当前位置:网站首页>Derivation of Kalman filter (KF) and extended Kalman filter (EKF)
Derivation of Kalman filter (KF) and extended Kalman filter (EKF)
2022-06-11 01:48:00 【Captain xiaoyifeng】
Background knowledge
Kalman filter is based on Bayesian filter and Gaussian distribution , So let's talk about these two first .
Bayesian filtering
First, some basic concepts and formulas are given
- Joint distribution
p ( x , y ) = p ( X = x , Y = y ) p(x,y)=p(X=x, Y=y) p(x,y)=p(X=x,Y=y)
Express x,y Probability of simultaneous occurrence - Conditional probability
p ( x ∣ y ) = p ( X = x ∣ Y = y ) p(x|y)=p(X=x|Y=y) p(x∣y)=p(X=x∣Y=y)
Express x stay y The probability of occurrence based on what has already occurred , set up x、y Are independent of each other ( It will be the same in the future ), Then there are
p ( x ∣ y ) = p ( x , y ) p ( y ) p(x|y)=\frac{p(x,y)}{p(y)} p(x∣y)=p(y)p(x,y) - Prior probability
It can be called experience , Before the current data is read , The probability distribution of the state estimated by the system - Posterior probability
After reading the data ( After observation ), The probability distribution of the state obtained by integrating the prior probability and the observation probability - Law of total probability
p ( x ) = ∑ y p ( x ∣ y ) p ( y ) ( leave scattered love condition ) p(x)=\sum_{y}p(x|y)p(y)( Discrete situation ) p(x)=y∑p(x∣y)p(y)( leave scattered love condition )
p ( x ) = ∫ p ( x ∣ y ) p ( y ) d y ( even To continue love condition ) p(x)=\int p(x|y)p(y)dy( Continuous situation ) p(x)=∫p(x∣y)p(y)dy( even To continue love condition ) - Bayes rule
p ( x ∣ y ) = p ( y ∣ x ) p ( x ) p ( y ) = p ( y ∣ x ) p ( x ) ∑ x ′ p ( y ∣ x ′ ) p ( x ′ ) ( leave scattered ) p(x|y)=\frac{p(y|x)p(x)}{p(y)}=\frac{p(y|x)p(x)}{\sum_{x^{'}}p(y|x^{'})p(x^{'})}( discrete ) p(x∣y)=p(y)p(y∣x)p(x)=∑x′p(y∣x′)p(x′)p(y∣x)p(x)( leave scattered )
p ( x ∣ y ) = p ( y ∣ x ) p ( x ) p ( y ) = p ( y ∣ x ) p ( x ) ∫ p ( y ∣ x ′ ) p ( x ′ ) d x ′ ( even To continue ) p(x|y)=\frac{p(y|x)p(x)}{p(y)}=\frac{p(y|x)p(x)}{\int p(y|x^{'})p(x^{'})dx^{'}}( continuity ) p(x∣y)=p(y)p(y∣x)p(x)=∫p(y∣x′)p(x′)dx′p(y∣x)p(x)( even To continue )
among x It's called state ,y It's called data , p ( x ) p(x) p(x) It is called a priori probability , p ( y ∣ x ) p(y|x) p(y∣x) go by the name of “ The inverse ” Conditional probability , and p ( y ) − 1 p(y)^{-1} p(y)−1 and x irrelevant , Often used as a coefficient η \eta η.
It should be noted that , In general ,x Is used as an argument during the operation , our p yes x Probability distribution function of ( It is Gaussian distribution in Kalman filter , In some cases it may be a piecewise function ), Not specific x The probability of . During the transition of state , The predicted probability distribution consists of all the possible x Take the weighted integral / Sum to get - integrity / Markov sex
Suppose a state x t x_t xt Can best predict the future , That is to say, all the control information in the past is contained in it and cannot have an impact on the future ( In other words, information from the past should be used in the future , Must depend on x t x_t xt), said x t x_t xt Is a full , Bayesian filtering is based on this assumption .
Bayesian filtering is based on Bayesian criterion , The basic method is to obtain a posteriori probability through a priori probability and observation value , Get a more accurate probability distribution .
The algorithm of Bayesian filtering is simply summarized as two ( 3、 ... and ) That's ok :
1 : b e l ‾ ( x t ) = ∫ p ( x t ∣ u t , x t − 1 ) b e l ( x t − 1 ) d x t − 1 ( even To continue ) 2 : b e l ‾ ( x t ) = ∑ p ( x t ∣ u t , x t − 1 ) b e l ( x t − 1 ) ( leave scattered ) 3 : b e l ( x t ) = η p ( z t ∣ x t ) b e l ‾ ( x t ) \begin{array}{l}1:\overline{bel}(x_t)=\int p(x_t|u_t,x_{t-1})bel(x_{t-1})dx_{t-1}( continuity )\\2:\overline{bel}(x_t)=\sum p(x_t|u_t,x_{t-1})bel(x_{t-1})( discrete )\\3:bel(x_t)=\eta p(z_t|x_t)\overline{bel}(x_t)\end{array} 1:bel(xt)=∫p(xt∣ut,xt−1)bel(xt−1)dxt−1( even To continue )2:bel(xt)=∑p(xt∣ut,xt−1)bel(xt−1)( leave scattered )3:bel(xt)=ηp(zt∣xt)bel(xt)
among :
- η \eta η It's the normalization factor , In the process of calculation, various constants are proposed and constantly changed .
- x x x Represents the state quantity
- z z z It means observation data
- u u u Represents the movement data recorded by the odometer
- b e l 、 b e l ‾ bel、\overline{bel} bel、bel representative Confidence value , b e l ( x t ) = p ( x t ∣ z t ) , bel(x_t)=p(x_t|z_t), bel(xt)=p(xt∣zt), I.e. obtained after observation x t x_t xt A probability distribution , b e l ‾ \overline{bel} bel Represents the confidence value of the internal prediction .
- p ( x t ∣ u t , x t − 1 ) p(x_t|u_t,x_{t-1}) p(xt∣ut,xt−1) Express State transition probability , Express x t − 1 、 u t x_{t-1}、u_t xt−1、ut In certain cases , x t x_t xt Probability distribution function of
- p ( z t ∣ x t ) p(z_t|x_t) p(zt∣xt) Apparent representation x t x_t xt In certain cases , z t z_t zt Probability distribution of ( adopt z About x Function of ), In fact, because of x It is unknown. ,z It is known. , In the process of calculation x As an independent variable ,z As a constant .
- That's ok 1、2 It stands for forecast Or call it Control updates
- That's ok 3 It stands for Observation update
The premise of the algorithm is the integrity assumption , If used p ( x t ∣ u t , x t − 1 ) p(x_t|u_t,x_{t-1}) p(xt∣ut,xt−1) To express p ( x t ∣ u 1 : t , x 0 : t − 1 , z 1 : t − 1 ) p(x_t|u_{1:t},x_{0:t-1},z_{1:t-1}) p(xt∣u1:t,x0:t−1,z1:t−1)
Simple deduction
forecast
b e l ‾ ( x t ) = p ( x t ∣ z 1 : t − 1 , u 1 : t ) = ∫ p ( x t ∣ x t − 1 , z 1 : t − 1 , u 1 : t ) p ( x t − 1 ∣ z 1 : t − 1 , u 1 : t ) d x t − 1 = ∫ p ( x t ∣ x t − 1 , u t ) b e l ( x t − 1 ) d x t − 1 \begin{aligned} \overline{bel}(x_t)&=p(x_t|z_{1:t-1},u_{1:t})\\ &=\int p(x_t|x_{t-1},z_{1:t-1},u_{1:t})p(x_{t-1}|z_{1:t-1},u_{1:t})dx_{t-1}\\ &=\int p(x_t|x_{t-1},u_{t})bel(x_{t-1})dx_{t-1}\\ \end{aligned} bel(xt)=p(xt∣z1:t−1,u1:t)=∫p(xt∣xt−1,z1:t−1,u1:t)p(xt−1∣z1:t−1,u1:t)dxt−1=∫p(xt∣xt−1,ut)bel(xt−1)dxt−1
Observation update
b e l ( x t ) = p ( x t ∣ z 1 : t , u 1 : t ) = p ( z t ∣ x t , z 1 : t − 1 , u 1 : t ) p ( x t ∣ z 1 : t − 1 , u 1 : t ) p ( z t ∣ z 1 : t − 1 , u 1 : t ) = η p ( z t ∣ x t , z 1 : t − 1 , u 1 : t ) p ( x t ∣ z 1 : t − 1 , u 1 : t ) = η p ( z t ∣ x t ) b e l ‾ ( x t ) \begin{aligned} bel(x_t)=p(x_t|z_{1:t},u_{1:t})&=\frac{p(z_t|x_t,z_{1:t-1},u_{1:t})p(x_t|z_{1:t-1},u_{1:t})}{p(z_t|z_{1:t-1,u_{1:t}})}\\ &=\eta p(z_t|x_t,z_{1:t-1},u_{1:t})p(x_t|z_{1:t-1},u_{1:t})\\ &=\eta p(z_t|x_t)\overline{bel}(x_t) \end{aligned} bel(xt)=p(xt∣z1:t,u1:t)=p(zt∣z1:t−1,u1:t)p(zt∣xt,z1:t−1,u1:t)p(xt∣z1:t−1,u1:t)=ηp(zt∣xt,z1:t−1,u1:t)p(xt∣z1:t−1,u1:t)=ηp(zt∣xt)bel(xt)
Gaussian distribution ( Normal distribution )
Bayesian filtering x The value range is discrete , So Bayesian filtering is not really an available algorithm , Bayesian filtering is based on Gaussian distribution Gauss filtering It can make x The values are continuous , Kalman filter is one of them .
The Gaussian distribution is represented by the following function
p ( x ) = ( 2 π σ 2 ) − 1 2 e − 1 2 ( x − μ ) 2 σ 2 ( x by mark The amount ) p(x)=(2\pi\sigma^2)^{-\frac12}e^{-\frac12\frac{(x-\mu)^2}{\sigma^2}}(x For the scalar ) p(x)=(2πσ2)−21e−21σ2(x−μ)2(x by mark The amount )
among σ 2 \sigma^2 σ2 Is variance , μ \mu μ Is the mean
p ( x ‾ ) = ( 2 π Σ ) − 1 2 e − 1 2 ( x ‾ − μ ‾ ) T Σ − 1 ( x ‾ − μ ‾ ) ( x ‾ by towards The amount ) p(\underline{x})=(2\pi\Sigma)^{-\frac12}e^{-\frac12{(\underline{x}-\underline{\mu})^T}{\Sigma^{-1}(\underline{x}-\underline{\mu})}}(\underline{x} Vector ) p(x)=(2πΣ)−21e−21(x−μ)TΣ−1(x−μ)(x by towards The amount )
among Σ \Sigma Σ Is variance ( Covariance matrix ), μ ‾ \underline{\mu} μ Is the mean
The reason why Gaussian distribution is used is that Gaussian distribution exists widely in nature , And has good properties , Although there are also shortcomings ( Unimodal ). In Kalman filter , There is no definite state , Measured value 、 Both the predicted quantity and the final correction value are expressed by Gaussian distribution .
In Gaussian distribution , p p p Integral ( Add up ) by 1, Of course, this is also the law of all probability distribution functions .
Fusion of Gaussian distributions
During the first derivation No, Use the following formula , But after using it, it seems that the following derivation is in vain … Dig a hole first
Gaussian distribution times Gaussian distribution or Gaussian distribution ( Structurally, it is obvious that )
For the product of Gaussian distribution X = X 1 X 2 X=X_1X_2 X=X1X2, among
{ X 1 ∼ N ( μ 1 , Σ 1 ) X 2 ∼ N ( μ 2 , Σ 2 ) \left\{\begin{array}{l}X_1\sim\mathbb{N}(\mu_1,\Sigma_1)\\X_2\sim\mathbb{N}(\mu_2,\Sigma_2)\end{array}\right. { X1∼N(μ1,Σ1)X2∼N(μ2,Σ2)
You can get the following results :
{ K = Σ 1 ( Σ 1 + Σ 2 ) − 1 ) μ = μ 1 + K ( μ 2 − μ 1 ) Σ = Σ 1 − K Σ 1 \left\{\begin{array}{l}K=\Sigma_1(\Sigma_1+\Sigma_2)^{-1})\\\mu=\mu_1+K(\mu_2-\mu_1)\\\Sigma=\Sigma_1-K\Sigma_1\end{array}\right. ⎩⎨⎧K=Σ1(Σ1+Σ2)−1)μ=μ1+K(μ2−μ1)Σ=Σ1−KΣ1
among K Is the Kalman gain , Prove slightly
Line generation correlation
Review by yourself / preview
Kalman filtering (KF)
Kalman filter is based on linear assumption , We assume that :
x t = A t x t − 1 + B t u t + ε t ( shape state turn move Letter Count ) x_t=A_tx_{t-1}+B_tu_t+\varepsilon_t( State transition function ) xt=Atxt−1+Btut+εt( shape state turn move Letter Count )
among ε t \varepsilon_t εt Yes, the mean is 0, The variance of R t R_t Rt Gaussian random vector
z t = C t x t + δ t ( measuring The amount Letter Count ) z_t=C_tx_t+\delta_t( Measurement function ) zt=Ctxt+δt( measuring The amount Letter Count )
among δ t \delta_t δt Yes, the mean is 0, The variance of Q t Q_t Qt Gaussian random vector
b e l ( x 0 ) = p ( x 0 ) ( first beginning Set up Letter degree ) bel(x_0)=p(x_0)( Initial confidence ) bel(x0)=p(x0)( first beginning Set up Letter degree )
among p p p Yes, the mean is μ 0 \mu_0 μ0, The variance of Σ 0 \Sigma_0 Σ0 Gaussian random vector
The Kalman filter can be expressed as the following lines of algorithms
1 : μ ‾ t = A t μ t − 1 + B t u t 2 : Σ ‾ t = A t Σ t − 1 A t T + R t 3 : K t = Σ ‾ t C t T ( C t Σ ‾ t C t T + Q t ) − 1 4 : μ t = μ ‾ t + K t ( z t − C t μ ‾ t ) 5 : Σ t = ( I − K t C t ) Σ ‾ t \begin{array}{l} 1:\overline{\mu}_t=A_t\mu_{t-1}+B_tu_t \\ 2:\overline{\Sigma}_t=A_t\Sigma_{t-1}A_t^{T}+R_t\\ 3:K_t=\overline{\Sigma}_tC_t^T(C_t\overline{\Sigma}_tC_t^T+Q_t)^{-1}\\ 4:\mu_t=\overline{\mu}_t+K_t(z_t-C_t\overline{\mu}_t)\\ 5:\Sigma_t=(I-K_tC_t)\overline{\Sigma}_t \end{array} 1:μt=Atμt−1+Btut2:Σt=AtΣt−1AtT+Rt3:Kt=ΣtCtT(CtΣtCtT+Qt)−14:μt=μt+Kt(zt−Ctμt)5:Σt=(I−KtCt)Σt
Here's the proof
KF Mathematical derivation of
forecast
According to Bayesian filtering , We get
b e l ‾ ( x t ) = ∫ p ( x t ∣ u t , x t − 1 ) b e l ( x t − 1 ) d x t − 1 \overline{bel}(x_t)=\int p(x_t|u_t,x_{t-1})bel(x_{t-1})dx_{t-1} bel(xt)=∫p(xt∣ut,xt−1)bel(xt−1)dxt−1
So there is
b e l ‾ ( x t ) = η ∫ e − L t d x t − 1 \overline{bel}(x_t)=\eta\int e^{-L_t}dx_{t-1} bel(xt)=η∫e−Ltdxt−1
among
L t = 1 2 ( x t − A t x t − 1 − B t u t ) T R t − 1 ( x t − A t x t − 1 − B t u t ) + 1 2 ( x t − 1 − μ t − 1 ) T Σ t − 1 − 1 ( x t − 1 − μ t − 1 ) L_t=\frac12(x_t-A_tx_{t-1}-B_tu_t)^TR_t^{-1}(x_t-A_tx_{t-1}-B_tu_t)+\frac12(x_{t-1}-\mu_{t-1})^T\Sigma_{t-1}^{-1}(x_{t-1}-\mu_{t-1}) Lt=21(xt−Atxt−1−Btut)TRt−1(xt−Atxt−1−Btut)+21(xt−1−μt−1)TΣt−1−1(xt−1−μt−1)
L t L_t Lt yes x t x_t xt It's also x t − 1 x_{t-1} xt−1 The quadratic function of
To avoid integral operations , We make
L t = L t ( x t − 1 , x t ) + L t ( x t ) L_t=L_t(x_{t-1},x_t)+L_t(x_t) Lt=Lt(xt−1,xt)+Lt(xt)
Propose an item that does not include x t − 1 x_{t-1} xt−1 Of L t ( x t ) L_t(x_t) Lt(xt)
b e l ‾ ( x t ) = η e − L t ( x t ) ∫ e − L t ( x t − 1 , x t ) d x t − 1 \overline{bel}(x_t)=\eta e^{-L_t(x_t)}\int e^{-L_t(x_{t-1},x_t)}dx_{t-1} bel(xt)=ηe−Lt(xt)∫e−Lt(xt−1,xt)dxt−1
The following L t ( x t − 1 , x t ) L_t(x_{t-1},x_t) Lt(xt−1,xt) Constructed as Quadratic type ( After formulation )( It is my understanding that doing so will not raise the question of x t x_t xt The item )
Next, calculate L t L_t Lt About x t − 1 x_{t-1} xt−1 The first and second derivatives of , obtain
L t ( x t − 1 , x t ) = 1 2 ( x t − 1 − Ψ [ A t T R t − 1 ( x t − B t u t ) + Σ t − 1 − 1 μ t − 1 ] ) T Ψ − 1 ( x t − 1 − Ψ [ A t T R t − 1 ( x t − B t u t ) + Σ t − 1 − 1 μ t − 1 ] ) L_t(x_{t-1},x_t)=\frac12(x_{t-1}-\Psi[A_t^TR_t^{-1}(x_t-B_tu_t)+\Sigma_{t-1}^{-1}\mu_{t-1}])^T\Psi^{-1}(x_{t-1}-\Psi[A_t^TR_t^{-1}(x_t-B_tu_t)+\Sigma_{t-1}^{-1}\mu_{t-1}]) Lt(xt−1,xt)=21(xt−1−Ψ[AtTRt−1(xt−Btut)+Σt−1−1μt−1])TΨ−1(xt−1−Ψ[AtTRt−1(xt−Btut)+Σt−1−1μt−1])
Again because
∫ d e t ( 2 π Ψ ) − 1 2 e − L t ( x t − 1 , x t ) d x t − 1 = 1 \int det(2\pi\Psi)^{-\frac12}e^{-L_t(x_{t-1},x_t)}dx_{t-1}=1 ∫det(2πΨ)−21e−Lt(xt−1,xt)dxt−1=1
therefore
∫ e − L t ( x t − 1 , x t ) d x t − 1 = d e t ( 2 π Ψ ) 1 2 \int e^{-L_t(x_{t-1},x_t)}dx_{t-1}=det(2\pi\Psi)^{\frac12} ∫e−Lt(xt−1,xt)dxt−1=det(2πΨ)21
therefore
b e l ‾ ( x t ) = η e − L t ( x t ) \overline{bel}(x_t)=\eta e^{-L_t(x_t)} bel(xt)=ηe−Lt(xt)
Now calculate L t ( x t ) L_t(x_t) Lt(xt):
L t ( x t ) = L t − L t ( x t − 1 , x t ) = . . . ( contain x t − 1 term whole Ministry eliminate Go to ) = 1 2 ( x t − B t u t ) T R t − 1 ( x t − B t u t ) + 1 2 μ t − 1 T Σ t − 1 − 1 μ t − 1 − 1 2 [ A t T R t − 1 ( x t − B t u t ) + Σ t − 1 − 1 μ t − 1 ] T ( A t T R t − 1 A t + Σ t − 1 − 1 ) [ A t T R t − 1 ( x t − B t u t ) + Σ t − 1 − 1 μ t − 1 ] \begin{aligned} L_t(x_t)&=L_t-L_t(x_{t-1},x_t)\\ &=...( contain x_{t-1} All items are deleted )\\ &=\frac12(x_t-B_tu_t)^TR_t^{-1}(x_t-B_tu_t)+\frac12\mu_{t-1}^T\Sigma_{t-1}^{-1}\mu_{t-1}-\frac12[A_t^TR_t^{-1}(x_t-B_tu_t)+\Sigma_{t-1}^{-1}\mu_{t-1}]^T(A_t^TR_t^{-1}A_t+\Sigma_{t-1}^{-1})[A_t^TR_t^{-1}(x_t-B_tu_t)+\Sigma_{t-1}^{-1}\mu_{t-1}] \end{aligned} Lt(xt)=Lt−Lt(xt−1,xt)=...( contain xt−1 term whole Ministry eliminate Go to )=21(xt−Btut)TRt−1(xt−Btut)+21μt−1TΣt−1−1μt−1−21[AtTRt−1(xt−Btut)+Σt−1−1μt−1]T(AtTRt−1At+Σt−1−1)[AtTRt−1(xt−Btut)+Σt−1−1μt−1]
Although this is not about x t x_t xt The quadratic form of ( After formulation ), But it's really a quadratic function , It just affects the previous coefficient .
Find a second derivative to get x t x_t xt The mean and variance of :
∂ L t ( x t ) ∂ x t = R t − 1 ( x t − B t u t ) − R t − 1 A t ( A t T R t − 1 A t + Σ t − 1 − 1 ) − 1 [ A t T R t − 1 ( x t − B t u t ) + Σ t − 1 − 1 μ t − 1 ] = [ R t − 1 − R t − 1 A t ( A t T R t − 1 A t + Σ t − 1 − 1 ) − 1 A t T R t − 1 ‾ ] ( x t − B t u t ) − R t − 1 A t ( A t T R t − 1 A t + Σ t − 1 − 1 ) − 1 Σ t − 1 − 1 μ t − 1 \begin{aligned} \frac{\partial L_t(x_t)}{\partial x_t}&=R_t^{-1}(x_t-B_tu_t)-R_t^{-1}A_t(A_t^TR_t^{-1}A_t+\Sigma_{t-1}^{-1})^{-1}[A_t^TR_t^{-1}(x_t-B_tu_t)+\Sigma_{t-1}^{-1}\mu_{t-1}]\\ &=[\underline{R_t^{-1}-R_t^{-1}A_t(A_t^TR_t^{-1}A_t+\Sigma_{t-1}^{-1})^{-1}A_t^TR_t^{-1}}](x_t-B_tu_t)-R_t^{-1}A_t(A_t^TR_t^{-1}A_t+\Sigma_{t-1}^{-1})^{-1}\Sigma_{t-1}^{-1}\mu_{t-1} \end{aligned} ∂xt∂Lt(xt)=Rt−1(xt−Btut)−Rt−1At(AtTRt−1At+Σt−1−1)−1[AtTRt−1(xt−Btut)+Σt−1−1μt−1]=[Rt−1−Rt−1At(AtTRt−1At+Σt−1−1)−1AtTRt−1](xt−Btut)−Rt−1At(AtTRt−1At+Σt−1−1)−1Σt−1−1μt−1
By Sherman Morrison formula ( It proved that the fight was too slow , Tips : Can pass [ A B C D ] [ x A x B ] = [ y A y B ] \begin{bmatrix} {A}&{B}\\ {C}&{D}\\ \end{bmatrix} \begin{bmatrix} {x_A}\\ {x_B}\\ \end{bmatrix} =\begin{bmatrix} {y_A}\\ {y_B}\\ \end{bmatrix} [ACBD][xAxB]=[yAyB] Find the block matrix [ A B C D ] \begin{bmatrix} {A}&{B}\\ {C}&{D}\\ \end{bmatrix} [ACBD] The expression of the two inverse matrices of , Using the equality of two inverse matrices, we get .)
R t − 1 − R t − 1 A t ( A t T R t − 1 A t + Σ t − 1 − 1 ) − 1 A t T R t − 1 = ( R t + A t Σ t − 1 A t T ) − 1 R_t^{-1}-R_t^{-1}A_t(A_t^TR_t^{-1}A_t+\Sigma_{t-1}^{-1})^{-1}A_t^TR_t^{-1}=(R_t+A_t\Sigma_{t-1}A_t^T)^{-1} Rt−1−Rt−1At(AtTRt−1At+Σt−1−1)−1AtTRt−1=(Rt+AtΣt−1AtT)−1
therefore
∂ L t ( x t ) ∂ x t = ( R t + A t Σ t − 1 A t T ) − 1 ( x t − B t u t ) − R t − 1 A t ( A t T R t − 1 A t + Σ t − 1 − 1 ) − 1 Σ t − 1 − 1 μ t − 1 = 0 \begin{aligned} \frac{\partial L_t(x_t)}{\partial x_t}&=(R_t+A_t\Sigma_{t-1}A_t^T)^{-1}(x_t-B_tu_t)-R_t^{-1}A_t(A_t^TR_t^{-1}A_t+\Sigma_{t-1}^{-1})^{-1}\Sigma_{t-1}^{-1}\mu_{t-1}\\ &=0 \end{aligned} ∂xt∂Lt(xt)=(Rt+AtΣt−1AtT)−1(xt−Btut)−Rt−1At(AtTRt−1At+Σt−1−1)−1Σt−1−1μt−1=0
obtain
x t = B t u t + ( R t + A t Σ t − 1 A t T ) R t − 1 A t ( A t T R t − 1 A t + Σ t − 1 − 1 ) − 1 Σ t − 1 − 1 μ t − 1 = B t u t + A t ( I + Σ t − 1 A t T R t − 1 A t ) ( I + Σ t − 1 A t T R t − 1 A t ) − 1 μ t − 1 = B t u t + A t μ t − 1 \begin{aligned} x_t&=B_tu_t+(R_t+A_t\Sigma_{t-1}A_t^T)R_t^{-1}A_t(A_t^TR_t^{-1}A_t+\Sigma_{t-1}^{-1})^{-1}\Sigma_{t-1}^{-1}\mu_{t-1}\\ &=B_tu_t+A_t(I+\Sigma_{t-1}A_t^TR_t^{-1}A_t)(I+\Sigma_{t-1}A_t^TR_t^{-1}A_t)^{-1}\mu_{t-1}\\ &=B_tu_t+A_t\mu_{t-1} \end{aligned} xt=Btut+(Rt+AtΣt−1AtT)Rt−1At(AtTRt−1At+Σt−1−1)−1Σt−1−1μt−1=Btut+At(I+Σt−1AtTRt−1At)(I+Σt−1AtTRt−1At)−1μt−1=Btut+Atμt−1
that
μ ‾ t = A t μ t − 1 + B t u t \overline\mu_t=A_t\mu_{t-1}+B_tu_t μt=Atμt−1+Btut
Σ ‾ t = [ ∂ 2 L t ( x t ) ∂ x t 2 ] − 1 = ( A t Σ t − 1 A t T + R t ) \overline\Sigma_{t}=[\frac{\partial^2 L_t(x_t)}{\partial x_t^2}]^{-1}=(A_t\Sigma_{t-1}A_t^T+R_t) Σt=[∂xt2∂2Lt(xt)]−1=(AtΣt−1AtT+Rt)
Survey update
b e l ( x t ) = η p ( z t ∣ x t ) b e l ‾ ( x t ) = η e − J t bel(x_t)=\eta p(z_t|x_t)\overline{bel}(x_t)=\eta e^{-J_t} bel(xt)=ηp(zt∣xt)bel(xt)=ηe−Jt
among
J t = 1 2 ( z t − C t x t ) T Q t − 1 ( z t − C t x t ) + 1 2 ( x t − μ ‾ t ) T Σ t − 1 ( x t − μ ‾ t ) J_t=\frac12(z_t-C_tx_t)^TQ_t^{-1}(z_t-C_tx_t)+\frac12(x_{t}-\overline\mu_{t})^T\Sigma_{t}^{-1}(x_{t}-\overline\mu_{t}) Jt=21(zt−Ctxt)TQt−1(zt−Ctxt)+21(xt−μt)TΣt−1(xt−μt)
To find the derivative, we get
Σ t = ( C T Q t − 1 C t + Σ ‾ t − 1 ) − 1 \begin{aligned} \Sigma_t&=(C^TQ_t^{-1}C_t+\overline{\Sigma}_t^{-1})^{-1}\\ \end{aligned} Σt=(CTQt−1Ct+Σt−1)−1
Because finding the minimum of a quadratic function , use μ t \mu_t μt Replace x t x_t xt:
C t T Q t − 1 ( z t − C t μ t ) = Σ ‾ t − 1 ( μ t − μ ‾ t ) C_t^TQ_t^{-1}(z_t-C_t\mu_t)=\overline{\Sigma}_t^{-1}(\mu_t-\overline{\mu}_t) CtTQt−1(zt−Ctμt)=Σt−1(μt−μt)
Left edge = C t T Q t − 1 ( z t − C t μ t + C t μ ‾ t − C t μ ‾ t ) = C t T Q t − 1 ( z t − C t μ ‾ t ) − C t T Q t − 1 C t ( μ t − μ ‾ t ) \begin{aligned} On the left &=C_t^TQ_t^{-1}(z_t-C_t\mu_t+C_t\overline{\mu}_t-C_t\overline{\mu}_t)\\ &=C_t^TQ_t^{-1}(z_t-C_t\overline{\mu}_t)-C_t^TQ_t^{-1}C_t (\mu_t-\overline{\mu}_t)\end{aligned} Left edge =CtTQt−1(zt−Ctμt+Ctμt−Ctμt)=CtTQt−1(zt−Ctμt)−CtTQt−1Ct(μt−μt)
Dai Huide
C t T Q t − 1 ( z t − C t μ ‾ t ) = Σ t − 1 ( μ t − μ ‾ t ) Σ t C t T Q t − 1 ( z t − C t μ ‾ t ) = ( μ t − μ ‾ t ) C_t^TQ_t^{-1}(z_t-C_t\overline{\mu}_t)=\Sigma_t^{-1}(\mu_t-\overline{\mu}_t)\\ \Sigma_tC_t^TQ_t^{-1}(z_t-C_t\overline{\mu}_t)=(\mu_t-\overline{\mu}_t) CtTQt−1(zt−Ctμt)=Σt−1(μt−μt)ΣtCtTQt−1(zt−Ctμt)=(μt−μt)
Make K = Σ t C t T Q t − 1 K=\Sigma_tC_t^TQ_t^{-1} K=ΣtCtTQt−1, call K Is the Kalman gain
μ t − μ ‾ t = K ( z t − C t μ ‾ t ) \mu_t-\overline{\mu}_t=K(z_t-C_t\overline{\mu}_t) μt−μt=K(zt−Ctμt)
K t = Σ t C t T Q t − 1 = Σ t C t T Q t − 1 ( C t Σ ‾ t C t T + Q t ) ( C t Σ ‾ t C t T + Q t ) − 1 = Σ t ( C t T Q t − 1 C t Σ ‾ t C t T + C t T Q t − 1 Q t ) ( C t Σ ‾ t C t T + Q t ) − 1 = Σ t ( C t T Q t − 1 C t Σ ‾ t C t T + C t T ) ( C t Σ ‾ t C t T + Q t ) − 1 = Σ t ( C t T Q t − 1 C t Σ ‾ t C t T + Σ ‾ t − 1 Σ ‾ t C t T ) ( C t Σ ‾ t C t T + Q t ) − 1 = Σ t ( C t T Q t − 1 C t + Σ ‾ t − 1 ) Σ ‾ t C t T ( C t Σ ‾ t C t T + Q t ) − 1 = Σ ‾ t C t T ( C t Σ ‾ t C t T + Q t ) − 1 \begin{aligned} K_t&=\Sigma_tC_t^TQ_t^{-1}\\ &=\Sigma_tC_t^TQ_t^{-1}(C_t\overline{\Sigma}_tC_t^T+Q_t)(C_t\overline{\Sigma}_tC_t^T+Q_t)^{-1}\\ &=\Sigma_t(C_t^TQ_t^{-1}C_t\overline{\Sigma}_tC_t^T+C_t^TQ_t^{-1}Q_t)(C_t\overline{\Sigma}_tC_t^T+Q_t)^{-1}\\ &=\Sigma_t(C_t^TQ_t^{-1}C_t\overline{\Sigma}_tC_t^T+C_t^T)(C_t\overline{\Sigma}_tC_t^T+Q_t)^{-1}\\ &=\Sigma_t(C_t^TQ_t^{-1}C_t\overline{\Sigma}_tC_t^T+\overline{\Sigma}_t^{-1}\overline{\Sigma}_tC_t^T)(C_t\overline{\Sigma}_tC_t^T+Q_t)^{-1}\\ &=\Sigma_t(C_t^TQ_t^{-1}C_t+\overline{\Sigma}_t^{-1})\overline{\Sigma}_tC_t^T(C_t\overline{\Sigma}_tC_t^T+Q_t)^{-1}\\ &=\overline{\Sigma}_tC_t^T(C_t\overline{\Sigma}_tC_t^T+Q_t)^{-1}\\ \end{aligned} Kt=ΣtCtTQt−1=ΣtCtTQt−1(CtΣtCtT+Qt)(CtΣtCtT+Qt)−1=Σt(CtTQt−1CtΣtCtT+CtTQt−1Qt)(CtΣtCtT+Qt)−1=Σt(CtTQt−1CtΣtCtT+CtT)(CtΣtCtT+Qt)−1=Σt(CtTQt−1CtΣtCtT+Σt−1ΣtCtT)(CtΣtCtT+Qt)−1=Σt(CtTQt−1Ct+Σt−1)ΣtCtT(CtΣtCtT+Qt)−1=ΣtCtT(CtΣtCtT+Qt)−1
here , You can continue to simplify Σ t \Sigma_t Σt
Σ t = ( C T Q t − 1 C t + Σ ‾ t − 1 ) − 1 = Σ ‾ t − Σ ‾ t C t T ( Q t + C t Σ ‾ t C t T ) − 1 C t Σ ‾ t = [ ( I − K t C t ) ] Σ ‾ t \begin{aligned} \Sigma_t&=(C^TQ_t^{-1}C_t+\overline{\Sigma}_t^{-1})^{-1}\\ &=\overline{\Sigma}_t-\overline{\Sigma}_tC_t^T(Q_t+C_t\overline{\Sigma}_tC_t^T)^{-1}C_t\overline{\Sigma}_t\\ &=[(I-K_tC_t)]\overline{\Sigma}_t \end{aligned} Σt=(CTQt−1Ct+Σt−1)−1=Σt−ΣtCtT(Qt+CtΣtCtT)−1CtΣt=[(I−KtCt)]Σt
Extended Kalman filter (EKF)
Considering the nonlinear case
x t = g ( u t , x t − 1 ) + ε t z t = h ( x t ) + δ t x_t=g(u_t,x_{t-1})+\varepsilon_t\\ z_t=h(x_t)+\delta_t xt=g(ut,xt−1)+εtzt=h(xt)+δt
Regarding this ,EKF Taylor expansion is proposed to retain the first derivative :
G t = ∂ g ( u t , x t − 1 ) ∂ x t − 1 , x t − 1 = μ t − 1 H t = ∂ h ( x t ) ∂ x t , x t = μ ‾ t G_t=\frac{\partial g(u_t,x_{t-1})}{\partial x_{t-1}},x_{t-1}=\mu_{t-1}\\ H_t=\frac{\partial h(x_{t})}{\partial x_{t}},x_t=\overline{\mu}_t Gt=∂xt−1∂g(ut,xt−1),xt−1=μt−1Ht=∂xt∂h(xt),xt=μt
that
g ( u t , x t − 1 ) = g ( u t , μ t − 1 ) + G t ( x t − 1 − μ t − 1 ) h ( x t ) = h ( μ ‾ t ) + H t ( x t − μ ‾ t ) g(u_t,x_{t-1})=g(u_t,\mu_{t-1})+G_t(x_{t-1}-\mu_{t-1})\\ h(x_t)=h(\overline{\mu}_t)+H_t(x_t-\overline{\mu}_t) g(ut,xt−1)=g(ut,μt−1)+Gt(xt−1−μt−1)h(xt)=h(μt)+Ht(xt−μt)
similar KF, It can be proved that EKF as follows :
1 : μ ‾ t = g ( u t , μ t − 1 ) 2 : Σ ‾ t = G t Σ t − 1 G t T + R t 3 : K t = Σ ‾ t H t T ( H t Σ ‾ t H t T + Q t ) − 1 4 : μ t = μ ‾ t + K t ( z t − h ( μ ‾ t ) ) 5 : Σ t = ( I − K t H t ) Σ ‾ t \begin{array}{l} 1:\overline{\mu}_t=g(u_t,\mu_{t-1}) \\ 2:\overline{\Sigma}_t=G_t\Sigma_{t-1}G_t^{T}+R_t\\ 3:K_t=\overline{\Sigma}_tH_t^T(H_t\overline{\Sigma}_tH_t^T+Q_t)^{-1}\\ 4:\mu_t=\overline{\mu}_t+K_t(z_t-h(\overline{\mu}_t))\\ 5:\Sigma_t=(I-K_tH_t)\overline{\Sigma}_t \end{array} 1:μt=g(ut,μt−1)2:Σt=GtΣt−1GtT+Rt3:Kt=ΣtHtT(HtΣtHtT+Qt)−14:μt=μt+Kt(zt−h(μt))5:Σt=(I−KtHt)Σt
边栏推荐
- Linux安装mysql数据库详解
- 2.1 ros+px4 simulation - Fixed Point flight control
- 卡尔曼滤波(KF)、拓展卡尔曼滤波(EKF)推导
- PX4从放弃到精通(二十四):自定义机型
- [VBA Script] extract the information and pending status of all annotations in the word document
- Sealem finance builds Web3 decentralized financial platform infrastructure
- Leetcode divide and conquer method
- 字节北京23k和拼多多上海28K,我该怎么选?
- LeetCode 1029 Two City Scheduling (dp)
- QGC ground station tutorial
猜你喜欢

threejs:两点坐标绘制贝赛尔曲线遇到的坑

How to download web photos

The problem of slow response of cs-3120 actuator during use

Sealem finance builds Web3 decentralized financial platform infrastructure

Leetcode linked list queue stack problem

Project_ Visual analysis of epidemic data based on Web Crawler
![[geometric vision] 4.2 piecewise linear transformation](/img/9e/ad010e0b55c88f2c0244442ae20fb3.jpg)
[geometric vision] 4.2 piecewise linear transformation
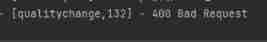
Daily problem essay | 21.11.29: use resttemplate to call external put request, and prompt '400 bad request'
![[cloud native | kubernetes] actual combat of ingress case](/img/99/1674f79e7ade0ec2f39e9b2c522d59.png)
[cloud native | kubernetes] actual combat of ingress case
Yunna Qingyuan fixed assets management and barcode inventory system
随机推荐
LeetCode 1029 Two City Scheduling (dp)
Threejs: streamer effect encapsulation
关于概率统计中的排列组合
Middleware_ Redis_ 05_ Persistence of redis
PX4装机教程(六)垂起固定翼(倾转)
Garbled code when the command parameter contains% in VisualStudio debugging
kubernetes 二进制安装(v1.20.15)(七)加塞一个工作节点
Threejs: how to get the boundingbox of geometry?
Exj shaped children will be satisfied with mbtxe due to disconnection
2.0 detailed explanation of ROS and Px4 communication
Daily problem essay | 21.11.29: use resttemplate to call external put request, and prompt '400 bad request'
MATLAB数组其他常见操作笔记
2.2. Ros+px4 simulation multi-point cruise flight - Square
[recommended by Zhihu knowledge master] castle in UAV - focusing on the application of UAV in different technical fields
Be careful, these hidden "bugs" of "array" to "collection"“
Leetcode 1605 find valid matrix given row and Column Sums
2021-2-14 gephi学习笔记
MATLAB数字运算函数笔记
CLIP论文详解
[leetcode] merge K ascending linked lists