当前位置:网站首页>Special training of C language array
Special training of C language array
2022-06-29 20:21:00 【An embedded enthusiast】
C Special training of language array
The first question is
If there is a statement char s1[10], s2[10] = {“books”}; The string books Store in array s1 The correct sentence for is ( )
A、strcpy(s1, s2);
B、s1 = {“books”};
C、s1 = s2;
D、strcpy(s2, s1);
answer :A
analysis : The array name represents the first address of the array , It's an address constant , So you can't assign values to array names ,C error .strcpy The function prototype is as follows
char *strcpy(char *dest, const char *src)
The second question is
The linear table is ________.
A、 A finite sequence , Can be null
B、 A finite sequence , Do not be empty
C、 An infinite sequence , Can be null
D、 An infinite sequence , Do not be empty
answer :A
analysis : Linear lists include linked list arrays , Arrays are finite , Linear tables can be initialized to null , When there are no elements in the linear table , Is an empty table .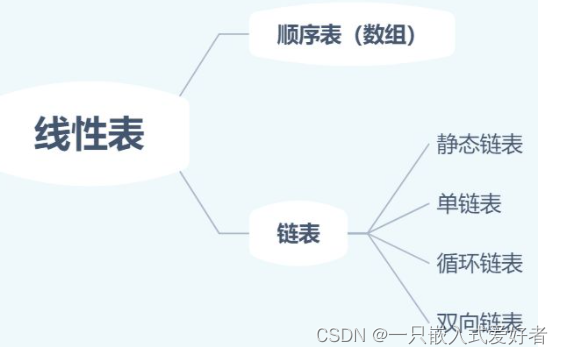
Recommended reading : Logical structure and physical structure
Third question
Which of the following correctly defines a one-dimensional array .()
A、char a[] = {‘0’, ‘1’, ‘2’, ‘3’, ‘\0’};
B、char a = {‘A’, ‘B’, ‘C’};
C、int a[] = “0123”;
D、int a[3] = {0, 1, 2, 3};
answer :A
analysis :B In the options a Not defined as an array , It's characters , Will make mistakes ;C Option integer array cannot be assigned string ;D The number of initial values defined by the option exceeds the length of the array ;
Fourth question
The keyword sequence with sequence table is {1,4,6,10,18,35,42,53,67,71,78,84,92,99}, When the binary search method is used, the key value is 35 When the node of , the () Search succeeded after comparison .
answer :4
analysis :
The first 1 Time
1,4,6,10,18,35,42,53,67,71,78,84,92,99
left=0,right=13,mind=6; mid The value is 42, Too big
The first 2 Time
1,4,6,10,18,35,42,53,67,71,78,84,92,99
left=0,right=5,mind=2; mid The value is 6, Too small
The first 3 Time
1,4,6,10,18,35,42,53,67,71,78,84,92,99
left=3,right=5,mind=4; mid The value is 18, Too small
The first 4 Time
1,4,6,10,18,35,42,53,67,71,78,84,92,99
left=5,right=5,mind=5; mid The value is 35, eureka
Fifth question
There are two general compression storage methods for sparse matrix , namely ()
A、 Two dimensional array and three-dimensional array
B、 Triples and hashes
C、 Triples and cross linked lists
D、 Hash and cross linked list
answer :C
analysis : A triple is an element that holds three pieces of information , Row numbers in the matrix , Column number and value , In this way, the value of 0 The elements of , Achieve compression . Cross linked list is equivalent to the set of adjacency table and inverse adjacency table , In an element, the values, the outgoing and incoming tables are stored , In this way, there is no need to store a large number of 0 Elements , And finding the incoming node of a node is as fast as finding the node .
A two-dimensional cross linked list is a list of elements that link left and right horizontal neighbors and up and down vertical neighbors at the same time .
Typically used for sparse matrix storage , Each element of the matrix is the following five tuples :
typedef struct OLNode
{
int LineNumber, ColumneNumber; // Line and column numbers
ElemType value; // value
struct OLNode *right, *down; // Colleague 、 Pointer to the next element in the same column
} OLNode, *OList;
Sixth question
Of the following options , Which option correctly defines a two-dimensional array ()
A、char a[2][2] = ‘a’, ‘b’, ‘c’, ‘d’;
B、int a[][] = { {1, 2, 3}, {4, 5, 6}};
C、int a[2][] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6};
D、int a[][4] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6};
answer :D
analysis : When defining a character array, it is not allowed to directly use “ character constants ” Give initial value in the way of ,C Language policy , It is not allowed to omit the length of the second dimension when defining a two-dimensional array , So options A、B、C error . It is allowed to omit the length of the first dimension when defining a two-dimensional array , So options D correct .
Question seven
It is known that int a[3][4]; Then the following can mean a[1][2] The value of the element is ()
A、*( *(a+1)+2)
B、 *(a+1+2)
C、(&a[0]+1)[2]
D、 *(a[0]+1)
answer :A
analysis : In a two-dimensional array , The array name is the address of the first array , Note that there a Not the address of the first element , It's the address of the first dimension array ,a[0][0] Is the address of the first element of the one-dimensional array . Address + 1 Move down one layer .
A, a It's a secondary pointer , Not a first level pointer ,*(a+1) The address of the second array of the
B, * (a+1+2) be equal to *(a+3), It's a int *, It means No 4 An array a[3] The address of , and **(a+3) Express a[3][0] Value , *((int *)(a+3)) It can also express a[3][0] Value
C. (&a[0]+1) It means No 2 An array a[1] The address of ,(&a[0]+1)[2] It's actually an array a[3] The address of , Change to ((int *)(&a[0]+1))[2] That's right
D. *(a[0]+1) yes a[0][1] Value
The eighth question
What results will be output by executing the following code snippet .()
int a[][3] = {
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9};
char k;
for (k = 0; k < 3; k ++)
printf("%d ",a[k][2-k]);
A、1 3 5
B、3 5 7
C、3 6 9
D、 Compilation error or nothing else
answer :B
analysis : A two-dimensional array must specify the number of columns , The topic has been specified and does not cross the boundary , So there's no mistake .
a[0][0]=1 a[0][1]=2 a[0][2]=3
a[1][0]=4 a[1][1]=5 a[1][2]=6
a[2][0]=7 a[2][1]=8 a[2][2]=9
for Loop output a[0][2]=3 a[1][1]=5 a[2][0]=7
Question 9
int A[2][3]={1,2,3,4,5,6}; be A[1][0] and *(*(A+1)+1) The values of ()
A、4 5
B、4 3
C、3 5
D、3 4
answer :A
analysis : Array A altogether 2 That's ok 3 Column , The first 0 Behavior 123, The first 1 Behavior 456.A[1][0] For the first time 1 Xing di 0 Column number 4. * (A+1) Point to array number 1 Xing di 0 Elements , * (A+1)+1 Point to array number 1 Xing di 1 Elements , Retake * It is the first 1 Xing di 1 The value of the elements 5, Therefore 4,5.
Question 10
The following statement is correct ()
A、 An array that is more than two dimensions is actually a special generalized table
B、 Once the array is created , The number of elements of the structure and the physical storage relationship between elements will not change
C、 Arrays are linear structures , Therefore, it can only be used to store linear tables
D、 Arrays are represented by sequential storage
answer :A B D
analysis : On this subject , We need to distinguish between the physical and logical structure of the data . Physical structure mainly refers to storage mode , Including linear storage and chain storage , It is considered from the perspective of computer storage . Logical structure refers to the relationship between data , There are linear relations and chain relations , Mainly from the perspective of artificial definition . An array is a table defined as a linear relationship , As for its storage structure , It can be stored by linear storage or chain storage .
Recommended reading : Logical structure and physical structure
Eleventh questions
边栏推荐
- go: 如何编写一个正确的udp服务端
- Bigder:自动化测试工程师
- 60 days of remote office experience sharing | community essay solicitation
- XSS vulnerability
- Sentinel's quick start takes you through flow control in three minutes
- Talk about the delta configuration of Eureka
- Spark存储体系底层架构剖析-Spark商业环境实战
- 数据链路层
- Proxmox cluster node crash handling
- jfinal中如何使用过滤器监控Druid监听SQL执行?
猜你喜欢

How to set a pod to run on a specified node

18. `bs object Node name next_ sibling` previous_ Sibling get sibling node

Detailed description of gaussdb (DWS) complex and diverse resource load management methods
![[compilation principle] type check](/img/fc/458871e2df4e0384f65e09faa909d7.png)
[compilation principle] type check

CorelDRAW最新24.1.0.360版本更新介绍讲解

.NetCore统一认证授权学习——Run(1)

How to solve the problem of insufficient memory space in Apple iPhone upgrade system?
![[notes] take notes again -- learn by doing Verilog HDL – 008](/img/7f/0ca73446247455ac4d8f9667083a87.png)
[notes] take notes again -- learn by doing Verilog HDL – 008

关于印发宝安区重点产业项目和总部项目遴选及用地保障实施细则(2022修订版)的通知
mysql中explain语句查询sql是否走索引,extra中的几种类型整理汇总
随机推荐
60 days of remote office experience sharing | community essay solicitation
How to use filters in jfinal to monitor Druid for SQL execution?
Nutch2.1 using eclipse debug to store the build process in MySQL on the windows platform
Jupyter service installation and startup
NLP - giza++ implements word alignment
Software engineering - principles, methods and Applications
Golang basic learning
liunx指令
Flume配置1——基础案例
Flutter calls Baidu map app to realize location search and route planning
A keepalived high availability accident made me learn it again!
[compilation principle] type check
Hangfire details
Linux Installation mysql5
18. `bs对象.节点名.next_sibling` previous_sibling 获取兄弟节点
使用Gunicorn部署web.py应用
[buuctf.reverse] 142_ [SUCTF2019]babyunic
Jupyter服务安装及启动
Three.js开发:粗线的画法
Dynamics CRM: 本地部署的服务器中, Sandbox, Unzip, VSS, Asynchronous还有Monitor服务的作用