当前位置:网站首页>Detailed explanation of JVM runtime data area and JMM memory model
Detailed explanation of JVM runtime data area and JMM memory model
2022-08-01 08:34:00 【Feifei Technology House】
1. JVM runtime data area
The JVM runtime data area can be divided into five blocks: metaspace, heap, virtual machine stack, native method stack, and program counter.

- Metaspace (method area): It stores class template objects and is an area shared by threads. On disk, there is generally no GC
- Heap space: the area shared by threads, the main position for object creation and GC
- Virtual machine stack: private to the thread, the basic unit is the stack frame, each stack frame corresponds to a method, the stack frame is composed as follows
- Local variable table: store method variable information
- Operand stack: the area where the method runs
- Dynamic linking: point to the method template object, and implement method rewriting together with the virtual method table
- Return address: the return address of the method
- Native method stack: thread private, execution area for native methods
- Program counter: thread private, responsible for recording where the thread executes during the process of thread context switching
2. JMM memory model
Hardware memory model

Usually, when the CPU needs to read the main memory, it will read the part of the main memory into the CPU cache or the internal register, and then perform the operation in the register.When the CPU needs to write the result back to main memory, it flushes the value of the internal registers to the cache, and then at some point flushes the value back to main memory.
In a multiprocessor system, each processor has its own cache, and they share the same main memory, so there is a cache coherency problem.In order to solve the problem of consistency, each processor needs to follow some protocols when accessing the cache, and operate according to the protocol when reading and writing. Such protocols include MSI, MESI, etc.
JMM
The JMM memory model divides the content into two parts: thread private memory and main memory. The corresponding relationship with the hardware memory model we mentioned earlier is as follows:

The interaction between private memory and main memory is controlled by the following eight operations:

3. Visible line and volatile keyword
In a nutshell, the volatile keyword prevents instruction reordering in the form of memory barriers to maintain variable ordering and visibility.
A line of code goes through the following stages from execution to execution:

The volatile keyword has the following two functions:
- Guarantees that volatile-modified shared variables are always visible to all threads, that is, when a thread modifies the value of a volatile-modified shared variable, the new value can always be immediately known to other threads.
- Disable instruction reordering optimization.
The JVM provides four types of memory barrier instructions:
- loadload: between two read operations
- storestore: between two writes
- loadstore: between read and write operations
- storelosd: between writes and reads

边栏推荐
- XX市消防救援指挥中心实战指挥平台多链路聚合解决方案实例
- 网络基础学习
- VoLTE Basic Learning Series | Enterprise Voice Network Brief
- ACmix 论文精读,并解析其模型结构
- Mysql database deployment and initialization steps
- 22 Grab the Seat 1 C.Grab the Seat (Geometry + Violence)
- leetcode-6134:找到离给定两个节点最近的节点
- GO error handling
- 【手撕AHB-APB Bridge】~ AHB地址总线的低两位为什么不用来表示地址呢?
- [Tear AHB-APB Bridge by hand]~ Why aren't the lower two bits of the AHB address bus used to represent the address?
猜你喜欢

Microsoft Azure & NVIDIA IoT developers season I | Azure IoT & NVIDIA Jetson development foundation
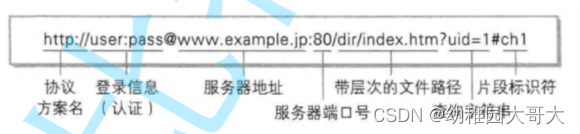
网络个各种协议

app 自动化 打开app (二)
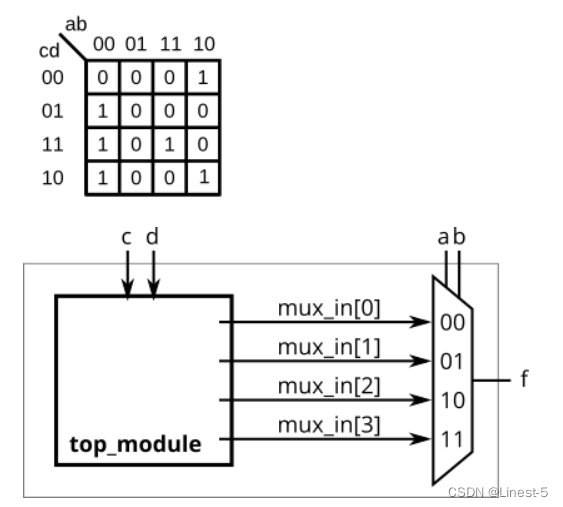
【HDLBits 刷题】Circuits(1)Combinational Logic
C语言中编译时出现警告C4013(C语言不加函数原型产生的潜在错误)
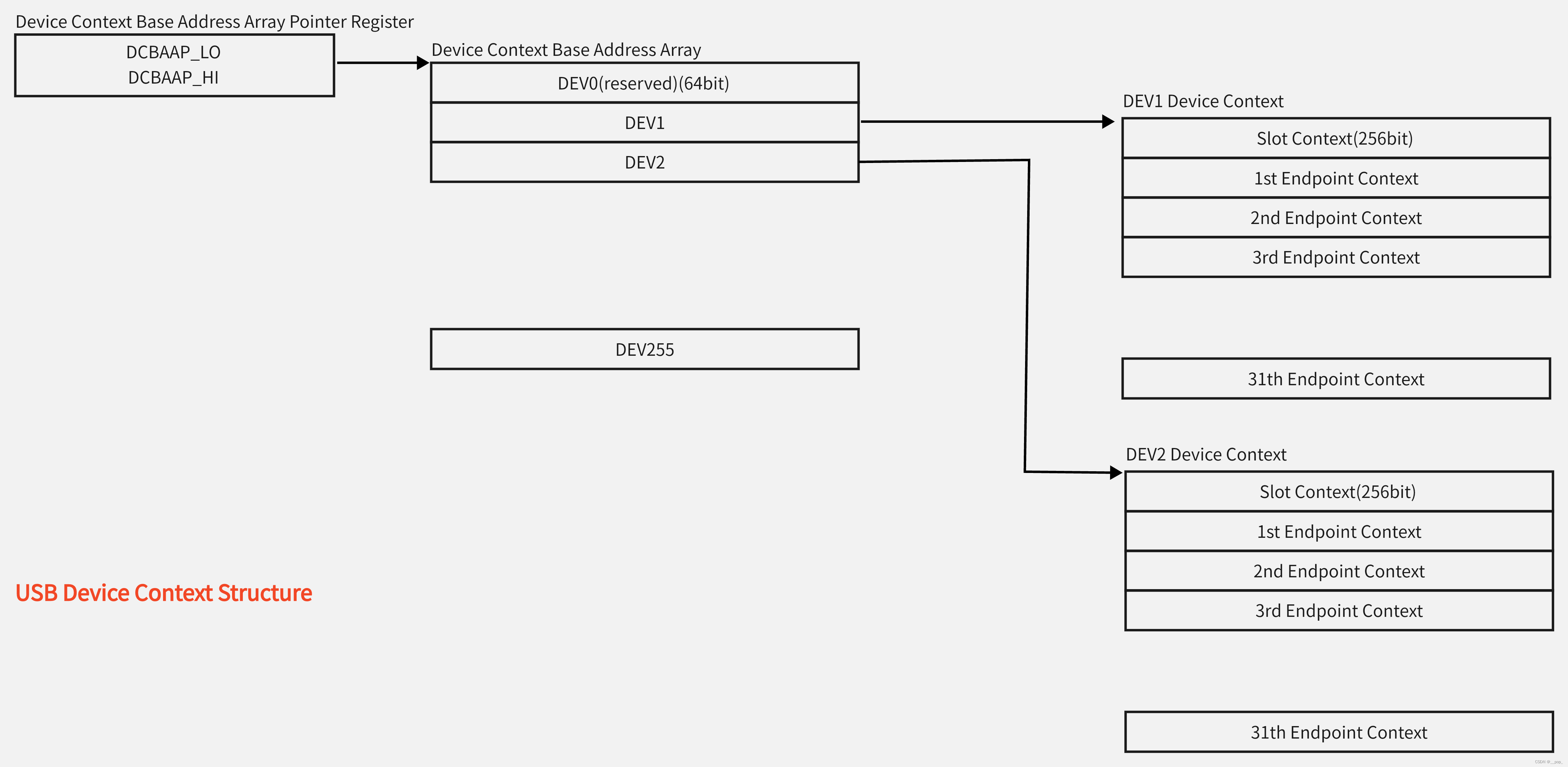
USB Protocol (2) Terminology

企业数据虚拟化综合指南
Prime Ring Problem(素数环问题)

HoloView 在 jyputer lab/notebook 不显示总结

Redis middleware (from building to refuse pit)
随机推荐
【STM32】入门(一):环境搭建、编译、下载、运行
力扣周赛304 6135. 图中的最长环 内向基环树
扁平数组转树结构实现方式
leetcode-6134: Find the closest node to the given two nodes
Case practice --- Resnet classic convolutional neural network (Mindspore)
pytest interface automation testing framework | pass in parameter values in the form of function return values
zip package all files in the directory (including hidden files/folders)
The socket option
Centos install php7.4, build hyperf, forward RDS
leetcode 42. Catch the rain
pytest接口自动化测试框架 | 单个/多个参数
毕业论文写作技巧
Redis 3.2.3 crashed by signal: 11 服务宕机问题排查
How to query database configuration parameters in GBase 8c, such as datestyle
pytest interface automation testing framework | skip test classes
Optimal dazzle Oracle database support what kinds of type of the time and date
Redis learning
Mysql数据库的部署以及初始化步骤
案例实践 --- Resnet经典卷积神经网络(Mindspore)
LabVIEW中局部变量和全局变量的分配