当前位置:网站首页>[dynamic programming] - Knapsack Problem
[dynamic programming] - Knapsack Problem
2022-06-27 12:59:00 【Xuanche_】

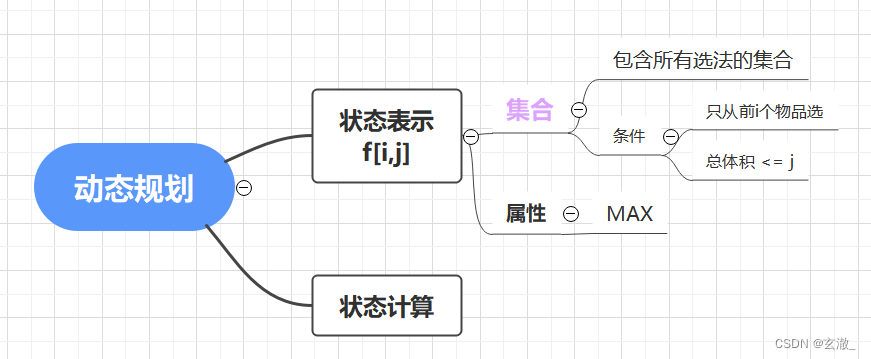
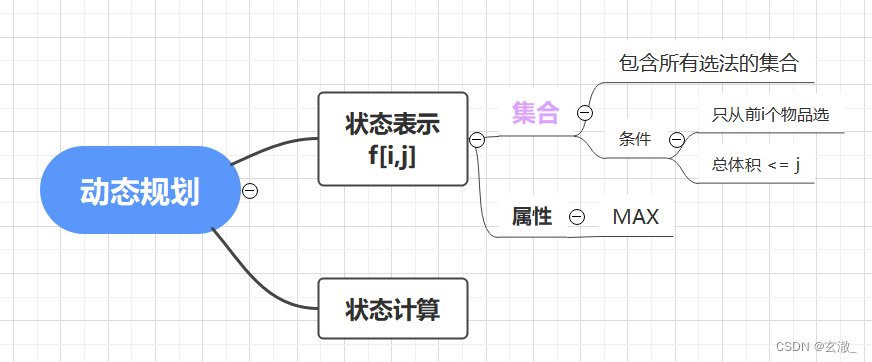
Classification of knapsack problem

01 knapsack problem
sample input
4 5 1 2 2 4 3 4 4 5sample output :
8
In the process of selection The first i The state transition equation of an object , We can take it out ![\small f[i-1,j-v[i]]](http://img.inotgo.com/imagesLocal/202206/27/202206271235354600_14.gif) The maximum value of plus w[i]
The maximum value of plus w[i]
No second choice i If it's an item , The equation of state transition is ![\small f[i][j] = f[i - 1,j]](http://img.inotgo.com/imagesLocal/202206/27/202206271235354600_11.gif)
![\small f[i,j]=max\begin{cases}f[i-1,j] & \\ f[i-1, j -V_i] +w_i &if(j\geqslant V_i) \end{cases}](http://img.inotgo.com/imagesLocal/202206/27/202206271235354600_6.gif)
![\small f[i]](http://img.inotgo.com/imagesLocal/202206/27/202206271235354600_21.gif)

#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1010;
int n, m;
int v[N], w[N];
int f[N][N];
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) cin >> v[i] >> w[i];
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
for(int j = 0; j <= m; j ++ )
{
f[i][j] = f[i - 1][j];
if(j >= v[i]) f[i][j] = max(f[i][j], f[i - 1][j - v[i]] + w[i]);
}
cout << f[n][m] << endl;
return 0;
}From two-dimensional optimization to one-dimensional optimization
adopt DP State transfer equation of , We found that , At each stage i The state of is only related to that of the previous stage i-1 The state of . under these circumstances , It can be used as “ Scrolling array ” Optimization method , Reduce time overhead .
because ![\small f[j] = max(f[j], f[j - v[i]] + w[i])](http://img.inotgo.com/imagesLocal/202206/27/202206271235354600_19.gif) there
there ![\small f[j - v[i]]](http://img.inotgo.com/imagesLocal/202206/27/202206271235354600_31.gif) Certain ratio
Certain ratio ![\small f[j]](http://img.inotgo.com/imagesLocal/202206/27/202206271235354600_39.gif) Calculated earlier , therefore
Calculated earlier , therefore ![\small f[j - v[i]]](http://img.inotgo.com/imagesLocal/202206/27/202206271235354600_31.gif) The result of calculation is i Layer of , And in our above DP Fang Chengzhong , What is used is The first i - 1 layer The data of , So if you traverse the volume from small to large , There will be “ Data pollution ” The situation of . So the enumeration of volume should be from large to small .
The result of calculation is i Layer of , And in our above DP Fang Chengzhong , What is used is The first i - 1 layer The data of , So if you traverse the volume from small to large , There will be “ Data pollution ” The situation of . So the enumeration of volume should be from large to small .
One dimensional optimization code implementation
#include <iostream> #include <cstring> using namespace std; const int N = 1010; int n, m; int v[N], w[N]; int f[N]; int main() { cin >> n >> m; for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) cin >> v[i] >> w[i]; for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) for(int j = m; j >= v[i]; j -- ) { f[j] = max(f[j], f[j - v[i]] + w[i]); } cout << f[m] << endl; return 0; }
Complete knapsack problem
sample input
4 5 1 2 2 4 3 4 4 5sample output :
10
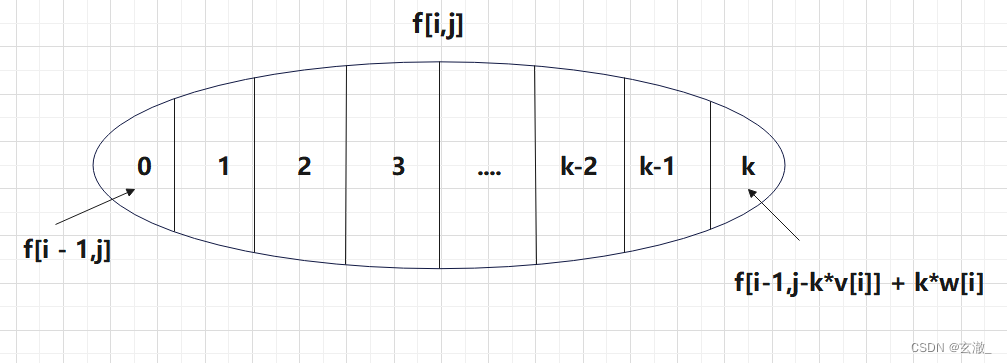
about Simple approach Yes : ![\small f[i,j]=f[i,j-k*v[i]]+k*w[i]](http://img.inotgo.com/imagesLocal/202206/27/202206271235354600_24.gif) analogy 01 knapsack problem
analogy 01 knapsack problem
Code implementation
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1010;
int n, m;
int v[N], w[N];
int f[N][N];
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) cin >> v[i] >> w[i];
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
for(int j = 0; j <= m; j ++ )
for(int k = 0; k * v[i] <= j; k ++ )
f[i][j] = max(f[i][j], f[i - 1][j - k * v[i]] + k * w[i]);
cout << f[n][m] << endl;
return 0;
}By comparing the following equations, we can find that :
obtain :
![\large {\color{Red} f[i,j] = max(f[i - 1,j], f[i, j - v] + w)}](//img.inotgo.com/imagesLocal/202206/27/202206271235354600_22.gif)
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1010;
int n, m;
int v[N], w[N];
int f[N][N];
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) cin >> v[i] >> w[i];
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
for(int j = 0; j <= m; j ++ )
{
f[i][j] = f[i - 1][j];
if(j >= v[i]) f[i][j] = max(f[i][j], f[i][j - v[i]] + w[i]);
}
cout << f[n][m] << endl;
return 0;
}One dimensional optimization
#include <iostream> #include <algorithm> using namespace std; const int N = 1010; int n, m; int v[N], w[N]; int f[N]; int main() { cin >> n >> m; for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) cin >> v[i] >> w[i]; for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) for(int j = v[i]; j <= m; j ++ ) { f[j] = max(f[j], f[j - v[i]] + w[i]); } cout << f[m] << endl; return 0; }
contrast 01 knapsack and Completely backpack problem , There are the following differences :
01 knapsack :![f[i,j] = max(f[i,j], f[i - 1][j-v[i]] + w[i])](http://img.inotgo.com/imagesLocal/202206/27/202206271235354600_40.gif)
Completely backpack :![f[i,j]=max(f[i,j],f[i][j - v[i]+ w[i])](http://img.inotgo.com/imagesLocal/202206/27/202206271235354600_15.gif)
For a complete backpack , The enumeration of volumes can from v[i] Enumerate to m, Because it every i Layer update I'm using a number i Layer data , non-existent “ Data pollution ” The problem of .
Multiple knapsack problem
sample input
4 5 1 2 3 2 4 1 3 4 3 4 5 2sample output :
10

![f[i,j]=max(f[i-1][j-v[i] * k] + w[i] * k)](http://img.inotgo.com/imagesLocal/202206/27/202206271235354600_29.gif)
Plain writing
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 110;
int n, m;
int v[N], w[N], s[N];
int f[N][N];
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) cin >> v[i] >> w[i] >> s[i];
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
for(int j = 0; j <= m; j ++ )
for(int k = 0; k <= s[i] && k * v[i] <= j; k ++ )
f[i][j] = max(f[i][j], f[i - 1][j - v[i] * k] + w[i] * k);
cout << f[n][m] << endl;
return 0;
}Binary optimization of multiple knapsacks
as everyone knows , from  this k individual 2 Select several addition from the integer powers of , It can show
this k individual 2 Select several addition from the integer powers of , It can show  Any integer between . further , We find satisfaction
Any integer between . further , We find satisfaction  Maximum integer for p, set up
Maximum integer for p, set up  that :
that :
- according to p The maximum of , Yes
 , Can be launched
, Can be launched  , therefore
, therefore  Choose a number of additions to show
Choose a number of additions to show  Any integer between ;
Any integer between ; - from
 Select several of them to add , It can show
Select several of them to add , It can show  Any integer between , According to the Ri The definition of ,
Any integer between , According to the Ri The definition of ,  , therefore ,
, therefore , Choose a few to show
Choose a few to show  Any integer between .
Any integer between .
in summary , We can take the quantity as  Of the i Break an item into p + 2 Items , Their volumes are :
Of the i Break an item into p + 2 Items , Their volumes are :

this p + 2 Items can be put together  Between all can be Vi Divisible number , And can not be rounded up to be greater than Ci * Vi Number of numbers . This is equivalent to the volume in the original problem being Vi Can use 0~Ci Time . This method only splits each item into
Between all can be Vi Divisible number , And can not be rounded up to be greater than Ci * Vi Number of numbers . This is equivalent to the volume in the original problem being Vi Can use 0~Ci Time . This method only splits each item into  individual , More efficient .
individual , More efficient .
Code implementation
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 25000, M = 2010;
int n, m;
int v[N], w[N];
int f[N];
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m;
int cnt = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
{
int a, b, s;
cin >> a >> b >> s;
int k = 1;
while(k <= s)
{
cnt ++ ;
v[cnt] = a * k;
w[cnt] = b * k;
s -= k;
k *= 2;
}
if(s > 0)
{
cnt ++;
v[cnt] = a * s;
w[cnt] = b * s;
}
}
n = cnt;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
for(int j = m; j >= v[i]; j -- )
f[j] = max(f[j], f[j - v[i]] + w[i]);
cout << f[m] << endl;
return 0;
}Group knapsack problem
sample input
3 5 2 1 2 2 4 1 3 4 1 4 5sample output :
8


AC Code
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 110;
int n, m;
int v[N][N], w[N][N], s[N];
int f[N];
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
{
cin >> s[i];
for(int j = 0; j < s[i]; j ++ )
cin >> v[i][j] >> w[i][j];
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
for(int j = m; j >= 0; j -- )
for(int k = 0; k < s[i]; k ++ )
if(v[i][k] <= j)
f[j] = max(f[j], f[j - v[i][k]] + w[i][k]);
cout << f[m] << endl;
return 0;
}边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
How to close windows defender Security Center
Make learning pointer easier (1)
全球最强截图软件 Snipaste
How to choose LAN instant messaging software
Industry insight - how should brand e-commerce reshape growth under the new retail format?
数字化新星何为低代码?何为无代码
Utilisation de la file d'attente des messages
ssh工作流程及原理
外包2年的我终于上岸了!记录我的字节跳动3轮面试,希望帮助到大家!
VS调试技巧
解除百度文库VIP、语雀、知乎付费限制,原来这么简单
Make learning pointer easier (2)
基于SSM实现招聘网站
GCC compiling dynamic and static libraries
自定义多线程基类threading.Event
栈的计算(入栈出栈顺序是否合法)-代码
nmcli team bridge 基本配置
Pycharm in Chinese
诗歌一首看看
阿胖的操作记录


![\small f[i,j] = max(f[i -1,j],f[i-1,j-v]+w,f[i-1,j-2v]+2w\cdots )](http://img.inotgo.com/imagesLocal/202206/27/202206271235354600_38.gif)
![\small f[i,j-v]=max( f[i-1,j-v],f[i-1],f[i-1,j-2v]+w,f[i-2,j-3v]+2w\cdots )](http://img.inotgo.com/imagesLocal/202206/27/202206271235354600_3.gif)
![\large {\color{Red} f[i,j] = max(f[i - 1,j], f[i, j - v] + w)}](http://img.inotgo.com/imagesLocal/202206/27/202206271235354600_22.gif)

 , Can be launched
, Can be launched  , therefore
, therefore  Choose a number of additions to show
Choose a number of additions to show  Any integer between ;
Any integer between ; Select several of them to add , It can show
Select several of them to add , It can show  Any integer between , According to the Ri The definition of ,
Any integer between , According to the Ri The definition of ,  , therefore ,
, therefore , Choose a few to show
Choose a few to show  Any integer between .
Any integer between .