当前位置:网站首页>js 迭代器 生成器 异步代码处理 promise+生成器 -> await/async
js 迭代器 生成器 异步代码处理 promise+生成器 -> await/async
2022-07-02 09:43:00 【大海里没有水】
一、迭代器
迭代器本身就是一个对象,可以帮助我们遍历另外一个对象
1、认识迭代器
// 下面是我们编写的一个迭代器,就是一个对象。帮我们遍历容器结构
// const iterator = {
// next: function () {
// return {
// done: true,
// value: 123,
// };
// },
// };
// 数组
const names = ["a", "b", "c"];
const iterator = names[Symbol.iterator]();
console.log(iterator.next());
console.log(iterator.next());
console.log(iterator.next());
console.log(iterator.next());
// 控制台依次打印:
// { value: 'a', done: false }
// { value: 'b', done: false }
// { value: 'c', done: false }
// { value: undefined, done: true }
console.log("================================");
// 创建一个迭代器对象来访问数组
let index = 0;
const namesIterator = {
next: function () {
// return { done: false, value: "a" };
// return { done: false, value: "b" };
// return { done: false, value: "c" };
if (index < names.length) {
return {
done: false, value: names[index++] };
} else {
return {
done: true, value: undefined };
}
},
};
console.log(namesIterator.next());
console.log(namesIterator.next());
console.log(namesIterator.next());
console.log(namesIterator.next());
console.log(namesIterator.next());
2 、迭代器函数
const names = ["a", "b", "c"];
const num = [10, 20, 30];
function createArrayIterator(arr) {
let index = 0;
return {
next: function () {
if (index < arr.length) {
return {
done: false,
value: arr[index++],
};
} else {
return {
done: true, value: undefined };
}
},
};
}
const namesIterator = createArrayIterator(names);
console.log(namesIterator.next());
console.log(namesIterator.next());
console.log(namesIterator.next());
console.log(namesIterator.next());
const numIterator = createArrayIterator(num);
console.log(numIterator.next());
console.log(numIterator.next());
console.log(numIterator.next());
console.log(numIterator.next());
3、可迭代对象

for-of就是迭代器本质啦
// const names = ["a", "b", "c"];
// // 创建一个迭代器对象来访问数组
// let index = 0;
// const namesIterator = {
// next: function () {
// if (index < names.length) {
// return { done: false, value: names[index++] };
// } else {
// return { done: true, value: undefined };
// }
// },
// };
// 可迭代对象
const iteratorObj = {
names: ["a", "b", "c"],
// 满足可迭代协议
[Symbol.iterator]: function () {
let index = 0;
return {
// 这里需要改成箭头函数
next: () => {
if (index < this.names.length) {
return {
done: false, value: this.names[index++] };
} else {
return {
done: true, value: undefined };
}
},
};
},
};
console.log(iteratorObj[Symbol.iterator]);
// 1.第一次调用iteratorObj[Symbol.iterator]
const iterator = iteratorObj[Symbol.iterator]();
console.log(iterator.next());
console.log(iterator.next());
console.log(iterator.next());
console.log(iterator.next());
// 第二次调用iteratorObj[Symbol.iterator]: 生成新的迭代器
const iterator1 = iteratorObj[Symbol.iterator]();
console.log(iterator1.next());
console.log(iterator1.next());
console.log(iterator1.next());
console.log(iterator1.next());
// 3.for...of 可以遍历的东西必须是一个可迭代对象
// for其实是语法糖,做的就是iterator.next(),拿到对象,然后在取.value。当done:false,就把value取出来。done为true的时候,就停止遍历
const obj = {
name: "chen",
age: 23,
};
for (const item of obj) {
console.log(item); //TypeError: obj is not iterable
}
4、原生迭代器对象
String、Array、Map、Set、arguments对象、NodeList集合都是, 注意:对象就不是了
// 内置创建可迭代对象
// 1、数组
const names = ["a", "b", "c"];
console.log(names[Symbol.iterator]);
const iterator = names[Symbol.iterator]();
console.log(iterator.next());
console.log(iterator.next());
console.log(iterator.next());
console.log(iterator.next());
// 2、Map / Set
const set = new Set();
set.add(10);
set.add(100);
set.add(1000);
console.log(set[Symbol.iterator]().next());
for (const item of set) {
console.log(item)
}
console.log('-----------')
// 3、函数中arguments也是一个可迭代对象
function foo(x, y, z) {
for (const arg of arguments) {
console.log(arg)
}
}
foo(10, 20, 30)
5、可迭代器对象的应用场景
// 1、for-of
// 2、展开运算符
const names = ["a", "b", "c"];
const obj = {
name: 'chen',
age: 23
}
// 不可以迭代
// for (const item of obj) {
// console.log(item)
// }
// 值得注意的是,下面这样是可以的
// 这是ES9中新增的一个特性,专门针对对象展开做的特殊处理,用的也不是迭代器。通过obj.entries()
const newObj = {
...obj }
console.log(newObj) //{ name: 'chen', age: 23 }
// 这种也不是使用迭代器,使用的还是entries()
const {
name, age } = obj
// 3、解构语法,使用的还是迭代器,调的是next().value
const [name1, name2, name3] = names
console.log(name1, name2, name3) // a b c
// 4、创建一些对象时
const set1 = new Set(names)
// const set2 = new Set(1334); //报错
// 创建数组
const arr1 = Array.from(names)
// 5、Promise.all
Promise.all(names).then(res => {
console.log(res) //[ 'a', 'b', 'c' ]
})
6、自定义类的可迭代性
// class Person {
// }
// // 不是可迭代对象
// const p1 = new Person();
// const p2 = new Person();
// 案例: 创建一个教师类,创建出来的对象都是可迭代对象
class Classroom {
constructor(address, name, students) {
this.address = address;
this.name = name;
this.students = students;
}
entry(newStudent) {
this.students.push(newStudent);
}
[Symbol.iterator]() {
let index = 0;
return {
next: () => {
if (index < this.students.length) {
return {
done: false, value: this.students[index++] };
} else {
return {
done: true, value: undefined }
}
}
}
}
}
const classroom = new Classroom('北京', '计算机教室', ['zhangsan', 'lisi', 'wangwu']);
classroom.entry('jianren')
// classroom不是可迭代的对象,如果想迭代,需要在类中加上[Symbol.iterator]
for (const item of classroom) {
console.log(item)
}
// 下面输出:
// zhangsan
// lisi
// wangwu
// jianren
// 如果是function,也是一样的
// function Person () {
// }
// Person.prototype[Symbol.iterator] = function(){
// }
二、生成器
1、什么是生成器 - 生成器函数

// 生成器函数, 有* ,通过yield控制代码执行流程,返回值就是一个迭代器
function* foo() {
console.log('函数开始执行~')
// 代码执行的时候暂停
// 第一段代码
const value = 100
console.log(value)
yield
// 第二段代码
const value1 = 200
console.log(value1)
yield
// 第三段代码
const value2 = 300
console.log(value2)
yield
console.log('函数执行结束!')
}
// 这么调用,一行代码不会执行
foo()
// 当我们调用生成器函数时,会返回一个生成器(特殊的迭代器)
const generator = foo()
// 执行第一段代码
generator.next()
// 执行第二段代码
generator.next()
// 执行第三段代码
generator.next()
2、生成器函数的执行流程
// 当遇到yield的时候只暂停函数的执行
// 当遇到return的时候,生成器就停止执行
function* foo() {
console.log('函数开始执行~')
const value = 100
console.log(value)
// return value,停止了。如果想返回,直接跟在后面
yield value * 200
const value1 = 200
console.log(value1)
yield
const value2 = 300
console.log(value2)
yield
console.log('函数执行结束!')
}
foo()
const generator = foo()
// generator.next()//100
// generator.next()//200
// generator.next()//300
// generator.next()
console.log(generator.next())
console.log(generator.next())
console.log(generator.next())
console.log(generator.next())
// 依次打印:
// { value: undefined, done: true }
// { value: undefined, done: true }
// { value: undefined, done: true }
// { value: undefined, done: true }
// 返回的就是迭代器:
// 100
// { value: undefined, done: false }
// 200
// { value: undefined, done: false }
// 300
// { value: undefined, done: false }
// 函数执行结束!
// { value: undefined, done: true }
3、生成器的next传递参数
function* foo() {
console.log('函数开始执行~')
const value = 100
console.log(value)
const n = yield value
const value1 = n * 10
console.log(value1)
yield
const value2 = 300
console.log(value2)
yield
console.log('函数执行结束!')
}
foo()
// 1. 生成器上的next方法可以传递参数
const generator = foo()
console.log(generator.next())
console.log(generator.next(10))
console.log(generator.next())
console.log(generator.next())
4、生成器替代迭代器的使用1
// 生成器替代迭代器
function* createArrayIterator(arr) {
let index = 0;
// 写法一:
// yield arr[index++]; //{ done: true, value: undefined };
// yield arr[index++];
// yield arr[index++];
// 写法二:
// yield 'a';
// yield 'b';
// yield 'c';
// 写法三:
// for (const item of arr) {
// yield item;
// }
// 写法四: yield* 可迭代对象
yield* arr
// return {
// next: function () {
// if (index < arr.length) {
// return {
// done: false,
// value: arr[index++],
// };
// } else {
// return { done: true, value: undefined };
// }
// },
// };
}
const names = ["a", "b", "c"]
const namesIterator = createArrayIterator(names);
console.log(namesIterator.next());
console.log(namesIterator.next());
console.log(namesIterator.next());
console.log(namesIterator.next());
5、生成器替代迭代器的使用2
// 生成器替代迭代器
function* createArrayIterator(arr) {
let index = 0;
yield* arr;
}
// 2.创建一个函数,这个函数可以迭代一个范围内的数字
// 10 20
// function createRangeIterator(start, end) {
// // 写法一:
// let index = start;
// return {
// next: function () {
// if (index < end) {
// return {
// done: false,
// value: index++,
// };
// } else {
// return { done: true, value: undefined };
// }
// },
// };
// }
function* createRangeIterator(start, end) {
// 写法一:
let index = start;
while (index < end) {
yield index++;
}
}
const iterator = createRangeIterator(10, 20);
console.log(iterator.next());
console.log(iterator.next());
console.log(iterator.next());
console.log(iterator.next());
// 输出如下:
// { done: false, value: 10 }
// { done: false, value: 11 }
// { done: false, value: 12 }
// { done: false, value: 13 }
6、异步代码的处理方案
function requestData(url) {
// 异步请求的代码会被放入到executor中
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve(url);
}, 1000);
});
}
// 1.第一种方案: 多次回调
// 回调地狱
// requestData('chen').then(res => {
// requestData(res + '/aaaa').then(res => {
// requestData(res + '/bbbb').then(res => {
// console.log(res);
// })
// })
// })
// 2.第二种方案: Promise中then的返回值来解决
// requestData('chen').then(res => {
// return requestData(res + '/aaaa')
// }).then(res => {
// return requestData(res + '/bbbb');
// }).then((res) => {
// console.log(res);
// })
// 3.第三种方案: Promise + generator实现(手动执行)
// function* getData() {
// const res1 = yield requestData("chen");
// const res2 = yield requestData(res1 + "/aaaa");
// const res3 = yield requestData(res2 + "/bbbb");
// console.log(res3);
// }
// const generator = getData();
// generator.next().value.then((res) => {
// // console.log(res); //如果想要拿到这个res,需要执行下一次next(),并把值传回去
// generator.next(res).value.then((res) => {
// // console.log(res);
// generator.next(res).value.then((res) => {
// console.log(res);
// });
// });
// });
// 3.第三种方案: Promise + generator实现(自动执行)
// function execGenerator(getFn) {
// const generator = getFn();
// // 使用递归
// function exec(res) {
// const result = generator.next(res);
// if (result.done) {
// return result.value;
// } else {
// result.value.then(res => {
// exec(res);
// })
// }
// }
// exec();
// }
// execGenerator(getData);
// 4.第四种方案: await/async
// function* getData() {
// const res1 = yield requestData("chen");
// const res2 = yield requestData(res1 + "/aaaa");
// const res3 = yield requestData(res2 + "/bbbb");
// console.log(res3);
// }
// 其实是yield的语法糖
async function getData() {
const res1 = await requestData("chen");
const res2 = await requestData(res1 + "/aaaa");
const res3 = await requestData(res2 + "/bbbb");
console.log(res3);
}
getData()
边栏推荐
- 字符串回文hash 模板题 O(1)判字符串是否回文
- [ybtoj advanced training guidance] judgment overflow [error]
- 2.6 using recursion and stack - [tower of Hanoi problem]
- Introduction to CPU instruction set
- 测试左移和右移
- 深拷貝 事件總線
- Embedded Software Engineer career planning
- SparkContext: Error initializing SparkContext解决方法
- post请求体内容无法重复获取
- 倍增 LCA(最近公共祖先)
猜你喜欢

Deep copy event bus

Mysql database foundation
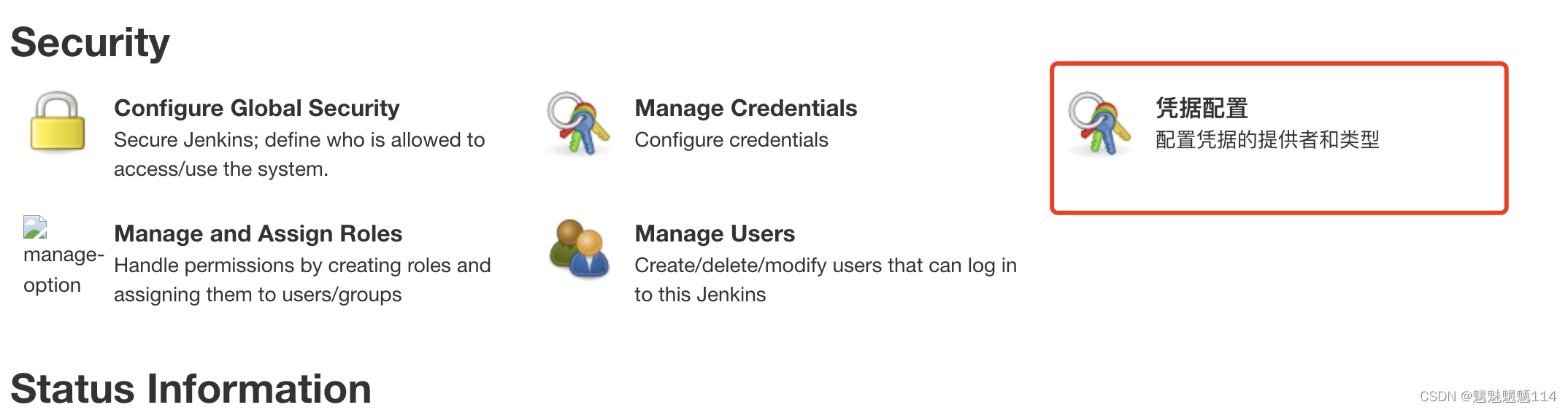
Jenkins voucher management
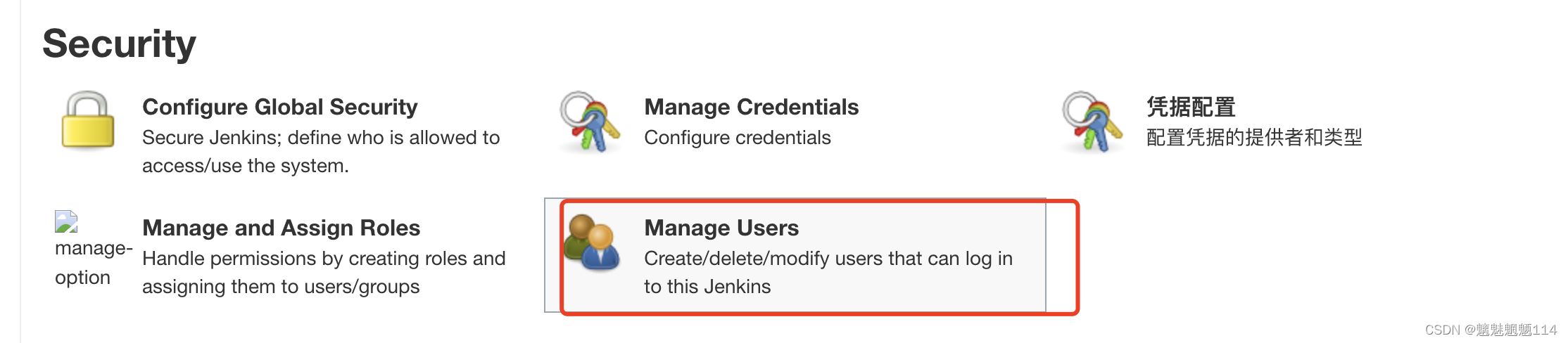
Jenkins user rights management
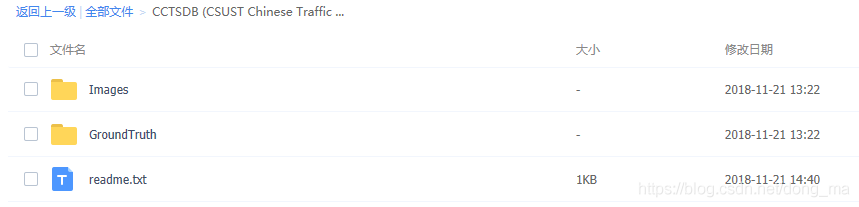
China traffic sign detection data set

SparkContext: Error initializing SparkContext解决方法
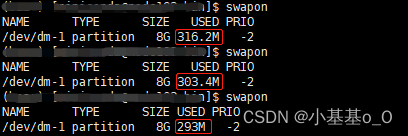
CDH存在隐患 : 该角色的进程使用的交换内存为xx兆字节。警告阈值:200字节
![[FFH] little bear driver calling process (take calling LED light driver as an example)](/img/e7/153ae9f1befc12825d277620049f9d.jpg)
[FFH] little bear driver calling process (take calling LED light driver as an example)
Openssh remote enumeration username vulnerability (cve-2018-15473)

Go学习笔记—多线程
随机推荐
[I'm a mound pytorch tutorial] learning notes
(C language) octal conversion decimal
mysql索引和事务
Lekao: 22 year first-class fire engineer "technical practice" knowledge points
Find the factorial of a positive integer within 16, that is, the class of n (0= < n < =16). Enter 1111 to exit.
Input a three digit number and output its single digit, ten digit and hundred digit.
Find the common ancestor of any two numbers in a binary tree
[ybtoj advanced training guidance] cross the river [BFS]
Leetcode209 subarray with the smallest length
Jenkins voucher management
From scratch, develop a web office suite (3): mouse events
mysql表的增删改查(进阶)
深拷貝 事件總線
String palindrome hash template question o (1) judge whether the string is palindrome
Leetcode - Sword finger offer 51 Reverse pairs in an array
JZ63 股票的最大利润
Those logs in MySQL
Multiply LCA (nearest common ancestor)
Drools dynamically add, modify, and delete rules
刷题---二叉树--2