当前位置:网站首页>无监督图像分类《SCAN:Learning to Classify Images without》代码分析笔记(1):simclr
无监督图像分类《SCAN:Learning to Classify Images without》代码分析笔记(1):simclr
2022-06-11 19:21:00 【秋山丶雪绪】
目录
前言
- SCAN 分为多个步骤,本文分析第一步 simclr.py 代码。
- 根据论文描述,第一步为前置任务(pretext task),用于训练特征提取网络。
- 核心思想是对同一张图像 P P P 变换两次得到 P 1 P_1 P1 和 P 2 P_2 P2,通过特征提取网络输出对应特征 T 1 T_1 T1 和 T 2 T_2 T2,最小化 T 1 T_1 T1 和 T 2 T_2 T2 特征距离(比和其他图像的特征距离近)。
- 代码最后阶段用 faiss 库生成 topk 用于后续步骤,因此需在 Linux 系统上运行。
simclr.py
# 输出路径
--config_env configs/env.yml
# 网络配置文件
--config_exp configs/pretext/simclr_cifar10.yml
0. 配置信息
# utils/config.py
p = create_config(args.config_env, args.config_exp)
p =
{
'setup': 'simclr',
'backbone': 'resnet18',
'model_kwargs': {
'head': 'mlp', 'features_dim': 128},
'train_db_name': 'cifar-10',
'val_db_name': 'cifar-10',
'num_classes': 10,
'criterion': 'simclr',
'criterion_kwargs': {
'temperature': 0.1},
'epochs': 500,
'optimizer': 'sgd',
'optimizer_kwargs': {
'nesterov': False, 'weight_decay': 0.0001, 'momentum': 0.9, 'lr': 0.4},
'scheduler': 'cosine',
'scheduler_kwargs': {
'lr_decay_rate': 0.1},
'batch_size': 128,
'num_workers': 8,
'augmentation_strategy': 'simclr',
'augmentation_kwargs': {
'random_resized_crop': {
'size': 32, 'scale': [0.2, 1.0]},
'color_jitter_random_apply': {
'p': 0.8},
'color_jitter': {
'brightness': 0.4, 'contrast': 0.4, 'saturation': 0.4, 'hue': 0.1},
'random_grayscale': {
'p': 0.2},
'normalize': {
'mean': [0.4914, 0.4822, 0.4465], 'std': [0.2023, 0.1994, 0.201]}},
'transformation_kwargs': {
'crop_size': 32, 'normalize': {
'mean': [0.4914, 0.4822, 0.4465], 'std': [0.2023, 0.1994, 0.201]}},
'pretext_dir': '/path/where/to/store/results/cifar-10\\pretext',
'pretext_checkpoint': '/path/where/to/store/results/cifar-10\\pretext\\checkpoint.pth.tar',
'pretext_model': '/path/where/to/store/results/cifar-10\\pretext\\model.pth.tar',
'topk_neighbors_train_path': '/path/where/to/store/results/cifar-10\\pretext\\topk-train-neighbors.npy',
'topk_neighbors_val_path': '/path/where/to/store/results/cifar-10\\pretext\\topk-val-neighbors.npy'}
1. Model
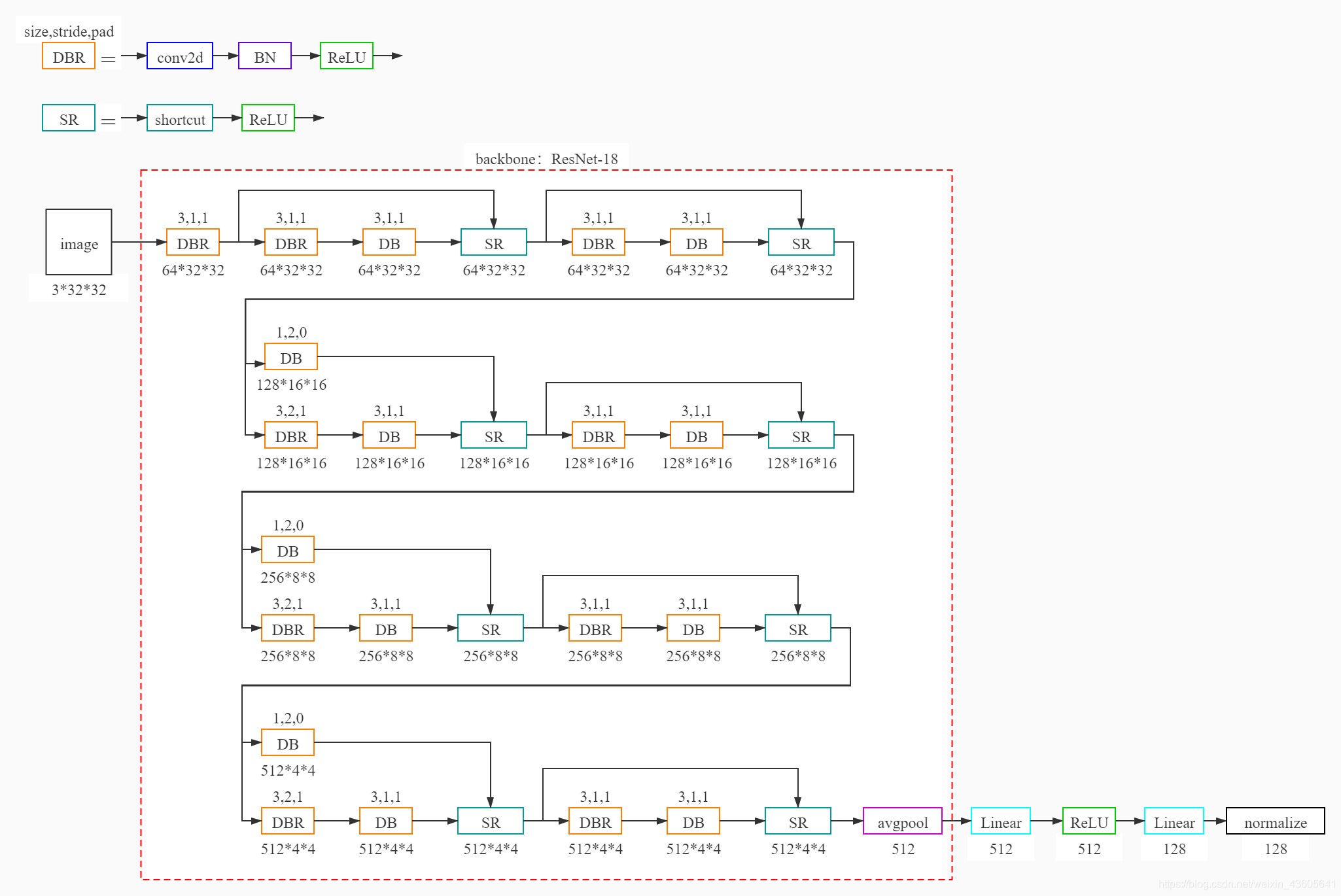
其中 normalize 为 L2_norm
model = get_model(p) # utils/common_config.py 44
# 在 get_model(p) 中分两步构建网络
from models.resnet_cifar import resnet18
backbone = resnet18()
from models.models import ContrastiveModel
model = ContrastiveModel(backbone, **p['model_kwargs']
2. Dataset
CIFAR-10简介
数量:60000
图片尺寸:32*32
图片格式:RGB
类别数量:10
训练集:50000
测试集:10000
train_transforms = get_train_transformations(p) # utils/common_config.py 207
val_transforms = get_val_transformations(p) # utils/common_config.py 247
# utils/common_config.py 120
train_dataset = get_train_dataset(p, train_transforms, to_augmented_dataset=True, split='train+unlabeled') # Split is for stl-10
# utils/common_config.py 160
val_dataset = get_val_dataset(p, val_transforms)
train_dataloader = get_train_dataloader(p, train_dataset) # utils/common_config.py 195
val_dataloader = get_val_dataloader(p, val_dataset) # utils/common_config.py 201
训练数据中包含 image_transform 和 augmentation_transform 两个相同的随机变换方式;假设原始图像为p,p分别通过 image_transform 和 augmentation_transform 进行变换得到 p1、p2,网络输入p1、p2后得到两个特征,网络通过缩小两个特征值的差异进行学习。
图像变换方式
vars(train_dataloader)
{
'dataset': <data.custom_dataset.AugmentedDataset object at 0x000001A883E57CC8>,
'num_workers': 8,
'pin_memory': True,
'timeout': 0,
'worker_init_fn': None,
'_DataLoader__multiprocessing_context': None,
'_dataset_kind': 0,
'batch_size': 128,
'drop_last': True,
'sampler': <torch.utils.data.sampler.RandomSampler object at 0x000001A883CB1808>,
'batch_sampler': <torch.utils.data.sampler.BatchSampler object at 0x000001A885466C48>,
'collate_fn': <function collate_custom at 0x000001A8827C4168>,
'_DataLoader__initialized': True}
----------------------------------------------------------------
vars(train_dataloader.dataset)
{
'dataset': <data.cifar.CIFAR10 object at 0x000001A8854503C8>,
'image_transform': Compose(
RandomResizedCrop(
size=(32, 32),
scale=(0.2, 1.0),
ratio=(0.75, 1.3333),
interpolation=PIL.Image.BILINEAR)
RandomHorizontalFlip(p=0.5)
RandomApply(
p=0.8
ColorJitter(brightness=[0.6, 1.4], contrast=[0.6, 1.4], saturation=[0.6, 1.4], hue=[-0.1, 0.1])
)
RandomGrayscale(p=0.2)
ToTensor()
Normalize(mean=[0.4914, 0.4822, 0.4465], std=[0.2023, 0.1994, 0.201])
),
'augmentation_transform': Compose(
RandomResizedCrop(
size=(32, 32),
scale=(0.2, 1.0),
ratio=(0.75, 1.3333),
interpolation=PIL.Image.BILINEAR)
RandomHorizontalFlip(p=0.5)
RandomApply(
p=0.8
ColorJitter(brightness=[0.6, 1.4], contrast=[0.6, 1.4], saturation=[0.6, 1.4], hue=[-0.1, 0.1])
)
RandomGrayscale(p=0.2)
ToTensor()
Normalize(mean=[0.4914, 0.4822, 0.4465], std=[0.2023, 0.1994, 0.201])
)
}
----------------------------------------------------------------
vars(train_dataloader.dataset.dataset)
{
'root': '/path/to/cifar-10/',
'transform': None,
'train': True,
'classes': ['airplane', 'automobile', 'bird', 'cat', 'deer', 'dog', 'frog', 'horse', 'ship', 'truck'],
'data': array([50000, 32, 32, 3]),
'targets':[50000],
'class_to_idx': {
'airplane': 0, 'automobile': 1, 'bird': 2, 'cat': 3, 'deer': 4, 'dog': 5, 'frog': 6, 'horse': 7, 'ship': 8, 'truck': 9}}
vars(val_dataloader)
{
'dataset': <data.cifar.CIFAR10 object at 0x00000207077BEA88>,
'num_workers': 8,
'pin_memory': True,
'timeout': 0,
'worker_init_fn': None,
'_DataLoader__multiprocessing_context': None,
'_dataset_kind': 0,
'batch_size': 128,
'drop_last': False,
'sampler': <torch.utils.data.sampler.SequentialSampler object at 0x00000207077C5508>,
'batch_sampler': <torch.utils.data.sampler.BatchSampler object at 0x00000207077C50C8>,
'collate_fn': <function collate_custom at 0x000002070278ADC8>,
'_DataLoader__initialized': True}
----------------------------------------------------------------
vars(val_dataloader.dataset)
{
'root': '/path/to/cifar-10/',
'transform': Compose(
CenterCrop(size=(32, 32))
ToTensor()
Normalize(mean=[0.4914, 0.4822, 0.4465], std=[0.2023, 0.1994, 0.201])
),
'train': False,
'classes': ['airplane', 'automobile', 'bird', 'cat', 'deer', 'dog', 'frog', 'horse', 'ship', 'truck'],
'data': array([10000, 32, 32, 3]),
'targets': [10000]
'class_to_idx': {
'airplane': 0, 'automobile': 1, 'bird': 2, 'cat': 3, 'deer': 4, 'dog': 5, 'frog': 6, 'horse': 7, 'ship': 8, 'truck': 9}}
3. Memory Bank
base_dataset = get_train_dataset(p, val_transforms, split='train') # Dataset w/o augs for knn eval
base_dataloader = get_val_dataloader(p, base_dataset)
# 50000, 128, 10, 0.1
memory_bank_base = MemoryBank(len(base_dataset),
p['model_kwargs']['features_dim'],
p['num_classes'], p['criterion_kwargs']['temperature'])
memory_bank_base.cuda()
memory_bank_val = MemoryBank(len(val_dataset),
p['model_kwargs']['features_dim'],
p['num_classes'], p['criterion_kwargs']['temperature'])
memory_bank_val.cuda()
----------------------------------------------------------------
vars(memory_bank_base)
{
'n': 50000,
'dim': 128,
'features': [50000,128] tensor,
'targets': [50000] tensor,
'ptr': 0,
'device': 'cuda:0',
'K': 100,
'temperature': 0.1,
'C': 10}
4. Criterion
这部分主要负责 loss 计算,可以暂时跳过,看到 6.2 训练 部分后返回看 loss。
(1)loss 代码梳理mask: [ b s , b s ] [bs, bs] [bs,bs] 单位矩阵contrast_features: [ b s ∗ 2 , 128 ] [bs*2, 128] [bs∗2,128] 两部分特征拼接anchor: [ b s , 128 ] [bs, 128] [bs,128] 第一部分特征dot_product: [ b s , b s ∗ 2 ] [bs, bs*2] [bs,bs∗2]torch.matmul(anchor, contrast_features.T) / 0.1logits: [ b s , b s ∗ 2 ] [bs, bs*2] [bs,bs∗2]dot_product 每行减去该行最大值,实际上就是减去左半部分主对角线的值mask: [ b s , b s ∗ 2 ] [bs, bs*2] [bs,bs∗2] 变为左右两个单位矩阵logits_mask: [ b s , b s ∗ 2 ] [bs, bs*2] [bs,bs∗2] 除了左半部分主对角线为0,其余全为1mask: [ b s , b s ∗ 2 ] [bs, bs*2] [bs,bs∗2] 变为左半部分0矩阵,右半部分单位矩阵exp_logits: [ b s , b s ∗ 2 ] [bs, bs*2] [bs,bs∗2]logits 取exp并将左半部分主对角线置0log_prob: [ b s , b s ∗ 2 ] [bs, bs*2] [bs,bs∗2]logits 每行减去 exp_logits 每行的和取logloss: log_prob 右半部分主对角线均值
(2)loss 分析
loss 的核心计算为 -log_softmax
loss 的下降可以通过缩小 P P P 与 P T P^T PT 的特征距离,以及扩大 P P P 与除 P T P^T PT 以外图像的特征距离
疑问:loss 是否会使 batch 中同类别图像特征距离扩大?或者只是在整体上 P T P^T PT 的特征距离比其它的更近?
(3)点积最大值为左半部分主对角线证明
设 F 1 , F 2 在 n o r m a l i z e 前 为 [ x 1 x 2 ⋯ x n ] , [ y 1 y 2 ⋯ y n ] 设F_1, F_2在normalize前为\begin{bmatrix} x_1 & x_2 & \cdots & x_n \end{bmatrix}, \begin{bmatrix} y_1 & y_2 & \cdots & y_n \end{bmatrix} 设F1,F2在normalize前为[x1x2⋯xn],[y1y2⋯yn]
F 1 ⋅ F 2 = x 1 y 1 + x 2 y 2 + ⋯ + x n y n x 1 2 + x 2 2 + ⋯ + x n 2 y 1 2 + y 2 2 + ⋯ + y n 2 F_1 \cdot F_2=\frac{x_1y_1+x_2y_2+\cdots+x_ny_n}{\sqrt{x_1^2+x_2^2+\cdots+x_n^2}\sqrt{y_1^2+y_2^2+\cdots+y_n^2}} F1⋅F2=x12+x22+⋯+xn2y12+y22+⋯+yn2x1y1+x2y2+⋯+xnyn
分 母 2 = x 1 2 y 1 2 x 1 2 y 2 2 ⋯ x 1 2 y n 2 x 2 2 y 1 2 x 2 2 y 2 2 ⋯ x 2 2 y n 2 ⋮ ⋮ ⋱ ⋮ x n 2 y 1 2 x n 2 y 2 2 ⋯ x n 2 y n 2 分母^2=\begin{matrix} x_1^2y_1^2 & x_1^2y_2^2 & \cdots & x_1^2y_n^2\\ x_2^2y_1^2 & x_2^2y_2^2 & \cdots & x_2^2y_n^2\\ \vdots & \vdots & \ddots & \vdots\\ x_n^2y_1^2 & x_n^2y_2^2 & \cdots & x_n^2y_n^2 \end{matrix} 分母2=x12y12x22y12⋮xn2y12x12y22x22y22⋮xn2y22⋯⋯⋱⋯x12yn2x22yn2⋮xn2yn2
分 子 2 = x 1 2 y 1 2 x 1 y 1 x 2 y 2 ⋯ x 1 y 1 x n y n x 2 y 2 x 1 y 1 x 2 2 y 2 2 ⋯ x 2 y 2 x n y n ⋮ ⋮ ⋱ ⋮ x n y n x 1 y 1 x n y n x 2 y 2 ⋯ x n 2 y n 2 分子^2=\begin{matrix} x_1^2y_1^2 & x_1y_1x_2y_2 & \cdots & x_1y_1x_ny_n\\ x_2y_2x_1y_1 & x_2^2y_2^2 & \cdots & x_2y_2x_ny_n\\ \vdots & \vdots & \ddots & \vdots\\ x_ny_nx_1y_1 & x_ny_nx_2y_2 & \cdots & x_n^2y_n^2 \end{matrix} 分子2=x12y12x2y2x1y1⋮xnynx1y1x1y1x2y2x22y22⋮xnynx2y2⋯⋯⋱⋯x1y1xnynx2y2xnyn⋮xn2yn2
∵ 分 母 2 − 分 子 2 沿 主 对 角 线 看 为 完 全 平 方 公 式 ∴ 分 母 2 − 分 子 2 ≥ 0 ∴ 仅 当 F 1 = F 2 时 , F 1 F 2 最 大 = 1 \begin{matrix} \because & 分母^2-分子^2沿主对角线看为完全平方公式 \\ \therefore & 分母^2-分子^2\ge0 \\ \therefore & 仅当 F_1=F_2 时,F_1F_2最大=1 \end{matrix} ∵∴∴分母2−分子2沿主对角线看为完全平方公式分母2−分子2≥0仅当F1=F2时,F1F2最大=1
criterion = get_criterion(p)
criterion = criterion.cuda()
# utils/common_config.py 14
def get_criterion(p):
if p['criterion'] == 'simclr':
from losses.losses import SimCLRLoss
criterion = SimCLRLoss(**p['criterion_kwargs'])
class SimCLRLoss(nn.Module):
# Based on the implementation of SupContrast
def __init__(self, temperature):
super(SimCLRLoss, self).__init__()
self.temperature = temperature
def forward(self, features):
""" input: - features: hidden feature representation of shape [b, 2, dim] output: - loss: loss computed according to SimCLR """
b, n, dim = features.size() # [128,2,128]
assert(n == 2)
mask = torch.eye(b, dtype=torch.float32).cuda()
# torch.unbind() 删除指定维度后返回一个元组,在这里为 ([128,128],[128,128])
# torch.cat() 按指定维度拼接,在这里为 [256,128]
contrast_features = torch.cat(torch.unbind(features, dim=1), dim=0)
anchor = features[:, 0] # anchor.size()=[128,128]
# Dot product
dot_product = torch.matmul(anchor, contrast_features.T) / self.temperature # dot_product.size()=[128,256]
# Log-sum trick for numerical stability
logits_max, _ = torch.max(dot_product, dim=1, keepdim=True) # logits_max.size()=[128,1]
logits = dot_product - logits_max.detach() # 相乘后每行减去该行的最大值
# repeat(重复次数, 维度)
mask = mask.repeat(1, 2) # mask.size()=[128,256]
# logits_mask 左半部分为1、0互换的单位矩阵右半部分为 ones 矩阵
logits_mask = torch.scatter(torch.ones_like(mask), 1, torch.arange(b).view(-1, 1).cuda(), 0)
mask = mask * logits_mask # 将 mask 的左半部分变成了0矩阵,右半部分依然是单位矩阵
# Log-softmax
exp_logits = torch.exp(logits) * logits_mask
log_prob = logits - torch.log(exp_logits.sum(1, keepdim=True))
# Mean log-likelihood for positive
# 实际上就是提取 log_prob 右半部分单位矩阵(左上至右下对角线)的均值
loss = - ((mask * log_prob).sum(1) / mask.sum(1)).mean()
return loss
5. Optimizer
optimizer = get_optimizer(p, model)
optimizer =
SGD (
Parameter Group 0
dampening: 0
lr: 0.4
momentum: 0.9
nesterov: False
weight_decay: 0.0001
)
6. Train
for epoch in range(start_epoch, p['epochs']):
# Adjust lr
lr = adjust_learning_rate(p, optimizer, epoch)
# Train
simclr_train(train_dataloader, model, criterion, optimizer, epoch)
# Fill memory bank
fill_memory_bank(base_dataloader, model, memory_bank_base)
# Evaluate (To monitor progress - Not for validation)
top1 = contrastive_evaluate(val_dataloader, model, memory_bank_base)
6.1 调整学习率
# Adjust lr
lr = adjust_learning_rate(p, optimizer, epoch)
# utils/common_config.py 280
def adjust_learning_rate(p, optimizer, epoch):
lr = p['optimizer_kwargs']['lr'] # 0.4
if p['scheduler'] == 'cosine':
eta_min = lr * (p['scheduler_kwargs']['lr_decay_rate'] ** 3) # 0.4 * (0.1 ** 3)
lr = eta_min + (lr - eta_min) * (1 + math.cos(math.pi * epoch / p['epochs'])) / 2
for param_group in optimizer.param_groups:
param_group['lr'] = lr
return lr
6.2 训练
一个 batch 的图像为 [ b s , 3 , 32 , 32 ] [bs, 3, 32, 32] [bs,3,32,32]
但网络的实际输入为 [ b s ∗ 2 , 3 , 32 , 32 ] [bs*2, 3, 32, 32] [bs∗2,3,32,32]
因此网络的输出为 [ b s ∗ 2 , 128 ] [bs*2, 128] [bs∗2,128],并 resize 为 [ b s , 2 , 128 ] [bs, 2, 128] [bs,2,128]
loss 计算看 4. Criterion
simclr_train(train_dataloader, model, criterion, optimizer, epoch)
# utils/train_utils.py
def simclr_train(train_loader, model, criterion, optimizer, epoch):
losses = AverageMeter('Loss', ':.4e')
progress = ProgressMeter(len(train_loader),
[losses],
prefix="Epoch: [{}]".format(epoch))
model.train()
for i, batch in enumerate(train_loader):
images = batch['image']
images_augmented = batch['image_augmented']
b, c, h, w = images.size() # images.size() = [128,3,32,32]
input_ = torch.cat([images.unsqueeze(1), images_augmented.unsqueeze(1)], dim=1)
# 增加一个维度然后cat, input_.size() = [128,2,3,32,32]
input_ = input_.view(-1, c, h, w) # input_.size() = [256,3,32,32]
input_ = input_.cuda(non_blocking=True)
targets = batch['target'].cuda(non_blocking=True)
output = model(input_).view(b, 2, -1) # output.size() = [128,2,128]
loss = criterion(output)
losses.update(loss.item())
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
if i % 25 == 0:
progress.display(i)
batch
{
'image':[128,3,32,32],
'target':[128],
'meta':{
'im_size':[2,32], 'index':[128], 'class_name':[128]},
'image_augmented':[128,3,32,32]}
6.3 Fill memory bank
得到网络对训练集(按照 val 变换)的输出特征以及标签
fill_memory_bank(base_dataloader, model, memory_bank_base)
6.4 Evaluate
验证集图像特征 F v a l F_{\mathrm{val}} Fval 与所有训练集图像特征 F t r a i n F_{\mathrm{train}} Ftrain 做点积,取出最大的100个,根据训练集标签类别索引做累加,取数值最高的索引作为 P v a l P_{\mathrm{val}} Pval 的类别,最后与 P v a l P_{\mathrm{val}} Pval 的真实标签对比计算准确度。
top1 = contrastive_evaluate(val_dataloader, model, memory_bank_base)
# utils/evaluate_utils.py
@torch.no_grad()
def contrastive_evaluate(val_loader, model, memory_bank):
top1 = AverageMeter('[email protected]', ':6.2f')
model.eval()
for batch in val_loader:
images = batch['image'].cuda(non_blocking=True)
target = batch['target'].cuda(non_blocking=True)
output = model(images)
output = memory_bank.weighted_knn(output)
acc1 = 100*torch.mean(torch.eq(output, target).float())
top1.update(acc1.item(), images.size(0))
return top1.avg
class MemoryBank(object):
def weighted_knn(self, predictions):
# perform weighted knn
retrieval_one_hot = torch.zeros(self.K, self.C).to(self.device) # [100,10]
batchSize = predictions.shape[0]
correlation = torch.matmul(predictions, self.features.t()) # [128,128] [50000,128].T
yd, yi = correlation.topk(self.K, dim=1, largest=True, sorted=True) # [128,100]点积最大的前100个
candidates = self.targets.view(1,-1).expand(batchSize, -1) # [128,50000]
retrieval = torch.gather(candidates, 1, yi) # [128,100] torch.gather(索引矩阵, 索引维度, 索引)
retrieval_one_hot.resize_(batchSize * self.K, self.C).zero_() # [12800,10]
retrieval_one_hot.scatter_(1, retrieval.view(-1, 1), 1) # [12800,10] (dim, index, value)
yd_transform = yd.clone().div_(self.temperature).exp_()
probs = torch.sum(torch.mul(retrieval_one_hot.view(batchSize, -1 , self.C),
yd_transform.view(batchSize, -1, 1)), 1) # [128, 100, 10]*[128, 100, 1] 求和后 [128, 10]
_, class_preds = probs.sort(1, True)
class_pred = class_preds[:, 0]
# 和训练集做点积,挑100个最大的统计标签,最多的为验证图像的类别
return class_pred
7. 存储模型和 topk
# Save final model
torch.save(model.state_dict(), p['pretext_model'])
# Mine the topk nearest neighbors at the very end (Train)
# These will be served as input to the SCAN loss.
print(colored('Fill memory bank for mining the nearest neighbors (train) ...', 'blue'))
fill_memory_bank(base_dataloader, model, memory_bank_base)
topk = 20
print('Mine the nearest neighbors (Top-%d)' %(topk))
indices, acc = memory_bank_base.mine_nearest_neighbors(topk)
print('Accuracy of top-%d nearest neighbors on train set is %.2f' %(topk, 100*acc))
np.save(p['topk_neighbors_train_path'], indices)
# Mine the topk nearest neighbors at the very end (Val)
# These will be used for validation.
print(colored('Fill memory bank for mining the nearest neighbors (val) ...', 'blue'))
fill_memory_bank(val_dataloader, model, memory_bank_val)
topk = 5
print('Mine the nearest neighbors (Top-%d)' %(topk))
indices, acc = memory_bank_val.mine_nearest_neighbors(topk)
print('Accuracy of top-%d nearest neighbors on val set is %.2f' %(topk, 100*acc))
np.save(p['topk_neighbors_val_path'], indices)
class MemoryBank(object):
def mine_nearest_neighbors(self, topk, calculate_accuracy=True):
# mine the topk nearest neighbors for every sample
import faiss
features = self.features.cpu().numpy()
n, dim = features.shape[0], features.shape[1]
index = faiss.IndexFlatIP(dim) # 点乘,归一化的向量点乘即cosine相似度(越大越好)
index = faiss.index_cpu_to_all_gpus(index)
index.add(features) # 添加训练时的样本
# indices 为相似向量的索引
distances, indices = index.search(features, topk+1) # Sample itself is included
# evaluate
if calculate_accuracy:
targets = self.targets.cpu().numpy()
neighbor_targets = np.take(targets, indices[:,1:], axis=0) # Exclude sample itself for eval
anchor_targets = np.repeat(targets.reshape(-1,1), topk, axis=1)
accuracy = np.mean(neighbor_targets == anchor_targets)
return indices, accuracy
else:
return indices
边栏推荐
- Replace the backbone of target detection (take the fast RCNN as an example)
- Internet_ Business Analysis Overview
- 【题解】Codeforces Round #798 (Div. 2)
- KMP!你值得拥有!!! 直接运行直接跑!
- 基于华为云图像识别标签实战
- Record the phpstudy configuration php8.0 and php8.1 extension redis
- Use canvas to add text watermark to the page
- cf:B. Array Decrements【模拟】
- SISO decoder for SPC (supplementary Chapter 1)
- [image denoising] impulse noise image denoising based on absolute difference median filter, weighted median filter and improved weighted median filter with matlab code attached
猜你喜欢

cf:F. Shifting String【字符串按指定顺序重排 + 分组成环(切割联通分量) + 各组最小相同移动周期 + 最小公倍数】

Understand how to get started with machine learning to quantify transactions?

关于富文本储存数据库格式转译问题

【Multisim仿真】利用运算放大器产生锯齿波
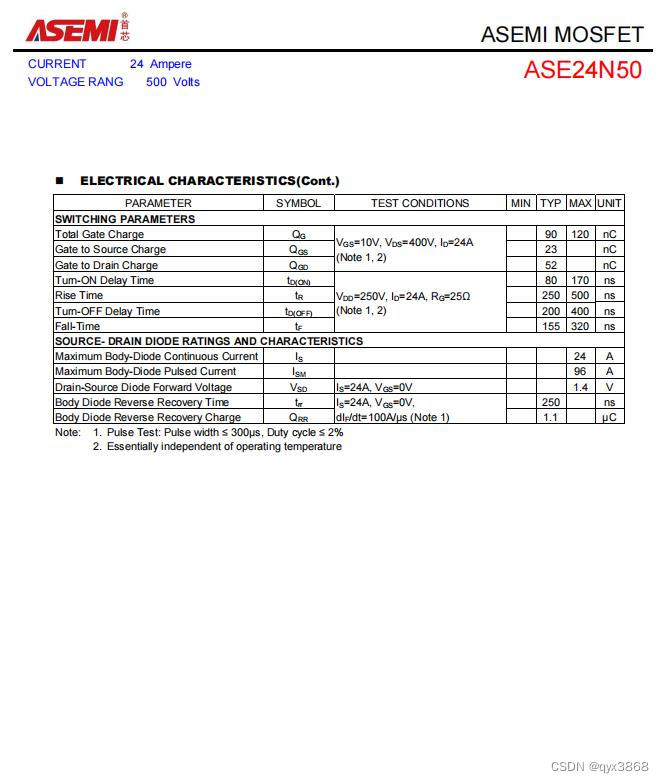
ASEMI的MOS管24N50参数,24N50封装,24N50尺寸
Highcharts sets the histogram width, gradient, fillet, and data above the column

What is the workflow of dry goods MapReduce?
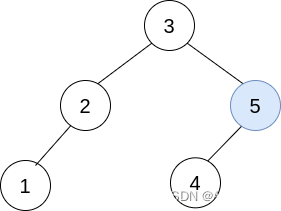
Merge multiple binary search trees

【图像去噪】基于马尔可夫随机场实现图像去噪附matlab代码

cf:B. Array Decrements【模拟】
随机推荐
How to manually execute workflow on SAP BTP
Cf:c. restoring the duration of tasks
leetcode:66. add one-tenth
SISO decoder for SPC (supplementary Chapter 1)
On Workflow selection
Do you know that public fields are automatically filled in
Programmers have changed dramatically in 10 years. Everything has changed, but it seems that nothing has changed
mysql 联合索引和BTree
【C语言刷题——Leetcode10道简单题】
WWDC22 开发者需要关注的重点内容
Judge whether it is a balanced binary tree
Flask CKEditor 富文本编译器实现文章的图片上传以及回显,解决路径出错的问题
Merge multiple binary search trees
Teach you how to learn the first set and follow set!!!! Hematemesis collection!! Nanny level explanation!!!
【Multisim仿真】利用运算放大器产生方波、三角波发生器
[solution] codeforces round 798 (Div. 2)
Swagger2 easy to use
kubernetes 二进制安装(v1.20.15)(八)部署 网络插件
2022各大厂最新总结的软件测试宝典,看完不怕拿不到offer
kubernetes 二进制安装(v1.20.15)(九)收尾:部署几个仪表盘