当前位置:网站首页>In depth understanding of JUC concurrency (I) what is JUC
In depth understanding of JUC concurrency (I) what is JUC
2022-07-02 06:14:00 【I think starfish_ ninety-eight】
List of articles
Basic knowledge of
What is? JUC
JUC Namely java.util.concurrent The following class package , Dedicated to multithreading development .
The advantages and disadvantages of concurrent programming
advantage
Make full use of multicore CPU Computing power
Multicore CPU In the background of , The trend of concurrent programming , Through the form of concurrent programming, multi-core can be CPU To the extreme , Improved performance .
It is convenient for business splitting , Improve the concurrent ability and performance of the system
The current system requires millions or even tens of millions of levels of concurrency , And multithreading concurrent programming is the foundation of developing high concurrent system , Using many thread mechanisms can greatly improve the overall concurrency and performance of the system .
shortcoming
Frequent context switching
The task is a context switch from saving to reloading , And every time you switch , Need to save the current status , In order to restore the previous state , And this switch is very lossy , Too often it can't take advantage of multithreaded programming
Thread safety problem
The most difficult problem in multithreading programming is thread safety in critical area , If you don't pay attention to it a little bit, you will get deadlock , Once a deadlock occurs, it will make the system function unavailable
Blocking and non blocking
The focus of blocking and non blocking is The behavior of a thread waiting for a message , While waiting for the news , The current thread is suspended , Or not suspended .
- Blocking : Call after sending out , Before the message returns , The current thread will be suspended , Until a message returns , The current thread will be activated
- Non blocking : Call after sending out , Does not block the current thread , And will return immediately
Synchronous and asynchronous
- Sync : When a synchronous call is sent , caller Always wait for the call result to return after , To carry out subsequent operations
- asynchronous : When an asynchronous call is sent , caller Regardless of whether the called method is completed , Will continue to execute the following code . Asynchronous call , To get results , There are generally two ways :
- Results of active polling asynchronous calls
- Callee passed callback To notify the caller of the result of the call
Concurrency and parallelism
Concurrent
Threads take turns using cpu This is called concurrency
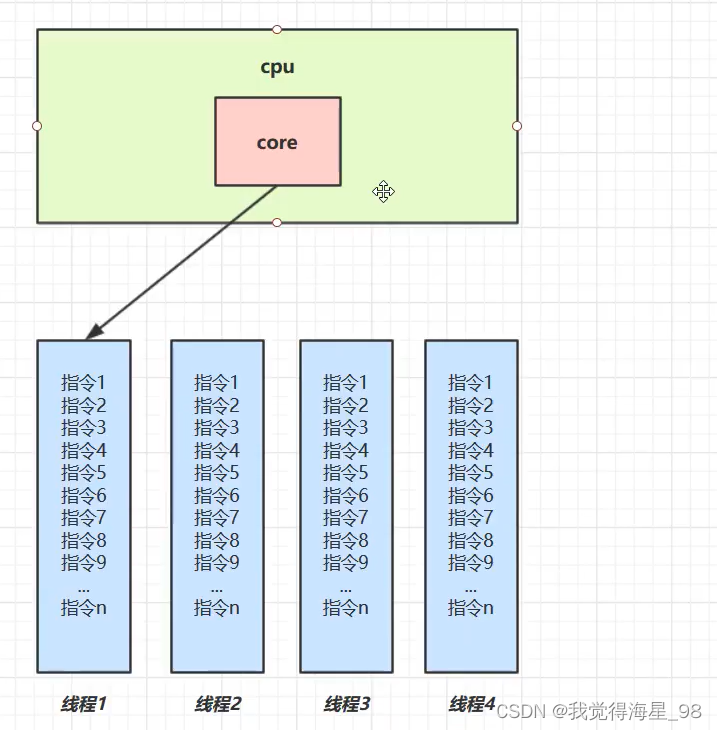
parallel
Multiple cpu Next , Each core can schedule running threads , At this time, the thread can be parallel
Processes and threads
process
A process can be considered an instance of a program . Most programs can run multiple instance processes at the same time ( For example, Notepad 、 drawing 、 The browser etc. ), Some programs can only start one instance process ( For example, Netease cloud music 、360 Safety guard ) etc.
Threads
- A process can be divided into one or more threads . A thread is a stream of instructions , Give instructions in a certain order to CPU perform
- Java in , Thread as the minimum scheduling unit , Process is the smallest unit of resource allocation , stay windows The middle process is inactive , Just as a container for threads
State of thread
public enum State {
// function
NEW,
// function
RUNNABLE,
// Blocking
BLOCKED,
// wait for
WAITING,
// Overtime waiting
TIMED_WAITING,
// End
TERMINATED;
}
- After the thread is created, it will be in the NEW( newly build ) state
- call start() Start running after method , And get the CPU Time slice (timeslice) After that RUNNING( function ) state
- When a thread calls Synchronization method when , Without obtaining the lock , The thread will enter the BLOCKED( Blocking ) state
- When the thread executes wait() After method , Thread entry WAITING( wait for ) state
- stay Wait state On the basis of the increase of the timeout limit , Such as through sleep(long millis) Method or wait(long millis) Method can put the thread into waiting timeout (TIMED WAITING) state
- After the thread runs, it will enter TERMINATED( End ) state
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
LeetCode 90. Subset II
LeetCode 78. subset

Contest3147 - game 38 of 2021 Freshmen's personal training match_ A: chicken
How to use mitmproxy

VRRP之监视上行链路
Data playback partner rviz+plotjuggler

Shenji Bailian 3.54-dichotomy of dyeing judgment

加密压缩文件解密技巧
Network related knowledge (Hardware Engineer)

Problems encountered in uni app development (continuous update)
随机推荐
Replace Django database with MySQL (attributeerror: 'STR' object has no attribute 'decode')
从设计交付到开发,轻松畅快高效率!
Contest3147 - game 38 of 2021 Freshmen's personal training match_ A: chicken
Happy Lantern Festival | Qiming cloud invites you to guess lantern riddles
复杂 json数据 js前台解析 详细步骤《案例:一》
ROS create workspace
亚马逊aws数据湖工作之坑1
Stc8h8k Series Assembly and c51 Real combat - NIXIE TUBE displays ADC, Key Series port reply Key number and ADC value
sudo提权
神机百炼3.54-染色法判定二分图
51单片机——ADC讲解(A/D转换、D/A转换)
STC8H8K系列汇编和C51实战——串口发送菜单界面选择不同功能
Contest3147 - game 38 of 2021 Freshmen's personal training match_ G: Flower bed
STC8H8K系列汇编和C51实战——数码管显示ADC、按键串口回复按键号与ADC数值
Detailed explanation of BGP message
Detailed steps of JS foreground parsing of complex JSON data "case: I"
Flutter hybrid development: develop a simple quick start framework | developers say · dtalk
LeetCode 83. Delete duplicate elements in the sorting linked list
Spark overview
Google play academy team PK competition, official start!