
final “*)” Represents the default mode , Among them * It's equivalent to a wildcard .
Case study :
What to eat today ? - - Seven days a week is not the same
case Statement execution flow : use first " A variable's value " With the model 1 Compare , If the values are the same, the execution mode 1
After the command sequence , Until I met a double semicolon “;;“ Jump back to esac, Means to end a branch : If and mode 1 It doesn't match , Then continue with the mode 2
Compare , If the values are the same, the execution mode 2 After the command sequence , Until I met a double semicolon “;;” Jump back to
esac, Means to end a branch ... . And so on , If no matching values are found , Then execute the default mode “*)” After the command sequence , Until I met esac End the branch after
Typical cases : Check the character type entered by the user
#!/bin/bash
read -P " Please enter a character , And press Enter Key confirmation : " KEY
case "SKEY" ir
[a-z]1[A-Z])
echo " You're typing in letters ”
;
[0-9])
echo " You're typing in numbers "
::
*)
echo " You type in spaces ,*,_ , Equal special character "
esac
#!/bin/bash
read -P " Please enter your score (0-100) :”score
[[ Sscore -ge 85 6& Sscore -le 100 ]] && a="great"
[[ $score -ge 70 &6 sscore -1t 85 ]] &6 a="standard"
[[ Sscore -ge 0 66 $score -1t 70 ]] 66 a="false"
case $a in
great)
echo "Sscore branch , good !"
;;
standard)
echo "sscore branch , qualified !"
;;
false )
echo "sscore branch , unqualified !"
;;
*)
echo " Incorrect input !"
esac
The first method
#!/bin/bash
read -P“ Please enter your score :”score
[ Sscore -eq 100 ] && a=0
[ Sscore -ge 90 ] 66[ $score -1t 100 ] 66 a=10
[ Sscore -ge 70 -a $score -le 89 ] 66 a=20
[ Sscore -ge 60 -a $score -le 69 ] && a=30
[ $score -ge 0 -a $score -1t 60 ] && a=40
case $a in
echo " Xiuer !”
;;
10)
echo "sscore branch , copy 10 All over !"
;;
20)
echo "Sscore branch , copy 20 All over !”
;;
30)
echo "sscore branch , copy 30 All over !"
;;
40 )
echo "sscore branch , Copy all 30 All over !"
;;
*)
echo
” Incorrect input !”
esac
The second method
read -P” Please enter your score :”score
case Sscore in
100 )
echo " Xiuer !”
;;
9(0-9])
echo "Sscore branch , copy 10 All over !"
;;
[78](0-9])
echo "sscore branch , copy 20 All over !"
;;
6[0-9])
echo "Sscore branch , copy 30 All over !"
;;
[0-9]1[1-5][0-9] )
echo "Sscore branch , Copy all 30 All over !"
;;
*)
echo” Incorrect input !”
esac
To write apache Start service script
#!/bin/bash
case $1 in
start)
/usr/bin/systemctl $1 httpd
/usr/bin/ps aux I grep httpd
echo "httpd start ”
;;
stop)
/usr/bin/systemct1 $1 httpd
/usr/bin/ps aux I grep httpd
echo "httpd stop"
;;
restart)
echo "httpd STOP..."
/usr/bin/ps aux I grep httpd
/usr/bin/systemct1 $1 httpd
echo "httpd restat..."
/usr/bin/ps aux I grep httpd
;;
status)
/usr/bin/systemctl $1 httpd
;;
*)
echo "plases input start | stop | restat | status"
esac
边栏推荐
- Mysql - - Index
- The latest analysis of R1 quick opening pressure vessel operation in 2022 and the examination question bank of R1 quick opening pressure vessel operation
- China's TPMS industry demand forecast and future development trend analysis report Ⓐ 2022 ~ 2028
- 90 后,辞职创业,说要卷死云数据库
- MySQL - idea connects to MySQL
- Station B, dark horse programmer, employee management system, access conflict related (there is an unhandled exception at 0x00007ff633a4c54d (in employee management system.Exe): 0xc0000005: read locat
- Exclusive interview with the person in charge of openkruise: to what extent has cloud native application automation developed now?
- Yyds dry inventory hcie security Day12: concept of supplementary package filtering and security policy
- A little understanding of GSLB (global server load balance) technology
- 2022-2-14 acwing1027 grid access
猜你喜欢

17 websites for practicing automated testing. I'm sure you'll like them

The post-90s resigned and started a business, saying they would kill cloud database
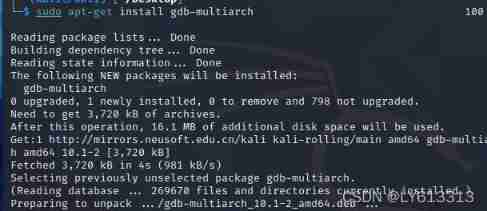
Kali2021.4a build PWN environment

2022 free examination questions for safety management personnel of hazardous chemical business units and reexamination examination for safety management personnel of hazardous chemical business units
2022 electrician (elementary) examination questions and electrician (elementary) registration examination
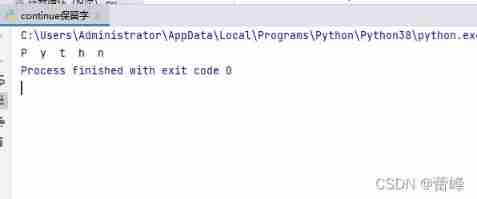
Control loop of program (while loop)

Goodbye 2021, how do programmers go to the top of the disdain chain?

MySQL——JDBC
Persistence of Nacos

2022 G3 boiler water treatment registration examination and G3 boiler water treatment examination papers
随机推荐
UI automation test: selenium+po mode +pytest+allure integration
Under the double reduction policy, research travel may become a big winner
常用sql集合
C程序设计的初步认识
MySQL - idea connects to MySQL
Is the account opening of Guotai Junan Securities safe and reliable? How to open Guotai Junan Securities Account
Monkey/ auto traverse test, integrate screen recording requirements
国泰君安证券开户是安全可靠的么?怎么开国泰君安证券账户
Tkinter Huarong Road 4x4 tutorial III
Exclusive interview with the person in charge of openkruise: to what extent has cloud native application automation developed now?
Preliminary understanding of C program design
4. Data splitting of Flink real-time project
MySQL - SQL injection problem
内存分析器 (MAT)
MySQL——JDBC
China's coal industry investment strategic planning future production and marketing demand forecast report Ⓘ 2022 ~ 2028
UC Berkeley proposes a multitask framework slip
90 後,辭職創業,說要卷死雲數據庫
MySQL——JDBC
Memory analyzer (MAT)