当前位置:网站首页>manipulation of file contents
manipulation of file contents
2022-08-04 04:12:00 【Master_hl】
目录
2.1 字节流-InputStream / FileInputStream
2.4 Close the resource optimization
3.1 字节流-OutputStream / FileOutputStream
1. 什么是流
2. 读文件
2.1 字节流-InputStream / FileInputStream
【方法】
修饰符及 返回值类 型 | 方法 | 说明 |
int | read() | 读取一个字节的数据,返回 -1 代表已经完全读完了 |
int | read(byte[] b) | 最多读取 b.length 字节的数据到 b 中,返回实际读到的数 量;返回 -1 代表以及读完了 |
int | read(byte[] b, int off, int len) | 读数据到 b 数组中,从 b[ off ] 开始放,返 回实际读到的数量;-1 代表以及读完了 |
void | close() | 关闭字节流 |
InputStream 是一个抽象类,不能直接实例化,它的实现类有很多,We only care about reading now,所以可以通过 FileInputStream 来实现.
打开文件
InputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream("test2.txt");For this one line of code,打开文件成功后,就得到了 InputStream 对象,Subsequent operations on the file,are all expanded through this object..
再者,It is not convenient for us to operate the hard disk directly,Constructs an object associated with it in memory,Manipulating this object is equivalent to manipulating hard disk data.
The action object is equal to the hard disk data,like a remote,When we turn on the air conditioner,Impossible to climb up with a ladder every time,Press the air conditioner switch by hand,Instead, operate the air conditioner through the air conditioner remote control..
关闭文件
inputStream.close();
// will throw a IOException,File not found exception thrown for open file,IOException是其父类为什么要关闭文件??
Closing files is mainly to release file descriptor table resources.
文件描述符表,The table is equivalent to a array,The subscript of this array is called "文件描述符",每次打开一个文件,Will occupy a place in the file descriptor table;每次关闭文件,Will release a position.and the file descriptor table,is online,如果一个进程,keep opening file,没有释放,This will cause our process to perform subsequent open file operations when,Failed to open file!!
读取文件
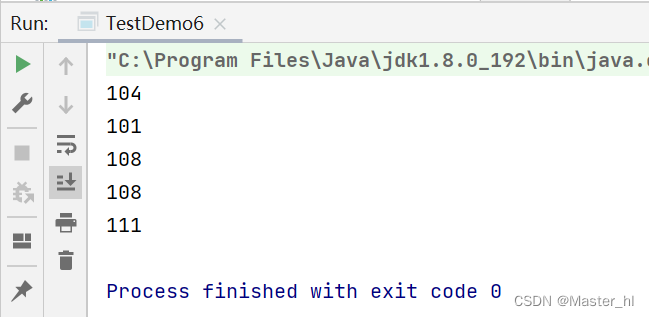
read() 代码示例
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 1.打开文件
InputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream("test2.txt");
// 2.读取文件
while(true) {
int b = inputStream.read();
if(b == -1) {
// 文件读完了
break;
}
// 因为 ASCII Code values are stored in bytes,So the output here is corresponding to each word ASCII 码值
System.out.println(b); // hello 对应的 ASCII 码值
}
// 3.关闭文件
inputStream.close();
}
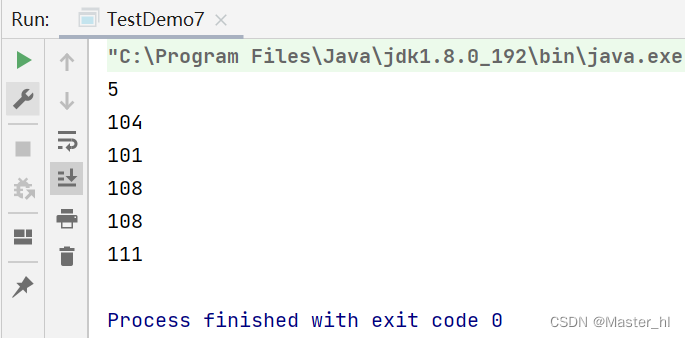
read(byte[] b)代码示例
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 1.打开文件
InputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream("test2.txt");
// 2.读取文件
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
// 返回的长度(字节)
int len = inputStream.read(buf);
System.out.println(len);
for(int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
System.out.println(buf[i]);
}
// 3.关闭文件
inputStream.close();
}
注意: If you are reading Chinese,UTF8 的编码格式,一个汉字占3个字节.
If you want to read Chinese in the console,The byte stream can only pass the specified encoding format,就比较麻烦.例如以下代码:
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 1.打开文件
InputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream("test2.txt");
// 2.读取文件
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
int len = inputStream.read(buf);
String s = new String(buf, 0, len, "UTF8");
System.out.println(s);
// 3.关闭文件
inputStream.close();
}为了解决上述问题,We can read through the character stream.
2.2 字符流-Reader / FileReader
The method here and the above InputStream Similar, but not too much introduction.
Read Chinese code example
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 字符流
Reader reader = new FileReader("test2.txt");
char[] buffer = new char[1024];
int len = reader.read(buffer);
for(int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
System.out.println(buffer[i]);
}
reader.close();
}Although the characters flow than pure byte stream that some may read Chinese,但还是不够方便.对于文本文件,还有更简单的写法.
2.3 通过 Scanner 进行字符读取
Scanner 构造方法
构造方法 | 说明 |
| Scanner(InputStream is, String charset) | 使用 charset 字符集进行 is 的扫描读取 (You can also not specify the encoding format,Using the default encoding format) |
代码示例
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
InputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream("test2.txt");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(inputStream);
// Use whatever type you want to read scanner what to call
String s = scanner.next();
System.out.println(s);
inputStream.close();
}2.4 Close the resource optimization
We read the Chinese code in the previous byte stream,发现如果在 read() An exception occurred while reading the file,就可能导致 close() 执行不到,按照我们以前的思路,使用 try...catch...finally,Put the closing resource in finally 中.
public static void main(String[] args) {
InputStream inputStream = null;
try {
// 打开文件(字节流)
inputStream = new FileInputStream("test2.txt");
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
int len = inputStream.read(buf);
// 读取中文
String s = new String(buf, 0, len, "UTF8");
System.out.println(s);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 关闭资源
try {
inputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}如果这样做的话,Our code looks smelly and long,A more recommended approach is the following:
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (InputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream("test2.txt")) {
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
int len = inputStream.read(buf);
// .........
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}This grammatical mechanism is called try with resources,This operation will try 执行结束后,自动调用 inputStream 的 close 方法(实现 Closeable Interface classes can do this).
3.写文件
3.1 字节流-OutputStream / FileOutputStream
【方法】
修饰符及返回值类型 | 方法 | 说明 |
void | write(int b) | 写入要给字节的数据 |
void | write(byte[] b) | 将 b 这个字符数组中的数据全部写入 os 中 |
| int | write(byte[] b, int off, int len) | 将 b 这个字符数组中从 off 开始的数据写入 os 中,一共写 len 个 |
| void | close() | 关闭字节流 |
void | flush() | I/O 的速度是很慢的,所以,大多的 OutputStream 为了减少设备操作的次数,When writing data, the data will be temporarily written to the buffer first..但造成一个结果,就是我们写的数据,很可能会遗留一部分在缓冲区中.需要在最后或者合适的位置,调用 flush(刷新)操作,将数据刷到设备中. |
代码示例
public static void main(String[] args) {
try(OutputStream outputStream = new FileOutputStream("test2.txt")) {
// 方法一
/* outputStream.write('h');
outputStream.write('e');
outputStream.write('l');
outputStream.write('l');
outputStream.write('o'); */
// 方法二
String s = " hello java";
outputStream.write(s.getBytes());
// clear old file contents,rewrite
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}注意:every time you rewrite,will clear the old file contents,rewrite.
But this native byte stream write file method,Still inconvenient to use.
3.2 字符流-Writer / FileWriter
代码示例
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (Writer writer = new FileWriter("test2.txt")) {
// Can write strings,就很方便
writer.write("hello world");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}in our character stream Writer Can also write strings,就很方便.还有一种方式 -- PrintWriter ,It provides a richer.
PrintWriter 代码示例
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (OutputStream outputStream = new FileOutputStream("test2.txt")) {
PrintWriter printWriter = new PrintWriter(outputStream);
printWriter.println("hello");
printWriter.println("你好");
printWriter.printf("%d: %s\n", 1, "Java");
// println 需要搭配 flush 使用
printWriter.flush();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}这里要注意使用 println need to remember later flush.
4.小程序示例
代码示例1
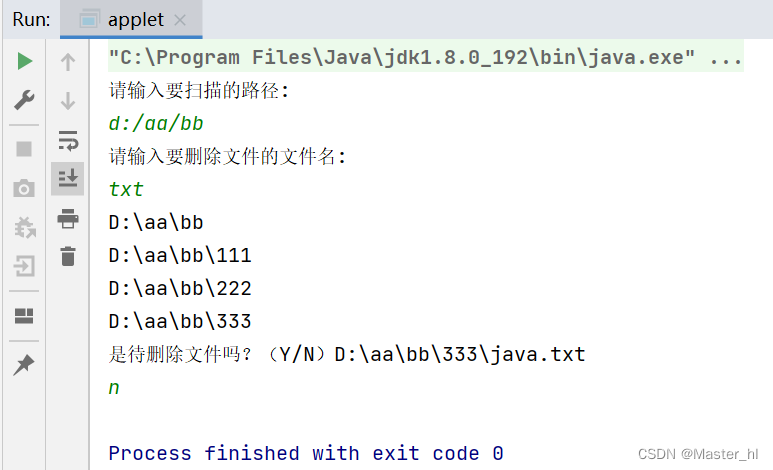
public class applet1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入要扫描的路径: ");
String path = scanner.next();
File rootPath = new File(path);
// 判断文件是否存在
if (!rootPath.exists()) {
System.out.println("您输入的路径不存在,Can't scan!");
return;
}
System.out.println("Please enter the filename of the file to delete: ");
String toDelete = scanner.next();
// 遍历目录,Find files to delete
dfsDir(rootPath, toDelete);
}
// 重点:The process of directories recursively
public static void dfsDir(File rootDir, String toDelete) {
// log for each recursion
try {
System.out.println(rootDir.getCanonicalPath());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// rootDir 对象代表的目录下的所有文件名
File[] files = rootDir.listFiles();
if (files == null) {
// 空目录,直接返回
return;
}
// 遍历每个文件
for (File file : files) {
if (file.isDirectory()) {
// 是目录,继续递归
dfsDir(file, toDelete);
} else {
tryDelete(file, toDelete);
}
}
}
public static void tryDelete(File file, String toDelete) {
if (file.getName().contains(toDelete)) {
try {
System.out.println("Is it a file to be deleted??(Y/N)" + file.getCanonicalPath());
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
String choice = scanner.next();
if (choice.equals("Y")) {
file.delete();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
代码示例2
进行普通文件的复制(regular file)
public class applet2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Please enter the path to copy files: ");
String srcPath = scanner.next();
File srcFile = new File(srcPath);
if(!srcFile.exists()) {
System.out.println("The file to be copied does not exist!");
return;
}
if(!srcFile.isFile()) {
System.out.println("To copy is not a normal file!");
return;
}
System.out.println("请输入要复制到的目标路径: ");
String destPath = scanner.next();
File destFile = new File(destPath);
if(destFile.exists()) {
System.out.println("The file to be copied already exists in the target path!");
return;
}
// 以上都是准备工作
// make a copy
try (InputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream(srcFile)) {
try(OutputStream outputStream = new FileOutputStream(destFile)) {
while(true) {
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
int len = inputStream.read(buf);
if(len == -1) {
break;
}
// write specific length,don't write arrays
outputStream.write(buf,0,len);
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("复制完成!");
}
}
问题1
while 循环里头,why when reading the file,Every time I know that I will continue reading where I left off.?
在读文件的时候,Inside the file object,有一个 "光标" ,通过这个 "光标" Indicates where the current file is read.每次读操作,都会让 "光标" 往后移动,一直到文件末尾,If you keep reading,will read a special character -- EOF(end of file),It means the file is read.
问题2
while 循环里头,写文件的时候,为什么不直接将 buf write array,Instead write the specific length?
举个极端的例子,The size of the file we want to copy is 2049 个字节,The first two times we read in the array are 1024,can read the array,So there is no influence of the entire array to write in,but the last byte,read into array,这时候返回的 len 是 1 ,At this point we again reading group is not appropriate.
问题3
The previous example was not demonstrated,The second write will clear the first write,write again??
Before running the program once,写一次,When writing the second time,We have already closed will flow.And here is the read and write at the same time,before reading the file again,The stream is always open,所以不会清空.
本篇博客就到这里了,谢谢观看!!
边栏推荐
- Mockito unit testing
- SQL query String field less than 10 how to check
- RSS订阅微信公众号初探-feed43
- new Date converts strings into date formats Compatible with IE, how ie8 converts strings into date formats through new Date, how to replace strings in js, and explain the replace() method in detail
- 哎,又跟HR在小群吵了一架!
- 基地址:环境变量
- Introduction to the memory model of the JVM
- 本周四晚19:00知识赋能第4期直播丨OpenHarmony智能家居项目之设备控制实现
- 7-1 LVS+NAT 负载均衡群集,NAT模式部署
- Explain详解与实践
猜你喜欢
8.Haproxy 搭建Web集群

6-port full Gigabit Layer 2 network managed industrial Ethernet switch Gigabit 2 optical 4 electrical fiber self-healing ERPS ring network switch
SVM介绍以及实战
7-3 LVS+Keepalived集群叙述与部署
Shell 函数
七夕节,我用代码制作了表白信封

【Ryerson情感说话/歌唱视听数据集(RAVDESS) 】
系统设计.秒杀系统

网络工程师入门必懂华为认证体系,附系统学习路线分享
用户与用户互发红包/支付宝C2C/B2C现金红包php源码示例/H5方式/兼容苹果/安卓
随机推荐
sql注入一般流程(附例题)
Mockito unit testing
【Ryerson情感说话/歌唱视听数据集(RAVDESS) 】
八年软件测试工程师带你了解-测试岗进阶之路
解决问题遇到的问题
系统设计.秒杀系统
Tensors - Application Cases
MySQL 查询练习(1)
docker+网桥+redis主从+哨兵模式
数据治理平台项目总结和分析
出现504怎么办?由于服务器更新导致的博客报504错误[详细记录]
db2中kettle报错 Field [XXX] is required and couldn‘t be found 解决方法
XSS related knowledge points
MySQL Query Exercise (1)
2022年软件测试——精选金融银行面试真题
LeetCode每日一题(2285. Maximum Total Importance of Roads)
创新互融|华秋赋能助力OpenHarmony生态硬件开发落地
JVM笔记
[Ryerson emotional speaking/singing audiovisual dataset (RAVDESS)]
XSS相关知识点