当前位置:网站首页>刷题---二叉树--2
刷题---二叉树--2
2022-07-02 09:42:00 【菜菜不恰菜】
平衡二叉树

解题思路:
一个二叉树每个节点 的左右两个子树的高度差的绝对值不超过 1 。题目中已经给出我们提示,我们需要先求出左子树的高度,在求出右子树的高度,然后看他们的高度差。
int getHeight(TreeNode root){
if(root==null){
return 0;
}
int lightLeft=getHeight(root.left);
int lightRight=getHeight(root.right);
return lightLeft>lightRight?lightLeft+1:lightRight+1;
}
public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null){
return true;
}
int left=getHeight(root.left);
int right=getHeight(root.right);
if(Math.abs(left-right)<=1&&isBalanced(root.left)&&isBalanced(root.right)){
return true;
}
return false;
}
还有一种方法我们可以在求高度的函数里面判断左右两个子树的高度差的绝对值是否超过 1,如果超过1就返回一个负数,这样如果最后结果返回一个负数,那么这个树就不是平衡二叉树。
private int getHeight1(TreeNode root){
if(root==null){
return 0;
}
int lightLeft=getHeight(root.left);
int lightRight=getHeight(root.right);
if(lightLeft>=0 && lightRight>=0 && Math.abs(lightLeft- lightRight)<=1){
return Math.max(lightLeft,lightRight)+1;
}else{
return -1;
}
}
public boolean isBalanced1(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null){
return true;
}
return getHeight1(root)>=0;
}
对称二叉树
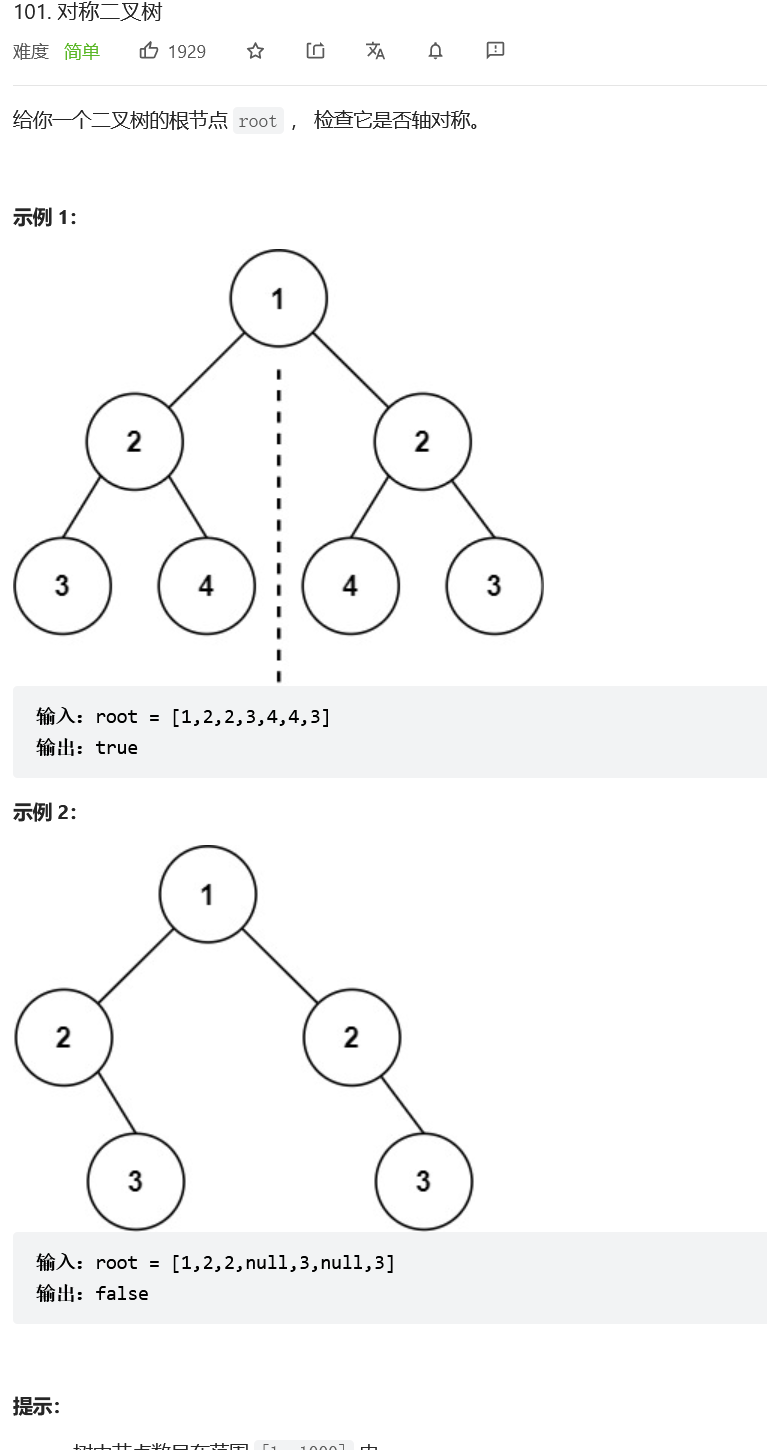 解题思路:
解题思路:
public boolean isSymmetricChild(TreeNode rightTree,TreeNode leftTree){
if(leftTree==null && rightTree!=null) return false;
if(leftTree!=null && rightTree==null) return false;
if(leftTree==null && rightTree==null) return true;
if(rightTree.val!=leftTree.val){
return false;
}
return isSymmetricChild(leftTree.left,rightTree.right)&&
isSymmetricChild(leftTree.right,rightTree.left);
}
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null) return true;
return isSymmetricChild(root.left,root.right);
}
二叉树遍历
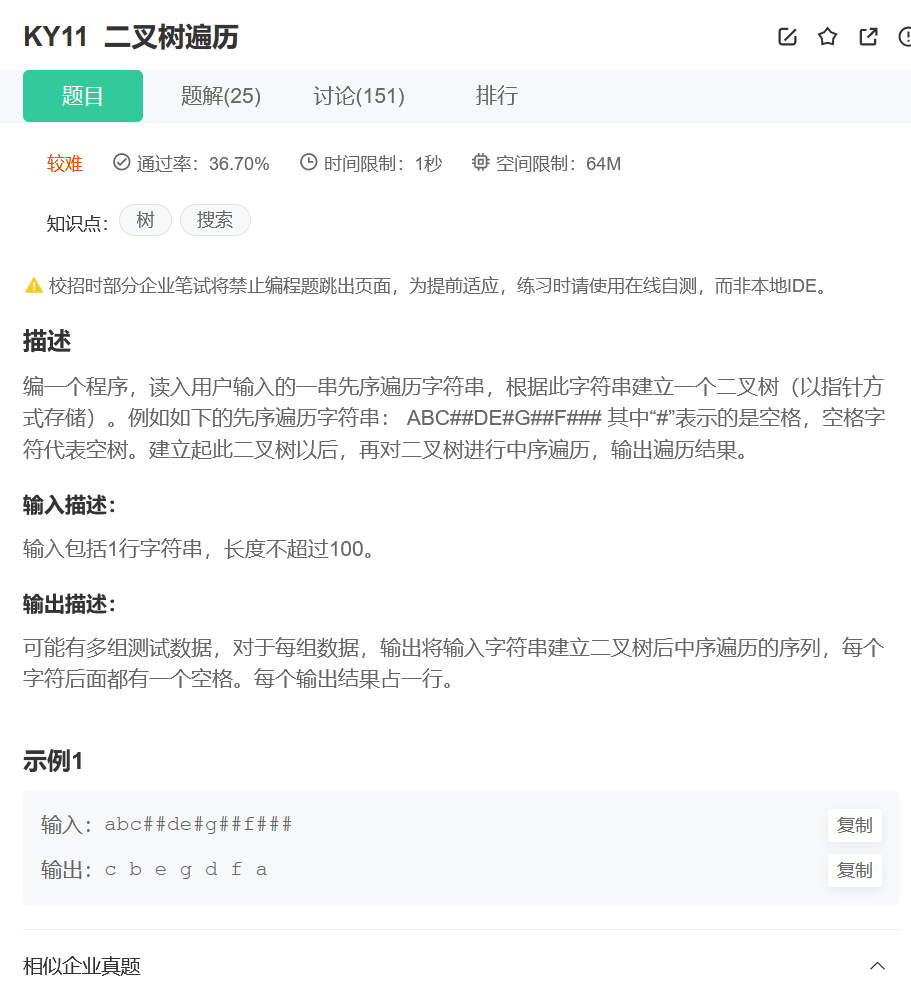 解题思路:题目给定的是前序遍历的结果,那么我们构建这棵二叉树的时候,也是要用前序遍历的方式来进行构建。
解题思路:题目给定的是前序遍历的结果,那么我们构建这棵二叉树的时候,也是要用前序遍历的方式来进行构建。

import java.util.*;
class TreeNode{
public char val;
public TreeNode left;
public TreeNode right;
public TreeNode(char val){
this.val=val;
}
}
public class Main{
public static int i = 0 ;
public static TreeNode createTree(String str) {
TreeNode root = null;
if(str.charAt(i) != '#') {
root = new TreeNode(str.charAt(i));
i++;
root.left = createTree(str);
root.right = createTree(str);
}else {
//遇到# 就是空树
i++;
}
return root;
}
public static void inorder(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) {
return;
}
inorder(root.left);
System.out.print(root.val+" ");
inorder(root.right);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
// 注意 hasNext 和 hasNextLine 的区别
while (in.hasNextLine()) {
// 注意多个输入
String str = in.nextLine();
TreeNode root = createTree(str);
inorder(root);
}
}
}
二叉树的最近公共祖先
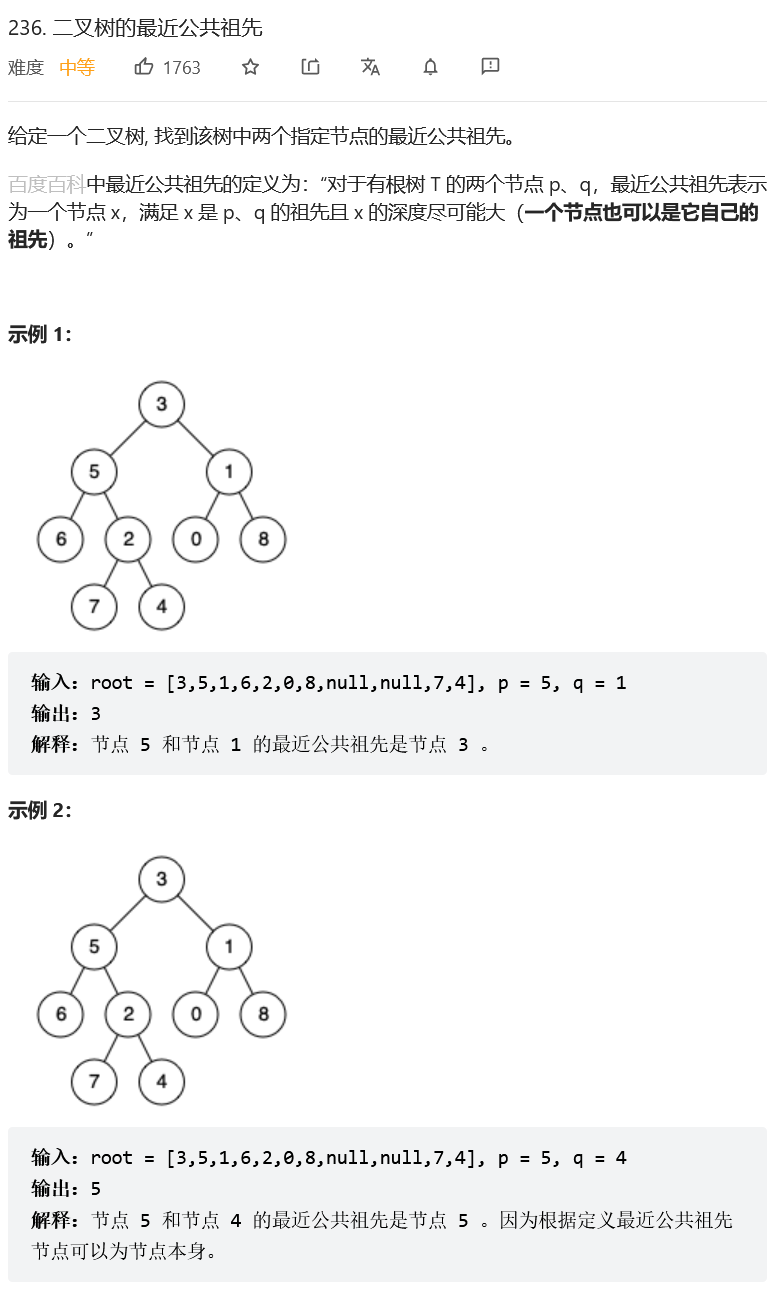
解题思路:
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if(root==null) return null;
if(p==root || q==root){
return root;
}
TreeNode left=lowestCommonAncestor(root.left,p,q);
TreeNode right=lowestCommonAncestor(root.right,p,q);
if(left!=null && right!=null){
return root;
}else if(left==null && right!=null){
return right;
}else if(left!=null && right==null){
return left;
}
return null;
}
还有第二种方法: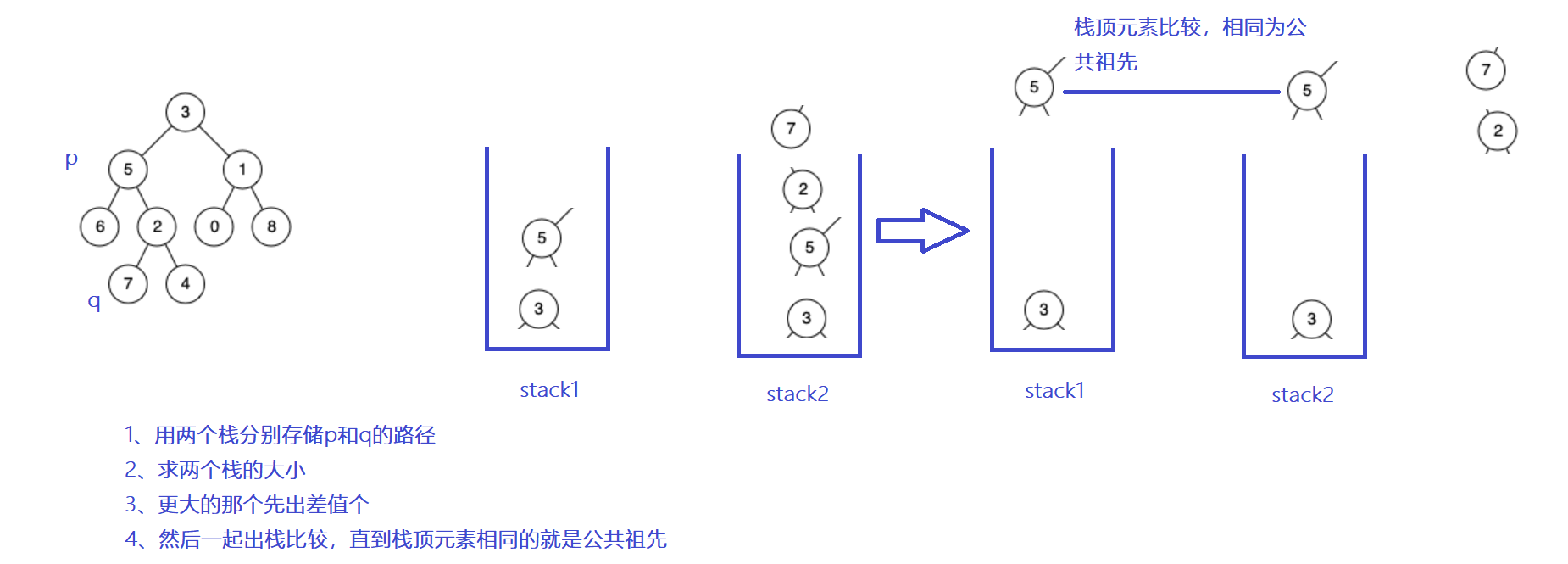
public boolean getPath(TreeNode root,TreeNode node,Stack<TreeNode> stack){
if(root==null || node==null) return false;
stack.push(root);
if(root==node) return true;
boolean flg=getPath(root.left,node,stack);
if(flg){
return true;
}
boolean flg1=getPath(root.right,node,stack);
if(flg1){
return true;
}
stack.pop();
return false;
}
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if(root==null) return null;
Stack<TreeNode> stack1=new Stack<>();
getPath(root,p,stack1);
Stack<TreeNode> stack2=new Stack<>();
getPath(root,q,stack2);
int size1=stack1.size();
int size2=stack2.size();
if(size1-size2>0){
int size=size1-size2;
while(size!=0){
stack1.pop();
size--;
}
while(!stack1.isEmpty() && !stack2.isEmpty()){
if(stack1.peek()==stack2.peek()){
return stack1.pop();
}else{
stack1.pop();
stack2.pop();
}
}
}else{
int size=size2-size1;
while(size!=0){
stack2.pop();
size--;
}
while(!stack1.isEmpty() && !stack2.isEmpty()){
if(stack1.peek()==stack2.peek()){
return stack1.pop();
}else{
stack1.pop();
stack2.pop();
}
}
}
return null;
}
二叉搜索树与双向链表
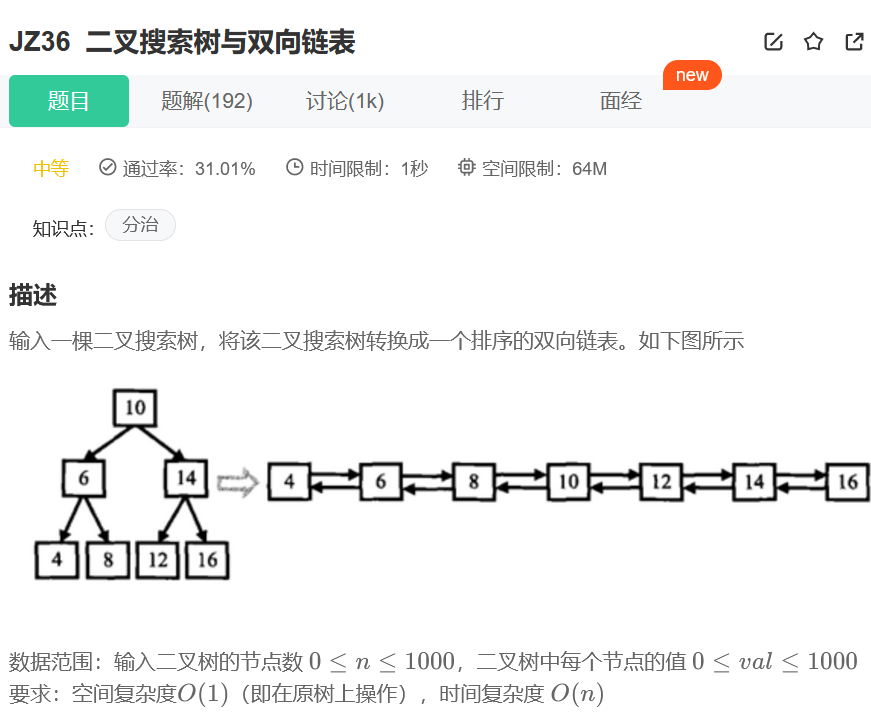 解题思路:
解题思路: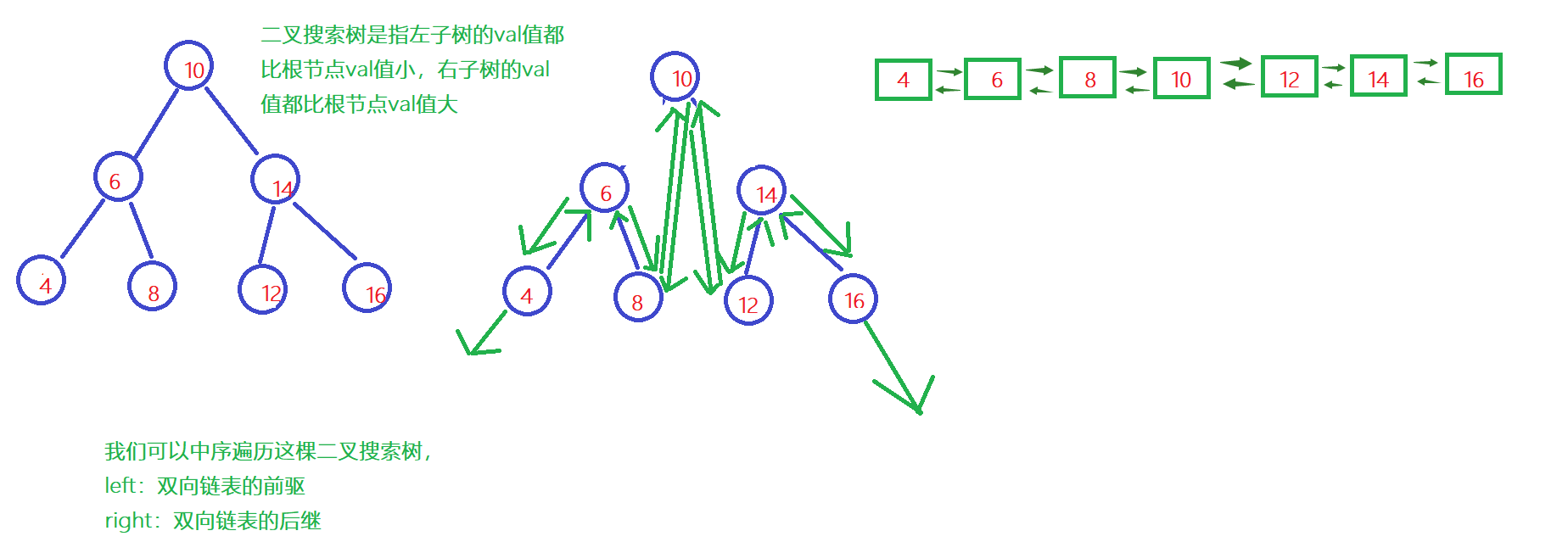
TreeNode pre=null;
public void inorder (TreeNode root){
if(root==null) return;
inorder(root.left);
root.left=pre;
if(pre!=null){
pre.right=root;
}
pre=root;
inorder(root.right);
}
public TreeNode Convert(TreeNode pRootOfTree) {
if(pRootOfTree==null) return null;
inorder(pRootOfTree);
TreeNode head=pRootOfTree;
while(head.left!=null){
head=head.left;
}
return head;
}
从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树

解题思路:
public int index=0;
public TreeNode createTreeByPandI(int[] preorder, int[] inorder,int inbegin,int inend){
if(inbegin>inend) return null;
TreeNode root=new TreeNode(preorder[index]);
//找到根节点在中序遍历的位置
int rootindex=findIndex(inorder,inbegin,inend,preorder[index]);
if(rootindex==-1){
return null;
}
index++;
//创建左子树和右子树
root.left=createTreeByPandI(preorder,inorder,inbegin,rootindex-1);
root.right=createTreeByPandI(preorder,inorder,rootindex+1,inend);
return root;
}
public int findIndex(int[] inorder,int inbegin,int inend,int key){
for(int i=inbegin;i<=inend;i++){
if(key==inorder[i]){
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {
if(inorder==null ||preorder==null) return null;
return createTreeByPandI(preorder,inorder,0,inorder.length-1);
}
从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
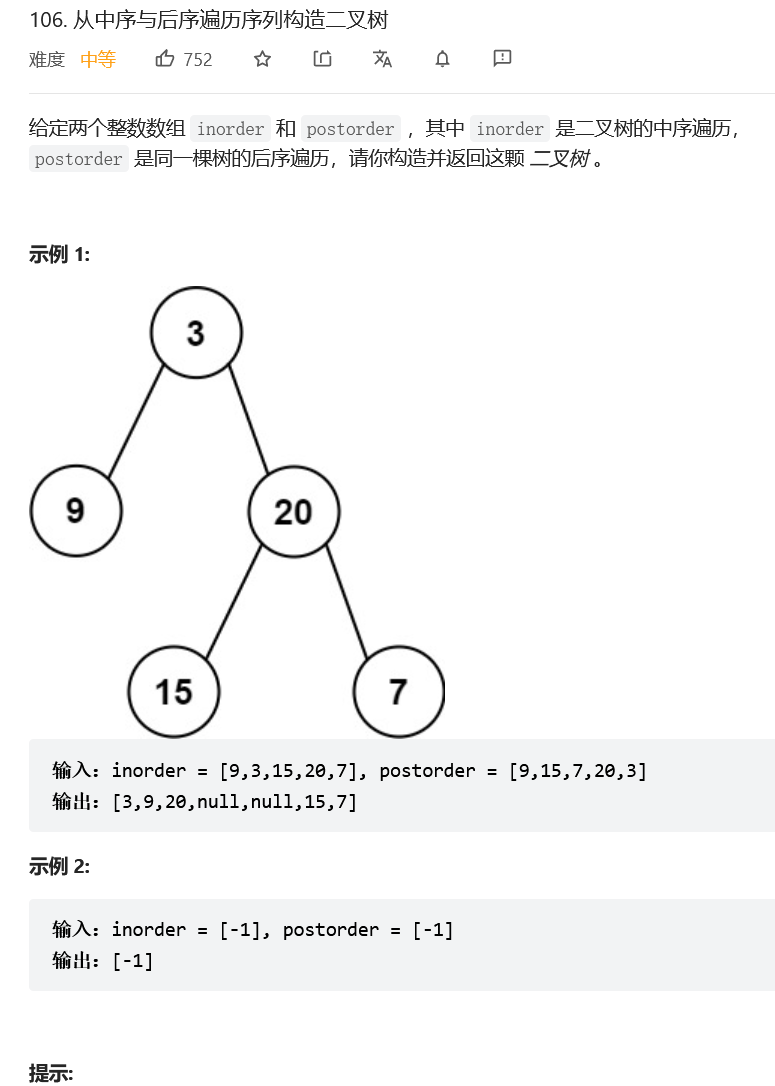 解题思路:
解题思路:
实现方法与上题大体相同,但是要注意左右子树创建的顺序。
public int index = 0;
public TreeNode createTreeByPandI(int[] postorder, int[] inorder,int inbegin,int inend){
if(inbegin>inend) return null;
TreeNode root=new TreeNode(postorder[index]);
//找到根节点在中序遍历的位置
int rootindex=findIndex(inorder,inbegin,inend,postorder[index]);
if(rootindex==-1){
return null;
}
index--;
//创建左子树和右子树
root.right=createTreeByPandI(postorder,inorder,rootindex+1,inend);
root.left=createTreeByPandI(postorder,inorder,inbegin,rootindex-1);
return root;
}
public int findIndex(int[] inorder,int inbegin,int inend,int key){
for(int i=inbegin;i<=inend;i++){
if(key==inorder[i]){
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] inorder, int[] postorder) {
if(inorder==null ||postorder==null) return null;
index=postorder.length-1;
return createTreeByPandI(postorder,inorder,0,inorder.length-1);
}
根据二叉树创建字符串
 解题思路:这里用StringBuilder存放字符串,会比较方便简单。看例子找规律,什么时候加"(“,什么时候加”)“,什么时候加”()",就看左子树和右子树是否为空。
解题思路:这里用StringBuilder存放字符串,会比较方便简单。看例子找规律,什么时候加"(“,什么时候加”)“,什么时候加”()",就看左子树和右子树是否为空。
public void treeToString(TreeNode root,StringBuilder sb){
if(root==null) return;
sb.append(root.val);
if(root.left!=null){
sb.append("(");
treeToString(root.left,sb);
sb.append(")");
}else{
if(root.right!=null){
sb.append("()");
}else{
return;
}
}
if(root.right==null){
return;
}else{
sb.append("(");
treeToString(root.right,sb);
sb.append(")");
}
}
public String tree2str(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null) return null;
StringBuilder sb=new StringBuilder();
treeToString(root,sb);
return sb.toString();
}
二叉树的前序遍历、中序遍历、后续遍历(非递归版实现)
解题思路:前序遍历:从根节点开始遍历,先遍历左子树,将遍历结果放入栈中,等遍历完左子树之后,弹出栈顶元素,栈顶元素有右子树就继续遍历,没有继续弹出下一个元素。如此循环,直到遍历完整棵树。中序遍历同理。后序遍历需要经过小小处理,因为如果不处理,会重复遍历。
//前序遍历
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
Stack<TreeNode> stack=new Stack<>();
List<Integer> ret=new ArrayList<>();
TreeNode cur=root;
while(cur!=null || !stack.isEmpty()){
while(cur!=null){
stack.push(cur);
ret.add(cur.val);
cur=cur.left;
}
TreeNode top=stack.pop();
cur=top.right;
}
return ret;
}
//中序遍历
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
Stack<TreeNode> stack=new Stack<>();
List<Integer> ret=new ArrayList<>();
TreeNode cur=root;
while(cur!=null || !stack.isEmpty()){
while(cur!=null){
stack.push(cur);
cur=cur.left;
}
TreeNode top=stack.pop();
ret.add(top.val);
cur=top.right;
}
return ret;
}
//后续遍历
public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
Stack<TreeNode> stack=new Stack<>();
List<Integer> ret=new ArrayList<>();
TreeNode cur=root;
TreeNode prev=null;
while(cur!=null || !stack.isEmpty()){
while(cur!=null){
stack.push(cur);
cur=cur.left;
}
TreeNode top=stack.peek();
//当栈顶元素以及被遍历过或者被打印过 弹出
if(top.right==null || top.right==prev){
stack.pop();
ret.add(top.val);
prev=top;//记录最近依次打印的结点
}else{
cur=top.right;
}
}
return ret;
}
二叉树的完全性检验
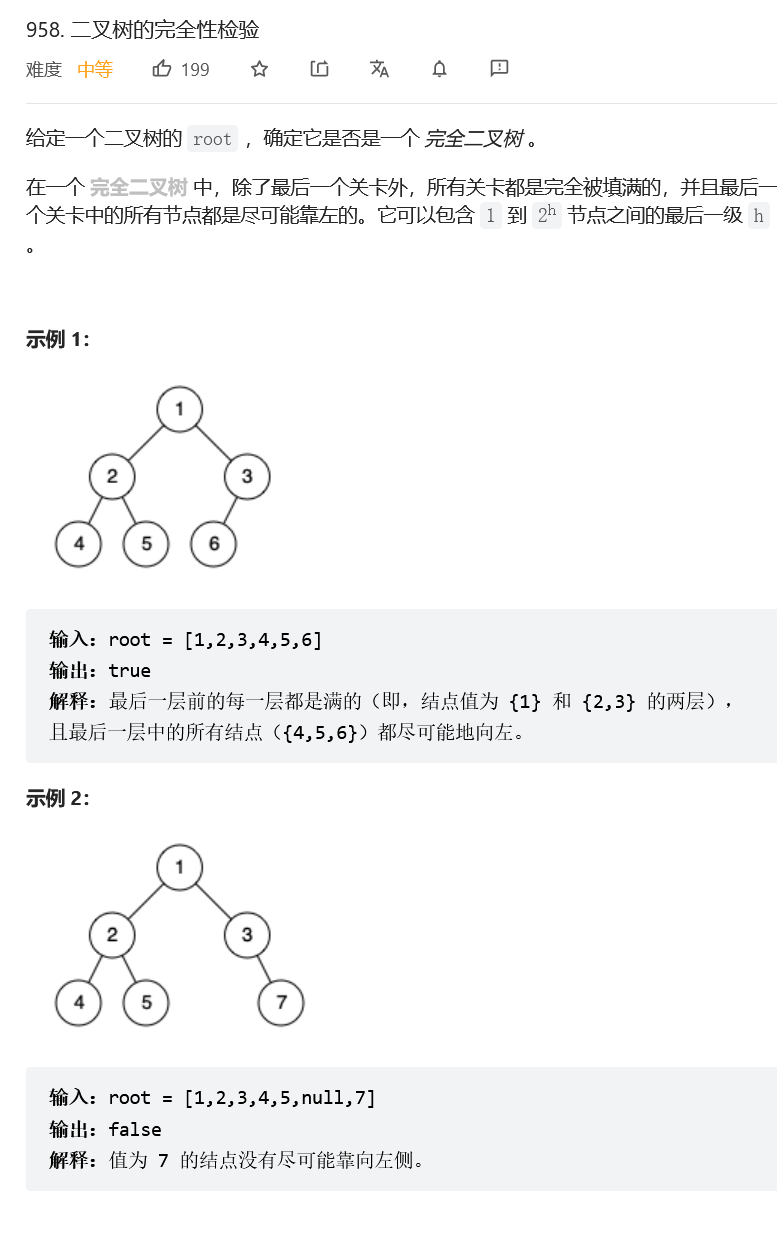
public boolean isCompleteTree(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null) return true;
Queue<TreeNode> queue=new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
boolean flg=false;
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
TreeNode tmp=queue.poll();
if(flg){
if(tmp.left!=null || tmp.right!=null){
return false;
}
}
if(tmp.left!=null && tmp.right!=null){
//左右孩子都有
queue.offer(tmp.left);
queue.offer(tmp.right);
}else if(tmp.right!=null){
//只有右孩子
return false;
}else if(tmp.left!=null){
//只有左孩子
queue.offer(tmp.left);
flg=true;
}else{
//左右孩子都没
flg=true;;
}
}
return true;
}
小结
以上就是今天的内容,有什么问题都可以在评论区留言哦
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢

Read the Flink source code and join Alibaba cloud Flink group..
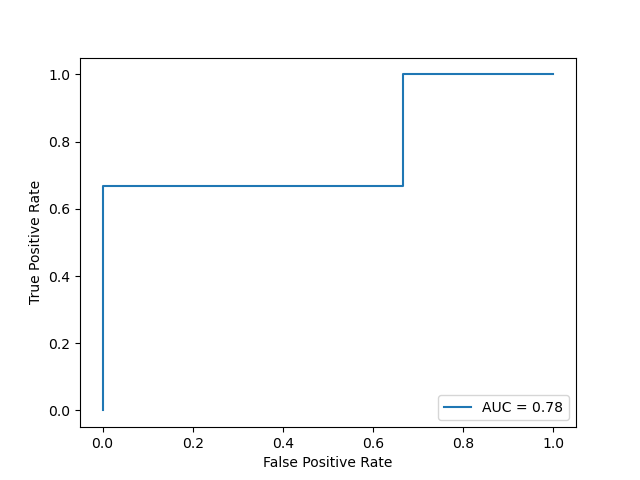
深入理解P-R曲线、ROC与AUC
![[visual studio 2019] create and import cmake project](/img/51/6c2575030c5103aee6c02bec8d5e77.jpg)
[visual studio 2019] create and import cmake project

Beautiful and intelligent, Haval H6 supreme+ makes Yuanxiao travel safer
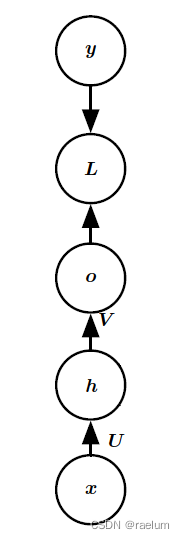
Natural language processing series (I) -- RNN Foundation
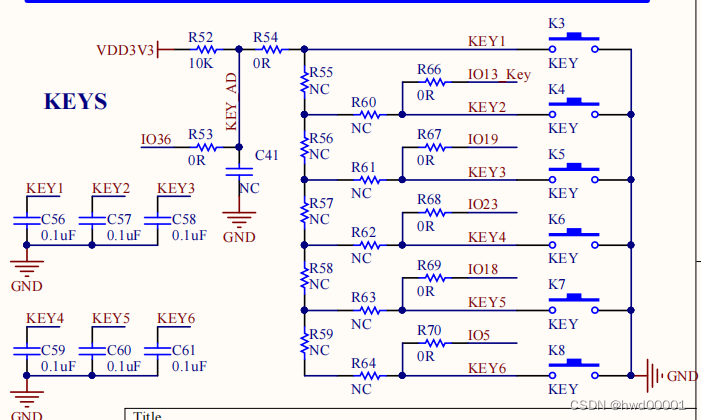
Esp32 audio frame esp-adf add key peripheral process code tracking

二分刷题记录(洛谷题单)区间的甄别
![[geek challenge 2019] upload](/img/04/731323142161a4994c14fedae38b81.jpg)
[geek challenge 2019] upload

还不会安装WSL 2?看这一篇文章就够了
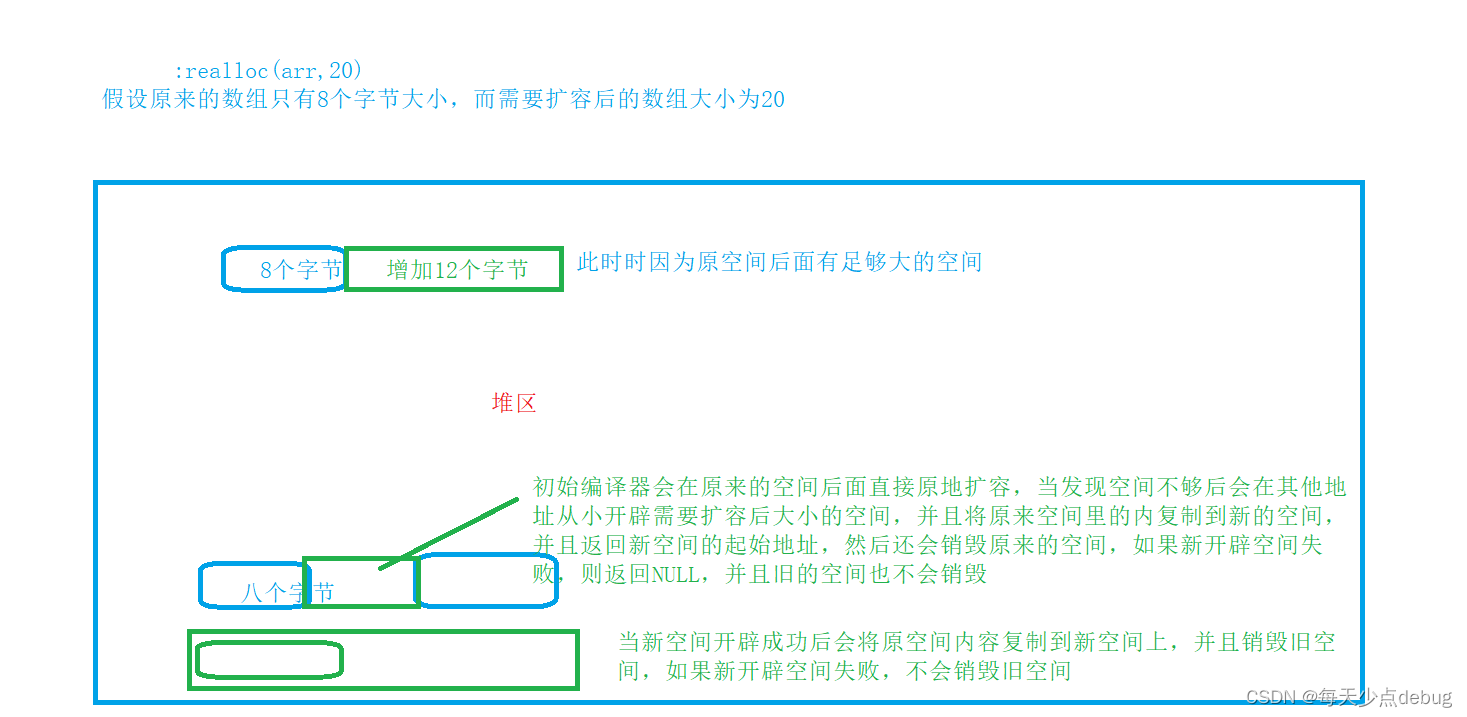
Dynamic memory (advanced 4)
随机推荐
Leetcode122 买卖股票的最佳时机 II
CMake交叉编译
YYGH-BUG-04
子线程获取Request
From scratch, develop a web office suite (3): mouse events
输入一个三位的数字,输出它的个位数,十位数、百位数。
How to Easily Create Barplots with Error Bars in R
GGPlot Examples Best Reference
还不会安装WSL 2?看这一篇文章就够了
ES集群中节点与分片的区别
自然语言处理系列(一)——RNN基础
字符串回文hash 模板题 O(1)判字符串是否回文
mysql索引和事务
求16以内正整数的阶乘,也就是n的阶层(0=<n<=16)。输入1111退出。
H5, add a mask layer to the page, which is similar to clicking the upper right corner to open it in the browser
b格高且好看的代码片段分享图片生成
【工控老马】西门子PLC Siemens PLC TCP协议详解
GGPUBR: HOW TO ADD ADJUSTED P-VALUES TO A MULTI-PANEL GGPLOT
ESP32 Arduino 引入LVGL 碰到的一些问题
Gaode map test case