当前位置:网站首页>并发之固定运行和交替运行方案
并发之固定运行和交替运行方案
2022-08-03 07:48:00 【七国的天下,我要九十九】
并发之固定运行和交替运行方案
例如,按规定先输出2再输出1
1 固定运行顺序
1 wait/notify方法
// 用来同步的对象
static Object obj = new Object();
// t2 运行标记, 代表 t2 是否执行过
static boolean t2runed = false;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
synchronized (obj) {
// 如果 t2 没有执行过
while (!t2runed) {
try {
// t1 先等一会
obj.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace()
}
}
}
System.out.println(1);
});
Thread t2 = new Thread(() -> {
System.out.println(2);
synchronized (obj) {
// 修改运行标记
t2runed = true;
// 通知 obj 上等待的线程(可能有多个,因此需要用 notifyAll)
obj.notifyAll();
}
});
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
按照wait/notify方法:
1 需要保证先wait再notify,否者wait线程永远都不能唤醒. 所以上面添加了标识来判断是否wait.
2 如存在干扰线程错误notify了wait线程,条件标识不满足需要重新等待,添加了while循环控制.
3 唤醒对象上的wait线程需要使用notifyAll,同步线程可能存在多个.
2 park/unpark方法
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
// 当没有『许可』时,当前线程暂停运行;有『许可』时,用掉这个『许可』,当前线程恢复运行
LockSupport.park();
System.out.println("1");
});
Thread t2 = new Thread(() -> {
System.out.println("2");
// 给线程 t1 发放『许可』(多次连续调用 unpark 只会发放一个『许可』)
LockSupport.unpark(t1);
});
t1.start();
t2.start();
与上面wait/notify方法相比,park 和 unpark 方法比较灵活:
1 他俩谁先调用,谁后调用无所谓。
2 是以线程为单位进行暂停和恢复
3 不需要额外同步对象和运行标记
2 交替输出
列如,线程 1 输出 a 5 次,线程 2 输出 b 5 次,线程 3 输出 c 5 次。要求输出 abcabcabcabcabc
1 wait/notify方法
class SyncWaitNotify {
private int flag;
private int loopNumber;
public SyncWaitNotify(int flag, int loopNumber) {
this.flag = flag;
this.loopNumber = loopNumber;
}
public void print(int waitFlag, int nextFlag, String str) {
for (int i = 0; i < loopNumber; i++) {
synchronized (this) {
while (this.flag != waitFlag) {
try {
this.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.print(str);
flag = nextFlag;
this.notifyAll();
}
}
}
}
测试类
SyncWaitNotify syncWaitNotify = new SyncWaitNotify(1, 5);
new Thread(() -> {
syncWaitNotify.print(1, 2, "a");
}).start();
new Thread(() -> {
syncWaitNotify.print(2, 3, "b");
}).start();
new Thread(() -> {
syncWaitNotify.print(3, 1, "c");
}).start();
/* 运行结果: abcabcabcabcabc */
2 lock/unlock方法
class AwaitSignal extends ReentrantLock {
public void start(Condition first) {
this.lock();
try {
log.debug("start");
first.signal();
} finally {
this.unlock();
}
}
public void print(String str, Condition current, Condition next) {
for (int i = 0; i < loopNumber; i++) {
this.lock();
try {
current.await();
log.debug(str);
next.signal();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
this.unlock();
}
}
}
// 循环次数
private int loopNumber;
public AwaitSignal(int loopNumber) {
this.loopNumber = loopNumber;
}
}
测试类
AwaitSignal as = new AwaitSignal(5);
Condition aWaitSet = as.newCondition();
Condition bWaitSet = as.newCondition();
Condition cWaitSet = as.newCondition();
new Thread(() -> {
as.print("a", aWaitSet, bWaitSet);
}).start();
new Thread(() -> {
as.print("b", bWaitSet, cWaitSet);
}).start();
new Thread(() -> {
as.print("c", cWaitSet, aWaitSet);
}).start();
as.start(aWaitSet);
/* 运行结果: abcabcabcabcabc */
3 prak/unprak方法
class SyncPark {
private int loopNumber;
private Thread[] threads;
public SyncPark(int loopNumber) {
this.loopNumber = loopNumber;
}
public void setThreads(Thread... threads) {
this.threads = threads;
}
public void print(String str) {
for (int i = 0; i < loopNumber; i++) {
LockSupport.park();
System.out.print(str);
LockSupport.unpark(nextThread());
}
}
private Thread nextThread() {
Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
int index = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < threads.length; i++) {
if(threads[i] == current) {
index = i;
break;
}
}
if(index < threads.length - 1) {
return threads[index+1];
} else {
return threads[0];
}
}
public void start() {
for (Thread thread : threads) {
thread.start();
}
LockSupport.unpark(threads[0]);
}
}
测试类
SyncPark syncPark = new SyncPark(5);
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
syncPark.print("a");
});
Thread t2 = new Thread(() -> {
syncPark.print("b");
});
Thread t3 = new Thread(() -> {
syncPark.print("c\n");
});
syncPark.setThreads(t1, t2, t3);
syncPark.start();
/* 运行结果: abcabcabcabcabc */
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
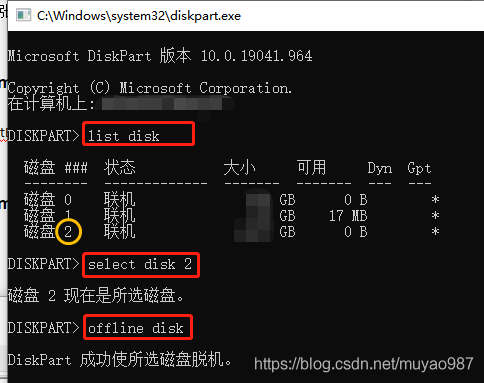
Eject stubborn hard drives with diskpart's offline command
2022下半年软考「高项&集成」复习计划ta来喽~
WordPress主题-B2美化通用子主题商业运营版
mysql5.7服务器The innodb_system data file 'ibdata1' must be writable导致无法启动服务器
JS函数获取本月的第一天和最后一天
Evaluate: A detailed introduction to the introduction of huggingface evaluation indicator module
请求与响应:响应
Charles packet capture tool learning record
ceph简介
“==”和equals的区别
consul理解
ArcEngine (1) Loading vector data
Postman will return to the interface to generate a json file to the local
DSP-ADAU1452输出通道配置
推荐系统-排序层-模型:Wide&Deep
frp:开源内网穿透工具
《剑指Offer》刷题之打印从1到最大的n位数
mysql 8.0.12 安装配置方法并--设置修改密码
工控机防勒索病毒浅析
sqlserver2019安装失败