当前位置:网站首页>Day35 LeetCode
Day35 LeetCode
2022-08-02 23:32:00 【the sun is falling】
1. 最近最少使用的缓存
运用所掌握的数据结构,设计和实现一个 LRU (Least Recently Used,最近最少使用) 缓存机制 .
实现 LRUCache 类:
- LRUCache(int capacity) 以正整数作为容量 capacity 初始化 LRU 缓存 .
- int get(int key)如果关键字 key 存在于缓存中,则返回关键字的值,否则返回 -1 .
- void put(int key, int value)如果关键字已经存在,则变更其数据值;如果关键字不存在,则插入该组「关键字-值」.当缓存容量达到上限时,它应该在写入新数据之前删除最久未使用的数据值,从而为新的数据值留出空间.
分析:
hash table used+双端队列来实现.Hash tables are used to store key-value pairs and make judgmentskey是否已经存在,A deque is used to maintain eachkey出现的顺序,The oldest unused data value is always at the end of the queue.
class LRUCache {
HashMap<Integer, Integer> map;
Deque<Integer> deque;
int capacity;
public LRUCache(int capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity;
map = new HashMap<>();
deque = new LinkedList<>();
}
public int get(int key) {
if (map.containsKey(key)) {
deque.remove(key);
deque.addFirst(key);
return map.get(key);
}
return -1;
}
public void put(int key, int value) {
if (map.containsKey(key)){
deque.remove(key);
deque.addFirst(key);
map.put(key, value);
}else {
if (deque.size() >= capacity){
int k = deque.pollLast();
map.remove(k);
}
map.put(key, value);
deque.addFirst(key);
}
}
}
2. 插入、Both random access and deletion areO(1)的容器
设计一个支持在平均 时间复杂度 O(1) 下,执行以下操作的数据结构:
- insert(val):当元素 val 不存在时返回 true ,并向集合中插入该项,否则返回 false .
- remove(val):当元素 val 存在时返回 true ,并从集合中移除该项,否则返回 false .
- getRandom:随机返回现有集合中的一项.每个元素应该有 相同的概率 被返回.
分析:
哈希表+List集合.ListUsed to store the value in the current structure,当执行insert(val)When first look in the hash table to see if there is thisval,有则返回false,没有则把val插入到list中去,and recorded in the hash tableval和它的位置.执行remove时,It is also to first go to the hash table to find out whether it is thereval,If there is, get the current firstlist最后面的值last,再把lastThe value is inserted into the originalval所在的位置,and update these in the hash table.getRandom实现比较简单,Generate a random number directly[0,List.size())区间,Then return the value of that subscript.
class RandomizedSet {
HashMap<Integer, Integer> set;
List<Integer> list;
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
public RandomizedSet() {
set = new HashMap<>();
list = new ArrayList<>();
}
/** Inserts a value to the set. Returns true if the set did not already contain the specified element. */
public boolean insert(int val) {
if (set.containsKey(val)) return false;
set.put(val, list.size());
list.add(val);
return true;
}
/** Removes a value from the set. Returns true if the set contained the specified element. */
public boolean remove(int val) {
if (set.containsKey(val)){
int idx = set.get(val);
int value = list.get(list.size()-1);
list.set(idx, value);
set.put(value, idx);
list.remove(list.size()-1);
set.remove(val);
return true;
}
return false;
}
/** Get a random element from the set. */
public int getRandom() {
Random r = new Random();
int idx = r.nextInt(list.size());
return list.get(idx);
}
}
3. 排序的循环链表
给定循环单调非递减列表中的一个点,写一个函数向这个列表中插入一个新元素 insertVal ,使这个列表仍然是循环升序的.
给定的可以是这个列表中任意一个顶点的指针,并不一定是这个列表中最小元素的指针.
如果有多个满足条件的插入位置,可以选择任意一个位置插入新的值,插入后整个列表仍然保持有序.
如果列表为空(给定的节点是 null),需要创建一个循环有序列表并返回这个节点.否则.请返回原先给定的节点.
分析:
如果循环链表为空,则插入一个新节点并将新节点的 next 指针指向自身,插入新节点之后得到只有一个节点的循环链表,该循环链表一定是有序的,将插入的新节点作为新的头节点返回.
如果循环链表的头节点的next 指针指向自身,则循环链表中只有一个节点,在头节点之后插入新节点,将头节点的next 指针指向新节点,将新节点的next 指针指向头节点,此时循环链表中有两个节点且一定是有序的,返回头节点.
如果循环链表中的节点数大于 1,则需要从头节点开始遍历循环链表,寻找插入新节点的位置,使得插入新节点之后的循环链表仍然保持有序.
用 cur 和next 分别表示当前节点和下一个节点,初始时cur 位于head,next 位于head 的下一个节点,由于链表中的节点数大于 1,因此curr.next=next.遍历过程中,判断值为insertVal 的新节点是否可以在curr 和 next 之间插入,如果符合插入要求则在 curr 和next 之间插入新节点,否则将 curr 和 next 同时向后移动,直到找到插入新节点的位置或者遍历完循环链表中的所有节点.要注意insertValThe case when less than all node values and greater than all node values,There is also the case when all values are equal.
class Solution {
public Node insert(Node head, int insertVal) {
if (head == null) {
Node node = new Node(insertVal);
node.next = node;
return node;
}
if (head.next == head){
Node node = new Node(insertVal);
node.next = head;
head.next = node;
return head;
}
Node cur = head;
Node next = head.next;
Node node = new Node(insertVal);
while (next != head){
if (insertVal>= cur.val && insertVal<=next.val){
cur.next = node;
node.next = next;
return head;
}
if (cur.val > next.val){
if (insertVal> cur.val || insertVal< next.val) {
cur.next = node;
node.next = next;
return head;
}
}
cur = cur.next;
next = next.next;
}
cur.next = node;
node.next = next;
return head;
}
}
4. 展平多级双向链表
多级双向链表中,除了指向下一个节点和前一个节点指针之外,它还有一个子链表指针,可能指向单独的双向链表.这些子列表也可能会有一个或多个自己的子项,依此类推,生成多级数据结构,如下面的示例所示.
给定位于列表第一级的头节点,请扁平化列表,即将这样的多级双向链表展平成普通的双向链表,使所有结点出现在单级双链表中.
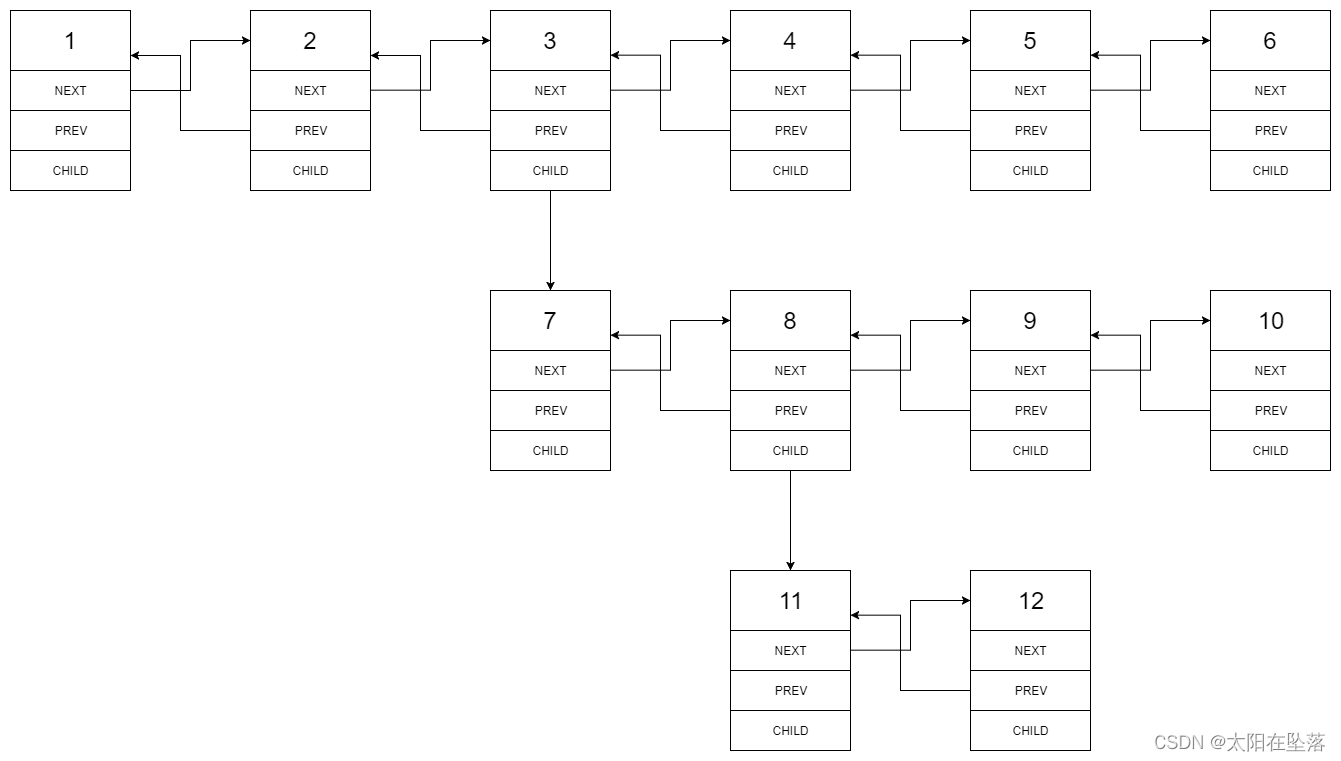

分析:
DFS.当遍历到某个节点node 时,如果它的 child 成员不为空,那么我们需要将child 指向的链表结构进行扁平化,并且插入node 与node 的下一个节点之间.
因此,我们在遇到 child 成员不为空的节点时,就要先去处理 child 指向的链表结构,这就是一个「深度优先搜索」的过程.当我们完成了对child 指向的链表结构的扁平化之后,就可以「回溯」到 node 节点.
为了能够将扁平化的链表插入node 与 node 的下一个节点之间,我们需要知道扁平化的链表的最后一个节点last,随后进行如下的三步操作:
- 将 node 与 node 的下一个节点next 断开;
- 将node 与 child 相连;
- 将 last 与 next 相连.
class Solution {
public Node flatten(Node head) {
dfs(head);
return head;
}
public Node dfs(Node node) {
Node cur = node;
// 记录链表的最后一个节点
Node last = null;
while (cur != null) {
Node next = cur.next;
// 如果有子节点,那么首先处理子节点
if (cur.child != null) {
Node childLast = dfs(cur.child);
next = cur.next;
// 将 node 与 child 相连
cur.next = cur.child;
cur.child.prev = cur;
// 如果 next 不为空,就将 last 与 next 相连
if (next != null) {
childLast.next = next;
next.prev = childLast;
}
// 将 child 置为空
cur.child = null;
last = childLast;
} else {
last = cur;
}
cur = next;
}
return last;
}
}
5. 设计循环队列
设计你的循环队列实现. 循环队列是一种线性数据结构,其操作表现基于 FIFO(先进先出)原则并且队尾被连接在队首之后以形成一个循环.它也被称为“环形缓冲器”.
循环队列的一个好处是我们可以利用这个队列之前用过的空间.在一个普通队列里,一旦一个队列满了,我们就不能插入下一个元素,即使在队列前面仍有空间.但是使用循环队列,我们能使用这些空间去存储新的值.
你的实现应该支持如下操作:
- MyCircularQueue(k): 构造器,设置队列长度为 k .
- Front: 从队首获取元素.如果队列为空,返回 -1 .
- Rear: 获取队尾元素.如果队列为空,返回 -1 .
- enQueue(value): 向循环队列插入一个元素.如果成功插入则返回真.
- deQueue(): 从循环队列中删除一个元素.如果成功删除则返回真.
- isEmpty(): 检查循环队列是否为空.
- isFull(): 检查循环队列是否已满.
分析:
使用Deque类来实现.
class MyCircularQueue {
Deque<Integer> queue;
int k;
public MyCircularQueue(int k) {
queue = new LinkedList<>();
this.k = k;
}
public boolean enQueue(int value) {
if (queue.size() >= k) return false;
queue.addLast(value);
return true;
}
public boolean deQueue() {
if (queue.size() == 0) return false;
queue.pollFirst();
return true;
}
public int Front() {
return queue.isEmpty()?-1:queue.getFirst();
}
public int Rear() {
return queue.isEmpty()?-1:queue.getLast();
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return queue.isEmpty();
}
public boolean isFull() {
return queue.size() == k;
}
}
边栏推荐
- shell:条件语句
- Bena的生命周期
- 成为黑客不得不学的语言,看完觉得你们还可吗?
- J9数字论:互联网跨链桥有什么作用呢?
- ImageNet下载及处理
- 【实战 已完结】WPF开发自动化生产管理平台
- 基于 outline 实现头像剪裁以及预览
- J9 Digital Currency Theory: Identifying Web3's New Scarcity: Open Source Developers
- setup syntax sugar defineProps defineEmits defineExpose
- Xcode13.1运行工程报错fatal error: ‘IFlyMSC/IFly.h‘ file not found的问题
猜你喜欢

Leetcode刷题——字符串相加相关题目(415. 字符串相加、面试题 02.05. 链表求和、2. 两数相加)

即时通讯开发移动端网络短连接的优化手段
Qt提升自定义控件,找不到头文件
美国爱荷华州立大学| Improving Distantly Supervised Relation Extraction by Natural Language Inference(通过自然语言推理改进远程监督关系提取)

【数据分析】:什么是数据分析?
ShardingSphere-proxy +PostgreSQL实现读写分离(静态策略)
浅议.NET遗留应用改造

程序员也许都缺一个“二舅”精神
遇上Mysql亿级优化,怎么办
OP-5,输入/输出信号范围-一信号处理能力
随机推荐
有效解决MySQL报错:ERROR 1045 (28000): Access denied for user ‘root‘@‘localhost‘ (using password: NO/YES)
程序员也许都缺一个“二舅”精神
什么是 IDE
Likou Question of the Day - Day 46 - 344. Reverse Strings
postgresql autovaccum自动清理
解析Collection接口中的常用的被实现子类重写的方法
姑姑:给小学生出点口算题
所谓武功再高也怕菜刀-分区、分库、分表和分布式的优劣
Silver circ: letter with material life insurance products should be by the insurance company is responsible for the management
Redis集群配置
golang源码分析之geoip2-golang
pytorch的tensor创建和操作记录
如何解决图像分类中的类别不均衡问题?不妨试试分开学习表征和分类器
【LeetCode】1161. 最大层内元素和
【LeetCode】1374. 生成每种字符都是奇数个的字符串
银保监会:人身险产品信披材料应由保险公司总公司统一负责管理
【数据分析】:什么是数据分析?
用了TCP协议,就一定不会丢包吗?
arm64麒麟安装paddlehub(国产化)
力扣每日一题-第46天-344. 反转字符串