当前位置:网站首页>pytorch的tensor创建和操作记录
pytorch的tensor创建和操作记录
2022-08-02 19:51:00 【此何人哉tan】
目录
Indexing, Slicing, Joining, Mutating Ops
一、Tensr
1、Tensor属性

numel # Returns the total number of elements in the input tensor.
repeat_interleaves
>>> a = torch.randn(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)
>>> torch.numel(a)
120
>>> a = torch.zeros(4,4)
>>> torch.numel(a)
16
>>> x = torch.tensor([1, 2, 3])
>>> x.repeat_interleave(2)
tensor([1, 1, 2, 2, 3, 3])
>>> y = torch.tensor([[1, 2], [3, 4]])
>>> torch.repeat_interleave(y, 2)
tensor([1, 1, 2, 2, 3, 3, 4, 4])
>>> torch.repeat_interleave(y, 3, dim=1)
tensor([[1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2],
[3, 3, 3, 4, 4, 4]])
>>> torch.repeat_interleave(y, torch.tensor([1, 2]), dim=0)
tensor([[1, 2],
[3, 4],
[3, 4]])
>>> torch.repeat_interleave(y, torch.tensor([1, 2]), dim=0, output_size=3)
tensor([[1, 2],
[3, 4],
[3, 4]]2、创建
(1)
(2) 其它
>>> torch.eye(3)
tensor([[ 1., 0., 0.],
[ 0., 1., 0.],
[ 0., 0., 1.]])二、Tensor基本操作
Indexing, Slicing, Joining, Mutating Ops
tensor.stack()
tensor.cat()
torch.squeeze()
torch.unsqueeze()
>>> x = torch.zeros(2, 1, 2, 1, 2)
>>> x.size()
torch.Size([2, 1, 2, 1, 2])
>>> y = torch.squeeze(x)
>>> y.size()
torch.Size([2, 2, 2])
>>> y = torch.squeeze(x, 0)
>>> y.size()
torch.Size([2, 1, 2, 1, 2])
>>> y = torch.squeeze(x, 1)
>>> y.size()
torch.Size([2, 2, 1, 2])三、Random sampling
bernoulli
multinomial
normal
poisson
rand
rand_like
randint
randint_like
randn
randn_like
randperm
# In-place random sampling
torch.Tensor.bernoulli_()
torch.Tensor.cauchy_()
torch.Tensor.exponential_()
torch.Tensor.geometric_()
torch.Tensor.log_normal_()
torch.Tensor.normal_()
torch.Tensor.random_()
torch.Tensor.uniform_() 四、数学运算
1、按元素操作
torch — PyTorch 1.12 documentation https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/torch.html#pointwise-ops
https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/torch.html#pointwise-ops
(1)加减乘除、绝对值
add
sub # subtract, Alias for torch.sub().
mul # multiply, Alias for torch.mul().
div # divide , Alias for torch.div().
abs # absolute, Alias for torch.abs()加法举例:
import torch
a_list = [[1, -2, 3], [-4, 5, -6]]
a_tensor = torch.tensor(list1)
print(a_tensor)
# output:
tensor([[ 1, -2, 3],
[-4, 5, -6]])
# 加法操作
# ops 1
a_tensor.add(10)
# output1
tensor([[11, 8, 13],
[ 6, 15, 4]])
# ops 2
b_tensor = torch.ones_like(a_tensor)
a_tensor.add(b_tensor, alpha=19) # alpha=1(默认),a_tensor = alpha*b_tensor + a_tensor
# output1
tensor([[20, 17, 22],
[15, 24, 13]])(2)指数、对数、幂运算、开方运算
(3)三角&反三角函数运算函数运算
(4)双曲线反双曲线运算
(5) 其他常用操作
clamp
reshape
view
clamp # clip Alias for torch.clamp().
a = torch.randn(4)
# output1
tensor([-1.7120, 0.1734, -0.0478, -0.0922])
torch.clamp(a, min=-0.5, max=0.5)
# output2
tensor([-0.5000, 0.1734, -0.0478, -0.0922])(6)
# torch.bmm
>>> input = torch.randn(10, 3, 4)
>>> mat2 = torch.randn(10, 4, 5)
>>> res = torch.bmm(input, mat2)
>>> res.size()
torch.Size([10, 3, 5])参考: torch.clamp — PyTorch 1.12 documentation
PyTorch:view() 与 reshape() 区别详解_地球被支点撬走啦的博客-CSDN博客_reshape和view
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢

A Review of Nature Microbiology: Focusing on the Algae--Ecological Interface of Phytoplankton-Bacteria Interactions
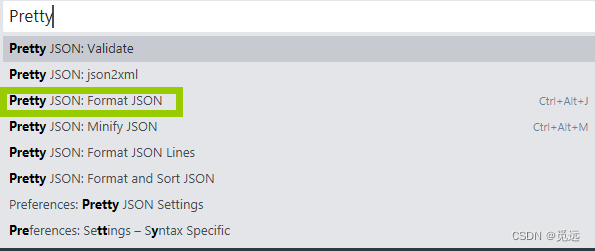
Fiddle设置接口数据用指定工具查看;Sublime Text设置json数据格式化转换
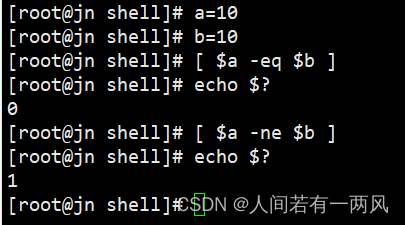
Shell: conditional statements
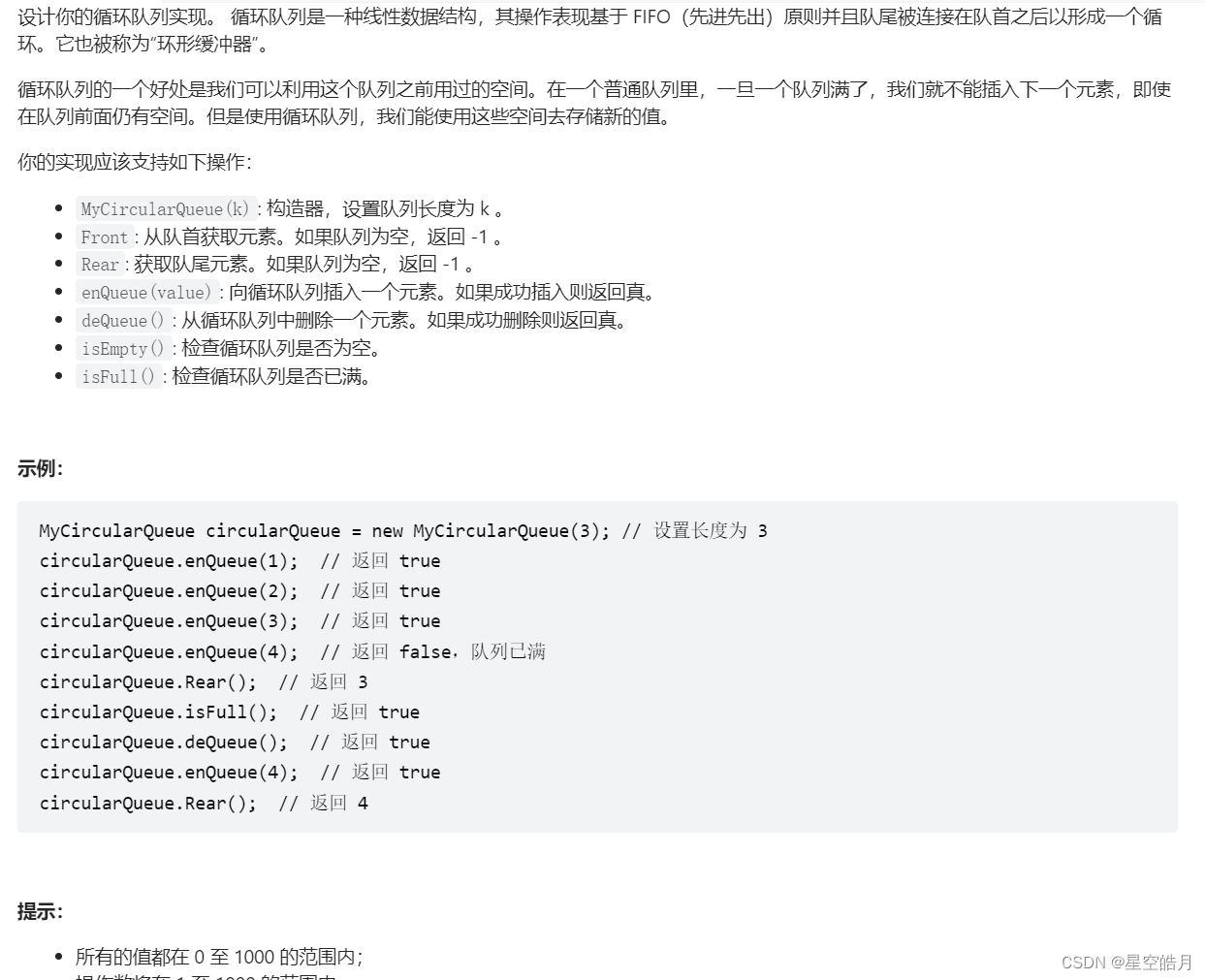
LeetCode:622. 设计循环队列【模拟循环队列】

基于 outline 实现头像剪裁以及预览

shell:条件语句
Office2021 安装MathType

J9 Digital Currency Theory: Identifying Web3's New Scarcity: Open Source Developers
Parse common methods in the Collection interface that are overridden by subclasses
分享一个 web 应用版本监测 (更新) 的工具库
随机推荐
SQL Server实现group_concat功能
MaxCompute 近期发布上线的版本的 SQL 引擎新功能参数化视图有什么优势?
OpenCV开发中的内存管理问题
golang刷leetcode 经典(10) tire树与ac自动机
7月29-31 | APACHECON ASIA 2022
Redis集群配置
MySQL安装时一直卡在starting server
ShapeableImageView 的使用,告别shape、三方库
【Psychology · Characters】Issue 1
我用这一招让团队的开发效率提升了 100%!
[安洵杯 2019]easy_web
如何ES源码中添加一个自己的API 流程梳理
Kali命令ifconfig报错command not found
顺序查找和折半查找,看这篇就够了
ECCV 2022 | 通往数据高效的Transformer目标检测器
2022-07-28
模板的进阶
es 读流程源码解析
程序员也许都缺一个“二舅”精神
ShardingSphere-proxy +PostgreSQL实现读写分离(静态策略)